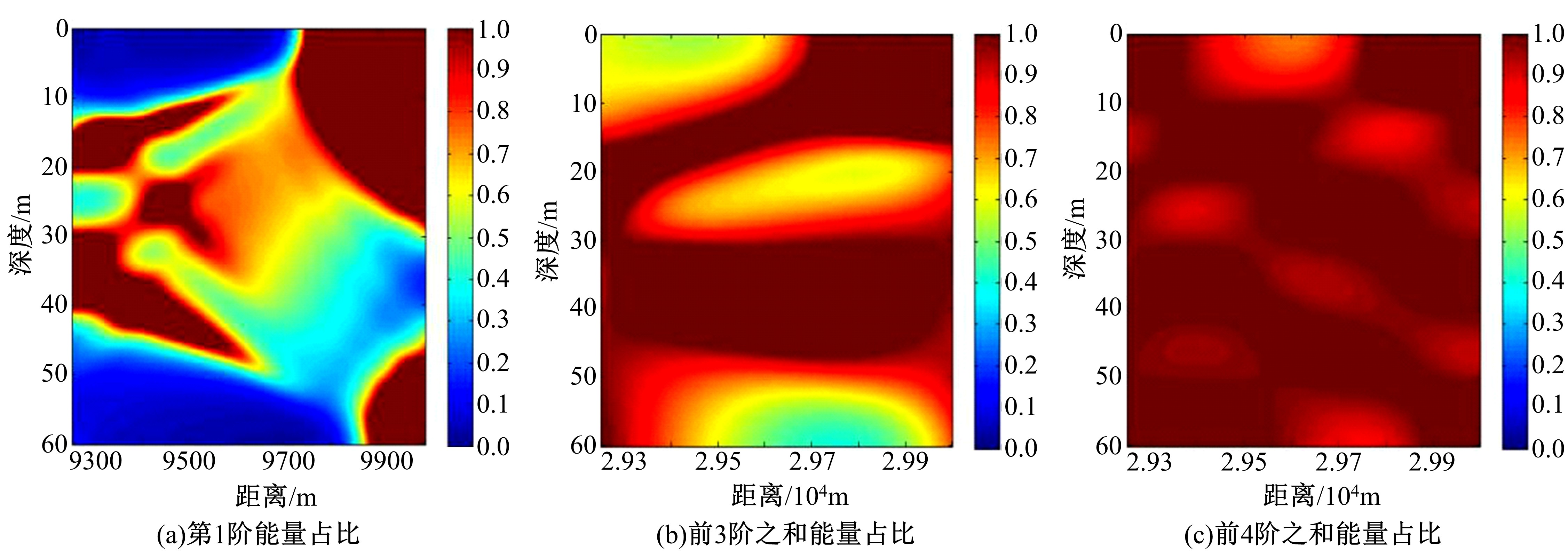
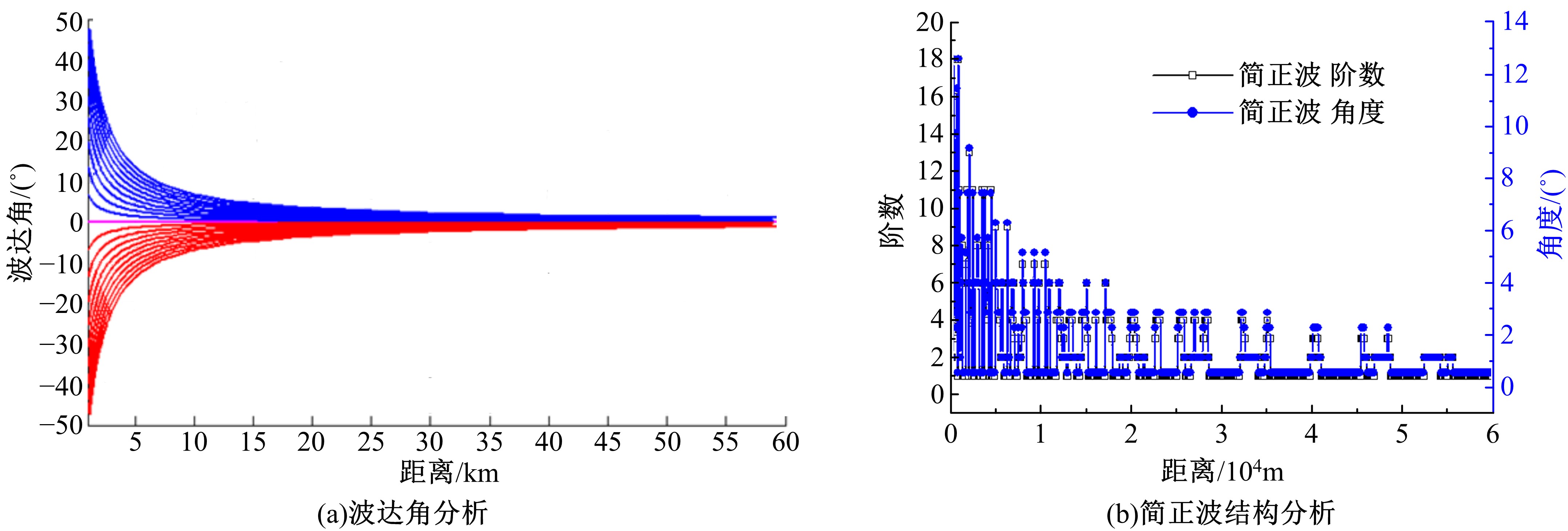
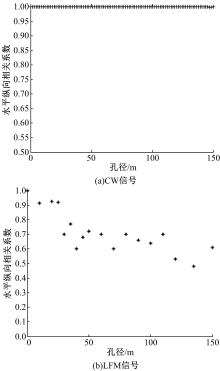
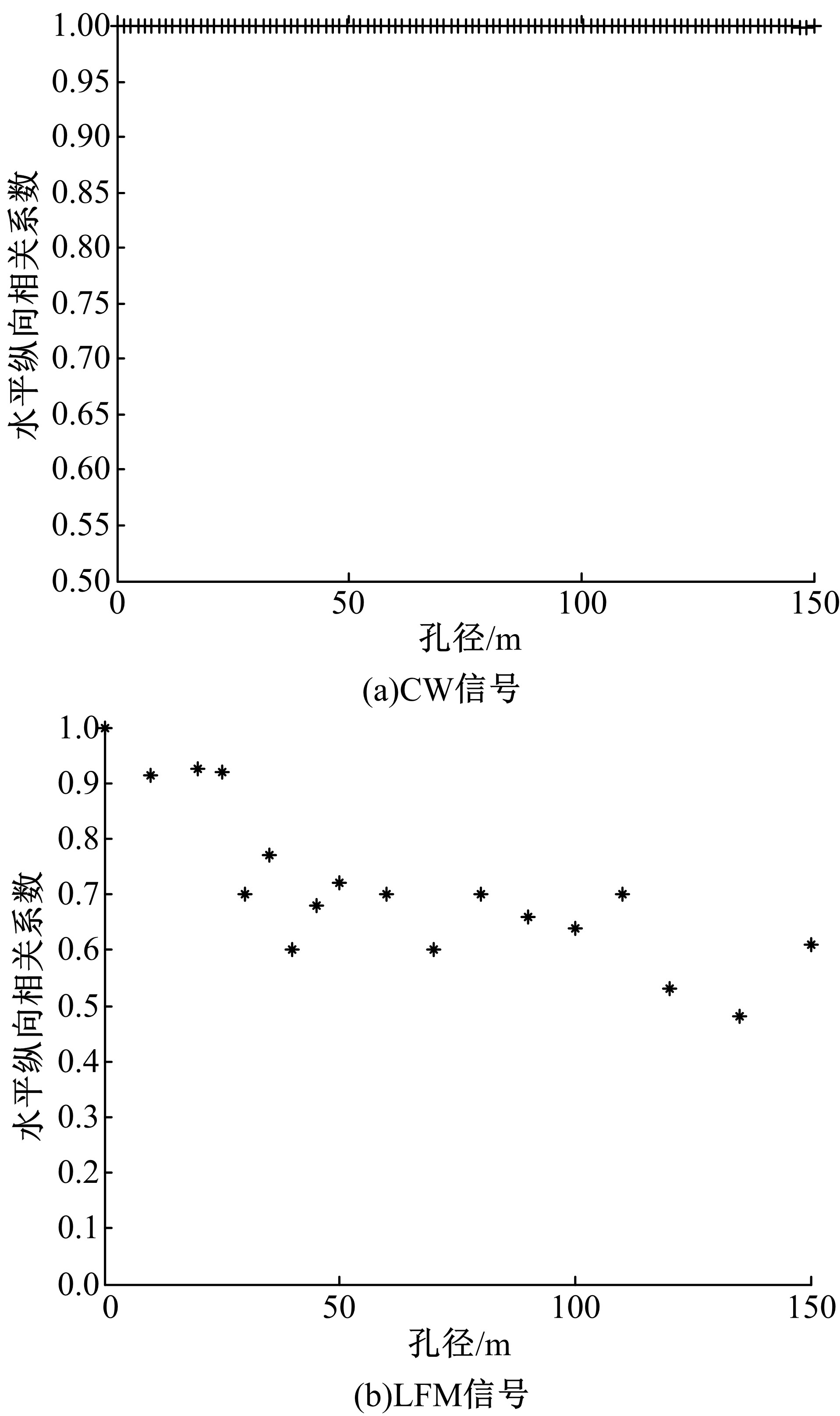
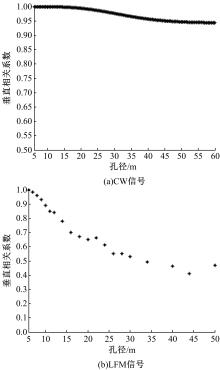
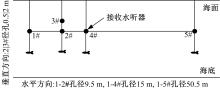
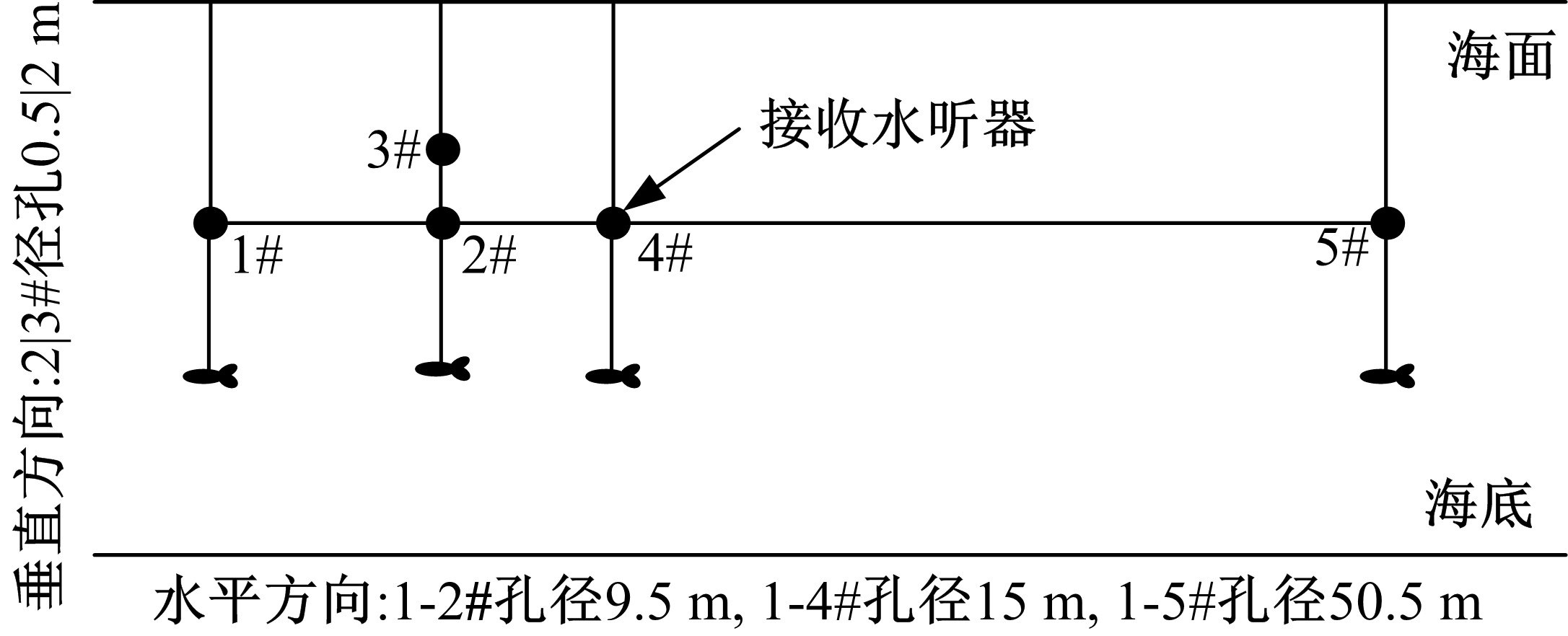
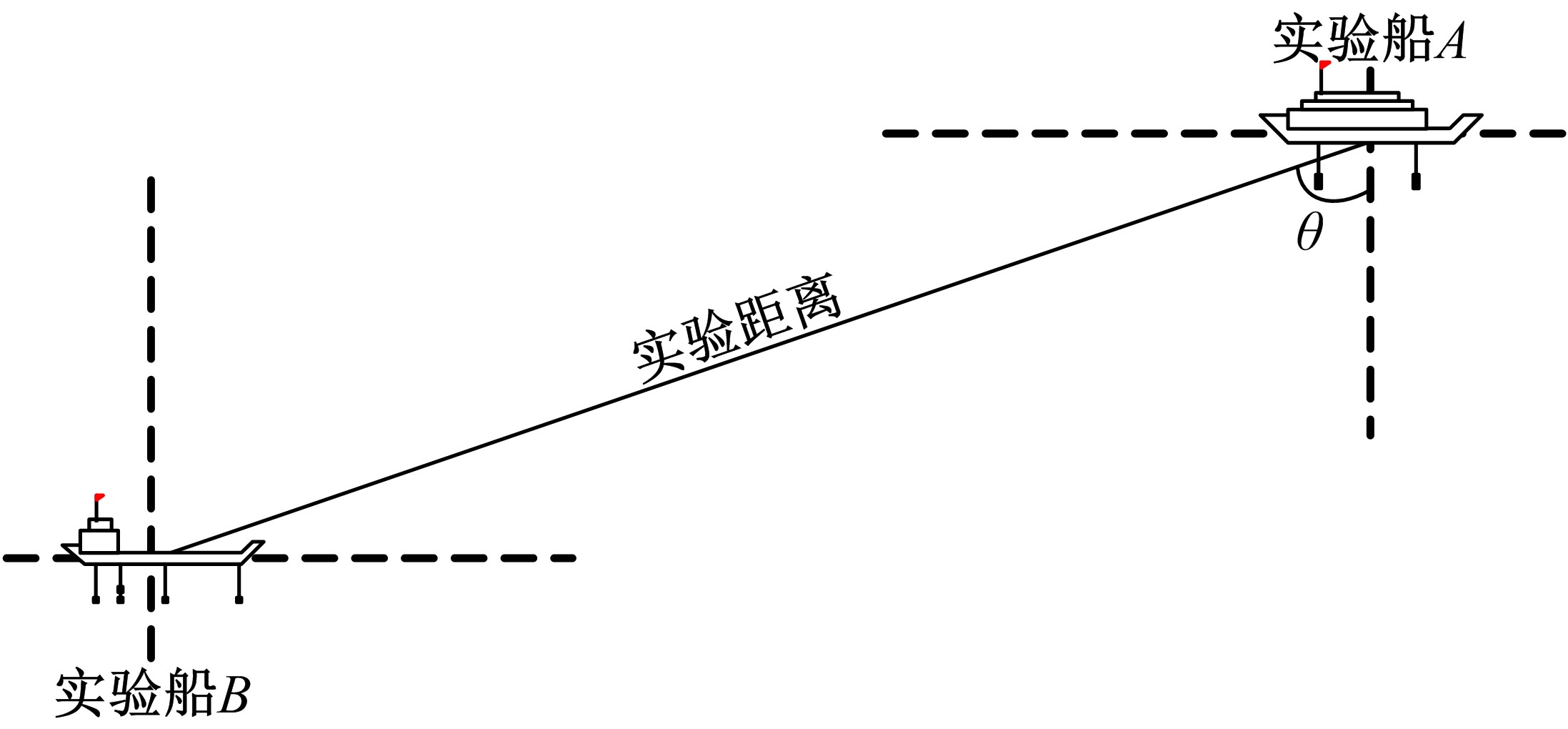
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1876-1885.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190484
Temporal and spatial distribution of incident sound field with low frequency in shallow water
Ling-guo ZHU1,2( ),An-bang ZHAO1(
),An-bang ZHAO1( ),Bao-shan YANG2,Zhong-cheng MA2,3,Wen-zhang LIU2,Liang-hao LYU2
),Bao-shan YANG2,Zhong-cheng MA2,3,Wen-zhang LIU2,Liang-hao LYU2
- 1.College of Underwater Acoustic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2.First Research Laboratory, Dalian Scientific Test & Control Technology Institute, Dalian 116013, China
