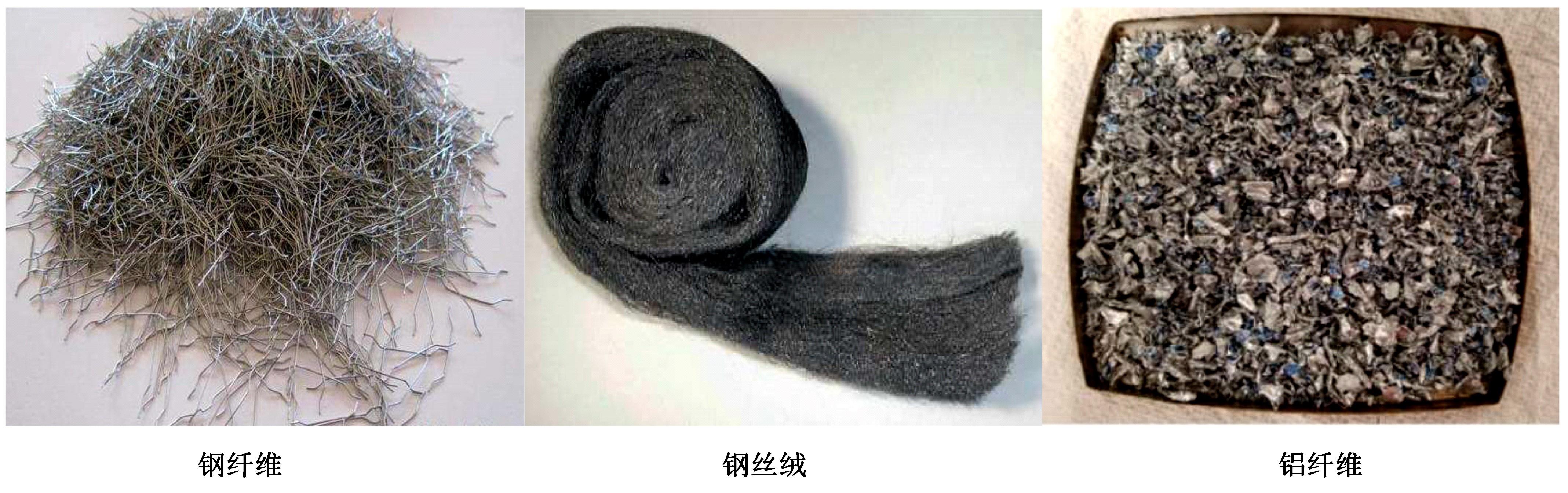
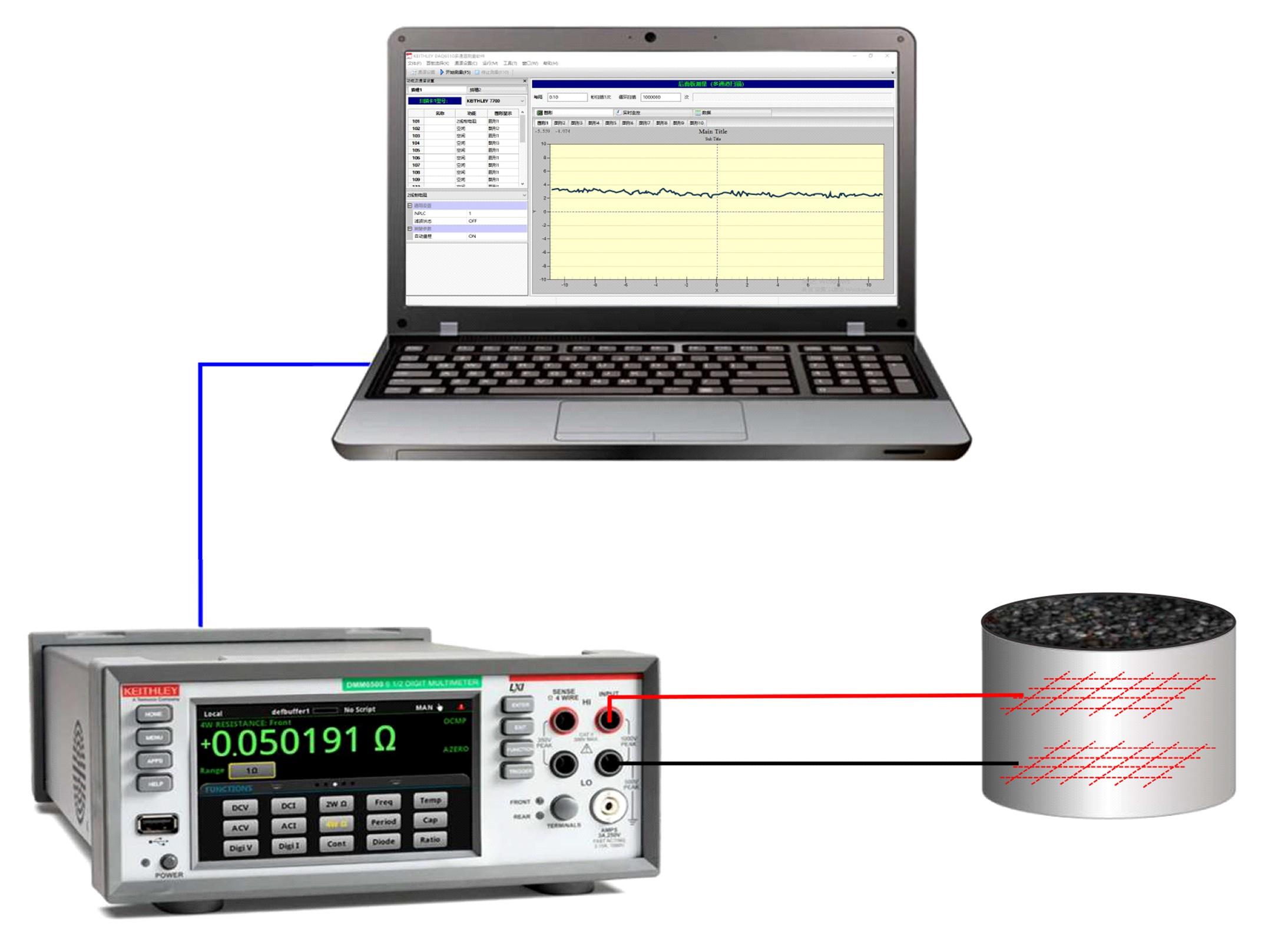
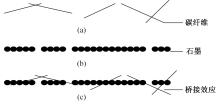
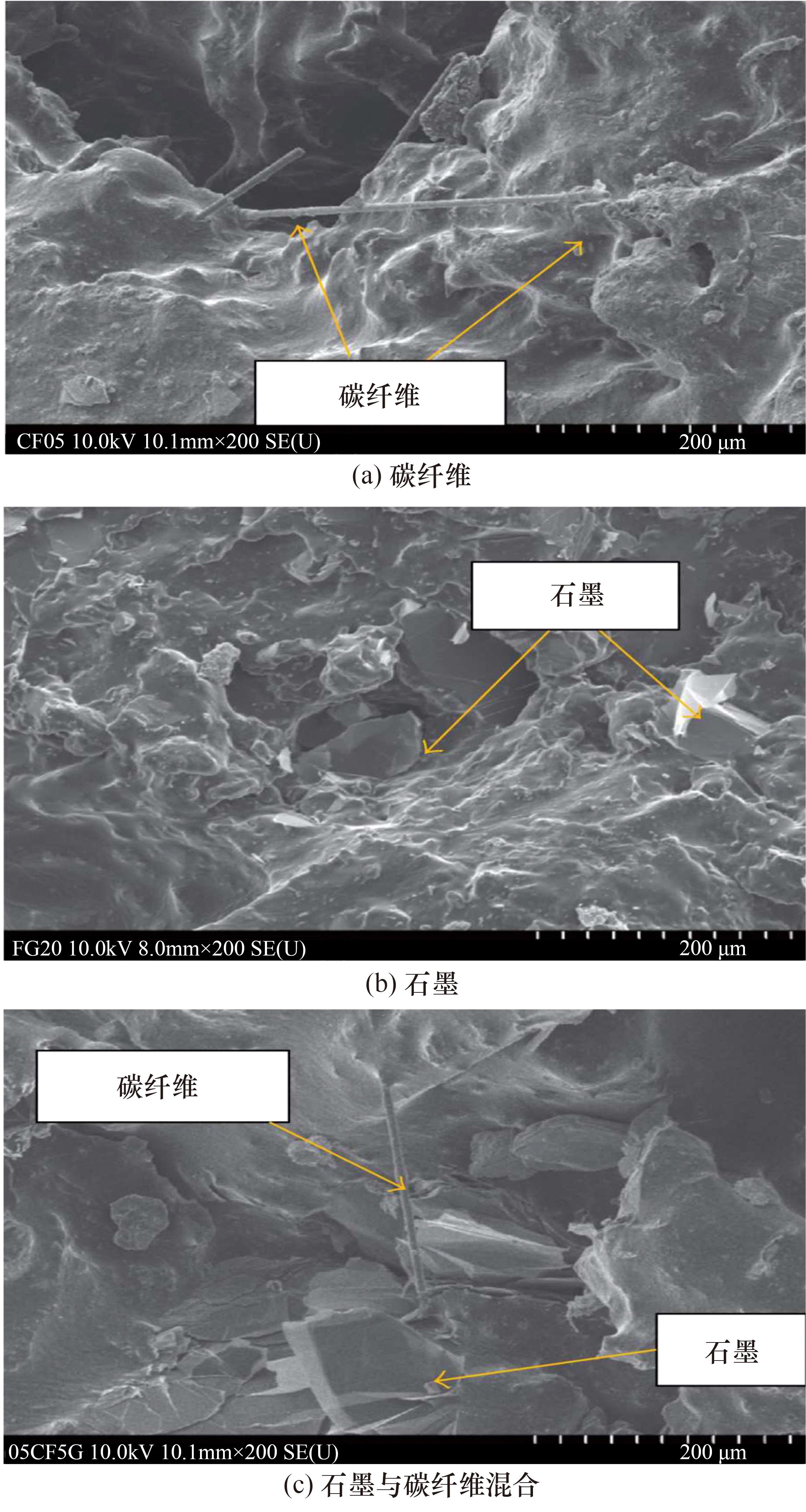
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 1-21.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230834
• 综述 •
导电沥青混凝土研究进展
王壮1( ),冯振刚1(
),冯振刚1( ),姚冬冬2,崔奇1,沈若廷2,李新军1
),姚冬冬2,崔奇1,沈若廷2,李新军1
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.吉林省交通科学研究所,长春 130012
Research progress of conductive asphalt concrete
Zhuang WANG1( ),Zhen-gang FENG1(
),Zhen-gang FENG1( ),Dong-dong YAO2,Qi CUI1,Ruo-ting SHEN2,Xin-jun LI1
),Dong-dong YAO2,Qi CUI1,Ruo-ting SHEN2,Xin-jun LI1
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Jilin Provincial Transport Scientific Research Institute,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
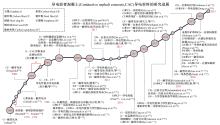
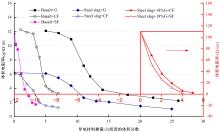
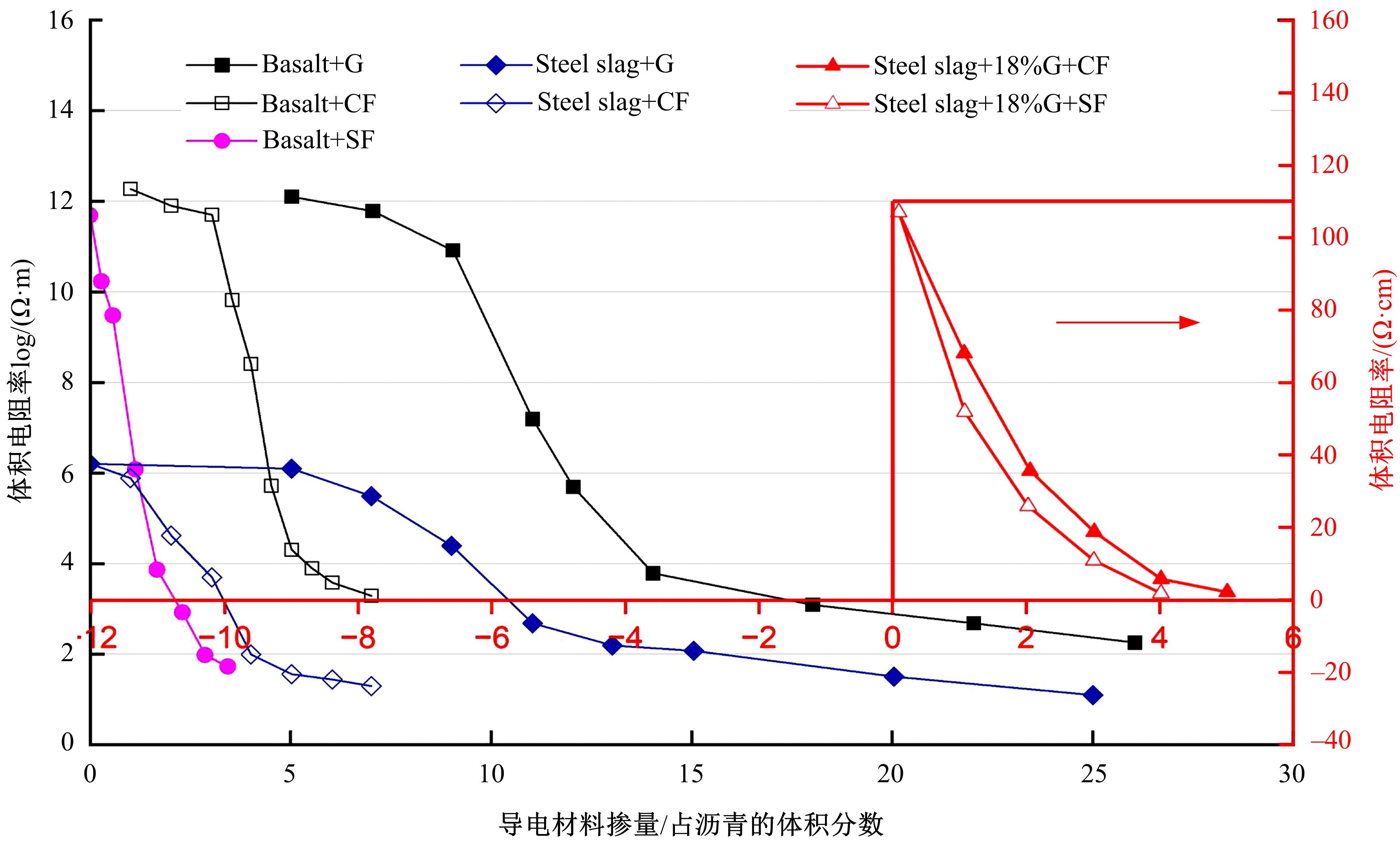
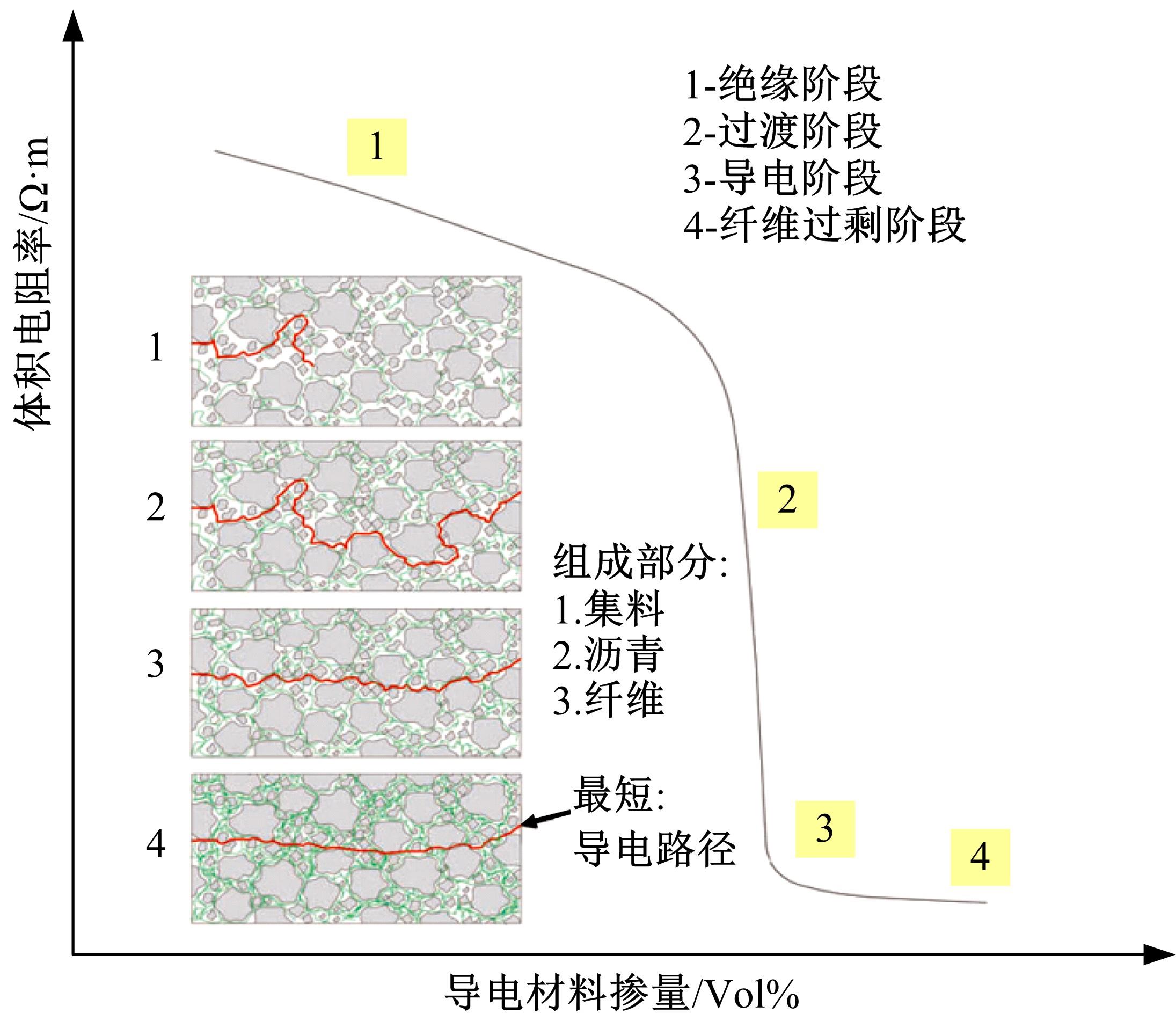
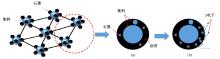
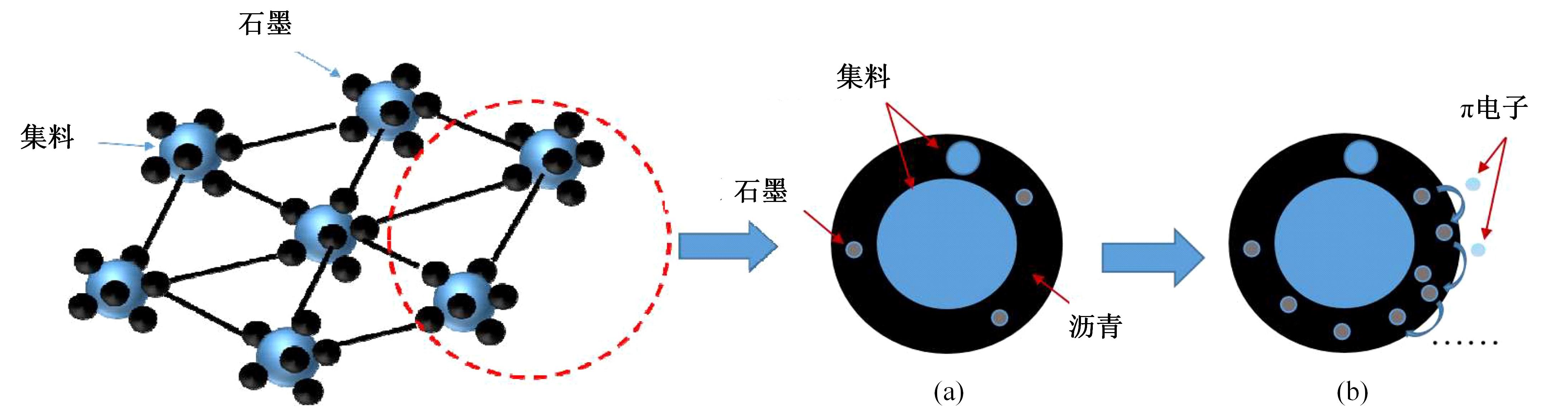
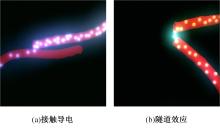
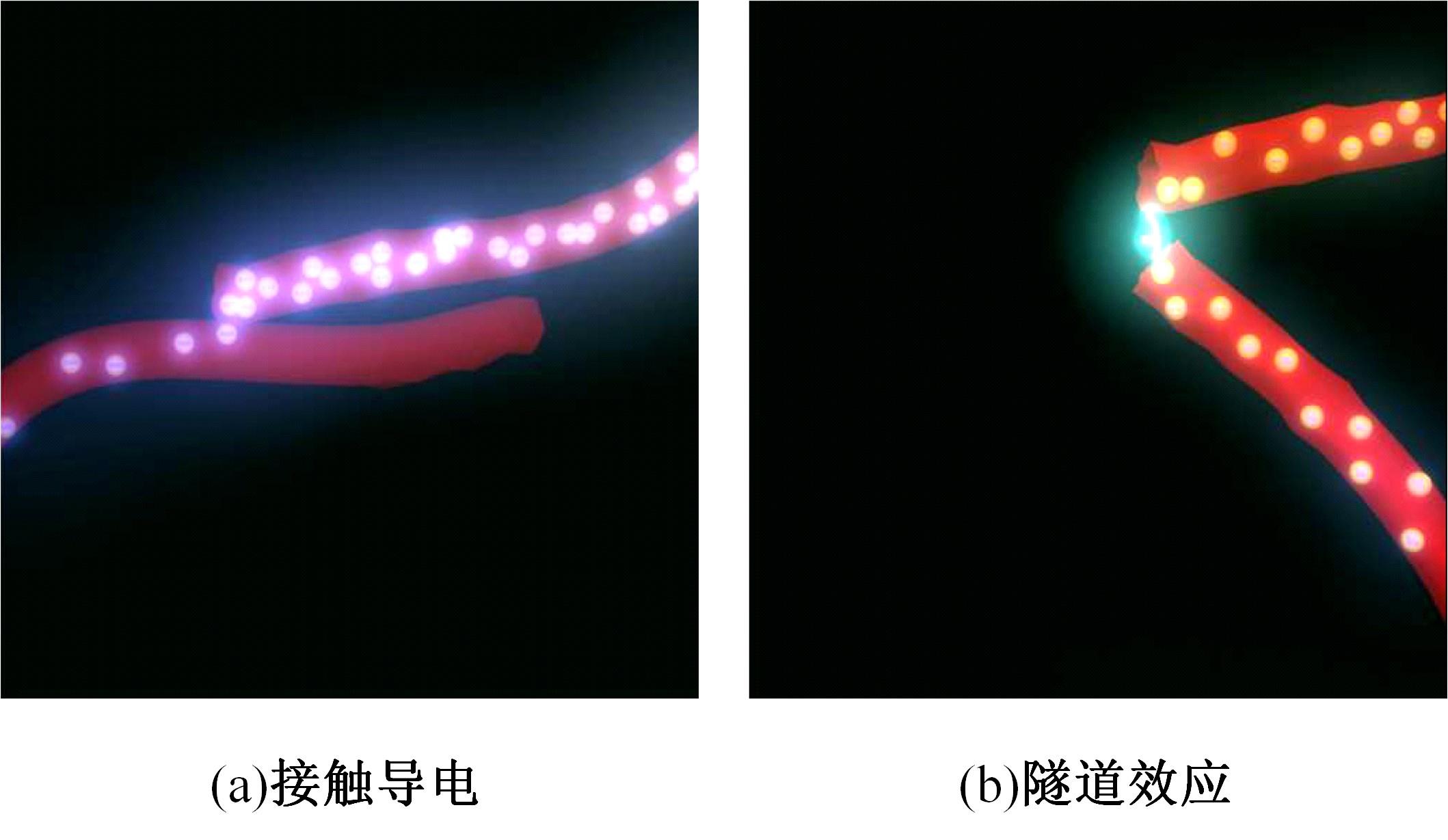
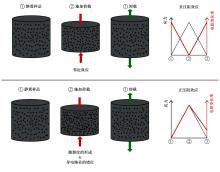
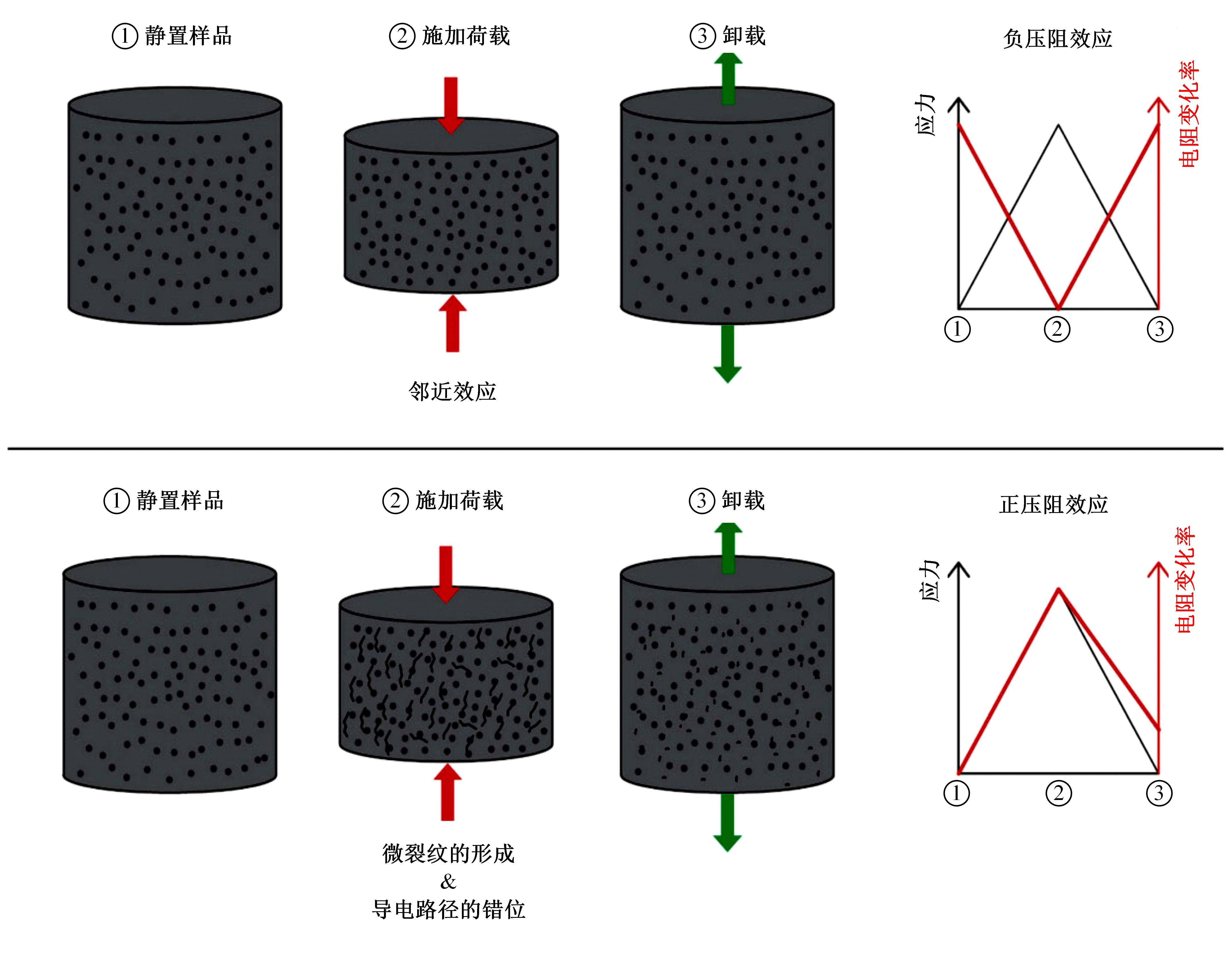
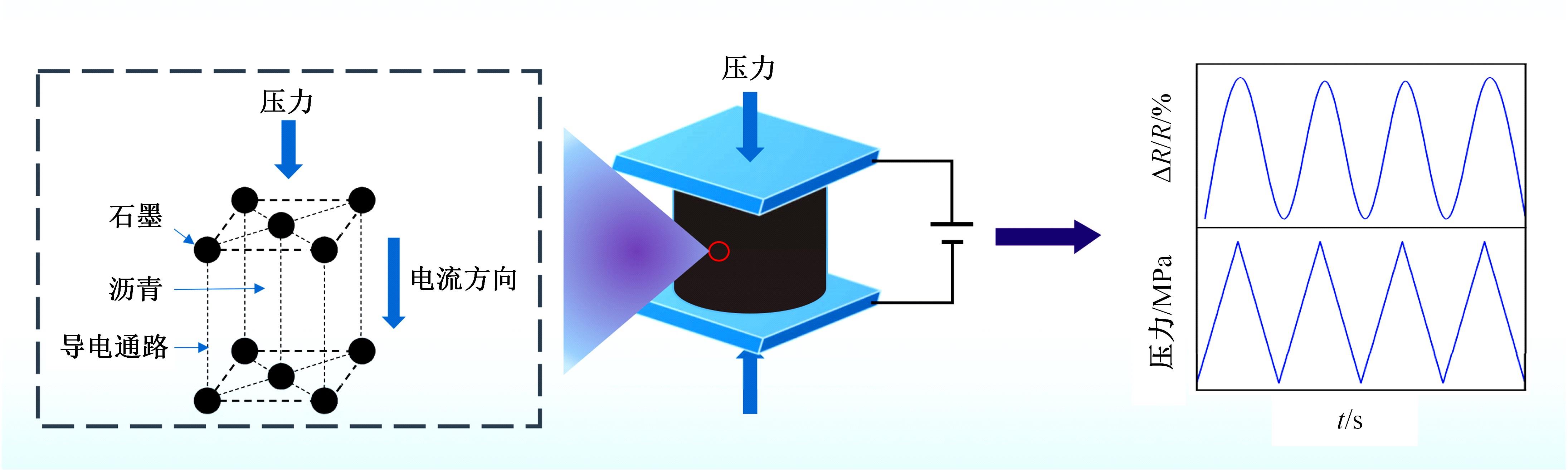
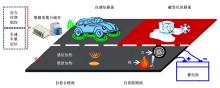
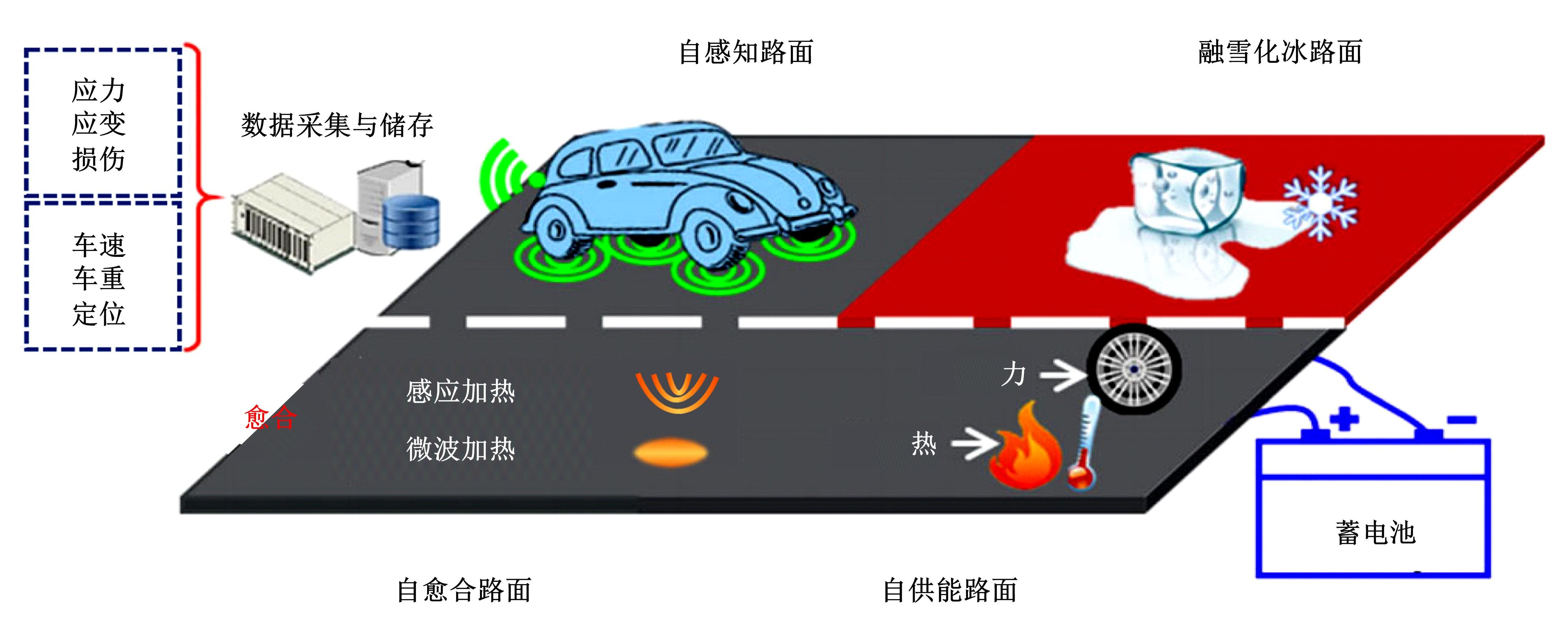
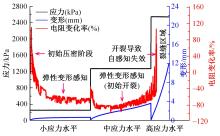
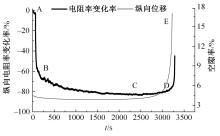
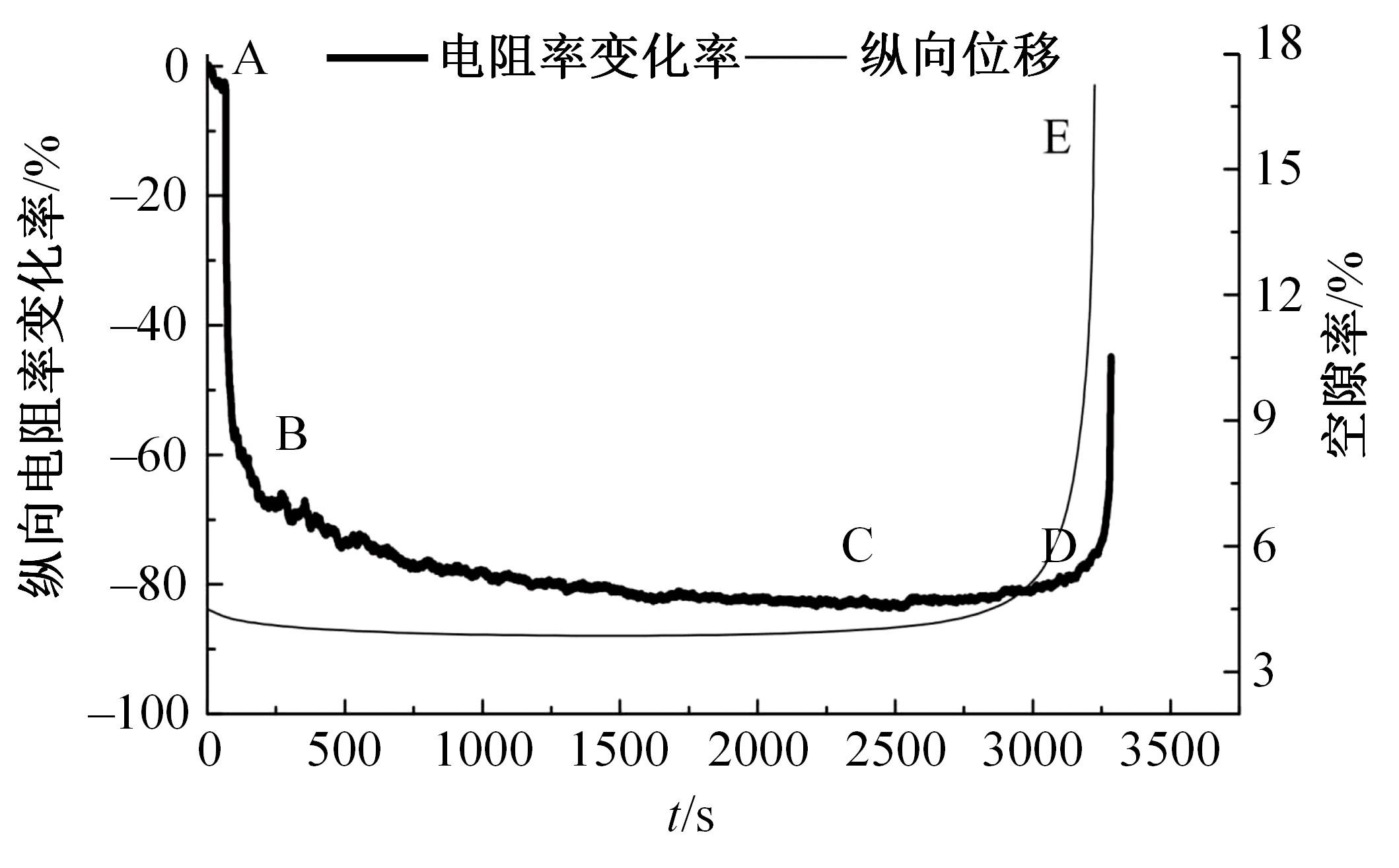
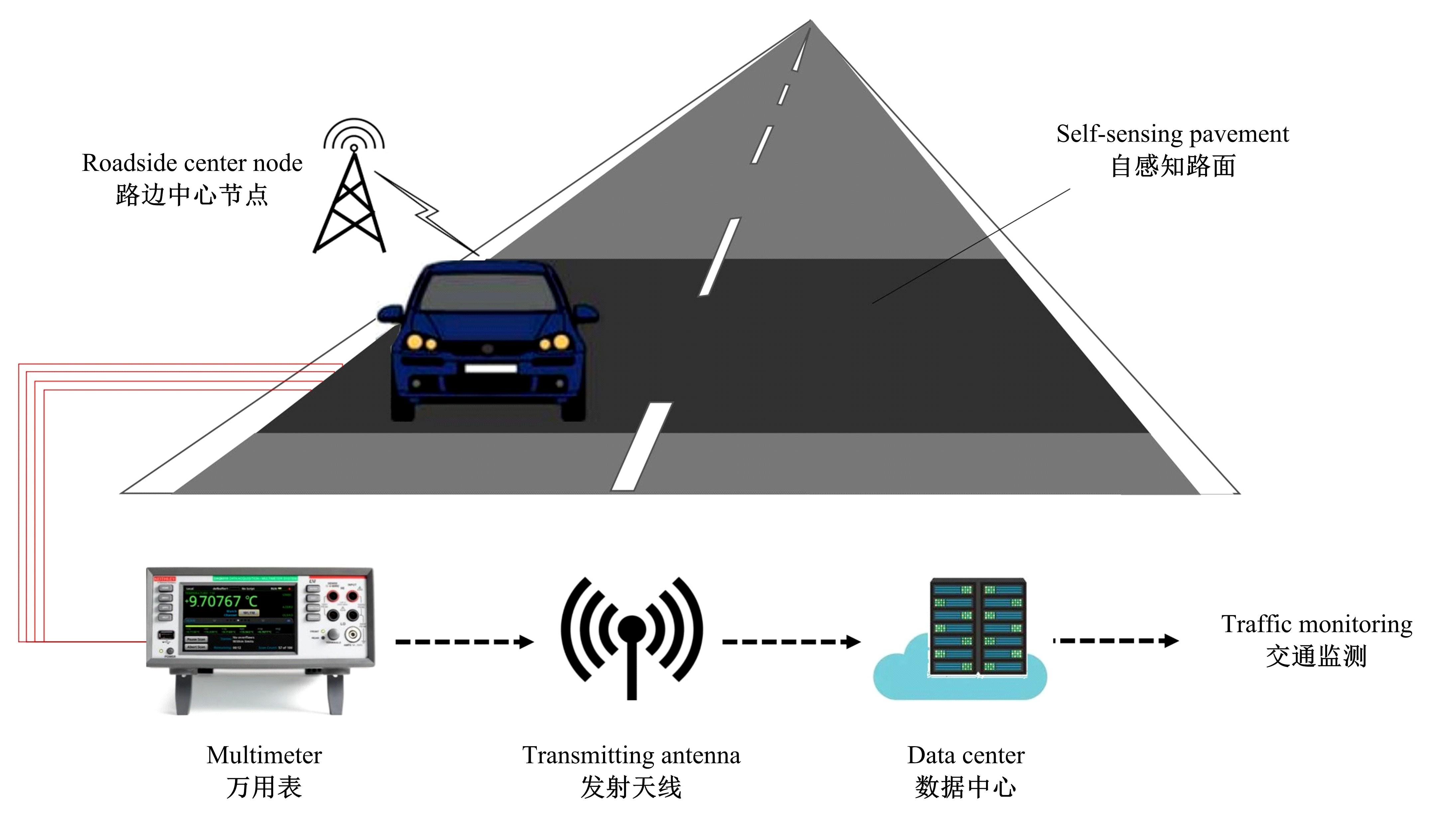
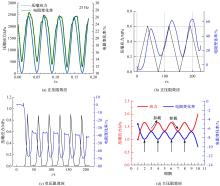
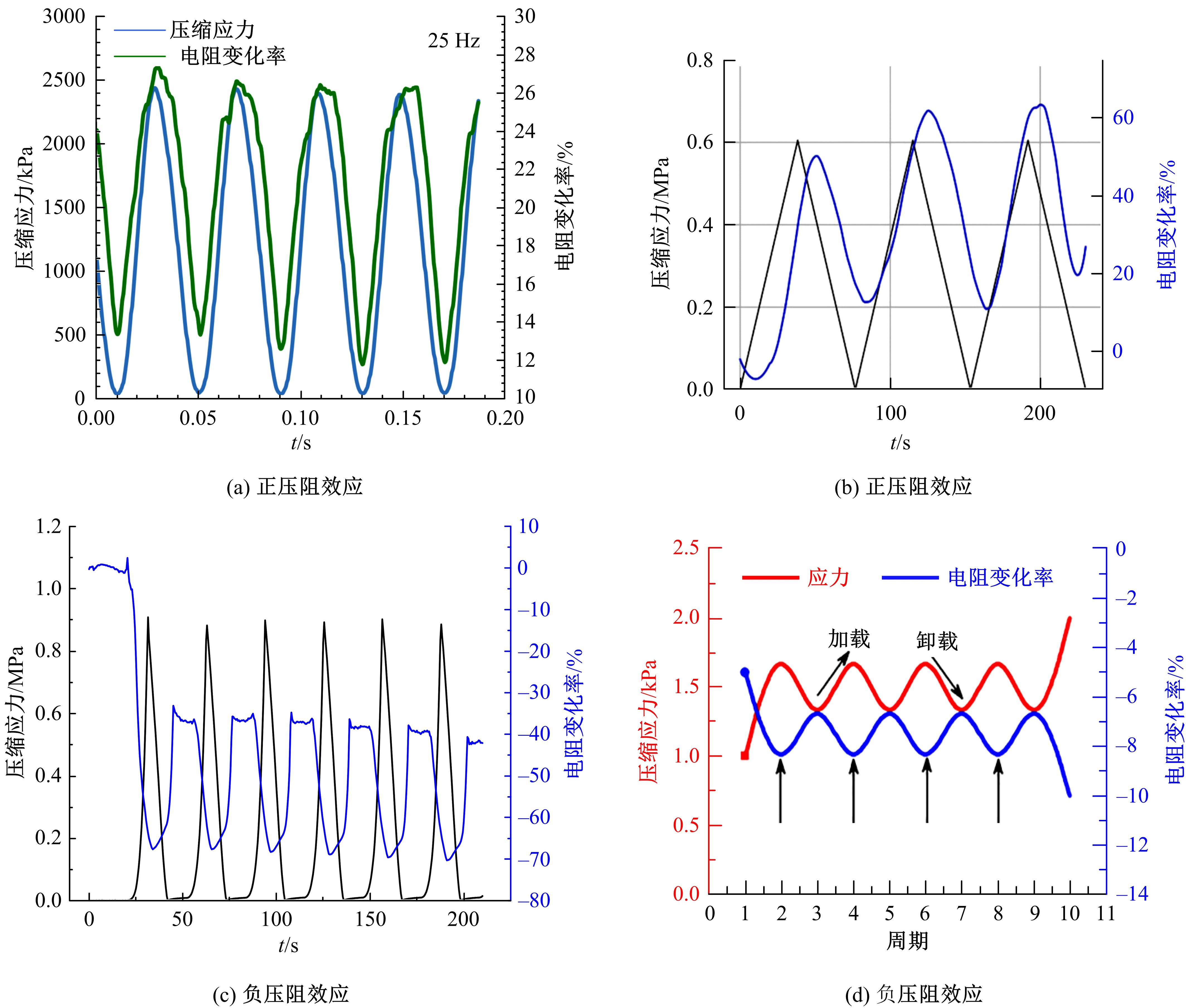
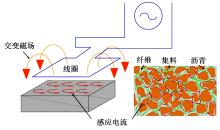
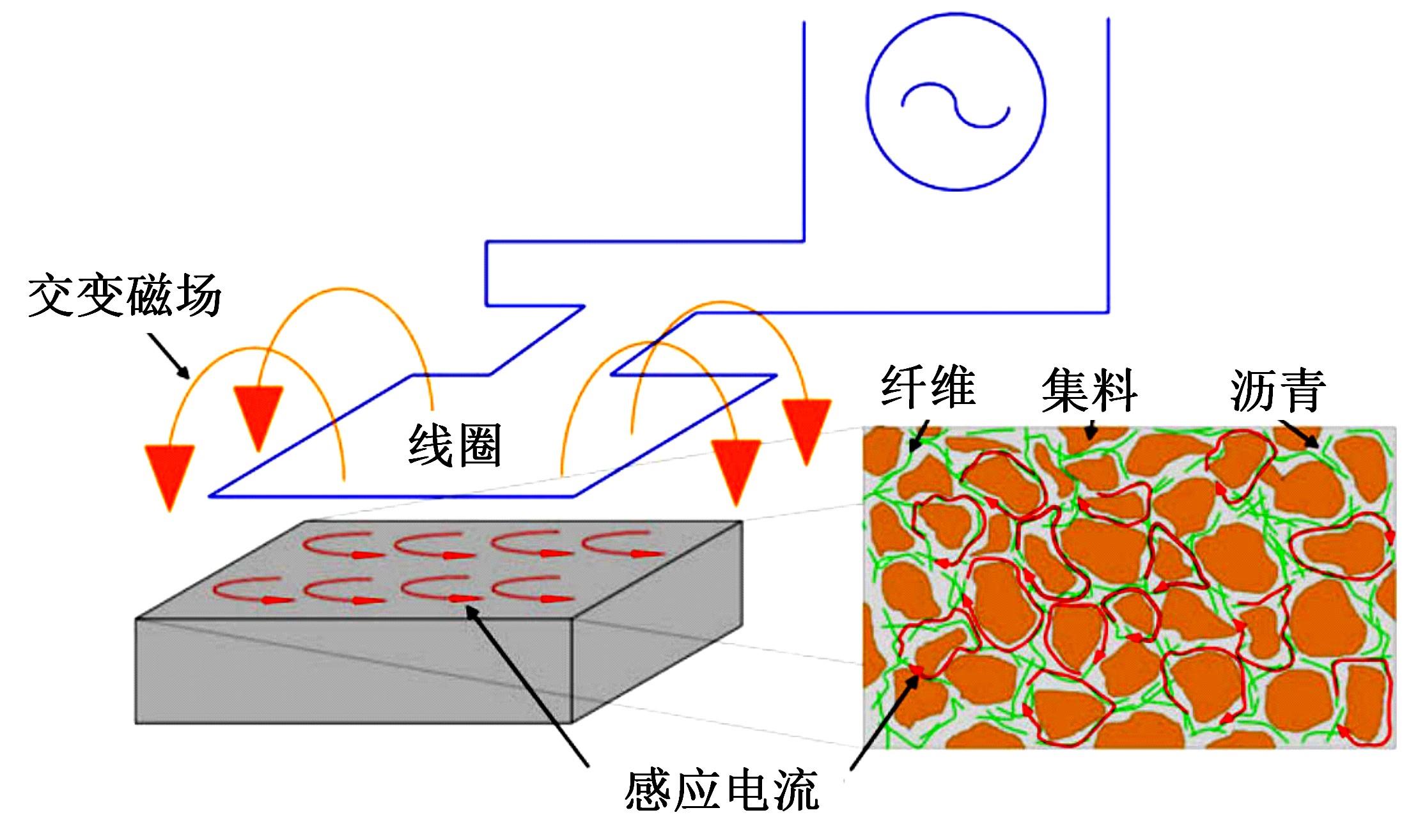
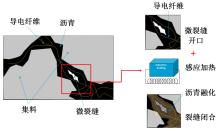
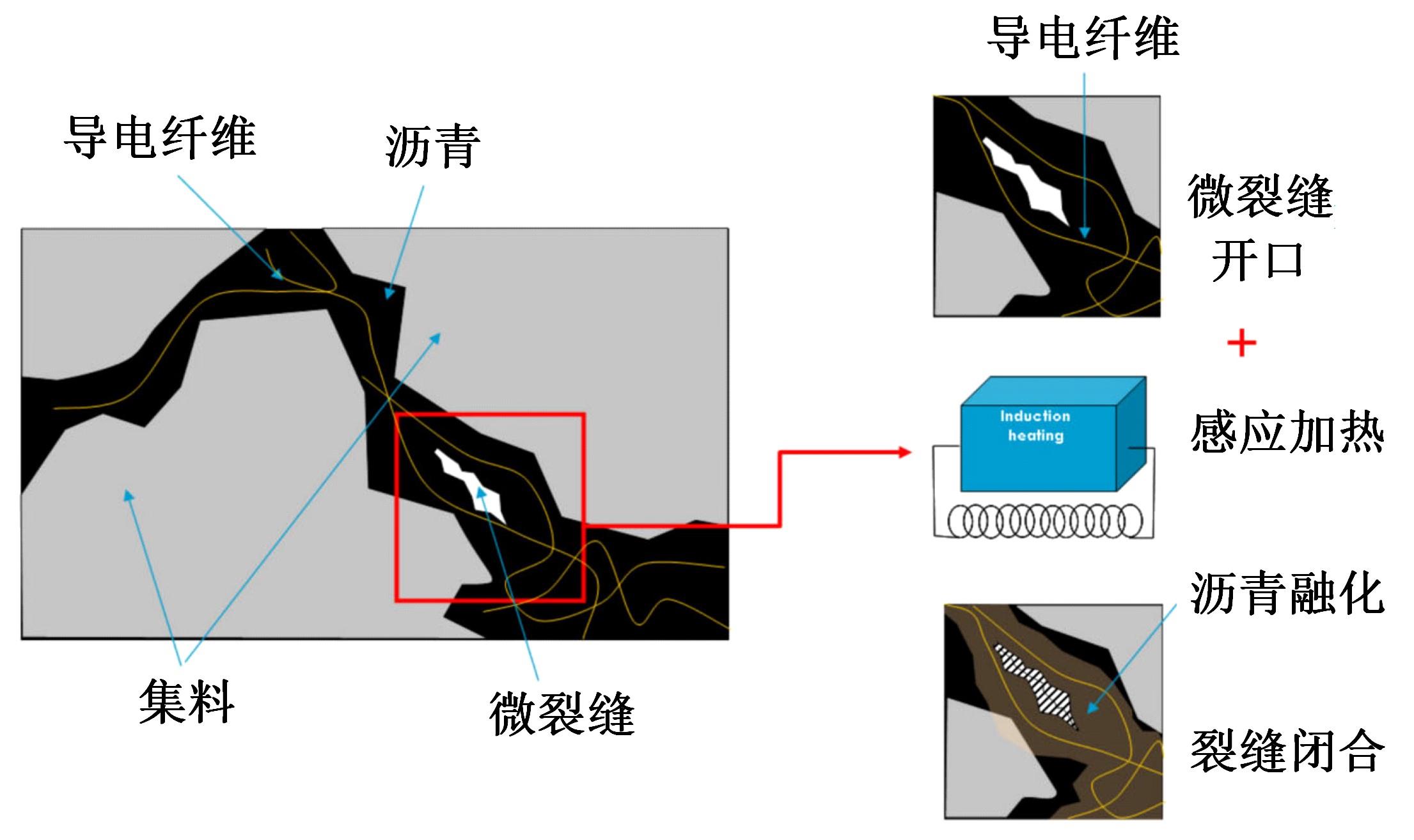
为厘清国内外导电沥青混凝土技术的研究进展,系统梳理了导电材料的分类及其在导电沥青混凝土中的应用现状,分析了不同类型导电沥青混凝土的导电性能和路用性能,论述了导电沥青混凝土的作用机理(导电机理、压阻机理和电热机理),探讨了导电沥青混凝土自诊断、自感知、感应加热自愈合、融雪化冰等功能特性,介绍了其在实际工程中的应用现状,并对导电沥青混凝土的未来发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
- U416.217
| 1 | Sun Y, Wu S, Liu Q, et al. Snow and ice melting properties of self-healing asphalt mixtures with induction heating and microwave heating[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 129: 871-883. |
| 2 | 谭忆秋, 张驰, 徐慧宁, 等. 主动除冰雪路面融雪化冰特性及路用性能研究综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(4): 1-17. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Zhang Chi, Xu Hui-ning, et al. Snow melting and deicing characteristics and pavement performance of active deicing and snow melting pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(4): 1-17. | |
| 3 | Arabzadeh A, Notani M A, Zadeh A K, et al. Electrically conductive asphalt concrete: an alternative for automating the winter maintenance operations of transportation infrastructure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 173: No. 106985. |
| 4 | Liu X, Wu S. Study on the graphite and carbon fiber modified asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(4): 1807-1811. |
| 5 | Liu L, Zhang X, Xu L, et al. Investigation on the piezoresistive response of carbon fiber-graphite modified asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 301: No. 124140. |
| 6 | Gulisano F, Buasiri T, Apaza F R A, et al. Piezoresistive behavior of electric arc furnace slag and graphene nanoplatelets asphalt mixtures for self-sensing pavements[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 142: No. 104534. |
| 7 | 何亮, 赵龙, 凌天清, 等. 密实型沥青混合料裂缝感应热自愈合性能研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(1): 17-24. |
| He Liang, Zhao Long, Ling Tian-qing, et al. Research on induction heating activated self-healing of cracks in dense graded asphalt mixture[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(1): 17-24. | |
| 8 | Karimi M M, Darabi M K, Jahanbakhsh H, et al. Effect of steel wool fibers on mechanical and induction heating response of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2020, 21(14): 1755-1768. |
