吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 46-54.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230107
丙泊酚后处理对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤的改善作用及其机制
- 1.中国医科大学附属第四医院麻醉科,辽宁 沈阳 110000
2.北部战区总医院麻醉科,辽宁 沈阳 110000
Improvement effect of propofol postconditioning on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism
Jun ZHU1,Nan ZHOU2,Deming LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Anesthesiology,Fourth Affiliated Hospital,China Medical University,Shenyang 110000,China
2.Department of Anesthesiology,General Hospital,Northern Theater Command,Shenyang 110000,China
摘要:
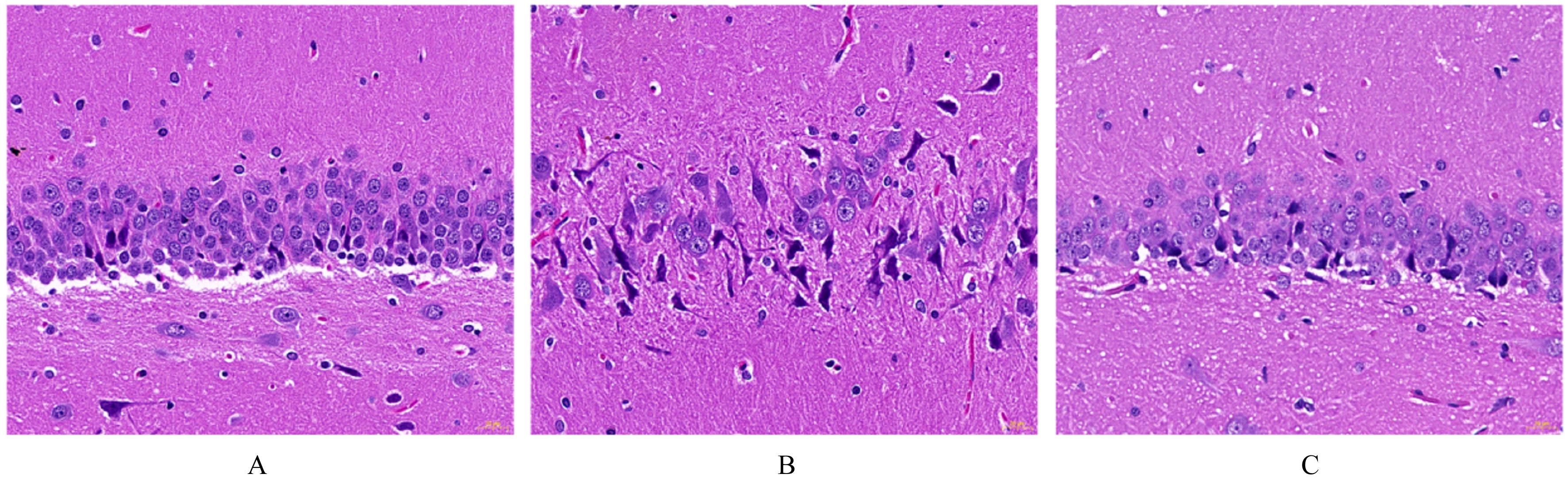
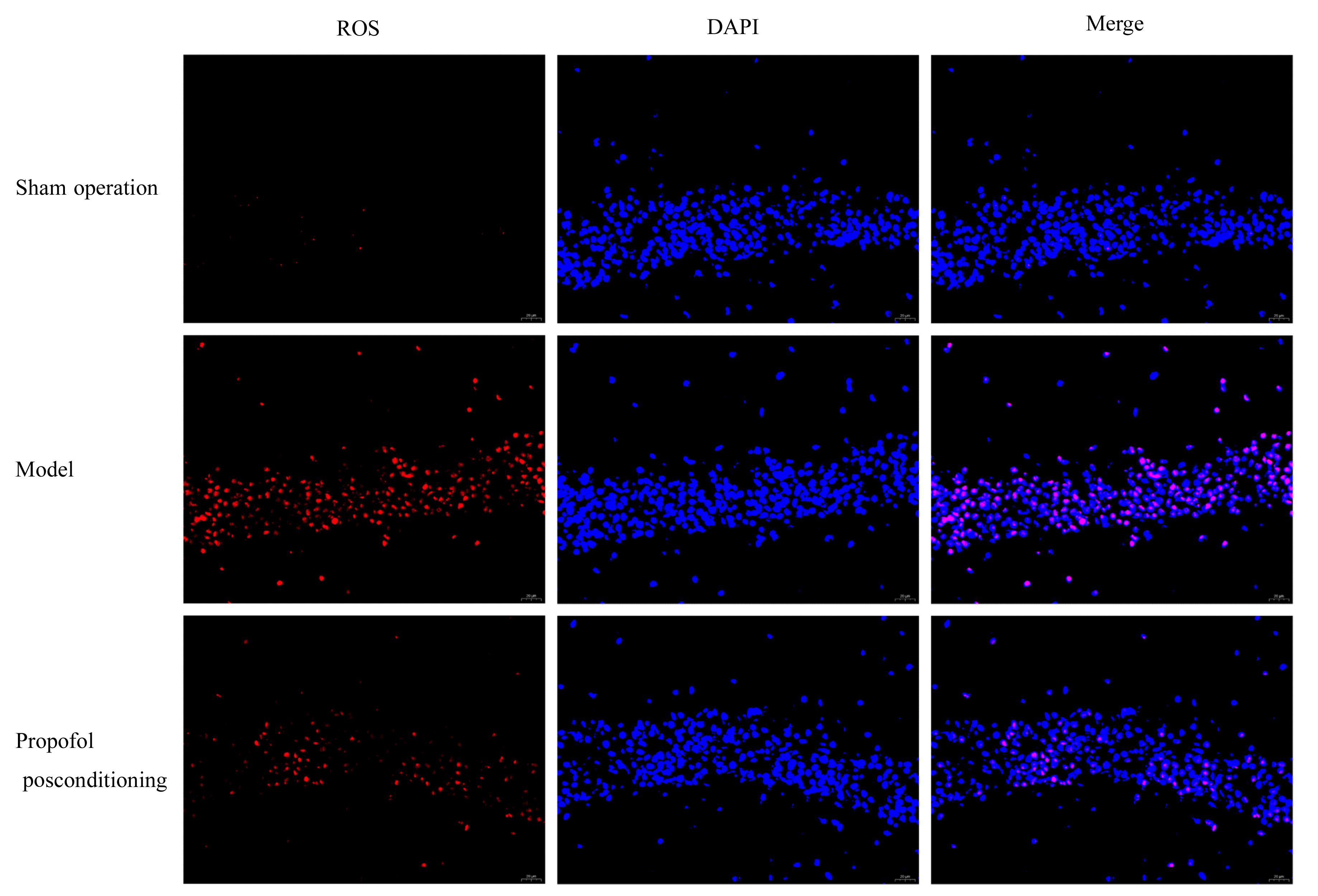
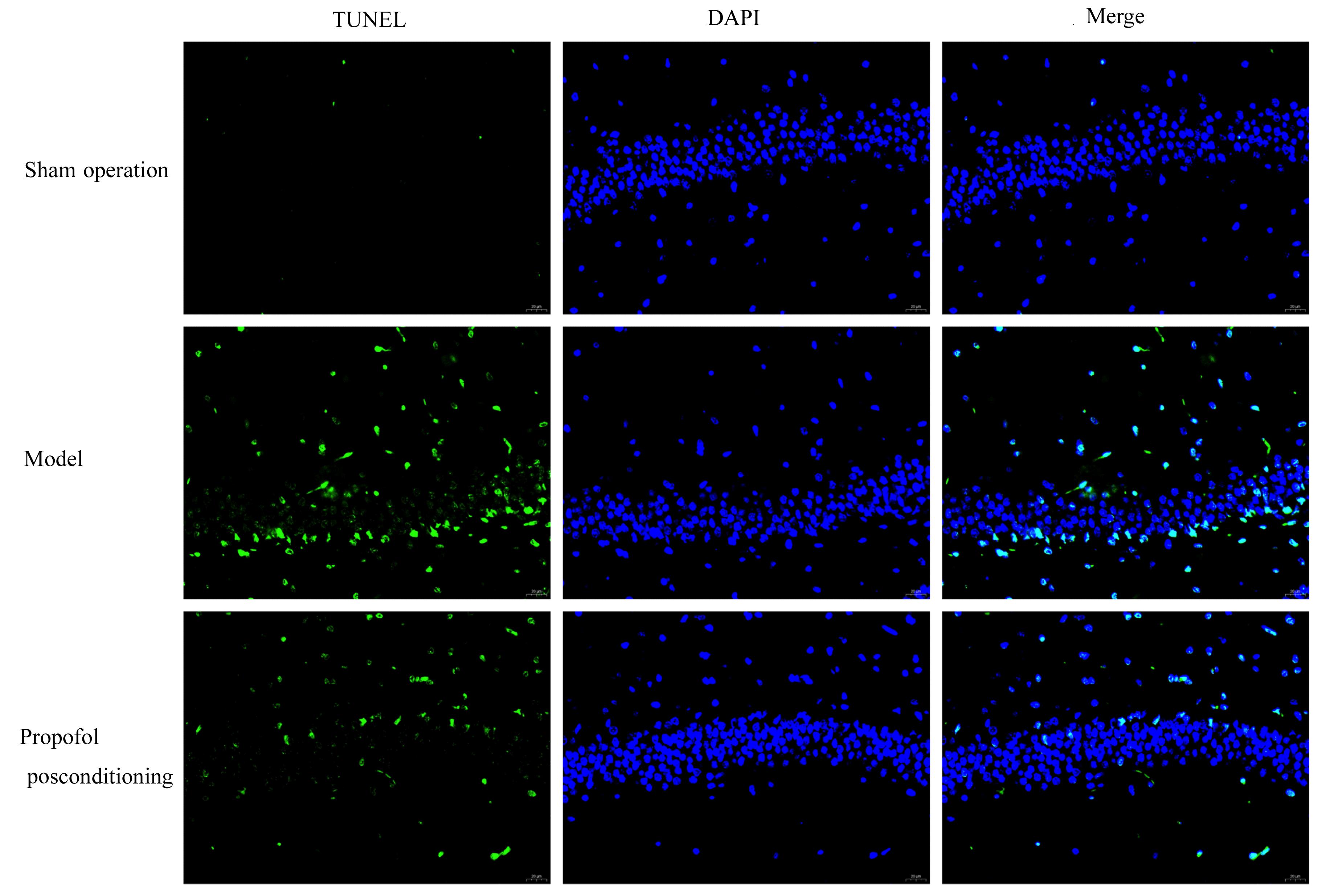
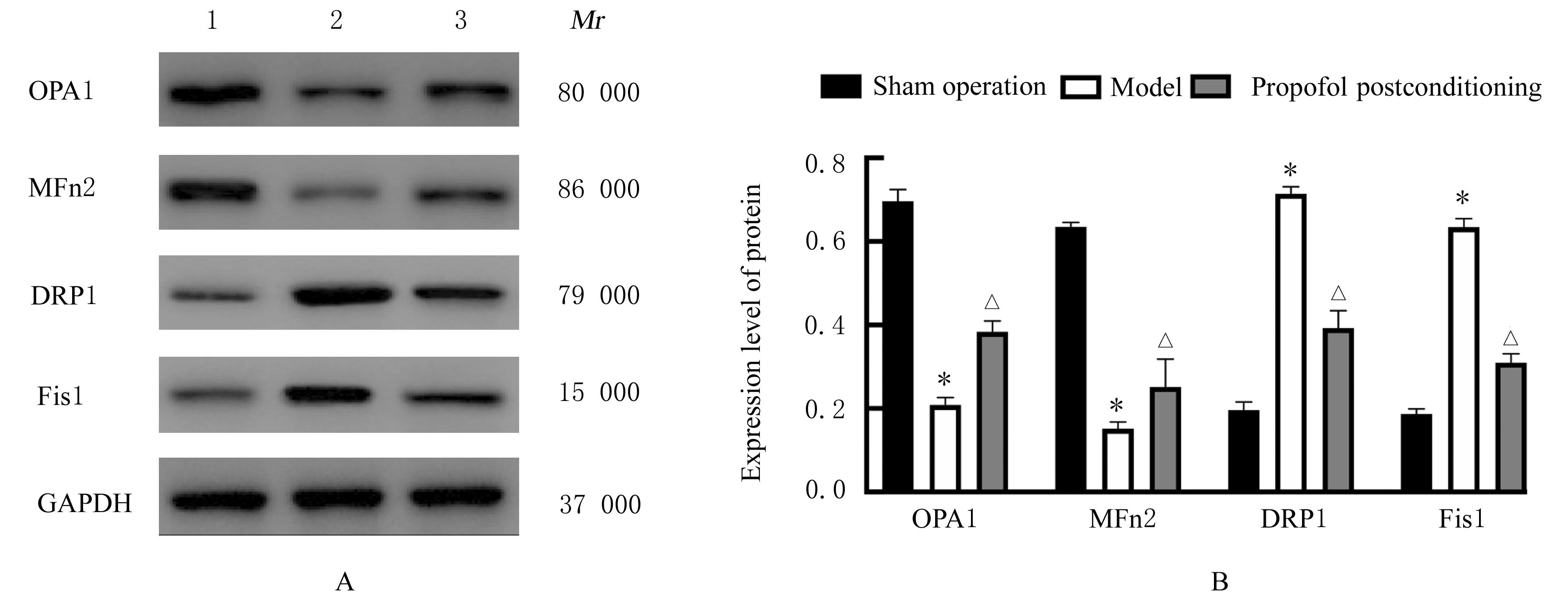
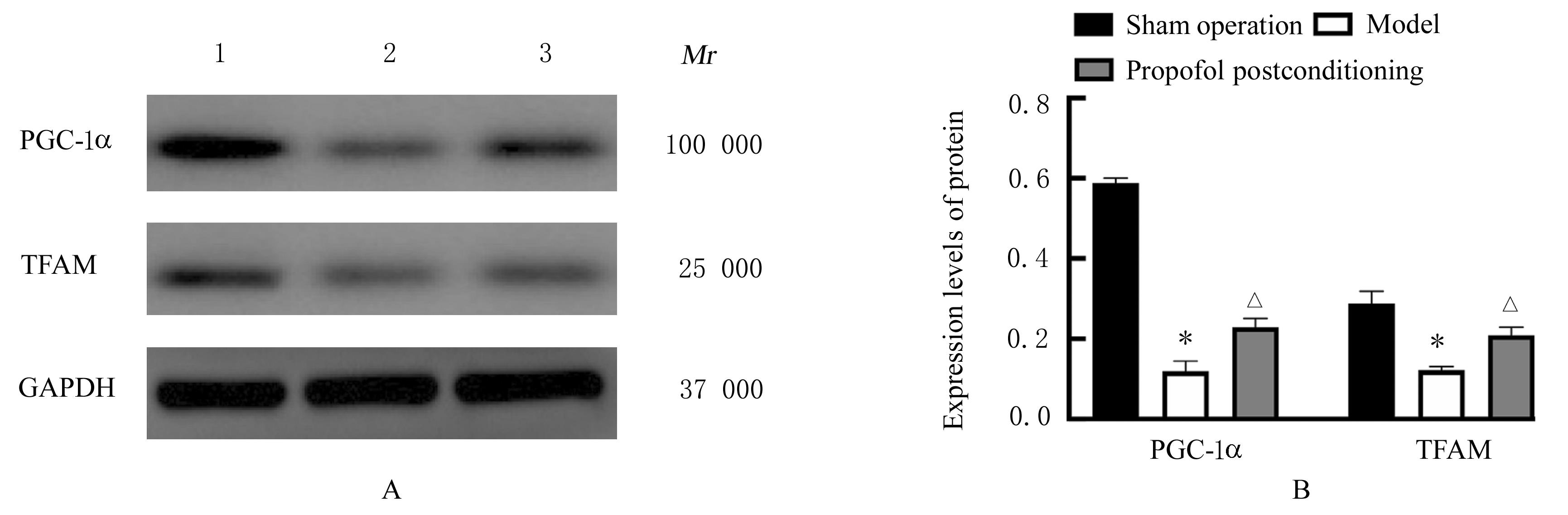
