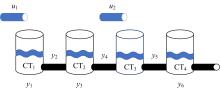
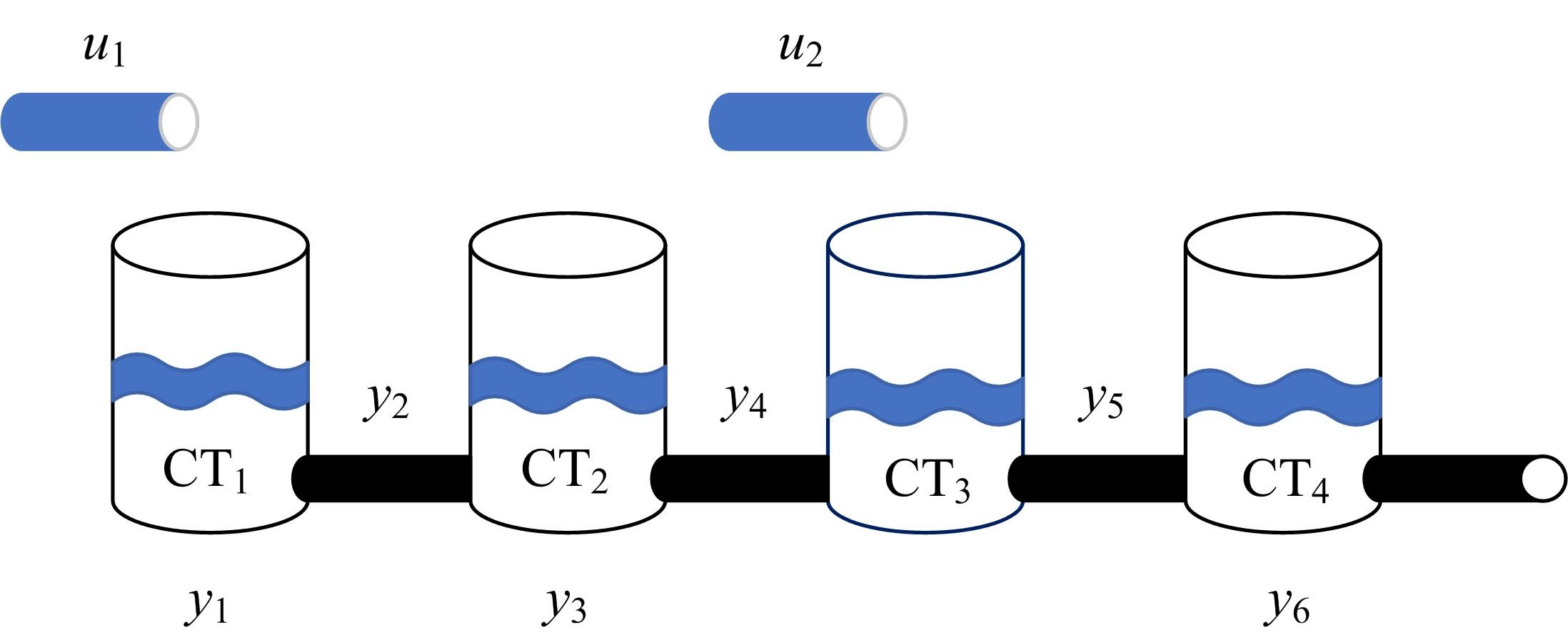
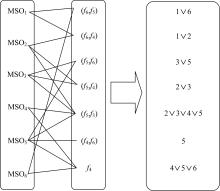
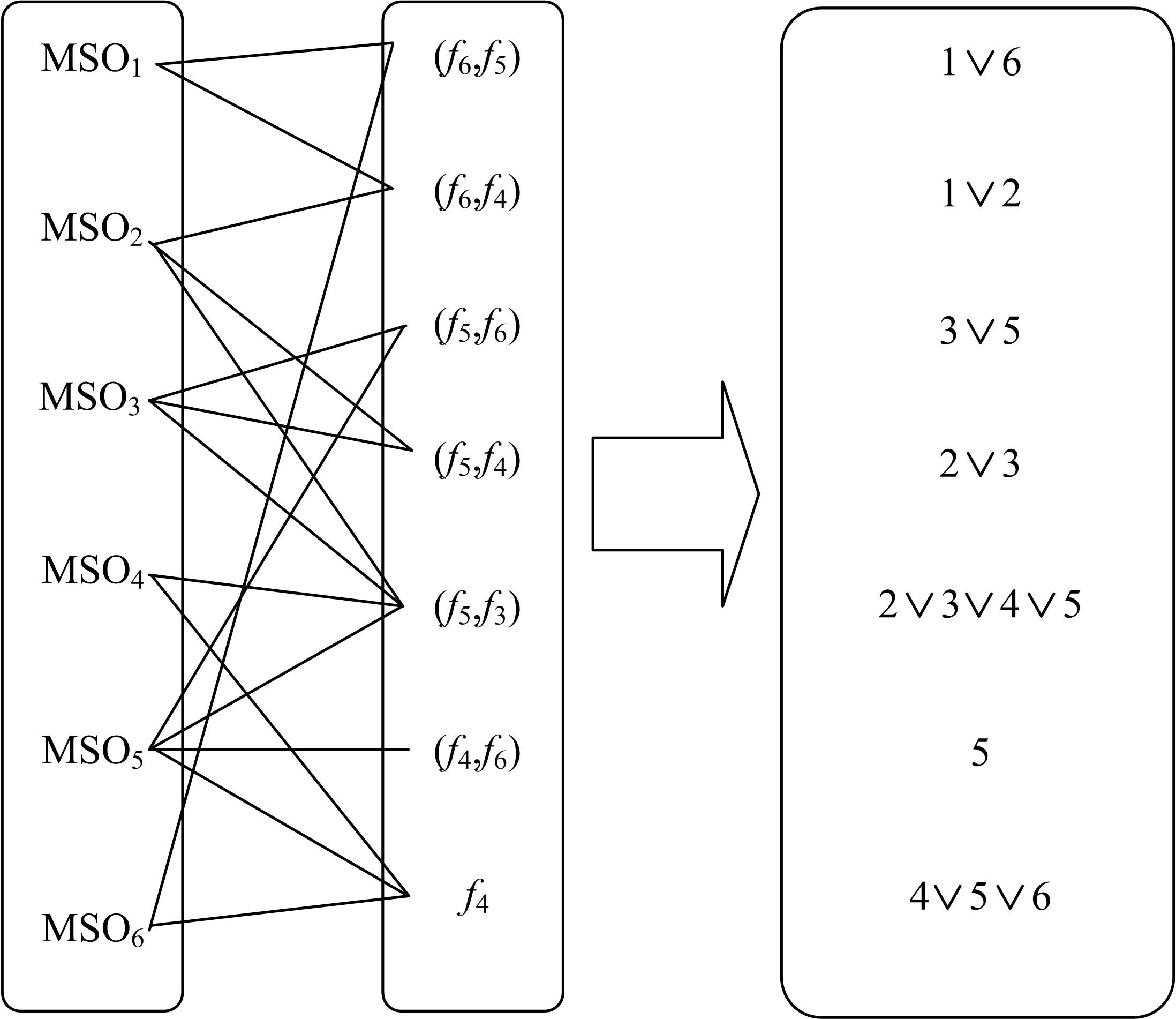
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1163-1173.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210792
Approach for generating minimal fault detectability and isolability set in dynamic system based on partial maximum satisfiability problem
Dan-tong OUYANG1,2( ),Rui SUN2,3,Xin-liang TIAN1,2,Li-ming ZHANG1,2(
),Rui SUN2,3,Xin-liang TIAN1,2,Li-ming ZHANG1,2( ),Ping-ping LIU1,2
),Ping-ping LIU1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP306
| 1 | Hwang I, Kim S, Kim Y, et al. A survey of fault detection, isolation, and reconfiguration methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2010, 18(3): 636-653. |
| 2 | De Kleer J, Williams B C. Diagnosing multiple faults[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1987, 32(1): 97-130. |
| 3 | 欧阳丹彤, 刘伯文, 刘梦, 等. 结合电路结构基于分块的诊断方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(7): 38-44. |
| Ouyang Dan-tong, Liu Bo-wen, Liu meng, et al. A block-based diagnostic method combinbing with the circuit structure[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(7): 38-44. | |
| 4 | Svard C, Nyberg M, Frisk E, et al. Realizability constrained selection of residual generators for fault diagnosis with an automotive engine application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, 2013, 43(6): 1354-1369. |
| 5 | Falkenberg T, Gregersen R, Blanke M. Navigation system fault diagnosis for underwater vehicle[J].IFAC-Papers on Line, 2014, 47(3): 9654-9660. |
| 6 | Svard C, Nyberg M. Automated design of an FDI-system for the wind turbine benchmark [J]. IFAC-Papers on Line, 2011, 44(1): 8307-8315. |
| 7 | Jung D. A generalized fault isolability matrix for improved fault diagnosability analysis[C]//The 3rd Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol), Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 519-524. |
| 8 | Sankavaram C, Kodali A, Pattipati K R, et al. Incremental classifiers for data-driven fault diagnosis applied to automotive systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 407-419. |