| 9 | Dong Z, Ullah S, Zhou T, et al. Self-monitoring of damage evolution in asphalt concrete based on electrical resistance change method[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2022, 50(5): 2698-2717. |
| 10 | Gulisano F, Abedi M A, Jurado-Piña R, et al. Stress and damage-sensing capabilities of asphalt mixtures incorporating graphene nanoplatelets[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2023, 359: No. 114494. |
| 11 | 黄如宝, 牛衍亮, 赵鸿铎, 等. 道路压电能量收集技术途径与研究展望[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 25(6): 1-8. |
| Huang Ru-bao, Niu Yan-liang, Zhao Hong-duo, et al. Technical approach and research prospect of piezoelectric energy harvest from highway[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2012, 25(6): 1-8. | |
| 12 | Xiang H, Wang J, Shi Z, et al. Corrigendum: theoretical analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesting from traffic induced deformation of pavements[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2014, 23(11): No. 119502. |
| 13 | Wang C, Wang H, Li Y. Study on technology of power pavement based on integration of piezoelectric material and pavement material[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2016, 33(11): 14-19. |
| 14 | Chen F, Balieu R. A state-of-the-art review of intrinsic and enhanced electrical properties of asphalt materials: Theories, analyses and applications[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 195: No. 109067. |
| 15 | Pan P, Wu S, Xiao F, et al. Conductive asphalt concrete: a review on structure design, performance, and practical applications[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2015, 26(7): 755-769. |
| 16 | Pan P, Wu S, Hu X, et al. Effect of material composition and environmental condition on thermal characteristics of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Materials, 2017, 10(3): No. 218. |
| 17 | García Á, Norambuena-Contreras J, Partl M N. Experimental evaluation of dense asphalt concrete properties for induction heating purposes[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 46: 48-54. |
| 18 | 刘小明, 吴少鹏, 杨小礼. 导电沥青混凝土的机敏特性[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 40(5): 1465-1470. |
| Liu Xiao-ming, Wu Shao-peng, Yang Xiao-li. Smart characteristics of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science), 2009, 40(5): 1465-1470. | |
| 19 | 刘志胜, 武胜兵, 刘鹏飞, 等. 导电沥青混凝土及其功能特性研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(): 374-378, 387. |
| Liu Zhi-sheng, Wu Sheng-bing, Liu Peng-fei, et al. Review on functional features of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Materials Reports, 2017, 31(Sup.1): 374-378, 387. | |
| 20 | Minsk L D. Eelectrically conductive asphalt for control of snow and ice accumulation[J]. Highway Research Record, 1968, 227: 57-63. |
| 21 | Zaleski P L D D J, Flood W H. Electrically conductive paving mixture and paving system[P]. US Patent,No.5707171. |
| 22 | Wu S, Mo L, Shui Z, et al. An improvement in electrical properties of asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Materials Science Edition), 2002, 17(4): 69-72. |
| 23 | 磨炼同. 导电沥青混凝土的制备与研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2004. |
| Mo Lian-tong. Preparation and research of electrically conductive asphalt concrete[D]. Wuhan: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2004. | |
| 24 | Wu S, Mo L, Shui Z, et al. Investigation of the conductivity of asphalt concrete containing conductive fillers[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(7): 1358-1363. |
| 25 | Liu X, Wu S, Ye Q, et al. Properties evaluation of asphalt-based composites with graphite and mine powders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22(3): 121-126. |
| 26 | Liu X, Wu S. Research on the conductive asphalt concrete's piezoresistivity effect and its mechanism[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009, 23(8): 2752-2756. |
