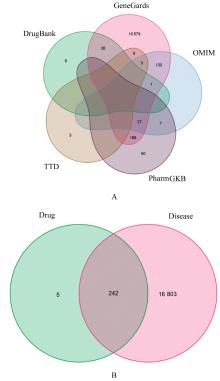
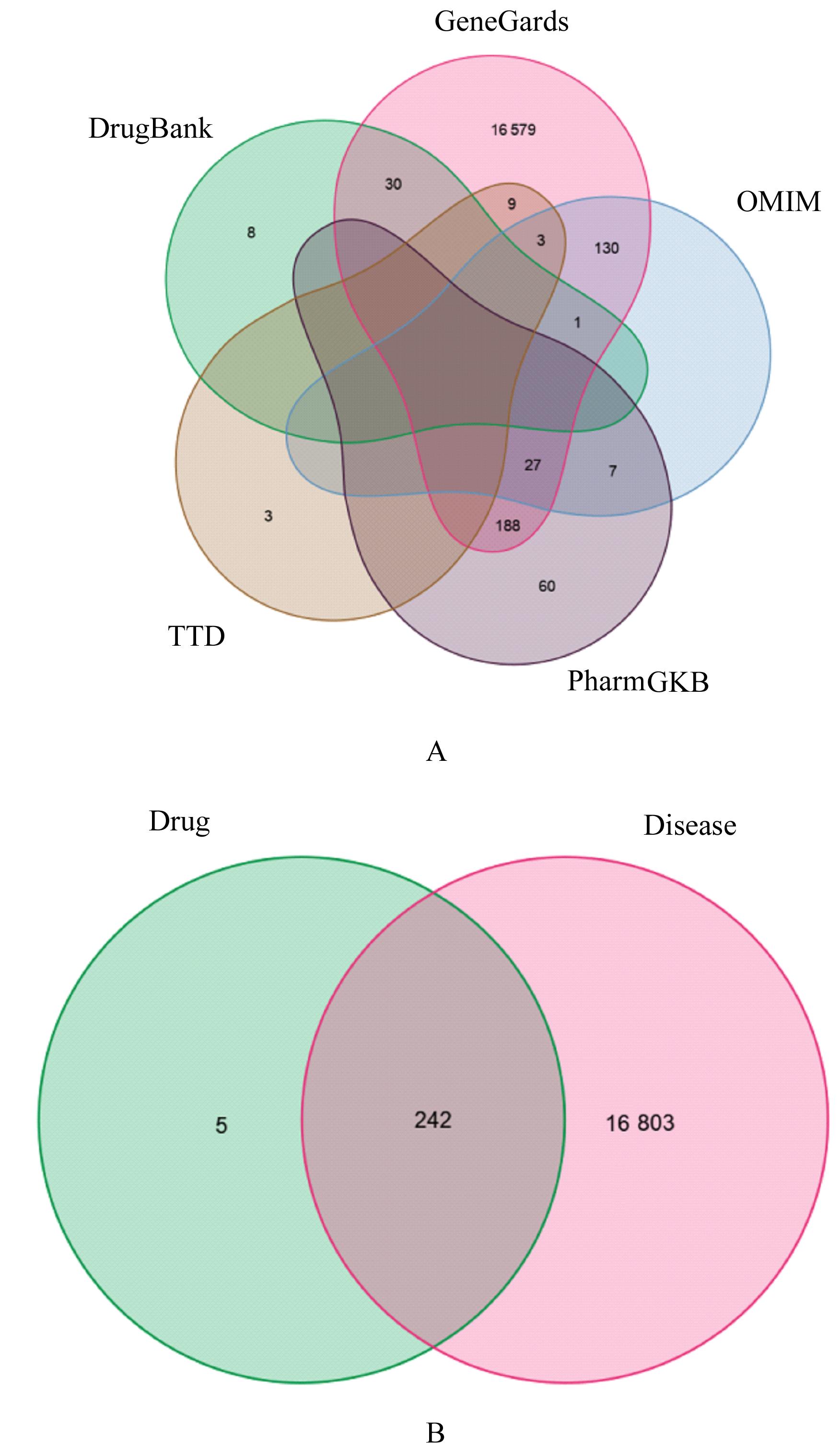
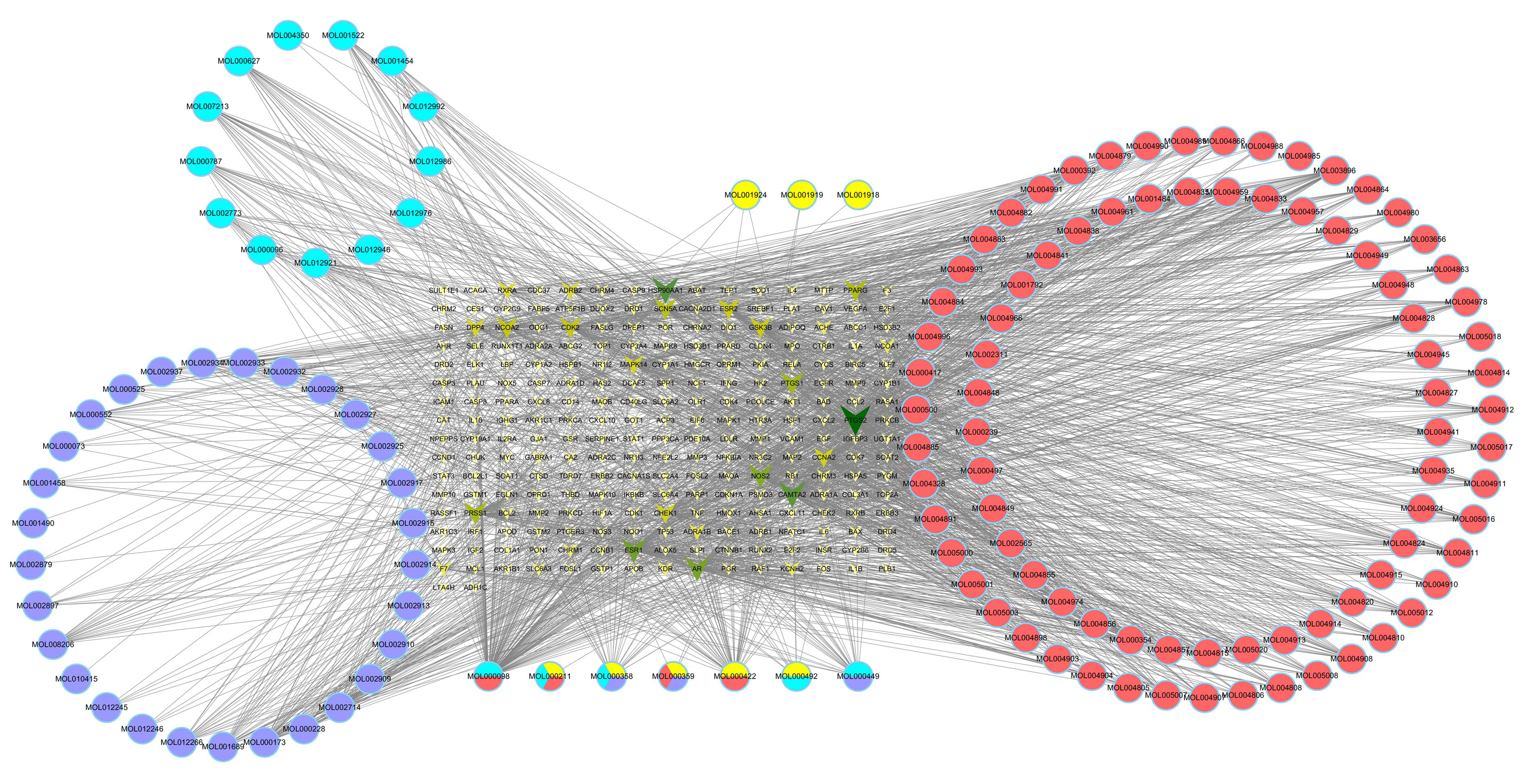
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 208-220.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240125
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Huangqin Tang in treatment of colorectal cancer
Aiying CHEN1,Jinwen JIANG1( ),Hui ZHANG2
),Hui ZHANG2
- 1.Affiliated Hainan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital,Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Haikou 570100,China
2.Department of Oncology,Hainan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital,Haikou 570100,China
-
Received:2023-02-11Online:2024-01-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Jinwen JIANG E-mail:174676785@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Aiying CHEN,Jinwen JIANG,Hui ZHANG. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Huangqin Tang in treatment of colorectal cancer[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 208-220.
