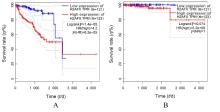
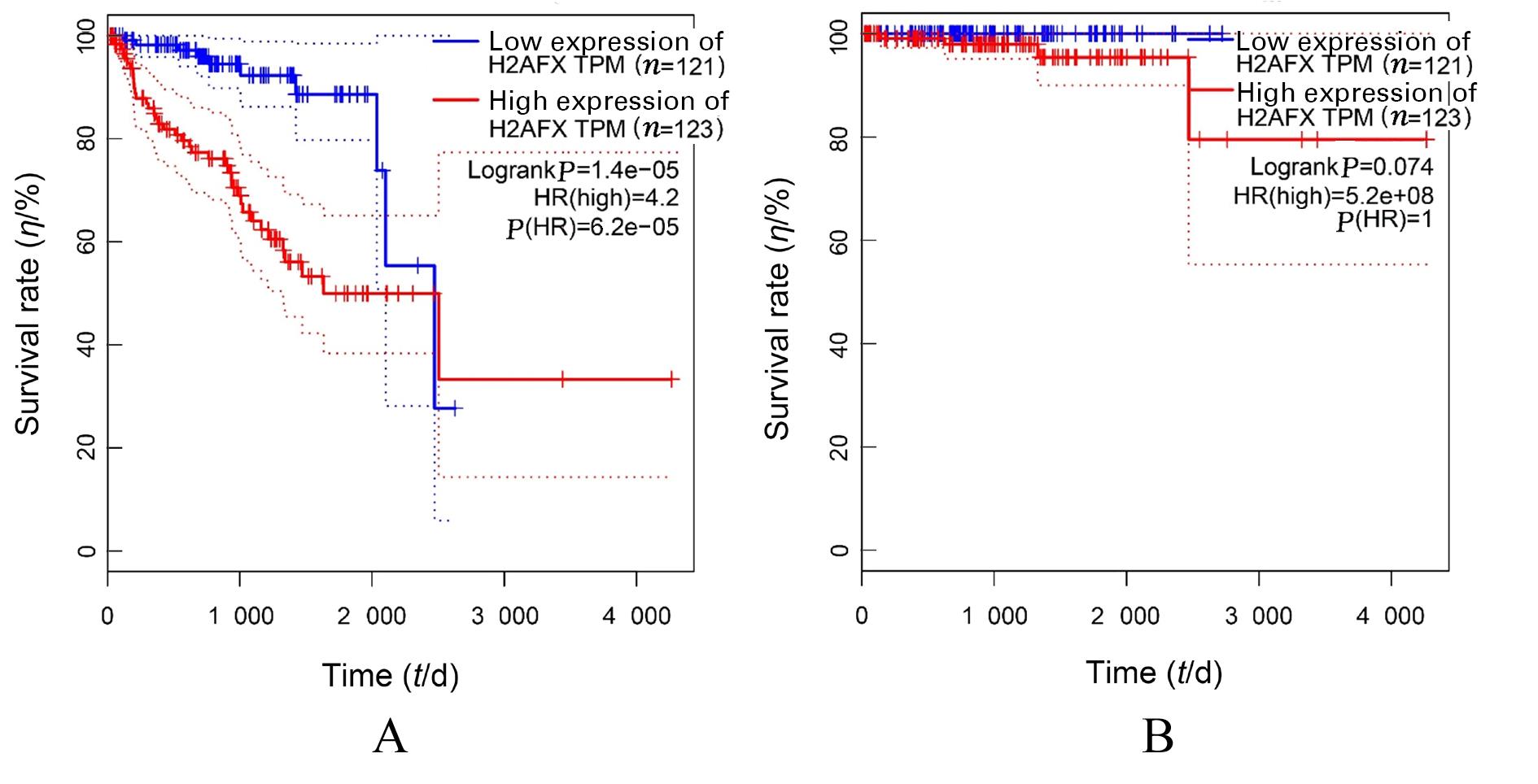
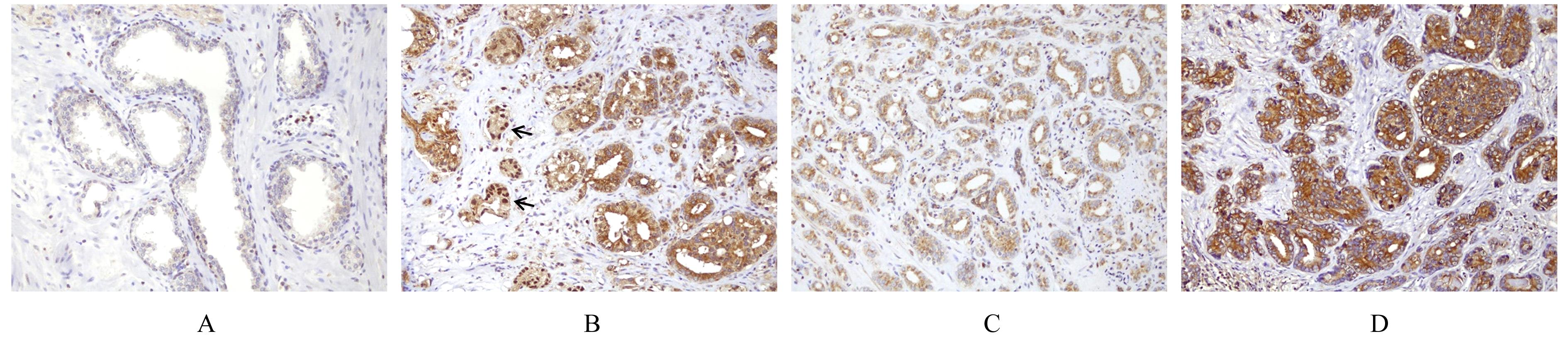
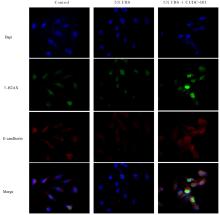
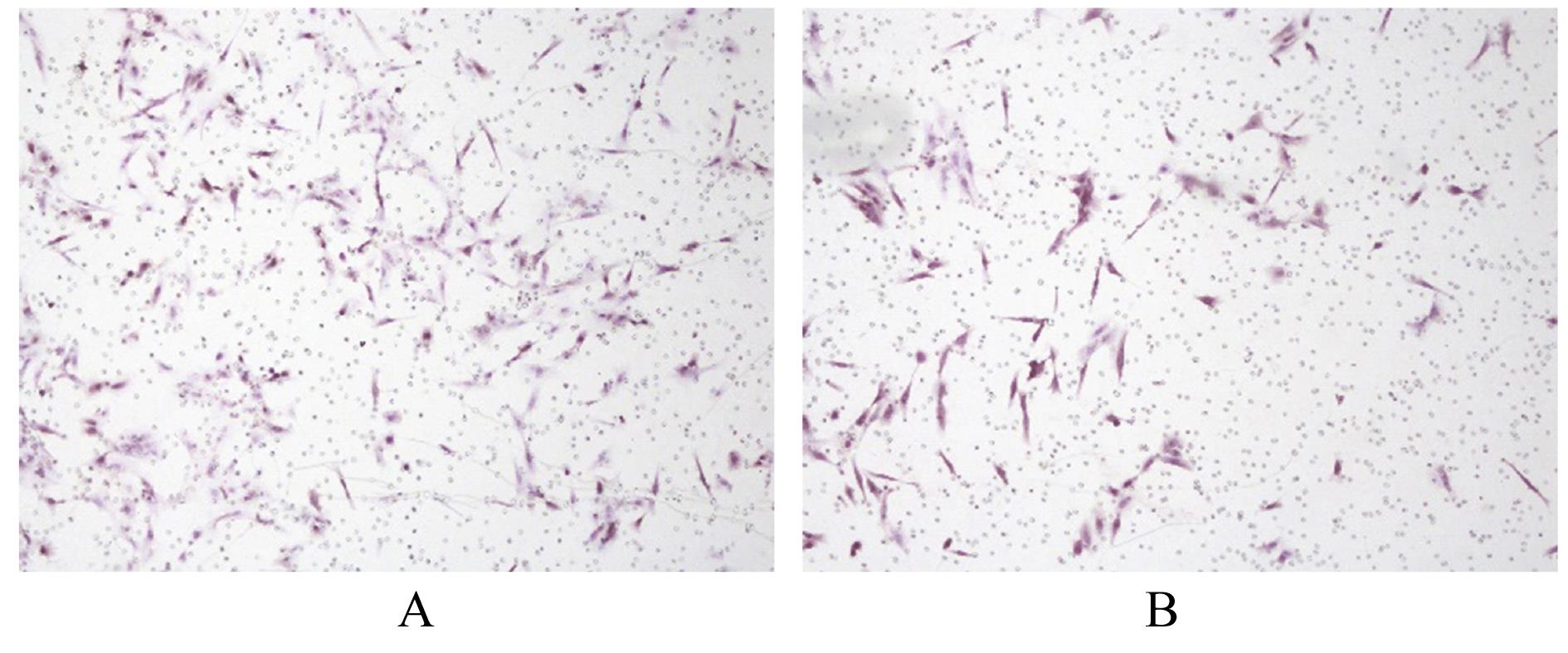
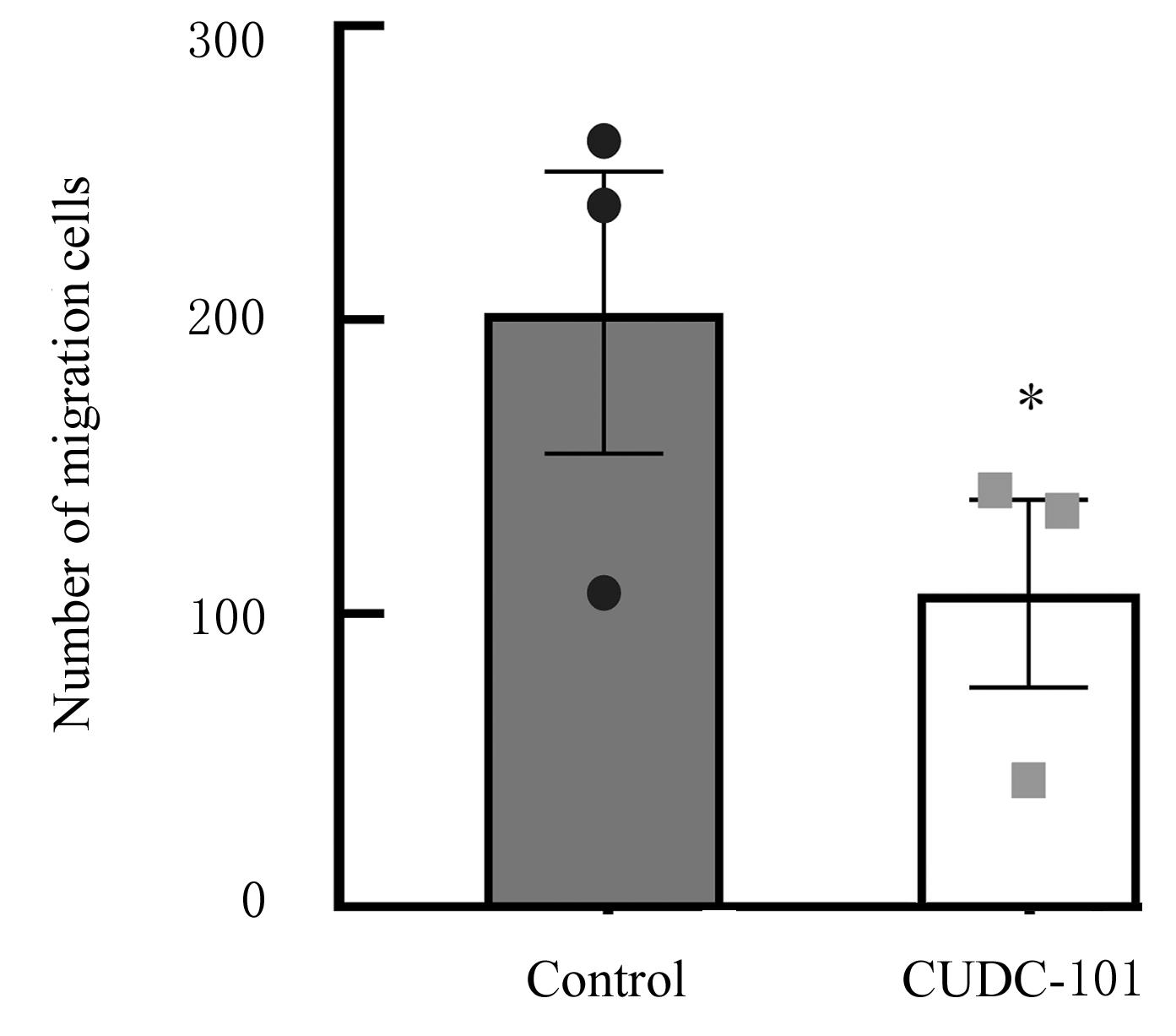
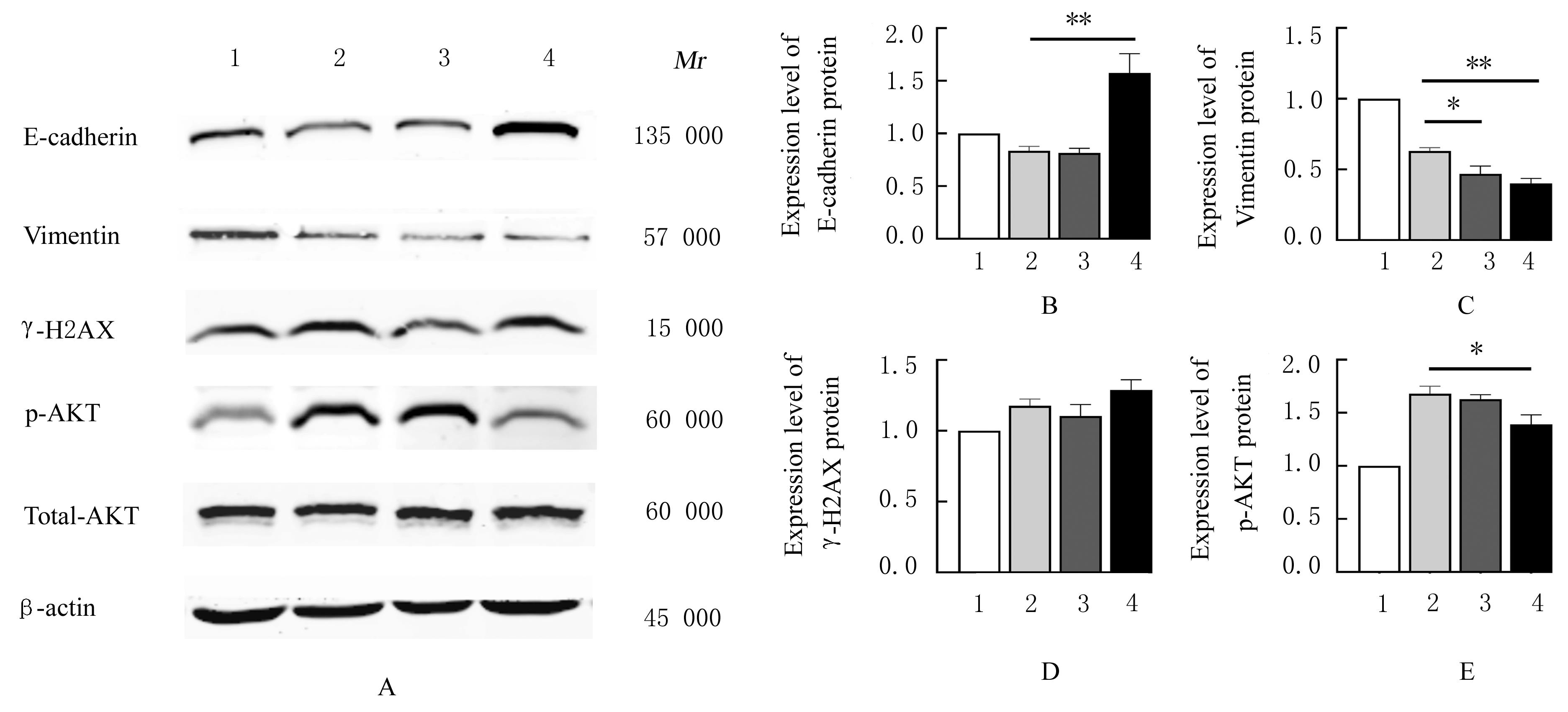
| [1] |
Haifeng WEI,Zhiqiang NI,Yanhong WEI,Qilai WANG,Shouqing LI,Yinfu MA,Yan TAN,Yanqiu FANG.
Effects of miR-126 over-expression and ADAM9 gene silencing on biological behavior of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 310-319.
|
| [2] |
Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI.
Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149.