| 27 | Park P. Characteristics and applications of high-performance fiber reinforced asphalt concrete[D]. Michigan: College of Engineering, University of Michigan, 2012. |
| 28 | Park P, Rew Y, Baranikumar A. Controlling conductivity of asphalt concrete with graphite[R]. Texas: Texas A&M Transportation Institute, 2014. |
| 29 | 吴少鹏, 磨炼同, 水中和. 石墨改性沥青混凝土的导电机制[J]. 自然科学进展, 2005, 14(4): 64-70. |
| Wu Shao-peng, Mo Lian-tong, Shui Zhong-he. The conductive mechanism of graphite modified asphalt concrete[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2005, 14(4): 64-70. | |
| 30 | Fitzgerald R L. Novel applications of caron fiber hot mix asphalt reinforcement and carbon-carbon pre-forms[D]. Michigan: College of Engineering, Michigan Technological University, 2000. |
| 31 | Moghadas N F, Vadood M, Baeetabar S. Investigating the mechanical properties of carbon fibre-reinforced asphalt concrete[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2014, 15(2): 465-475. |
| 32 | Abtahi S M, Sheikhzadeh M, Hejazi S M. Fiber-reinforced asphalt-concrete-a review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(6): 871-877. |
| 33 | 冯新军, 查旭东, 程景. PAN基碳纤维导电沥青混凝土的制备及性能[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 25(2): 27-32. |
| Feng Xin-jun, Zha Xu-dong, Cheng Jing. Preparation and performance of PAN-based carbon fiber conductive asphalt concrete[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2012, 25(2): 27-32. | |
| 34 | 宋鹏. 石墨烯导电沥青混凝土制备及性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2019. |
| Song Peng. Study on preparation and properties of graphene conductive asphalt concrete[D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic and Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 35 | 谭忆秋, 刘凯, 王英园. 碳纤维/石墨烯导电沥青混凝土的非线性伏安特性[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2019, 22(2): 278-283. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Liu Kai, Wang Ying-yuan. Nonlinear voltammetric characteristics of carbon fiber/graphene conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2019, 22(2): 278-283. | |
| 36 | 查旭东, 陈勇强, 程景. 短切PAN基碳纤维导电沥青混合料性能试验研究[J]. 功能材料, 2012, 43(7): 872-876. |
| Zha Xu-dong, Chen Yong-qiang, Cheng Jing. Experimental research on performances for conductive asphalt mixture with chopped PAN-based carbon fiber[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2012, 43(7): 872-876. | |
| 37 | 程景. PAN基碳纤维导电沥青混凝土研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学交通运输工程学院, 2010. |
| Cheng Jing. Research on conductive asphalt concrete with PAN-based carbon fiber[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2010. | |
| 38 | 胡天文, 霍海峰, 张佩浩, 等. 碳纤维沥青混凝土导电特性研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2017, 44(10): 58-61, 80. |
| Hu Tian-wen, Huo Hai-feng, Zhang Pei-hao, et al. Conductive characteristic research of carbon fiber asphalt concrete[J]. New Building Materials, 2017, 44(10): 58-61, 80. | |
| 39 | 黄维蓉, 杨玉柱, 宋鹏, 等. 石墨烯-碳纤维导电沥青混凝土电热性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(8): 269-273. |
| Huang Wei-rong, Yang Yu-zhu, Song Peng, et al. Study on electrothermal property of rGO-CF conductive asphalt concrete[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(8): 269-273. | |
| 40 | Wang Y, Tan Y, Liu K, et al. Preparation and electrical properties of conductive asphalt concretes containing graphene and carbon fibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 318: No. 125875. |
| 41 | 杨振华. 石墨碳纤维导电沥青混凝土的制备及性能研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学交通运输工程学院, 2015. |
| Yang Zhen-hua. Research on preparation and performance of conductive graphite carbon fiber asphalt concrete[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2015. | |
| 42 | Ullah S, Yang C, Cao L, et al. Material design and performance improvement of conductive asphalt concrete incorporating carbon fiber and iron tailings[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 303: No. 124446. |