share this article
Tab.1
Main active compounds of Huangqin Tang"
| Mol ID | Molecular name | OB(η/%) | DL | Herb | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 | Dazao, Gancao | 136 |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 | Baishao, Gancao | 53 |
| MOL000173 | Wogonin | 30.68 | 0.23 | Huangqin | 39 |
| MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | 42.56 | 0.20 | Gancao | 36 |
| MOL004328 | Naringenin | 59.29 | 0.21 | Gancao | 35 |
| MOL002714 | Baicalein | 33.52 | 0.21 | Huangqin | 33 |
| MOL000497 | Licochalcone A | 40.79 | 0.29 | Gancao | 30 |
| MOL000392 | Formononetin | 69.67 | 0.21 | Gancao | 30 |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 | Gancao | 28 |
| MOL002565 | Medicarpin | 49.22 | 0.34 | Gancao | 27 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 | Dazao, Huangqin | 27 |
| MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 | Baishao, Dazao, Huangqin | 27 |
| MOL000500 | Vestitol | 74.66 | 0.21 | Gancao | 26 |
| MOL004978 | 2-[(3R)-8,8-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrano[6,5-f] chromen-3-yl]-5-methoxyphenol | 36.21 | 0.52 | Gancao | 26 |
| MOL004891 | Shinpterocarpin | 80.30 | 0.73 | Gancao | 26 |
| MOL004835 | Glypallichalcone | 61.60 | 0.19 | Gancao | 25 |
| MOL005003 | Licoagrocarpin | 58.81 | 0.58 | Gancao | 24 |
| MOL004974 | 3'-Methoxyglabridin | 46.16 | 0.57 | Gancao | 24 |
| MOL004957 | HMO | 38.37 | 0.21 | Gancao | 24 |
| MOL002928 | Oroxylin A | 41.37 | 0.23 | Huangqin | 23 |
| OB:Oral bioavailability;DL:Drug-likeness. | |||||
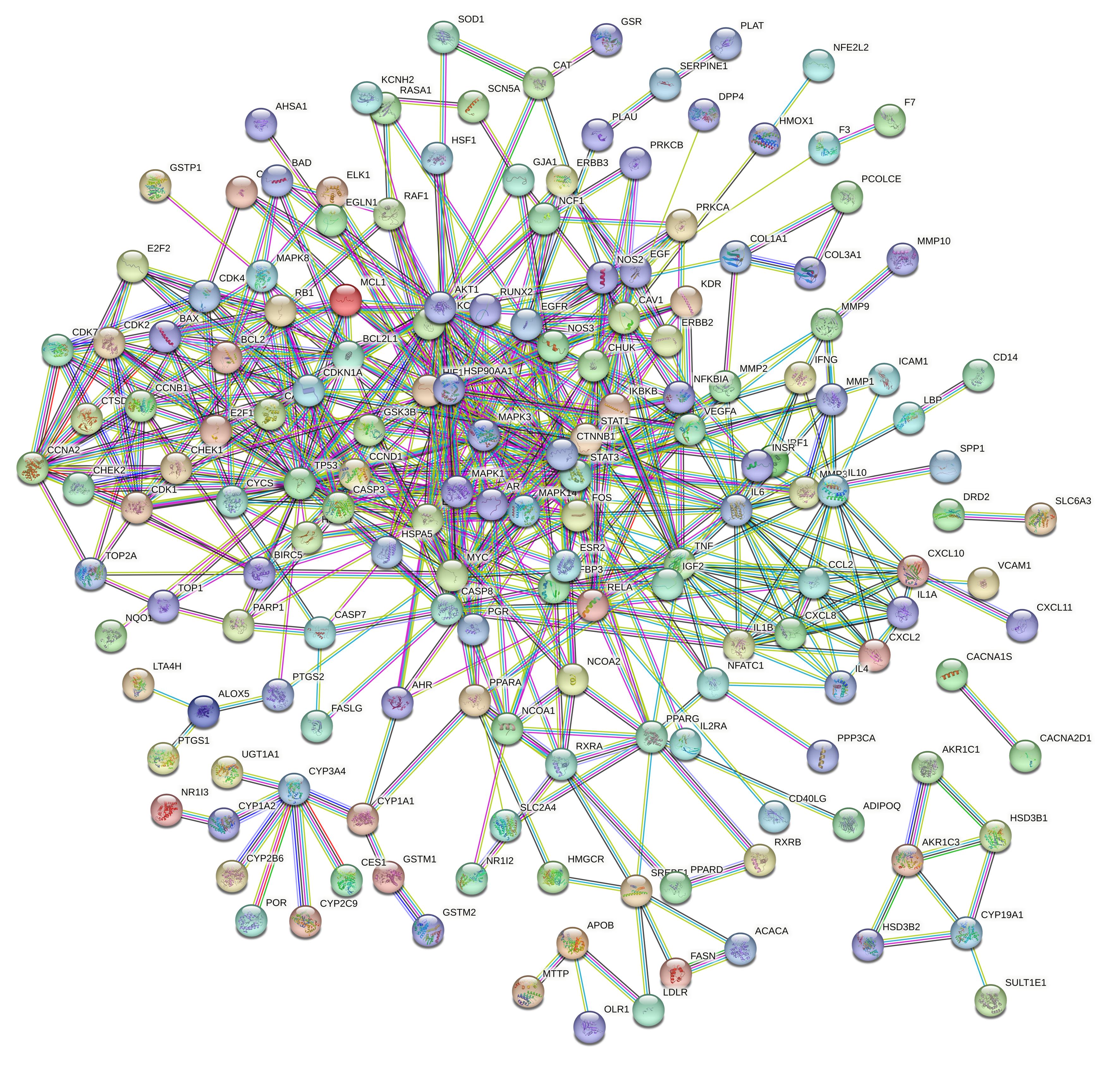
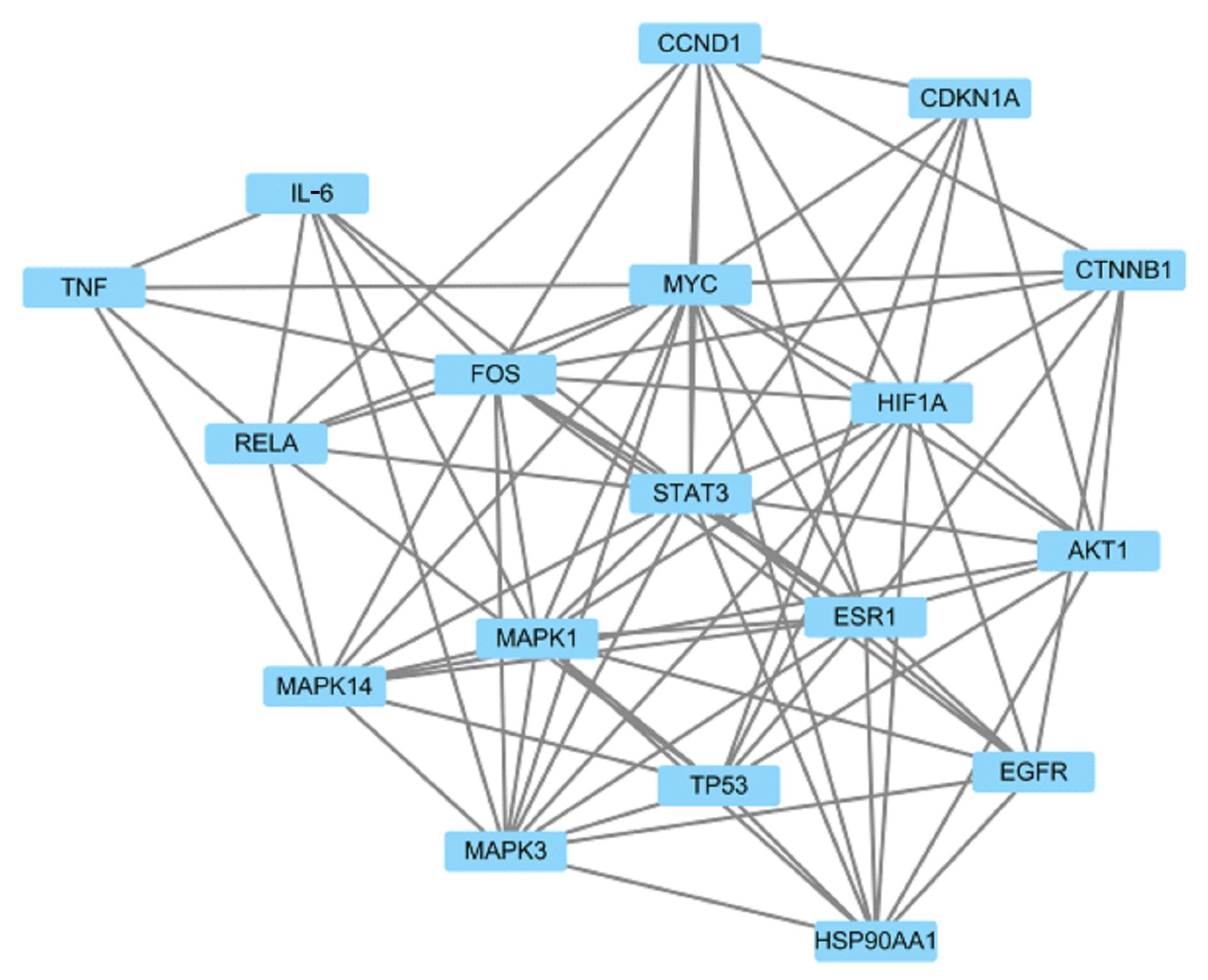
Tab.2
Potential core targets of Huangqin Tang in treatment of CRC"
| Target | Target name | BC | CC | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
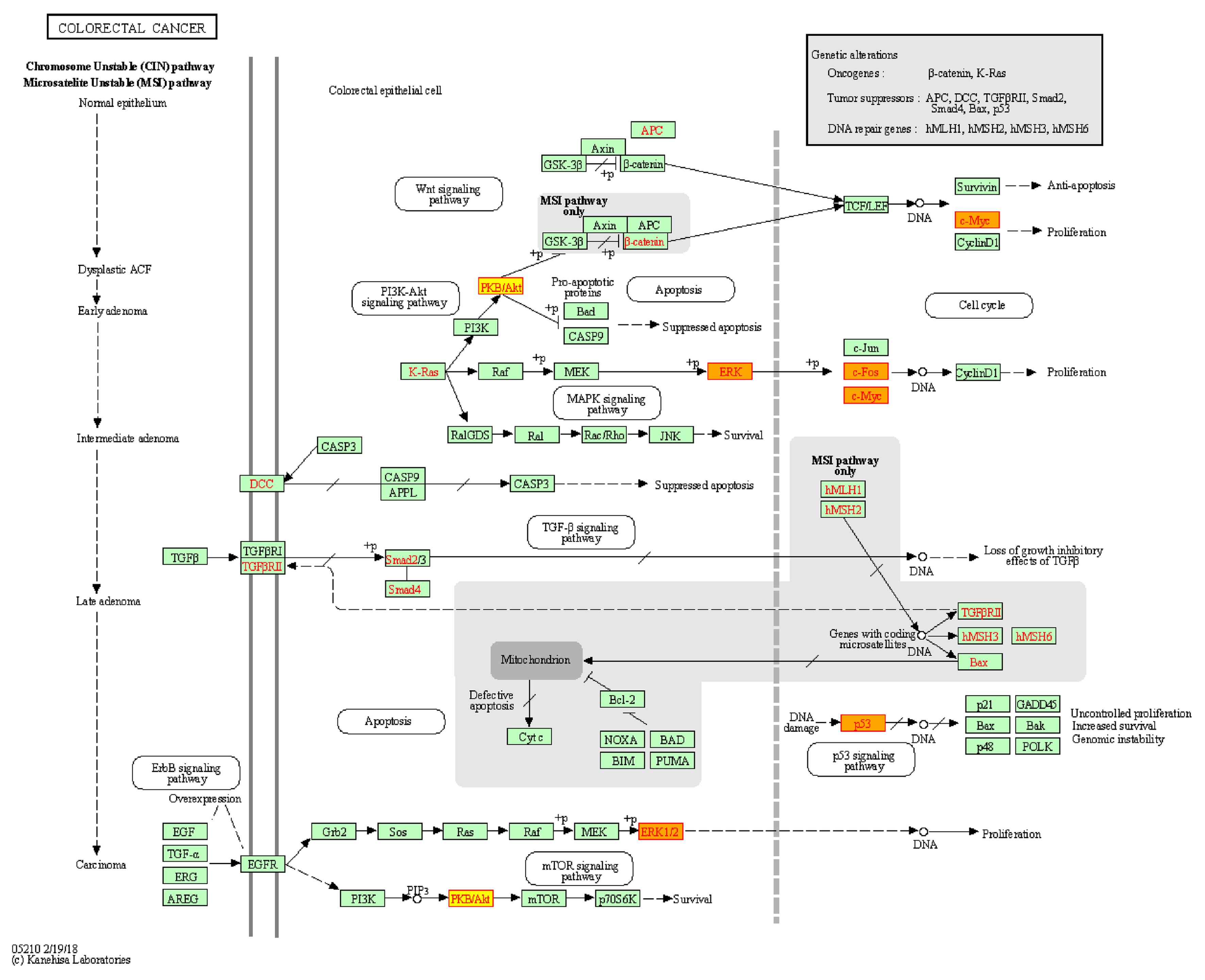
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | 393.235 814 3 | 0.670 886 076 | 27 |
| AKT1 | Protein kinase B1 | 176.409 101 2 | 0.609 195 402 | 21 |
| HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 207.695 211 6 | 0.595 505 618 | 21 |
| MAPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | 147.378 085 6 | 0.616 279 070 | 20 |
| FOS | FOS proto-oncogene | 201.558 640 0 | 0.609 195 402 | 20 |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 | 173.513 651 2 | 0.576 086 957 | 19 |
