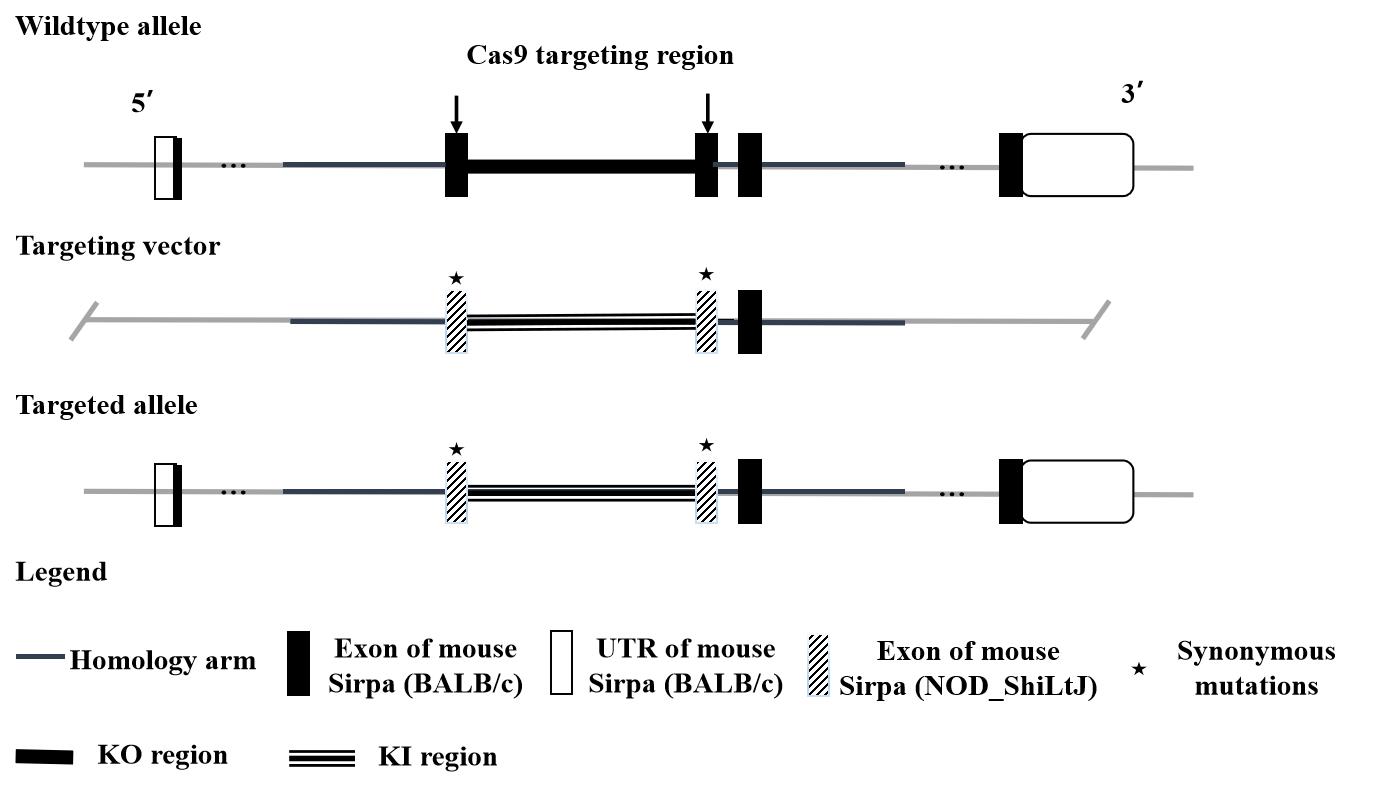
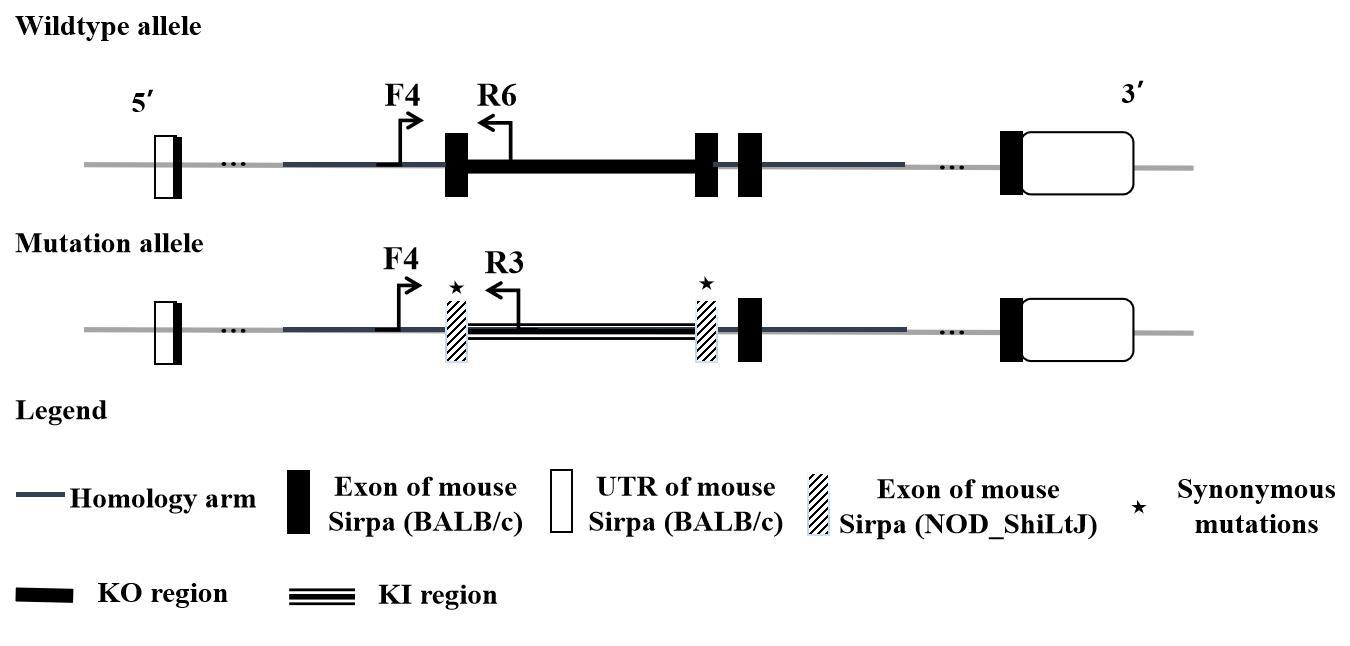