| 9 | Jung D, Sundström C. A combined data-driven and model-based residual selection algorithm for fault detection and isolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems, 2019, 27(2): 616-630. |
| 10 | Frisk E, Krysander M. Residual selection for consistency based diagnosis using machine learning models[J]. IFAC-Papers on Line, 2018, 51(24): 139-146. |
| 11 | Jung D, Frisk E. Residual selection for fault detection and isolation using convex optimization[J]. Automatica, 2018, 97: 143-149. |
| 12 | 田乃予, 欧阳丹彤, 刘梦, 等. 基于子集一致性检测的诊断解极小性判定方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(7): 1396-1407. |
| Tian Nai-yu, Ouyang Dan-tong, Liu Meng, et al. A method of minimality-checking of fiagnosis based on subset consistency detection[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(7): 1396-1407. | |
| 13 | Nejjari A F, Sarrate E R, Rosich O A.Optimal sensor placement for fuel cell system diagnosis using BILP formulation[C]∥The 18th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Marrakech, Morocco, 2010: 1296-1301. |
| 14 | Khorasgani H, Biswas G. Structural fault detection and isolation in hybrid systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(4): 1585-1599. |
| 15 | Pérez-Zuiga G, Rivas-Perez R, Sotomayor J, et al. Fault detection and isolation system based on structural analysis of an industrial seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(9): 1100. |
| 16 | Khorasgani H, Biswas G, Jung D. Minimal structurally overdetermined sets selection for distributed fault detection[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis, Paris, France, 2015: 75-82. |
| 17 | Krysander M, Åslund J, Nyberg M. An efficient algorithm for finding minimal over-constrained sub-systems for model-based diagnosis[J]. IEEE Trans on Systems,Man and Cybernetics–Part A: Systems and Humans, 2008, 38(1): 197-206. |
| 18 | Svard C, Nyberg M. Residual generators for fault diagnosis using computation sequences with mixed causality applied to automotive systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics–Part A: Systems and Humans, 2010, 40(6): 1310-1328. |
| 19 | Blanke M, Kinnaert M, Lunze J, et al. Diagnosis and fault-tolerant control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006. |
