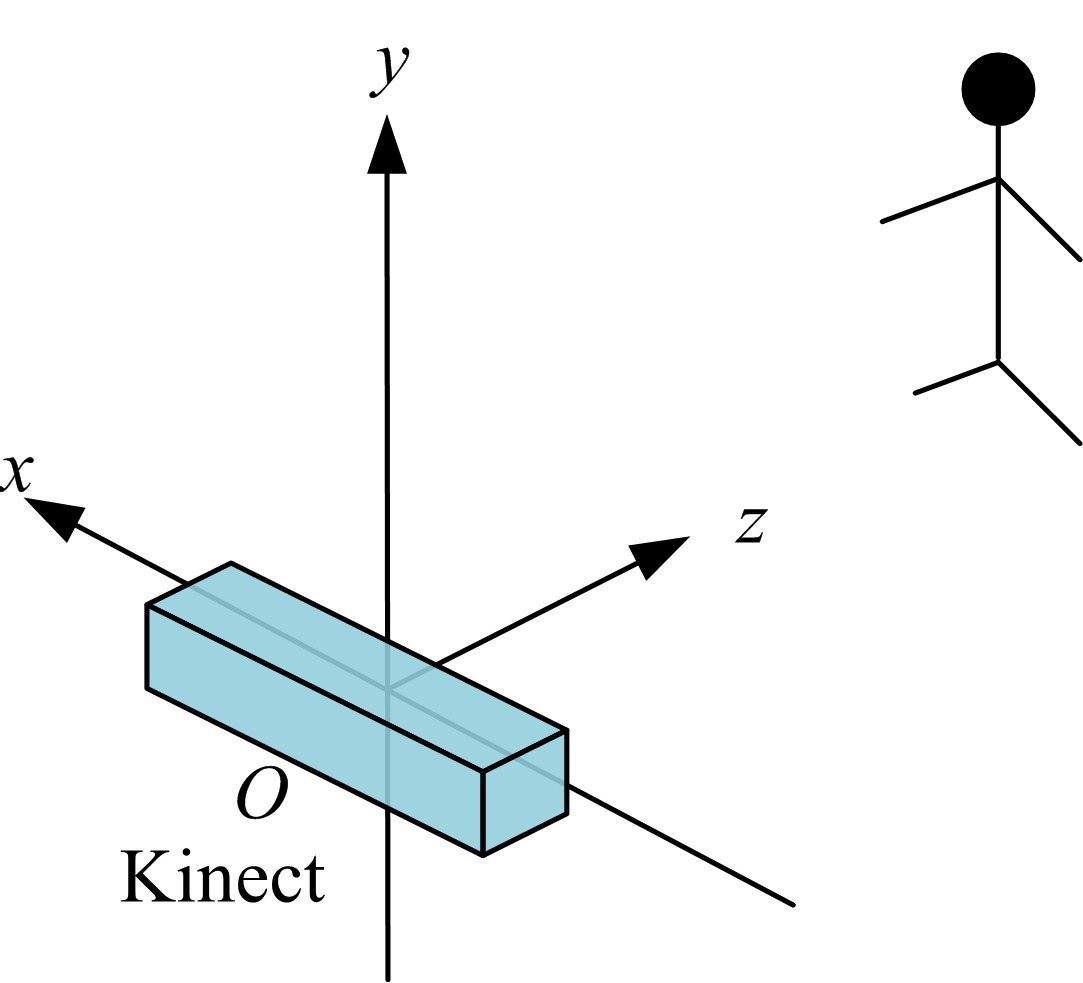
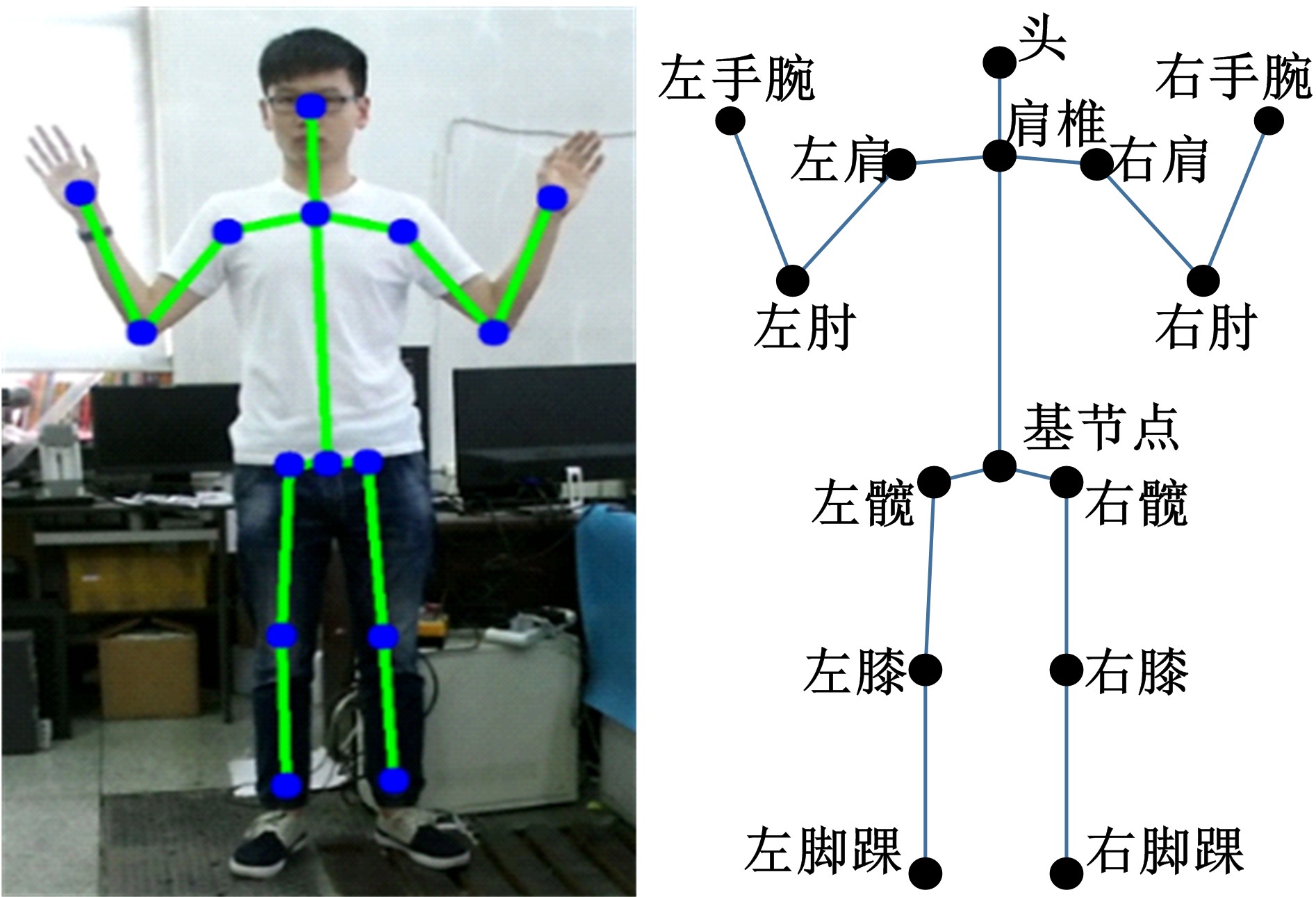
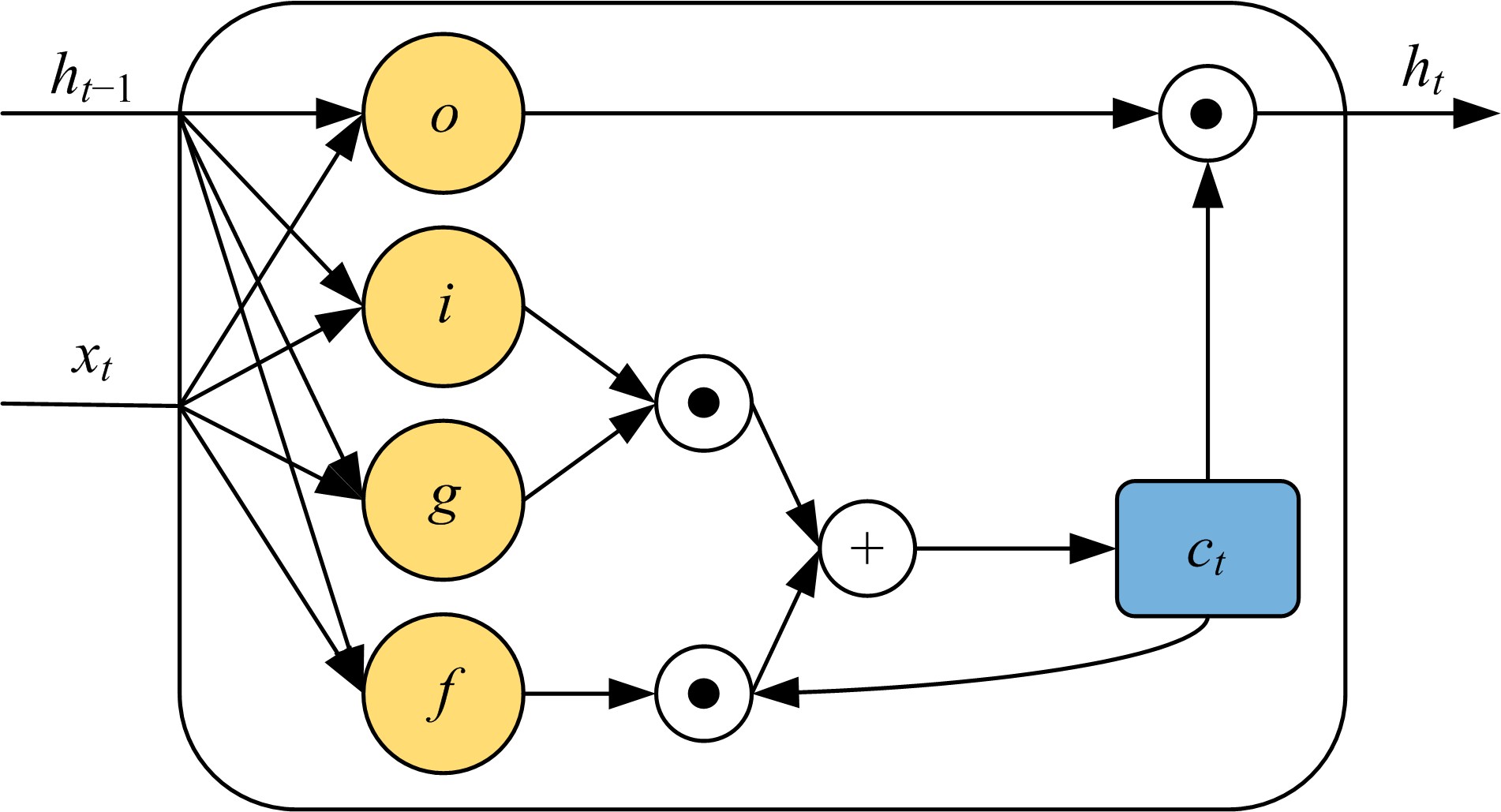
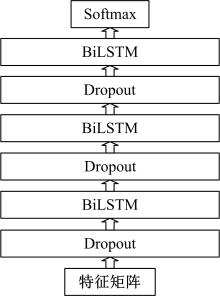
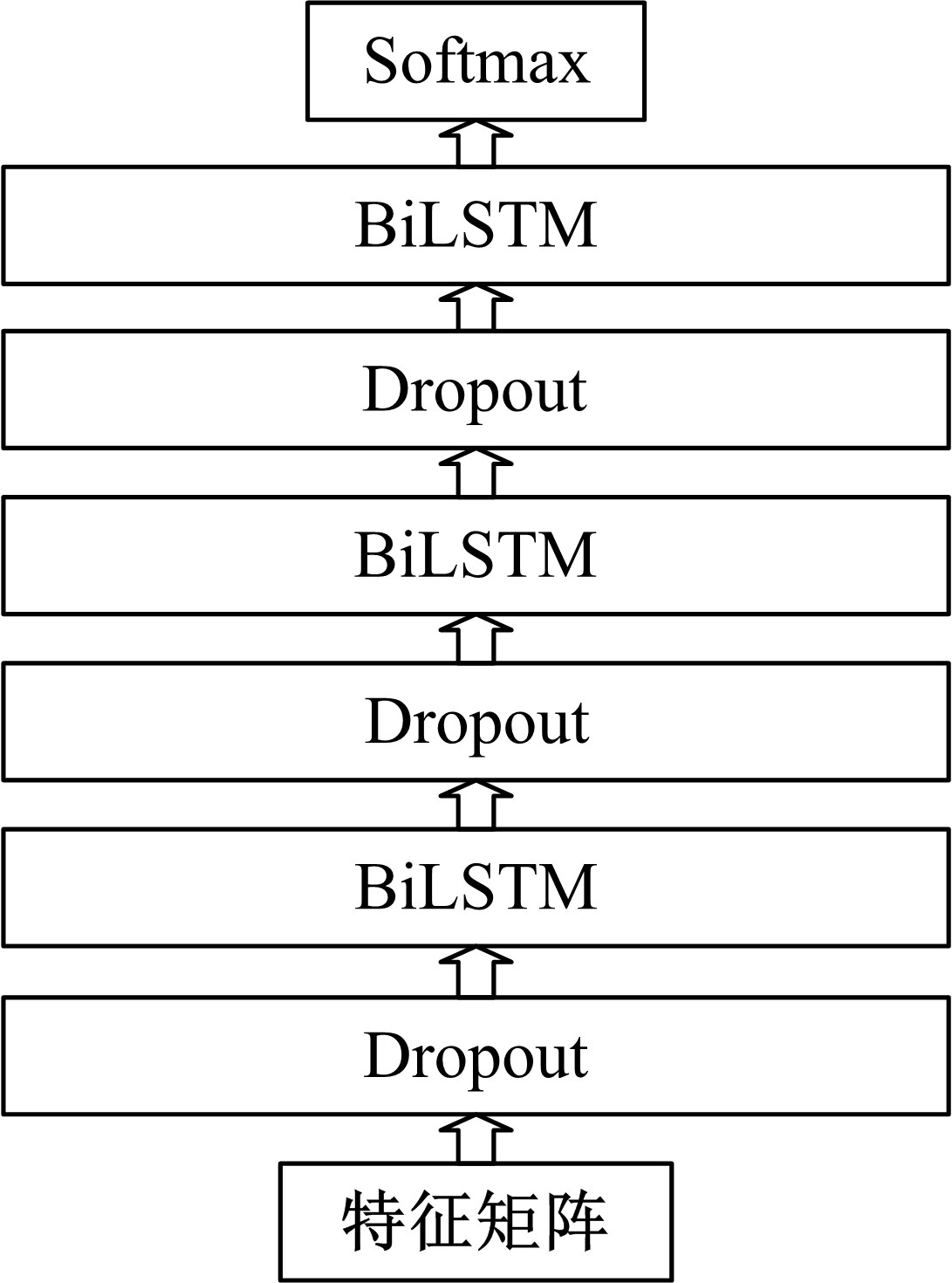
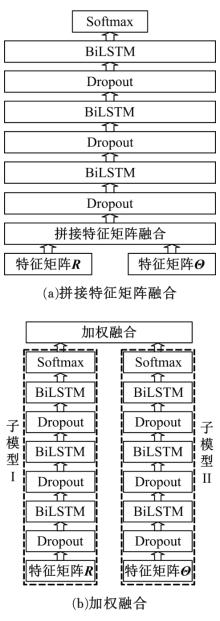
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 445-453.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190231
Intelligent manipulation method of crane based on BiLSTM model
Tao NI( ),Hai-qiang LIU,Lin-lin WANG,Shao-yuan ZOU,Hong-yan ZHANG,Ling-tao HUANG(
),Hai-qiang LIU,Lin-lin WANG,Shao-yuan ZOU,Hong-yan ZHANG,Ling-tao HUANG( )
)
- School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- TH218
| 1 | 臧大进, 戚玉强. 塔式起重机智能监控系统的研制[J]. 冶金设备, 2009(1): 50-53. |
| Zang Da-jin, Qi Yu-qiang. Development of intelligent monitoring system of tower cranes[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2009(1): 50-53. | |
| 2 | 潘斌, 汪小东. 塔式起重机安全管理的特点及对策[J]. 工业设计, 2011(6): 136. |
