吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 460-470.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250220
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
双酚S和双酚F对雄性生殖系统损伤信号通路的生物信息学分析及其实验验证
石雨1,李景芝2,陈洪强3,周诗梦4,王娜5,曹佳6,尹俐1( ),刘文斌3,6(
),刘文斌3,6( )
)
- 1.重庆理工大学药学与生物工程学院药学系,重庆 400054
2.重庆市巴南区疾病预防控制中心 传染病防控与免疫规划科,重庆 401320
3.陆军军医大学军事预防医学系军队环境卫生学教研室,重庆 400038
4.陆军军医大学西南医院乳腺甲状腺外科,重庆 400038
5.贵州医科大学公共卫生与健康 学院环境污染与疾病监控教育部重点实验室,贵州 贵阳 561113
6.陆军军医大学军事预防医学系 毒理学研究所,重庆 400038
Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of BPS and BPF on signaling pathways of male reproductive system damage
Yu SHI1,Jingzhi LI2,Hongqiang CHEN3,Shimeng ZHOU4,Na WANG5,Jia CAO6,Li YIN1( ),Wenbin LIU3,6(
),Wenbin LIU3,6( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmacy,College of Pharmacy and Bioengineering,Chongqing University of Technology,Chongqing 400054,China
2.Department of Infectious Disease Prevention and Immunization Program,Center for Disease Control and Prevention,Banan District,Chongqing 401320,China
3.Department of Environmental Health,College of Preventive Medicine,Army Medical University,Chongqing 400038,China
4.Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery,Southwest Hospital,Army Medical University,Chongqing 400038,China
5.Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution and Disease Monitoring and Control,Ministry of Education,School of Public Health,Guizhou Medical University,Guiyang 561113,China
6.Institute of Toxicology,College of Preventive Medicine,Army Medical University,Chongqing 400038,China
摘要:
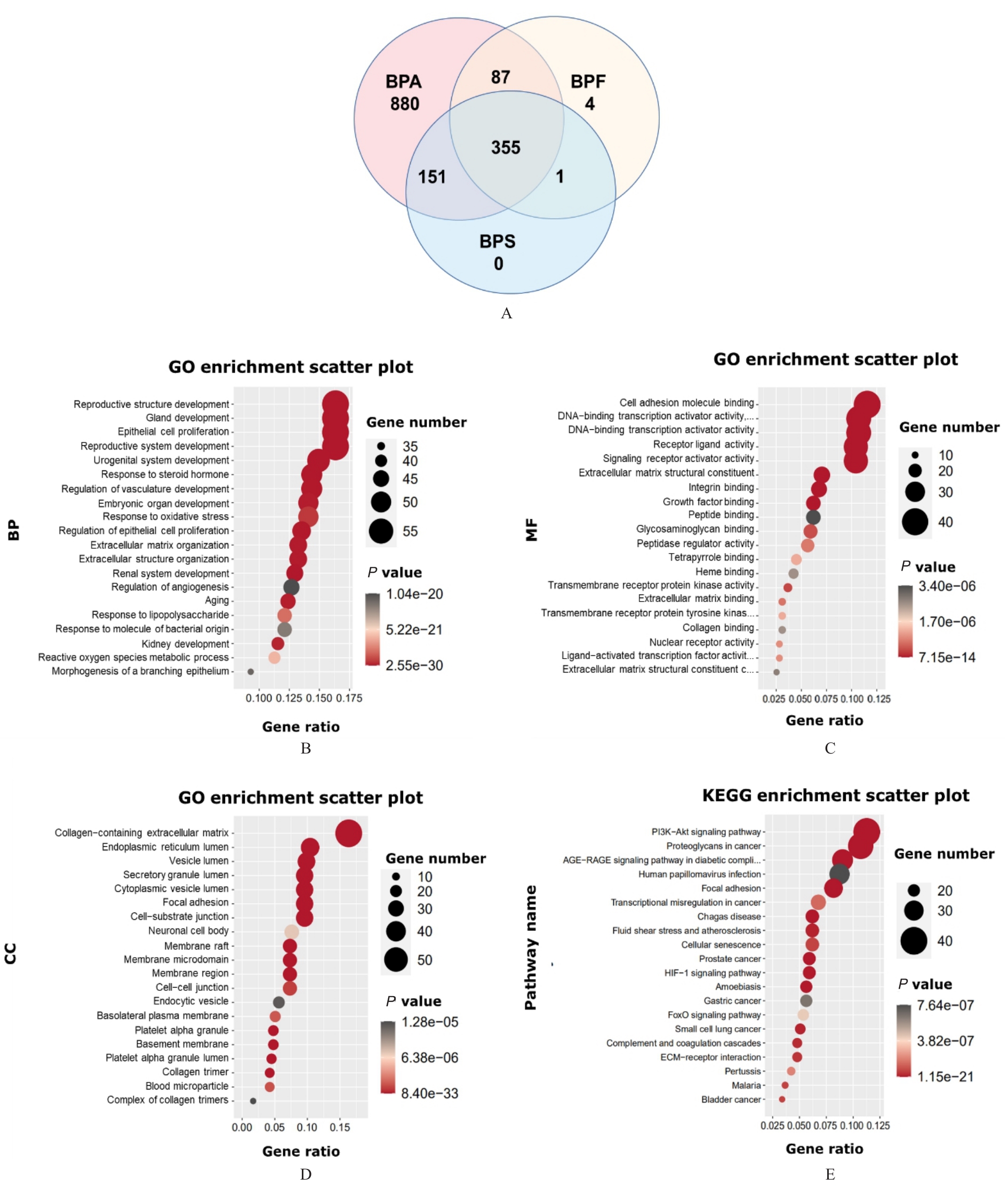