| 43 | Huang B, Chen X, Shu X. Effects of electrically conductive additives on laboratory-measured properties of asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2009, 21(10): 612-617. |
| 44 | Messaoud M, Glaoui B, Abdelkhalek O. The effect of adding steel fibers and graphite on mechanical and electrical behaviors of asphalt concrete[J]. Civil Engineering Journal, 2022, 8(2): 348-361. |
| 45 | García Á, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M. Two ways of closing cracks on asphalt concrete pavements: microcapsules and induction heating[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2010, 417: 573-576. |
| 46 | García Á, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M, et al. Induction heating of mastic containing conductive fibers and fillers[J]. Materials and Structures, 2011, 44: 499-508. |
| 47 | Dai Q, Wang Z, Hasan M R M. Investigation of induction healing effects on electrically conductive asphalt mastic and asphalt concrete beams through fracture-healing tests[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 729-737. |
| 48 | Liu Q, Schlangen E, García Á, et al. Induction heating of electrically conductive porous asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(7): 1207-1213. |
| 49 | Liu Q, Schlangen E, Vdv M, et al. Mechanical properties of sustainable, self-healing porous asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2010, 17: 58-65. |
| 50 | Liu Q, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M, et al. Healing of porous asphalt concrete via induction heating[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2010, 11(Sup.1): 527-542. |
| 51 | Liu Q, García Á, Schlangen E, et al. Induction healing of asphalt mastic and porous asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(9): 3746-3752. |
| 52 | Liu Q, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M, et al. Evaluation of the induction healing effect of porous asphalt concrete through four point bending fatigue test[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 29: 403-409. |
| 53 | 李波, 李艳博, 梁秀娟. 添加钢棉的多孔沥青混凝土感应愈合性能研究[J]. 中外公路, 2015, 35(4): 239-243. |
| Li Bo, Li Yan-bo, Liang Xiu-juan. Study on induction healing performance of porous asphalt concrete with steel wool.[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2015, 35(4): 239-243. | |
| 54 | Hosseinian S M, Najafi Moghaddam Gilani V, Mehraban Joobani P, et al. Investigation of moisture sensitivity and conductivity properties of inductive asphalt mixtures containing steel wool fiber[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020:No.8890814. |
| 55 | Liu Z, Wang Y, Meng Y, et al. Comprehensive performance evaluation of steel fiber-reinforced asphalt mixture for induction heating[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2022, 23(11): 3838-3849. |
| 56 | García Á, Norambuena-Contreras J, Partl M N. A parametric study on the influence of steel wool fibers in dense asphalt concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2014, 47: 1559-1571. |
| 57 | Norambuena-Contreras J, Serpell R, Vidal G V, et al. Effect of fibres addition on the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures with crack-healing purposes by microwave radiation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 127: 369-382. |
| 58 | Norambuena-Contreras J, García Á. Self-healing of asphalt mixture by microwave and induction heating[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 106: 404-414. |
| 59 | Pamulapati Y, Elseifi M A, Cooper Iii S B, et al. Evaluation of self-healing of asphalt concrete through induction heating and metallic fibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 146: 66-75. |
| 60 | Liu J, Xu J, Liu Q, et al. Steel slag for roadway construction: a review of material characteristics and application mechanisms[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2022, 34(6): No. 03122001. |