| Pan Bin, Wang Xiao-dong. Safety management characteristics and countermeasures of tower crane[J]. Design Ideas, 2011(6): 136. | |
| 3 | 腾文花. 关于塔吊使用的安全监控措施[J]. 建筑安全, 2007, 22(11): 36-36. |
| Teng Wen-hua. Safety monitoring measures for tower crane use[J]. Construction Safety, 2007, 22(11): 36-36. | |
| 4 | 李雄祥, 潘英俭, 廖拓. 起重机械的工作特点及发展趋势[J]. 中国水运: 理论版, 2007, 5(1): 171. |
| Li Xiong-xiang, Pan Ying-jian, Liao Tuo. Working characteristics and development trend of hoisting machinery[J]. China Water Transport, 2007, 5(1): 171. | |
| 5 | 张敏. 起重机检验中危险因素的识别与控制[J]. 科技风, 2015(12): 100. |
| Zhang Min. Identification and control of dangerous factors in crane inspection [J]. Technology Wind, 2015(12): 100. | |
| 6 | 尹浩. 港口门式起重机安全监控管理系统研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院, 2015. |
| Yin Hao. Safety management characteristics and countermeasures of tower crane[D]. Wuhan: School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Wuhan Textile University, 2015. | |
| 7 | 贾秋枫. 大型履带式起重机吊装市场现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油化工建设, 2008, 30(5): 20-22. |