3.Echo Research Laboratory, Science and Technology on Underwater Test and Control Laboratory, Dalian 116013, China
CLC Number:
- TB567
| 1 | 张仁和. 海洋声场的时间、频率与空间相干结构及其对阵列信号处理的影响[C/OL].[2005-01-01]. |
| 2 | Guo L H, Gong Z X, Wu L X. Space and time coherence of acoustic field in shallow water[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2001, 18(10): 1366-1368. |
| 3 | 林旺生, 梁国龙, 付进, 等. 浅海矢量声场干涉结构形成机理及试验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(14): 265-273. |
| Lin Wang-sheng, Liang Guo-long, Fu-jin, et al. The mechanism of the interference structure in shallow water vector acoustic field and experimental investigation[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(14): 265-273. | |
| 4 | Zhang R H, Zhang S R, Xiao J Q, et al. Spatial coherence and temporal stability of the long-range sound field in shallow water[J]. Chinese Journal of Acoustic, 1984(4): 83-94. |
| 5 | 宫在晓. 浅海低频声场的时空相干特性及其应用[D]. 北京: 中国科学院声学研究所, 2001. |
| Gong Zai-xiao. The spectial and temporal characteristics of sound field with low frequency in shallow water: research and appliction[D]. Beijing: Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2001. | |
| 6 | 舒象兰, 韩树平. 多途海洋声信道中声场相干性研究[C]∥全国声学设计与噪声振动控制工程暨配套装备学术会议, 青岛, 2010: 68-70. |
| 7 | 程广利, 张敏明, 胡金华. 浅海相干声场不确定性研究[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(1): 105-110. |
| Cheng Guang-li, Zhang Min-ming, Hu Jin-hua. Uncertainty of coherent acoustic field in shallow water[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 30(1): 105-110. | |
| 8 | 陈庚, 籍顺心. 菲律宾海声传播信道时空相关性变化实验[J]. 声学学报, 1994, 19(4): 266-277. |
