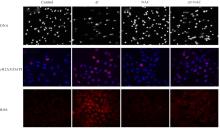
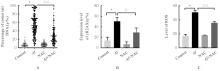
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1205-1216.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240503
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
Effect of Aspergillus fumigatus on DNA damage and IL-33 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells and its mechanism
Qiao WANG,Ziling ZENG,Xing WANG,Ning MA,Zhibin WANG,Guofeng XU,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG,Yuejiao LI,Hongmei TANG( ),Yun ZHANG(
),Yun ZHANG( )
)
- Laboratory of Inflammation and Allergy,Affiliated Hospital,Southwest Medical University,Luzhou 646000,China
-
Received:2023-09-07Online:2024-09-28Published:2024-10-28 -
Contact:Hongmei TANG,Yun ZHANG E-mail:hmtang@swmu.edu.cn;zhangyun000hf@163.com
CLC Number:
- R392.12
Cite this article
Qiao WANG,Ziling ZENG,Xing WANG,Ning MA,Zhibin WANG,Guofeng XU,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG,Yuejiao LI,Hongmei TANG,Yun ZHANG. Effect of Aspergillus fumigatus on DNA damage and IL-33 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1205-1216.
share this article
| 1 | LATGÉ J P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 1999, 12(2): 310-350. |
| 2 | BIGOT J, GUILLOT L, GUITARD J, et al. Bronchial epithelial cells on the front line to fight lung infection-causing Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1041. |
| 3 | RICHARD N, MARTI L, VARROT A, et al. Human bronchial epithelial cells inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus germination of extracellular conidia via FleA recognition[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 15699. |
| 4 | CUI X, CHEN F Y, ZHAO J Y, et al. Involvement of JNK signaling in Aspergillus fumigatus-induced inflammatory factors release in bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 1293. |
| 5 | DRAKE L Y, KITA H. IL-33: biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 278(1): 173-184. |
| 6 | DIETZ C J, SUN H, YAO W C, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus induction of IL-33 expression in chronic rhinosinusitis is PAR2-dependent[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(10): 2230-2235. |
| 7 | YOU J, LIN J, ZHOU Y F, et al. Role of the IL-33/ST2/p38 signaling pathway in the immune response of corneal epithelial cells to Aspergillus fumigatus infection[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2019, 12(4): 549-556. |
| 8 | KHOSRAVI A R, SHOKRI H, HASSAN AL-HEIDARY S, et al. Evaluation of murine lung epithelial cells (TC-1 JHU-1) line to develop Th2-promoting cytokines IL-25/IL-33/TSLP and genes Tlr2/Tlr4 in response to Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. J Mycol Med, 2018, 28(2): 349-354. |
| 9 | CHAN T K, LOH X Y, PEH H Y, et al. House dust mite-induced asthma causes oxidative damage and DNA double-strand breaks in the lungs[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2016, 138(1): 84-96.e1. |
| 10 | NIU B Y, LI W K, LI J S, et al. Effects of DNA damage and oxidative stress in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to PM2.5 from Beijing, China, in winter[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(13): 4874. |
| 11 | LI A M, ZHANG Y C, MA Y F, et al. The effects of coal dust exposure on DNA damage and repair of human bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Toxicol Ind Health, 2022, 38(7): 389-398. |
| 12 | IMANISHI T, ISHIHARA C, BADR M E L S, et al. Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 3566. |
| 13 | STAV-NORAAS T E, EDELMANN R J, POULSEN L C, et al. Endothelial IL-33 expression is augmented by adenoviral activation of the DNA damage machinery[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 198(8): 3318-3325. |
| 14 | HUANG C Q, LIU J Y, HE L, et al. The long noncoding RNA noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD)-microRNA-496-Interleukin-33 axis affects carcinoma-associated fibroblasts-mediated gastric cancer development[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 11738-11755. |
| 15 | VAN DE VEERDONK F L, GRESNIGT M S, ROMANI L, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus morphology and dynamic host interactions[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(11): 661-674. |
| 16 | LATGÉ J P, CHAMILOS G. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis in 2019[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 33(1): e00140-18. |
| 17 | THANNICKAL V J, FANBURG B L. Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2000, 279(6): L1005-L1028. |
| 18 | ALBANO G D, GAGLIARDO R P, MONTALBANO A M, et al. Overview of the mechanisms of oxidative stress: impact in inflammation of the airway diseases[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(11): 2237. |
| 19 | SAÏD-SADIER N, PADILLA E, LANGSLEY G, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus stimulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through a pathway requiring ROS production and the Syk tyrosine kinase[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(4): e10008. |
| 20 | SRINIVAS U S, TAN B W Q, VELLAYAPPAN B A, et al. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 25: 101084. |