| 61 | Ahmedzade P, Sengoz B. Evaluation of steel slag coarse aggregate in hot mix asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1/3): 300-305. |
| 62 | Jiao W, Sha A, Liu Z, et al. Study on thermal properties of steel slag asphalt concrete for snow-melting pavement[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277: No. 123574. |
| 63 | Huang L, Lin D, Luo H, et al. Effect of field compaction mode on asphalt mixture concrete with basic oxygen furnace slag[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 34: 16-27. |
| 64 | Qazizadeh M J, Farhad H, Kavussi A, et al. Evaluating the fatigue behavior of asphalt mixtures containing electric arc furnace and basic oxygen furnace slags using surface free energy estimation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 188: 355-361. |
| 65 | Yi H, Xu G, Cheng H, et al. An overview of utilization of steel slag[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2012, 16: 791-801. |
| 66 | Wu S, Xue Y, Ye Q, et al. Utilization of steel slag as aggregates for stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixtures[J]. Building and Environment, 2007, 42(7): 2580-2585. |
| 67 | Chen F, Chen M, Wu S, et al. Research on pavement performance of steel slag conductive asphalt concrete for deicing and snow melting[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2012, 509: 168-174. |
| 68 | Xie J, Wu S, Lin J, et al. Recycling of basic oxygen furnace slag in asphalt mixture: material characterization & moisture damage investigation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 36: 467-474. |
| 69 | 何亮, 詹程阳, 吕松涛, 等. 钢渣沥青混合料应用现状[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 15-33. |
| He Liang, Zhan Cheng-yang, Song-tao Lyu, et al. Application status of steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 15-33. | |
| 70 | Vo H V, Park D W, Seo W J, et al. Evaluation of asphalt mixture modified with graphite and carbon fibers for winter adaptation: thermal conductivity improvement[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(1): No. 04016176. |
| 71 | García Á, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M, et al. Electrical conductivity of asphalt mortar containing conductive fibers and fillers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009, 23(10): 3175-3181. |
| 72 | Wang H, Yang J, Liao H, et al. Electrical and mechanical properties of asphalt concrete containing conductive fibers and fillers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 122: 184-190. |
| 73 | 王向阳, 高宇星. 碳纤维石墨导电沥青混凝土的制备及导电性能研究[J]. 公路, 2012, 56(1): 139-142. |
| Wang Xiang-yang, Gao Yu-xing. Research on preparation and conductive performance of conductive carbon fiber graphite asphalt concrete[J]. Highway, 2012, 56(1): 139-142. | |
| 74 | Wu S, Pan P, Chen M, et al. Analysis of characteristics of electrically conductive asphalt concrete prepared by multiplex conductive materials[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2013, 25(7): 871-879. |
| 75 | Yang H, Ouyang J, Cao P, et al. Effect of steel wool and gaphite on the electrical conductivity and pavement properties of asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2022, 34(3): No. 04021466. |
| 76 | Gürer C, Fidan U, Korkmaz B E. Investigation of using conductive asphalt concrete with carbon fiber additives in intelligent anti-icing systems[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2023, 24(1): No. 2077941. |
| 77 | 张园. 多相复合导电沥青混凝土的制备与性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2010. |
| Zhang Yuan. Preparation and properties investigation of multiplex electrically conductive asphalt concrete[D]. Wuhan: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2010. | |
| 78 | Callomamani L A P, Bala N, Hashemian L. Comparative analysis of the impact of synthetic fibers on cracking resistance of asphalt mixes[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2022, 16(4): 992-1008. |