| ESR1 | Estrogen receptor 1 | 107.373 380 9 | 0.588 888 889 | 17 |
| MYC | MYC proto-oncogene | 83.621 194 3 | 0.595 505 618 | 17 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 139.960 208 6 | 0.557 894 737 | 17 |
| MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 90.592 859 5 | 0.588 888 889 | 16 |
| RELA | Nuclear factor kappa-B p65 subunit | 115.213 967 0 | 0.576 086 957 | 16 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 | 128.678 836 9 | 0.552 083 333 | 16 |
| CTNNB1 | Catenin beta 1 | 112.855 398 0 | 0.569 892 473 | 16 |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | 66.109 788 1 | 0.582 417 582 | 15 |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 | 103.066 384 4 | 0.569 892 473 | 15 |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A | 88.195 300 7 | 0.540 816 327 | 15 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | 20.689 214 2 | 0.535 353 535 | 13 |
| HIF1A | Hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha | 20.502 639 3 | 0.557 894 737 | 13 |
| BC:Betweenness centrality; CC:Closeness centrality. | ||||
Tab.3
Molecular docking binding energy of CRC core key targets and main active ingredients of Huangqin Tang"
| Target | Uniprot-ID | PDB-ID | Ligand | TCMSP-ID | Binding energy (kcal?mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
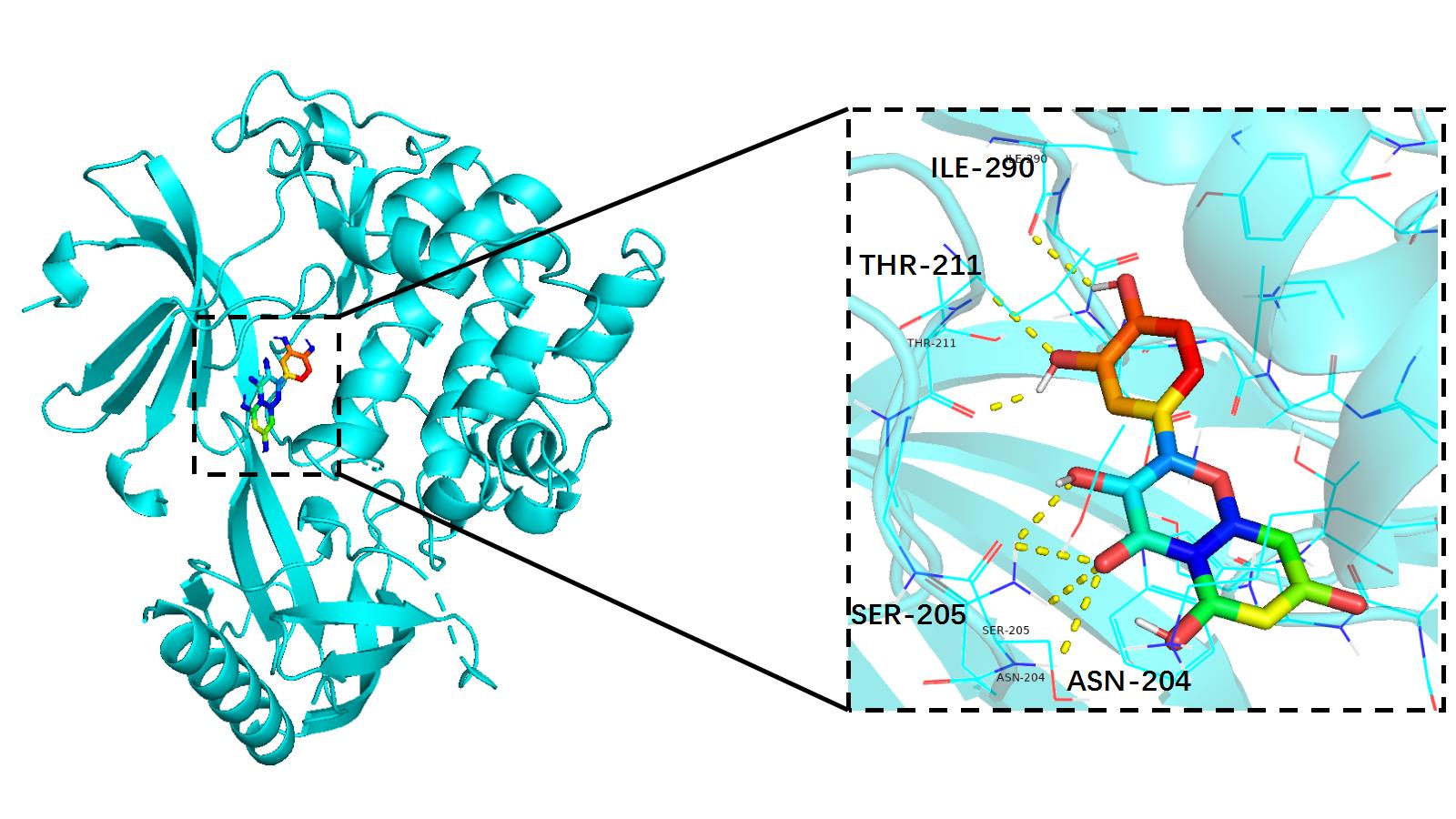
| AKT1 | P31749 | 7NH5 | Quercetin | MOL000098 | -10.4 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 7NH5 | Kaempferol | MOL000422 | -9.2 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 7NH5 | Wogonin | MOL000173 | -9.6 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 7NH5 | Naringenin | MOL004328 | -9.5 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 7NH5 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | MOL003896 | -9.5 |
| MAPK3 | P27361 | 4QTB | Quercetin | MOL000098 | -9.3 |
| MAPK3 | P27361 | 4QTB | Kaempferol | MOL000422 | -9.0 |
| MAPK3 | P27361 | 4QTB | Wogonin | MOL000173 | -9.2 |
| MAPK3 | P27361 | 4QTB | Naringenin | MOL004328 | -9.4 |
| MAPK3 | P27361 | 4QTB | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | MOL003896 | -9.6 |
| FOS | P01100 | 1A02 | Quercetin | MOL000098 | -8.2 |
| FOS | P01100 | 1A02 | Kaempferol | MOL000422 | -8.0 |
| FOS | P01100 | 1A02 | Wogonin | MOL000173 | -7.7 |
| FOS | P01100 | 1A02 | Naringenin | MOL004328 | -7.8 |