|
| [3] |
Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG.
Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32.
|
| [4] |
Tao HE,Zhenjiang LI,Bingqian DING.
Influence of ligustrazine on growth of glioma stem cells subcutaneous xenografts in nude mice, TGF-β signaling pathway, and epithelial-mesenchymal transiton
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1437-1444.
|
| [5] |
Hui YE,Zhe SUN,Liting ZHOU,Wen QI,Lin YE.
Bioinformatics analysis on differentially expressed genes in lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA Databases
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1491-1503.
|
| [6] |
Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI.
Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527.
|
| [7] |
Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU.
Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139.
|
| [8] |
Rui LI,Xiaodong TAN,Yaoyuan HU.
Inhibitory effect of pachylic acid on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 315-323.
|
| [9] |
Meng QYU,Hong ZHENG,Yan LI,Boxue CHEN,Yuzhu JIANG,Shenggao WANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG.
Inhibitory effect of fermented red ginseng total saponins high glucose-induced renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1182-1189.
|
| [10] |
Chaofeng ZHOU,Shifan ZHOU,Qing TIAN,Sai WANG,Honglin LI,Chunzheng MA.
Effect of lncRNA-NORAD overexpression on biological behaviors of esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 33-43.
|
| [11] |
Peisen HU,Hongquan CUI,Junfeng ZHAO,Zhizhou WU,Jiaotuo WANG.
Regulatory effect of Danggui Liuhuang Decoction on immune function of prostate cancer-bearing mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1469-1475.
|
| [12] |
Juan CAO,Weibo LI,Xiu GUO,Bo LI,Chunling DONG.
Effects of targeted silencing of heat shock protein 27 on invasion and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 971-977.
|
| [13] |
Mingbo JIA,Ying SUN,Ying WANG,Yanke SONG,Liyan ZHAO.
Inhibitory effect of nitidine chloride on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 73-81.
|
| [14] |
Yang ZHANG,Huamao JIANG.
Inhibitory effect of nobiletin on growth of human prostate cancer DU145 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1260-1266.
|
| [15] |
WEI Xujing, LI Lin, ZHANG Hongzhen, WANG Jing, XU Jing.
Effects of LncRNA CCAT1 on proliferation,invasion and migration of endometrial cancer cells through TGF-β1/smad signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1016-1022.
|
 ),Zhenling LI1(
),Zhenling LI1( )
)