目的 通过生物信息学方法和实验验证,探讨新型双酚类污染物双酚S(BPS)和双酚F(BPF)诱导男性生殖系统损伤的信号通路。 方法 生物信息学分析,从比较毒理基因组学数据库(CTD)筛选出与BPF和BPS相关的男性生殖系统疾病基因,并通过基因本体论(GO)的功能富集和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路富集分析,预测可能的信号通路及关键基因。采用细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测不同浓度(1×10-3、1×10-2、1×10-1、1×100、1×101和1×102 μmol·L-1)BPS和BPF作用下各组细胞活力;将TM3细胞分为对照组(0.1% DMSO)、不同剂量BPS和不同剂量BPF组,采用20、40和80 μmol·L-1 BPS及BPF分别处理细胞72 h后,采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting法检测各组细胞中关键基因mRNA及蛋白表达水平。 结果 生物信息学分析,通过CTD筛选出的分别与BPS及BPF相关的男性系统疾病基因数为507及447个。GO富集分析,筛选出的基因主要富集于生殖系统发育和生殖结构发育等生物过程(BP)。KEGG通路分析,这些基因主要富集于磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K/AKT)、缺氧诱导因子1(HIF-1)和细胞衰老等信号通路(P<0.001)中。实验验证,与对照组比较,1×102 μmol·L-1 BPF和BPS组细胞活力明显降低(P<0.05),1×10-3~1×101 μmol·L-1 BPF和BPS组细胞活力无明显变化,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。BPS处理后,与对照组比较,低、中和高剂量BPS组细胞中PI3K、AKT、缺氧诱导因子1α(HIF-1α)及CREB结合蛋白(CBP)mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05),PI3K蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)相关X蛋白(Bax)蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),丝氨酸蛋白酶肽酶抑制因子B支成员10(SERPINB10)mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.01);中和高剂量BPS组细胞中Bax及细胞纤毛内转运同源蛋白80(IFT80)mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05);低和高剂量BPS组细胞中Bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);低和中剂量BPS组细胞中附加性梳基因2(ASXL2)mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.01)。BPF处理后,与对照组比较,低、中和高剂量BPF组细胞中Bcl-2、HIF-1α及染色体结构维持蛋白质1B(SMC1B)mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05),IFT80 mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.01),Bax蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01);低和高剂量BPF组细胞中PI3K、AKT及环指蛋白130(RNF130)mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05);中剂量组BPF细胞中CBP mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05),RNF130 mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05);高剂量BPF组细胞中PI3K和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 BPF和BPS可通过PI3K/AKT以及HIF-1信号通路产生生殖细胞毒性,损害男性生殖健康,RNF130和SMC1B可能是其诱导生殖毒性的重要靶点。
中图分类号:
- R114