| FOS | P01100 | 1A02 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | MOL003896 | -7.2 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 7BWN | Quercetin | MOL000098 | -8.9 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 7BWN | Kaempferol | MOL000422 | -8.4 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 7BWN | Wogonin | MOL000173 | -8.8 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 7BWN | Naringenin | MOL004328 | -8.4 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 7BWN | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | MOL003896 | -8.1 |
| MYC | P01106 | 1A93 | Quercetin | MOL000098 | -5.3 |
| MYC | P01106 | 1A93 | Kaempferol | MOL000422 | -5.2 |
| MYC | P01106 | 1A93 | Wogonin | MOL000173 | -5.1 |
| MYC | P01106 | 1A93 | Naringenin | MOL004328 | -5.0 |
| MYC | P01106 | 1A93 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | MOL003896 | -4.9 |
| 1 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, SAUER A G, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(3): 145-164. |
| 2 | 田传鑫, 赵 磊. 结直肠癌及结直肠癌肝转移流行病学特点[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2021,28(13):1033-1038. |
| 3 | 尹周一, 王梦圆, 游伟程, 等. 2022美国癌症统计报告解读及中美癌症流行情况对比[J]. 肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2022, 8(2): 54-63. |
| 4 | SIEGEL R L, TORRE L A, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence in young adults[J].Gut,2019,68(12):2179-2185. |
| 5 | 杨宇飞. 中医药在结直肠癌治疗中的优势与展望[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2020, 40(11): 1294-1297. |
| 6 | 刘 强, 胡志敏. 胡志敏教授治疗大肠癌的经验[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2009, 4(9): 616-617. |
| 7 | 邬晓东, 管 艳. 周岱翰治疗大肠癌的中医临证思路[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2015, 32(2): 366-368. |
| 8 | 欧 燕, 戴 艺, 蒲俊勇. 黄芩汤在消化系统肿瘤化疗患者中的应用进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(9):1802-1806. |
| 9 | 迟宏罡, 郑学宝, 赵 兵, 等. 黄芩汤对葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的结肠炎小鼠结肠黏膜NF-κB p65的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2015, 30(2): 565-568. |
| 10 | XING S Q, WANG Y F, HU K W, et al. WGCNA reveals key gene modules regulated by the combined treatment of colon cancer with PHY906 and CPT11[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(9): BSR20200935. |
| 11 | 马 伟, 孙嘉莹, 任伟超, 等. 网络药理学: 中医药研究开发的新技术[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(3): 412-415. |