| 20 | Krysander M, Åslund J, Frisk E. A structural algorithm for finding testable sub-models and multiple fault isolability analysis[C]∥The 21st International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis (DX-10), Portland, USA, 2010: |
| 21 | Reiter R. A theory of diagnosis from first principles [J].Artificial Intelligence, 1987, 32(1): 57-96. |
| 22 | Frisk E, Krysander M, Jung D. A toolbox for analysis and design of model based diagnosis systems for large scale models[J]. IFAC-Papers on Lines, 2017, 50(1): 3287-3293. |
| 23 | Robinson J A, Davis M, Logemann G, et al. A machine program for theorem-proving[J]. Journal of Symbolic Logic, 1967, 32(1): 118-394. |
| 24 | Cai S W, Luo C, Zhang H. From decimation to local search and back: a new approach to MaxSAT[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne,Australia, 2017: 571-577. |
| 25 | 刘思光, 欧阳丹彤, 王艺源,等. 结合SE-Tree结构特征的极小碰集求解算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(11): 2556-2566. |
| Liu Si-guang, Ouyang Dan-tong, Wang Yi-yuan, et al. Minimal collision set solving algorithm combined with SE-Tree structural features[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2016, 53(11): 2556-2566. | |
| 26 | Koshimura M, Zhang T, Fujita H, et al. Qmaxsat: a partial max-sat solver[J]. Journal on Satisfiability Boolean Modeling & Computation,2012,8(1/2): 95-100. |
| 27 | Dulmage A L, Mendelsohn N S. Coverings of bipartite graphs[J]. Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 1958, 10: 517-534. |
| [1] | Dan-tong OU-YANG,Rui SUN,Xin-liang TIAN,Bo-han GAO. Set blocking⁃based approach to sensor selection in uncertain systems [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 547-554. |
| [2] | Jie CAO,Jia-lin MA,Dai-lin HUANG,Ping YU. A fault diagnosis method based on multi Markov transition field [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [3] | Jin-hua WANG,Jia-wei HU,Jie CAO,Tao HUANG. Multi⁃fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on adaptive variational modal decomposition and integrated extreme learning machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 318-328. |