| 79 | Liu X, Liu W, Wu S, et al. Effect of carbon fillers on electrical and road properties of conductive asphalt materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 68: 301-306. |
| 80 | Pan P, Wu S, Hu X, et al. Effect of freezing-thawing and ageing on thermal characteristics and mechanical properties of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 140: 239-247. |
| 81 | Gao H, Zhang L, Zhang D, et al. Mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced asphalt concrete: finite element simulation and experimental study[J]. e-Polymers, 2021, 21(1): 533-548. |
| 82 | Kim S, Choi S, Oh E, et al. Revisit to three-dimensional percolation theory: Accurate analysis for highly stretchable conductive composite materials[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-10. |
| 83 | Kirkpatrick S. Percolation and conduction[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1973, 45(4): 574-588. |
| 84 | Zhang C, Zhu J, Ouyang M, et al. Conductive network formation and electrical properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites: Percolation and dynamic percolation[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2009, 114(3): 1405-1411. |
| 85 | 石东海. 聚合物基复合材料 PTC 性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2008. |
| Shi Dong-hai. Study on PTC effect in polymer-based composites[D]. Beijing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2008. | |
| 86 | 宋固全, 陈忠良, 陈煜国. 有效介质理论在复合型导电高分子材料研究中的应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 2013, 41(11): 152-154. |
| Song Gu-quan, Chen Zhong-liang, Chen Yu-guo. Application of the effective media theory in the research of composite polymer materials[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2013, 41(11): 152-154. | |
| 87 | 汤浩, 陈欣方, 罗云霞. 复合型导电高分子材料导电机理研究及电阻率计算[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 1996, 12(2): 1-7. |
| Tang Hao, Chen Xin-fang, Luo Yun-xia. Conductive mechanism research and resistivity calculation of composite conductive polymer materials[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 1996, 12(2): 1-7. | |
| 88 | Sun C, Qin L, Wu S, et al. The influence of electrode on resistivity of conductive asphalt concrete for self-monitoring[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2012, 509: 203-208. |
| 89 | Ullah S, Wan S, Yang C, et al. Self‐stress and deformation sensing of electrically conductive asphalt concrete incorporating carbon fiber and iron tailings[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2022, 29: 1-17. |
| 90 | Vo H V, Park D-W. Application of conductive materials to asphalt pavement[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2017(1): 1-7. |
| 91 | Tang N, Pan W, Chen Y, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of piezoresistance of asphalt concrete containing graphite[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016, 852: 1383-1390. |
| 92 | Rizvi H R, Khattak M J, Madani M, et al. Piezoresistive response of conductive hot mix asphalt mixtures modified with carbon nanofibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 106: 618-631. |
| 93 | Chen Z, Liu R, Hao P, et al. Developments of conductive materials and characteristics on asphalt concrete: a review[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2019, 48(3): 2144-2161. |
| 94 | Dong S, Zhang W, D'alessandro A, et al. Developing highly conductive asphalt concrete by incorporating stainless steel fibers/wires for smart pavement[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2023, 58: 11062-11084. |
| 95 | Wang H, Yang J, Liao H. Advances in self-monitoring asphalt concrete[C]∥The 15th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals, Beijing, China, 2015: 810-822. |
| 96 | Wu S, Liu X, Ye Q, et al. Self-monitoring electrically conductive asphalt-based composite containing carbon fillers[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16: 512-516. |