| 12 | MCDOWELL C, FAROOQ U, HASEEB M. Inflammatory bowel disease[M]. Treasure Island:StatPearls Publishing, 2021:2-5. |
| 13 | 李培华, 蔺 超, 何 柳, 等. 炎症相关结直肠癌致病因素分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022,30(24):4562-4567. |
| 14 | 阎 玲. 黄芩汤加减联合美沙拉嗪治疗溃疡性结肠炎临床观察[J]. 四川中医, 2019, 37(5): 101-103. |
| 15 | 王会录, 王孝郎. 黄芩汤加味辅助美沙拉嗪治疗溃疡性结肠炎39例[J]. 现代中医药, 2019, 39(3): 56-58. |
| 16 | 迟宏罡, 张淑华, 于丰彦, 等. 黄芩汤对结肠炎相关结肠癌Notch/Wnt信号通路的影响[J]. 广东医科大学学报, 2018, 36(4): 375-380. |
| 17 | 张旖晴, 魏 玮, 程 遥, 等. 基于网络药理学研究黄芩汤对小鼠溃疡性结肠炎及相关癌症的保护作用[J]. 世界中医药, 2022, 17(16): 2287-2291, 2298. |
| 18 | 迟宏罡, 赵 兵, 郑学宝, 等. 黄芩汤体外诱导人结肠癌SW620细胞凋亡及其对凋亡相关因子表达的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2015, 17(1): 56-60. |
| 19 | 宋振民, 宋会群, 宋沛沛. 黄芩汤联合化疗治疗结肠癌临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2020, 52(17): 25-27. |
| 20 | 曹纬国, 刘志勤, 邵 云, 等. 黄酮类化合物药理作用的研究进展[J]. 西北植物学报, 2003, 23(12): 2241-2247. |
| 21 | 林增海, 陆 军, 王凯松. 槲皮素抗结肠癌细胞SW480生长的作用机制研究[J]. 医学分子生物学杂志, 2021, 18(5): 366-371. |
| 22 | YANG L, LIU Y Q, WANG M, et al. Quercetin-induced apoptosis of HT-29colon cancer cells via inhibition of the Akt-CSN6-Myc signaling axis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(5): 4559-4566. |
| 23 | TEZERJI S, NAZARI ROBATI F, ABDOLAZIMI H, et al. Quercetin’s effects on colon cancer cells apoptosis and proliferation in a rat model of disease[J]. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2022, 48: 441-445. |
| 24 | 蔡剑辉, 任约翰, 厉金雷, 等. 槲皮素调控白细胞介素-6/信号转导及转录激活蛋白3信号通路在结肠炎性相关结肠癌小鼠模型的机制研究[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020, 20(6): 896-899. |
| 25 | 李 暐, 杜秉娜, 张 嵘, 等. 山柰酚对人结肠癌SW48细胞增殖的抑制作用[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2009, 26(9): 727-730. |
| 26 | CHIN H K, HORNG C T, LIU Y S, et al. Kaempferol inhibits angiogenic ability by targeting VEGF receptor-2 and downregulating the PI3K/AKT, MEK and ERK pathways in VEGF-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J]. Oncol Rep,2018,39(5):2351-2357. |
| 27 | 毛海燕, 殷旭东, 乔大伟, 等. 汉黄芩素调控胆绿素还原酶A对结肠癌细胞的抑制作用[J]. 中成药, 2021, 43(8): 2181-2188. |
| 28 | 李彦萍, 龚燚婷, 王嘉馨, 等. 基于网络药理学的汉黄芩素抑制人结直肠癌细胞SW480增殖机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(8): 1772-1778. |
| 29 | 黄 敏, 吴传中, 郝传铮, 等. 柚皮素对结直肠癌细胞侵袭能力及细胞中MMP-2、MMP-9表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2017, 37(19): 4750-4752. |