| [4] | Shao-jiang DONG,Peng ZHU,Xue-wu PEI,Yang LI,Xiao-lin HU. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing under variable operating conditions based on subdomain adaptation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [5] | Wei LUO,Bo LU,Fei CHEN,Teng MA. Fault diagnosis method of NC turret based on PSO⁃SVM and time sequence [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [6] | Fei-yue DENG, LYUHao-yang,Xiao-hui GU,Ru-jiang HAO. Fault diagnosis of high⁃speed train axle bearing based on a lightweight neural network Shuffle⁃SENet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. |
| [7] | Long ZHANG,Tian-peng XU,Chao-bing WANG,Jian-yu YI,Can-zhuang ZHEN. Gearbox fault diagnosis baed on convolutional gated recurrent network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [8] | Xiao⁃lei CHEN,Yong⁃feng SUN,Ce LI,Dong⁃mei LIN. Stable anti⁃noise fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on CNN⁃BiLSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [9] | Xian-jun DU,Liang-liang JIA. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on optimized stacked denoising auto encoders [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2827-2838. |
| [10] | Fei CHEN,Zheng YANG,Zhi-cheng ZHANG,Wei LUO. Fault diagnosis method of rotating machinery for unlabeled data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2514-2522. |
| [11] | Jie CAO,Zhi-Dong HE,Ping YU,Jin-hua WANG. Bearing fault diagnosis method under unbalanced data distribution [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2523-2531. |
| [12] | Dan-tong OUYANG,Bi-ge ZHANG,Nai-yu TIAN,Li-ming ZHANG. Fail data reduction algorithm combining configuration checking with local search [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [13] | Lao-hu YUAN,Dong-shan LIAN,Liang ZHANG,Yi LIU. Fault diagnosis of key mechanical components of aircraft based on densenet and support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1635-1641. |
| [14] | Dan-tong OUYANG,Yang LIU,Jie LIU. Fault diagnosis method based on test set under fault response guidance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [15] | Wei LI,Jian CHEN,Shan-yong TAO. Method of enhancing stochastic resonance signal of self⁃adaptive coupled periodic potential system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1091-1096. |
|
||