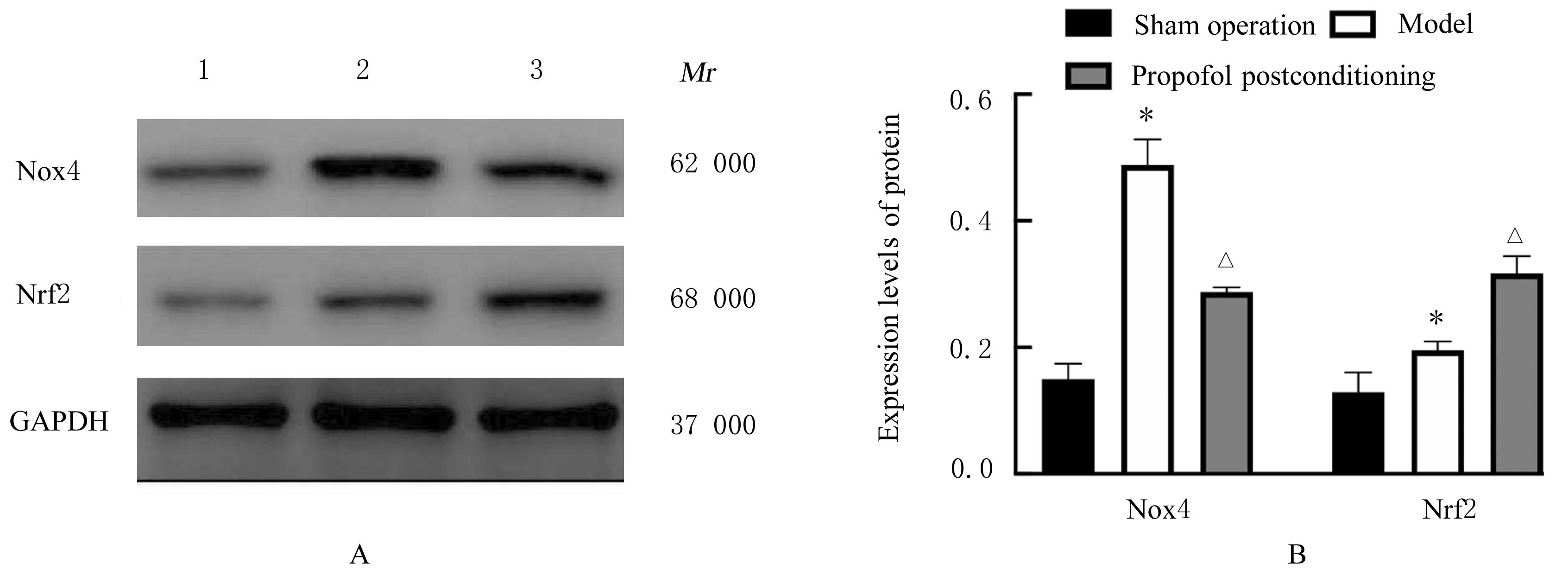
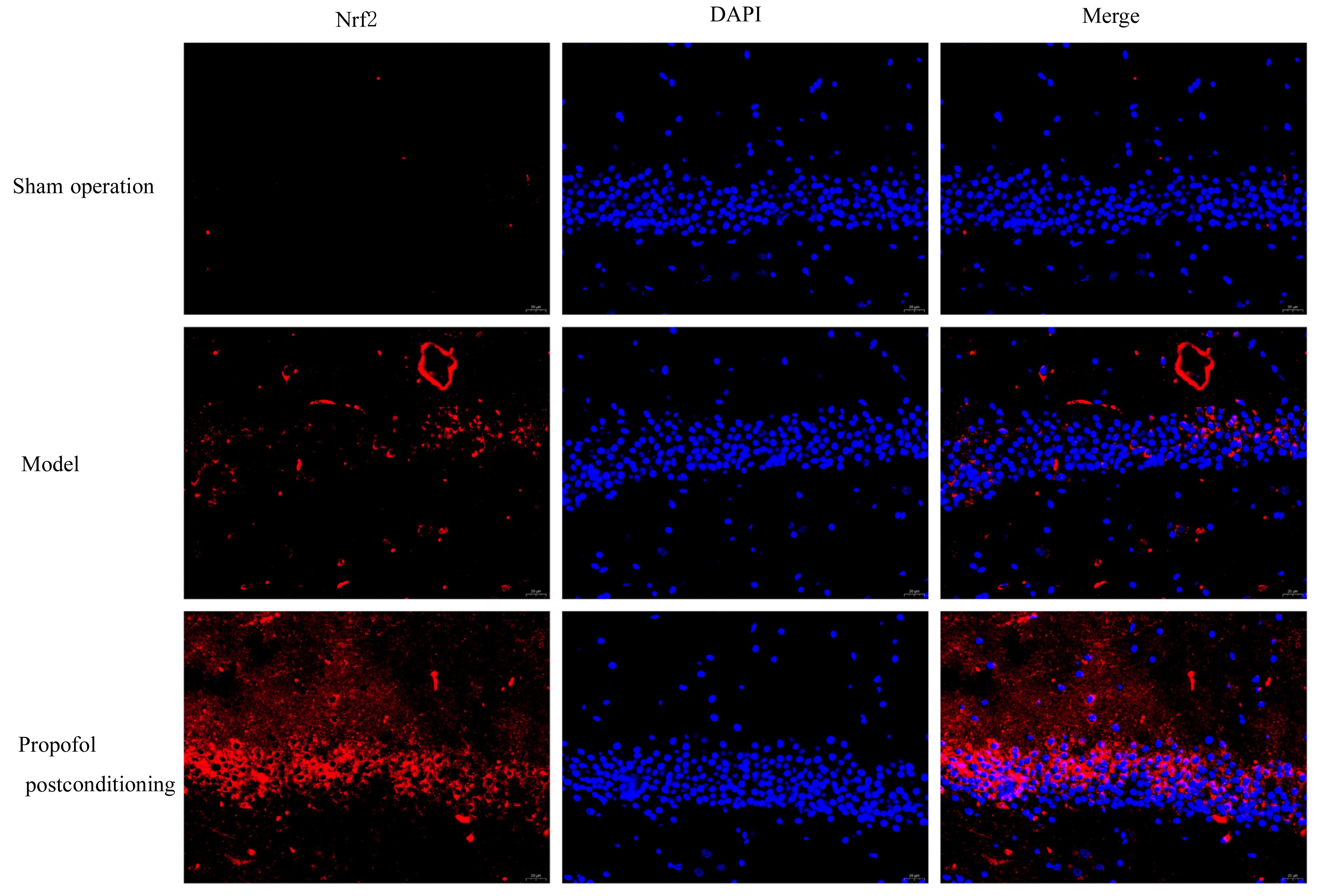
目的 探讨丙泊酚后处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经功能的改善作用及其对脑线粒体损伤的保护作用,阐明其作用机制。 方法 24只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和丙泊酚后处理组,每组8只。模型组和丙泊酚后处理组大鼠采用结扎颈动脉法建立大脑中动脉阻塞局灶性脑缺血再灌注模型,丙泊酚后处理组大鼠于再灌注即刻股静脉输注20 mg·kg-1·h-1丙泊酚2 h,假手术组和模型组大鼠给予等量生理盐水。