| 30 | 周 跃, 周燕红. 柚皮素联合5-FU对大肠癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J]. 湖北科技学院学报(医学版), 2020, 34(5): 369-372, 394. |
| 31 | 许 欣, 姚冬颖. 结直肠癌中Girdin和Akt1蛋白的表达及临床意义[J]. 河北医药, 2016, 38(15): 2259-2261, 2266. |
| 32 | 阮善明, 周萌萌, 袁 莉, 等. 解毒三根汤对结肠癌SW480细胞侵袭转移及AKT/GSK-3β信号通路的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2019, 60(16): 1401-1406. |
| 33 | DING L, WANG L Y, SUI L M, et al. Claudin-7 indirectly regulates the integrin/FAK signaling pathway in human colon cancer tissue[J].J Hum Genet,2016,61(8): 711-720. |
| 34 | HOLM M, SARASWAT M, JOENVÄÄRÄ S, et al. Colorectal cancer patients with different C-reactive protein levels and 5-year survival times can be differentiated with quantitative serum proteomics[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0195354. |
| 35 | LI H, ZHANG J L, TONG J H M, et al. Targeting the oncogenic p53 mutants in colorectal cancer and other solid tumors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(23): 5999. |
| 36 | 任 辉, 姜 涛, 边学海, 等. 癌基因C-myc在结直肠癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2007, 11(10): 1381-1383. |
| 37 | 唐 剑, 贺菊乔, 杨怡玲, 等. PI3K/Akt信号通路对人结肠癌HT-29细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2018, 32(3): 218-221. |
| 38 | RYCHAHOU P G, MURILLO C A, EVERS B M. Targeted RNA interference of PI3K pathway components sensitizes colon cancer cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)[J]. Surgery, 2005, 138(2): 391-397. |
| 39 | 周 慧, 海广范, 张 涛, 等. 癌症治疗中PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路及靶向抑制剂研究进展[J]. 中国药业, 2023, 32(5): 127-135. |
| [1] | Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG. Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167. |
| [2] | Chunling WANG,Sinuo WU,Xiaoyan YU,Weidong ZHANG. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on effective chemical components and action targets of epimedium in treatment of hypothalamus-pituitary- adrenal gland/ gonad / thyroid gland axis function damage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1296-1303. |
| [3] | Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN. Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017. |
| [4] | Li JIN,Xiaohong ZHANG,Chaoyang HU,Fengzhi LI,Yongliang CUI,Yang LI,Qianqian LIU,Yanjun QIAO. Effects of quercetin on growth and lung metastasis of transplanted tumor and cell invasion, and cell migration in human lung cancer A549 cells transplanted tumor model mice and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1018-1026. |