| 97 | Liu X, Nie Z, Wu S, et al. Self-monitoring application of conductive asphalt concrete under indirect tensile deformation[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2015, 3: 70-77. |
| 98 | Zhu F, Cheung L, Dong Z. Research on the relationship between the loading and the conductivity of smart asphalt concrete[C]∥Performance Modeling and Evaluation of Pavement Systems and Materials: Selected Papers from the 2009 GeoHunan International Conference, Changsha, China, 2009, 354: 165-170. |
| 99 | Wu S, Mo L, Shui Z. Piezoresistivity of graphite modified asphalt-based composites[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2003, 249: 391-396. |
| 100 | Liu X, Wu S, Li N, et al. Self-monitoring application of asphalt concrete containing graphite and carbon fibers[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2008, 23(2): 268-271. |
| 101 | Karimi M M, Amani S, Jahanbakhsh H, et al. Induced heating-healing of conductive asphalt concrete as a sustainable repairing technique: a review[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2021, 4: No. 100188. |
| 102 | Sun D, Sun G, Zhu X, et al. A comprehensive review on self-healing of asphalt materials: mechanism, model, characterization and enhancement[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 256: 65-93. |
| 103 | Liang B, Lan F, Shi K, et al. Review on the self-healing of asphalt materials: mechanism, affecting factors, assessments and improvements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 266: No. 120453. |
| 104 | García Á, Bueno M, Norambuena-Contreras J, et al. Induction healing of dense asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 1-7. |
| 105 | Menozzi A, García Á, Partl M N, et al. Induction healing of fatigue damage in asphalt test samples[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 74: 162-168. |
| 106 | Jahanbakhsh H, Karimi M M, Jahangiri B, et al. Induction heating and healing of carbon black modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 174: 656-666. |
| 107 | Liu Q, Schlangen E, Van De Ven M F C. Induction Healing of Porous Asphalt[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2012, 2305: 95-101. |
| 108 | Chen M, Wu S, Wang H, et al. Study of ice and snow melting process on conductive asphalt solar collector[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(12): 3241-3250. |
| 109 | 李科宏, 熊锐, 蒋汶玉, 等. 基于感应加热的钢丝绒纤维沥青混合料除冰性能评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(32): 313-321. |
| Li Ke-hong, Xiong Rui, Jiang Wen-yu, et al. Evaluation of deicing performance of steel wool fiber asphalt mixture based on induction heating[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(32): 313-321. | |
| 110 | 纪括, 熊锐, 李科宏, 等. 感应加热沥青混合料融雪化冰性能研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(2): 450-454, 475. |
| Ji Kuo, Xiong Rui, Li Ke-hong, et al. Research progress on the performance of induction heating asphalt mixture for melting snow and deicing[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(2): 450-454, 475. | |
| 111 | Bai B C, Park D-W, Vo H V, et al. Thermal properties of asphalt mixtures modified with conductive fillers[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015, 16(1): 255-260. |
| 112 | 吕林女, 敖灶鑫, 丁庆军, 等. 钢渣导电沥青混凝土的制备与性能研究[J]. 公路, 2009, 53(2): 132-136. |
| Lin-nv Lyu, Ao Zao-xin, Ding Qing-jun, et al. Preparation of conductive asphalt concrete added with steel slag and studies on its properties[J]. Highway, 2009, 53(2): 132-136. | |
| 113 | 何永佳, 敖灶鑫, 吕林女, 等. 融雪化冰用钢渣导电沥青混凝土的电阻稳定性[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2011, 37(1): 80-84. |
| He Yong-jia, Ao Zao-xin, Lin-nv Lyu, et al. Electrical resistance stability on conductive asphalt concrete using steel slag as aggregate for deicing and snow-melting[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2011, 37(1): 80-84. | |