| Jia Qiu-feng. On the large scale crawler cranes hoisting business in China[J]. Petroleum & Chemical Construction, 2008, 30(5): 20-22. | |
| 8 | Zhang C C. Design of a crane intelligent control system[C]∥International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research, Busan, South Korea, 2016: 861-864. |
| 9 | An J Q, Chen F, Chen X, et al. Three dimensional hoisting simulation system based on virtual reality for truck crane[C]∥2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 2015: 8892-8897. |
| 10 | 祁家榕, 张昌伟. 行为识别技术的研究与发展[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2017, 7(4): 24-26, 30. |
| Qi Jia-rong, Zhang Chang-wei. Research and development of behavior recognition technology[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2017, 7(4): 24-26, 30. | |
| 11 | 倪涛, 赵泳嘉, 张红彦, 等. 基于Kinect动态手势识别的机械臂实时位姿控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(10): 417-423, 407. |
| Ni Tao, Zhao Yong-jia, Zhang Hong-yan, et al. Real-time mechanical arm position and pose control system by dynamic hand gesture recognition based on kinect device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(10): 417-423, 407. | |
| 12 | Canal G, Escalera S, Angulo C. A real-time human-robot interaction system based on gestures for assistive scenarios[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 149: 65-77. |
| 13 | 张质文, 王金诺, 程文明, 等. 起重机设计手册[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社, 2013. |
| 14 | 石忠晓. 智能化起重机安全监控系统[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学机械工程学院, 2003. |
| Shi Zhong-xiao. Intelligent crane safety monitoring system[D]. Dalian: School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2003. | |
| 15 | 韩旭. 应用Kinect的人体行为识别方法研究与系统设计[D]. 济南: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Han Xu. The human behavior recognition research and system design using kinect[D]. Jinan: School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2013. | |
| 16 | Zhang S, Yang Y, Xiao J, et al. Fusing feometric features for skeleton-based action recognition using multilayer LSTM networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(9): 2330-2343. |
| 17 | Cho K, Van M B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]∥Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724-1734. |
| 18 | 王鑫, 吴际, 刘超, 等. 基于LSTM循环神经网络的故障时间序列预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(4): 772-784. |
| Wang Xin, Wu Ji, Liu Chao, et al. Exploring LSTM based recurrent neural network for failure time series prediction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(4): 772-784. | |
| 19 | Greff K, Srivastava R K, Koutník J, et al. LSTM: a search space odyssey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(10): 2222-2232. |
| 20 | GB5 082-1985起重吊运指挥信号[S]. |
| [1] | DING Ning, WANG Long-shan, HE Ping. Design Principle of Rare Earth-Lifting Permanent Magnetic Crane [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2001, (1): 86-90. |
|
||