| Chen Geng, Ji Shun-xin. Experiment study about correlation variation of acoustic propagation channel in philippines sea[J]. ACTA Acoustic, 1994, 19(4): 266-277. | |
| 9 | Wan L, Zhou J X, Roger P H, et al. Spatial coherence measurements from low L-shape arrays in shallow water[J]. Acostical Physis, 2009, 55(3): 383-392. |
| 10 | Yang J. Spatial coherence in shallow water waveguide[D]. Atlanta: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2007. |
| 11 | 毛岱山. 浅海声信道信号时间相关特性研究[J]. 海洋技术, 2006, 25(2): 67-69, 120. |
| Mao Dai-shan. Study on the characteristics of time-correlation in the shallow water acoustic channel[J]. Ocean Technology, 2006, 25(2): 67-69, 120. | |
| 12 | 孙梅, 李风华, 张仁和. 浅海声场垂直振速与水平振速相关特性及应用[J]. 声学学报, 2011, 36(2): 215-220. |
| Sun Mei, Li Feng-hua, Zhang Ren-he. Correlation characteristics of vertical particle velocity and horizontal particle velocity in shallow water and the application[J]. ACTA Acoustic, 2011, 36(2): 215-220. | |
| 13 | 王升, 马力, 郭圣明. 浅海单模入射声场目标回波特性研究[J]. 声学技术, 2015, 34(1): 18-22. |
| Wang Sheng, Ma Li, Guo Sheng-ming. Research on target echo characteristics ensonified by a signal mode in shallow water[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2015, 34(1): 18-22. | |
| 14 | 苏晓星. 浅海声场的水平纵向相关与波导不变性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2006. |
| Su Xiao-xing. Longitudinal correlations and waveguide invariance of the acoustical field in shallow water[D]. Beijing: School of Graduate, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. |
| [1] | ZHAO An-bang, CHENG Yue, ZHOU Bin, AN Tian-si, LYU Liang-hao. OFDM system based on parametric array in underwater acoustic communication [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 979-984. |
|
||