| 21 | NEOFYTOU E, TZORTZAKI E G, CHATZIANTONIOU A, et al. DNA damage due to oxidative stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(12): 16853-16864. |
| 22 | SHARMA S, ALDRED M A. DNA damage and repair in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(10): 1224. |
| 23 | CAO C, LAI T W, LI M, et al. Smoking-promoted oxidative DNA damage response is highly correlated to lung carcinogenesis[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(14): 18919-18926. |
| 24 | SCHMITZ J, OWYANG A, OLDHAM E, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines[J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(5): 479-490. |
| 25 | MARÉCHAL A, ZOU L E. DNA damage sensing by the ATM and ATR kinases[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2013, 5(9): a012716. |
| 26 | SALMINEN A, KAUPPINEN A, KAARNIRANTA K. Emerging role of NF-κB signaling in the induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)[J]. Cell Signal, 2012, 24(4): 835-845. |
| 27 | MITCHELL J P, CARMODY R J. NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation[J]. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2018, 335: 41-84. |
| 28 | ZHANG L W, WAN Y, MA L, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB/IL-33/ST2 axis ameliorates acute bronchiolitis induced by respiratory syncytial virus[J]. J Immunol Res, 2021, 2021: 6625551. |
| 29 | SUN H, XU X Y, TIAN X L, et al. Activation of NF-κB and respiratory burst following Aspergillus fumigatus stimulation of macrophages[J]. Immunobiology, 2014, 219(1): 25-36. |
| 30 | CISZEWSKI W M, TAVECCHIO M, DASTYCH J, et al. DNA-PK inhibition by NU7441 sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation and doxorubicin[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2014, 143(1): 47-55. |
| [1] | Buqi NA,Chunji QUAN,Fang ZHAO,Fan YANG,Ru XIAO,Xuemei JIN,Zhenling LI. Effect of histone deacetylase inhibitor CUDC-101 on DNA damage, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer DU145 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 400-410. |
| [2] | Jianguo ZHOU,Hongjian JIANG,Qihui ZHU,Gengqiang ZHANG,Qilin DENG,Ling QI,Kaishu LI,Hongquan YU. Effect of general transcription factor 2I on temozolomide chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 457-464. |
| [3] | Yu ZHANG,Xianling LU. Expressions of IL-33, IL-8, and NETs in lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 498-507. |
| [4] | Hongmei TANG,Yuejiao LI,Xing WANG,Zhibin WANG,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG. Effect of Jiegeng Yuanshen Tang on airway inflammation and mucus secretion in allergic asthmatic mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 10-17. |
| [5] | Naixu SHI,Miao HAO,Tianfu ZHANG,Kelin ZHAO,Ziyan HUANG,Chunyan LI,Xiaofeng WANG. Inhibitory effect of baicalein on proliferation of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 985-993. |
| [6] | Bo HUANG,Jie DING,Hongrong GUO,Hongjuan WANG,Jianqun XU,Quan ZHENG. Effects of HIF-1α/ROS on apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer A549 cells under hypoxia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 682-690. |
| [7] | Xuechun DU,Baosheng LI,Shuwei QIAO,Yanzhen OU,Zhen LI,Weiyan MENG. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis-LPS on expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors in macrophages [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1148-1155. |
| [8] | Haixin QU,Erwei YUAN,Weiping GUO,Yajing ZHANG,Wenxia MA,Dan WU. Improvement effect of luteolin on acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway activation in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 676-683. |
| [9] | Yinong LIU,Qiang ZHANG,Li XU. Improvement effect of atorvastatin on vascular endothelial dysfunction induced by Ox-LDL/β2GPⅠ/anti-β2GPⅠ complex and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 317-323. |
| [10] | Yang ZHOU,Xuguang MI,Wenxing PU,Wentao WANG,Meng JING,Fankai MENG. Ameliorative effect of melatonin on oxidative stress of human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 340-347. |
| [11] | Chaofeng ZHOU,Shifan ZHOU,Qing TIAN,Sai WANG,Honglin LI,Chunzheng MA. Effect of lncRNA-NORAD overexpression on biological behaviors of esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 33-43. |
| [12] | Dan MAO,Zhishuang LI,Jiaxin CHENG,Ping HOU. Effect of Shenxianshengmai Oral Liquid on ROS expression in mice with sick sinus syndrome and its regulation on HCN4 ion channel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1353-1361. |
| [13] | Congling HOU, Xiaofan LU, Xiaoting LEI, Bin LI, Runyang ZHAO. Effect of isorhynchophylline on apoptosis and release of inflammatory factors in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by TNF-α via up-regulating miR-192-5p and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 595-607. |
| [14] | Ying YANG, Wei ZHAO, Dan LYU. Effect of C19ORF12 on proliferation and chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer MKN45 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 687-693. |
| [15] | Shurong ZHANG,Qiying ZHANG. Regulatory effect of luteolin on Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis through TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 315-322. |
|
||