| 114 | Jiao W, Sha A, Liu Z, et al. Utilization of steel slags to produce thermal conductive asphalt concretes for snow melting pavements[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 261: No. 121197. |
| 115 | Stratfull R F. Experimental cathodic protection of a bridge deck[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1974, 500: 1-15. |
| 116 | Fromm H J. Electrically conductive asphalt mixes for the cathodic protection of concrete bridge decks[C]∥Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists. Minneapolis, USA, 1976: 382-399. |
| 117 | Liu X, Yu G. Combined effect of microwave and activated carbon on the remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 63(2): 228-235. |
| 118 | Huang B, Cao J, Chen X, et al. Laboratory investigation into electrically conductive HMA mixtures[J]. Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, 2006, 75: 1235-1253. |
| 119 | Wu S, Zhang Y, Chen M. Research on mechanical characteristics of conductive asphalt concrete by indirect tensile test[C]∥Fourth International Conference on Experimental Mechanics, Singapore, 2010: 1720-1727. |
| 120 | 姚占勇, 韩杰, 商庆森, 等. 碳纤维石墨导电沥青砂浆压敏性能研究[J]. 山东大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(1): 80-85. |
| Yao Zhan-yong, Han Jie, Shang Qing-sen, et al. Research on pressure sensitivity of the conductive asphalt mortar with carbon fiber and graphite powders[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2013, 43(1): 80-85. | |
| 121 | Rew Y, Baranikumar A, Tamashausky A V, et al. Electrical and mechanical properties of asphaltic composites containing carbon based fillers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 135: 394-404. |
| 122 | Karimi M M, Jahanbakhsh H, Jahangiri B, et al. Induced heating-healing characterization of activated carbon modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 178: 254-271. |
| 123 | Moreno-Navarro F, Sol-Sanchez M, Gamiz F, et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of graphene modified asphalt binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 180: 265-274. |
| 124 | Nazki M A, ChopraT, Chandrappa A K. Rheological properties and thermal conductivity of bitumen binders modified with graphene[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 238: No. 117693. |
| 125 | Xin X, Qiu Z, Luan X, et al. Novel conductive polymer composites for asphalt pavement structure in situ strain monitoring: influence of CB/CNT and GNP/CNT nano/micro hybrid fillers on strain sensing behavior[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(5): 3945-3956. |
| [1] | 赵胜前,丛卓红,游庆龙,李源. 沥青-集料黏附和剥落研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2437-2464. |
| [2] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [3] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [4] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [5] | 张青霞,侯吉林,安新好,胡晓阳,段忠东. 基于车辆脉冲响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [6] | 姜屏,陈业文,陈先华,张伟清,李娜,王伟. 改性石灰土在干湿和冻融循环下的无侧限抗压性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1809-1818. |
| [7] | 司春棣,崔亚宁,许忠印,凡涛涛. 层间粘结失效后桥面沥青铺装层细观力学行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
| [8] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [9] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [10] | 惠冰,杨心怡,张乐扬,李扬. 检测车轨迹偏移对沥青路面磨耗计算误差的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1756-1764. |
| [11] | 李崛,张安顺,张军辉,钱俊峰. 级配碎石基层结构动力响应模型测试及数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1782-1789. |
| [12] | 李博,李欣,芮红,梁媛. 基于变分模态分解和灰狼优化极限学习机的隧道口边坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1853-1860. |
| [13] | 刘状壮,郑文清,郑健,李轶峥,季鹏宇,沙爱民. 基于网格化的路表温度感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1746-1755. |
| [14] | 王宁,马涛,陈丰,付永强. 影响智能骨料感知的关键因素及数据分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1799-1808. |
| [15] | 黄晓明,赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
|
||