| [5] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [6] | Yumeng LIU,Song LENG, SARENGAOWA,Daijie LIN,Linsheng XIE,Mengrui LI,Xiao XU,Wannan LI. Network pharmacology analysis based on therapeutic effect of Sanghuang on pneumonia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 923-930. |
| [7] | Shan LIU,Zhaodong XING,Ping HUANG. Effect of expression of miR-17-5p in exosomes derived from colorectal cancer cells on chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 975-984. |
| [8] | Shengyu YAN,Changhua LIU,Zhijie XU,Yating DING,Yafeng XIE,Qiao ZHANG,Wanying LIU. Effect of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 on proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 656-664. |
| [9] | Yushuang GONG,Yefan FU,Huijing XU,Jian GUO,Lin XIANG,Rui HU,Rui FAN,Jie WANG,Miao LI,Meiyan SUN. Network pharmacology analysis on mechanism of Tonifying Slpeen and Kidney Empirical Prescription in treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 261-271. |
| [10] | Zhouquan LI,Hui LI,Ying TANG,Lijun YANG,Yinghong JIANG,Lipin YIN. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Tongluo Tangtai Power in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 341-350. |
| [11] | Jinjin YUE,Yixin PANG,Xiumei ZHANG. Regulatory effect of silent information regulator 2 on aerobic glycolysis and growth and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 385-394. |
| [12] | Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU. Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 74-83. |
| [13] | Shaojie FU,Sensen SU,Yiying CHEN,Zhonggao XU. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on mechanism of Shenqi Dihuang Decoction in treatment of membranous nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1518-1527. |
| [14] | Yan SUN,Xinhua DONG,Dongying LI,Qingfen ZHENG,Huiyu YANG,Bingrong LIU. Investigation and analysis on cognition of first-degree relatives of patients with colorectal cancer on colorectal cancer screening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1065-1070. |
| [15] | Qiuting CAO,Jingchun HAN,Xiaofei ZHANG. Effect of silencing helicase BLM gene on chemotherapy sensitivity of irinotecan in colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 657-667. |
|
||