各组大鼠于再灌注24 h后进行神经功能缺损评分,采用HE染色法观察各组大鼠海马组织病理形态表现,采用相关试剂盒检测各组大鼠海马组织中氧化应激相关因子活性和水平,采用活性氧(ROS)荧光探针检测各组大鼠脑海马组织中ROS水平,采用TUNEL法检测各组大鼠海马组织中TUNEL阳性细胞率,采用Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马组织中线粒体裂变、融合和生物发生相关蛋白及烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸酯氧化酶4(Nox4)和核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)蛋白表达水平,免疫荧光法检测各组大鼠海马组织中Nrf2蛋白表达水平。 结果 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠神经功能缺损评分明显升高(P<0.05),大鼠海马组织病理损伤明显,海马组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)活性和总抗氧化力(T-AOC)水平明显降低(P<0.01),丙二醛(MDA)和ROS水平及TUNEL阳性细胞率明显升高(P<0.05),动力相关蛋白1(DRP1)、裂变蛋白1(Fis1)、Nox4和Nrf2蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),视神经萎缩症蛋白1(OPA1)、线粒体融合蛋白2(Mfn2)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α(PGC-1α)和线粒体转录因子 A(TFAM)蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,丙泊酚后处理组大鼠神经功能缺损评分明显降低(P<0.05),大鼠海马组织病理损伤明显改善,大鼠海马组织中SOD及GSH-Px活性和T-AOC水平明显升高(P<0.05),MDA 水平、ROS水平和TUNEL阳性细胞率明显降低(P<0.05),DRP1、Fis1和Nox4蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),OPA1、Mfn2、PGC-1α、TFAM和Nrf2蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 丙泊酚后处理可抑制脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马组织细胞凋亡和氧化应激,促进线粒体融合和生物发生并抑制线粒体裂变,改善大鼠神经功能损伤,其机制可能与调控Nox4/Nrf2信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R743.3