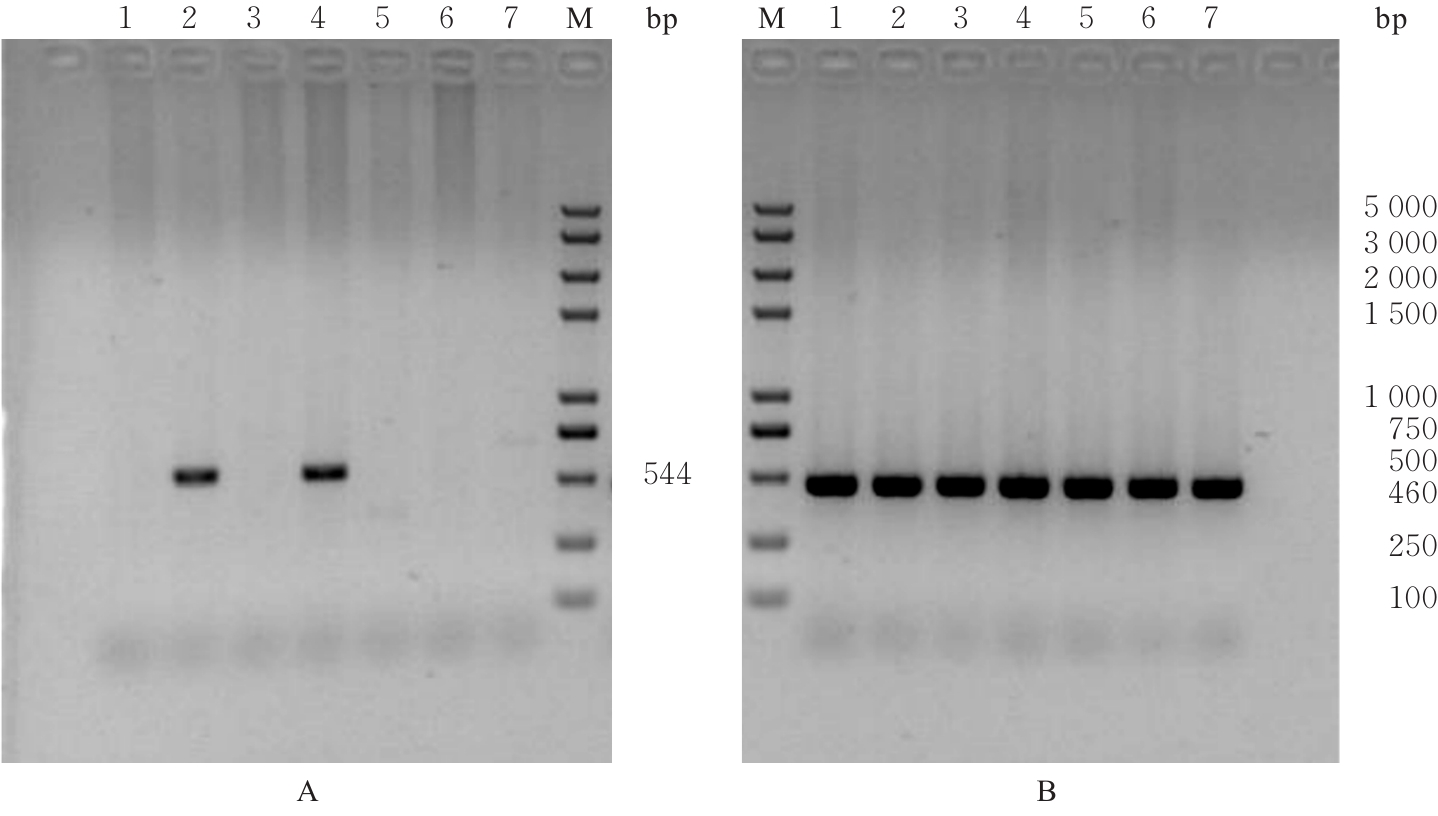
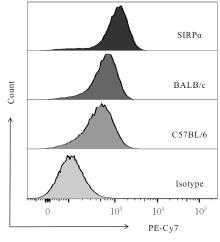
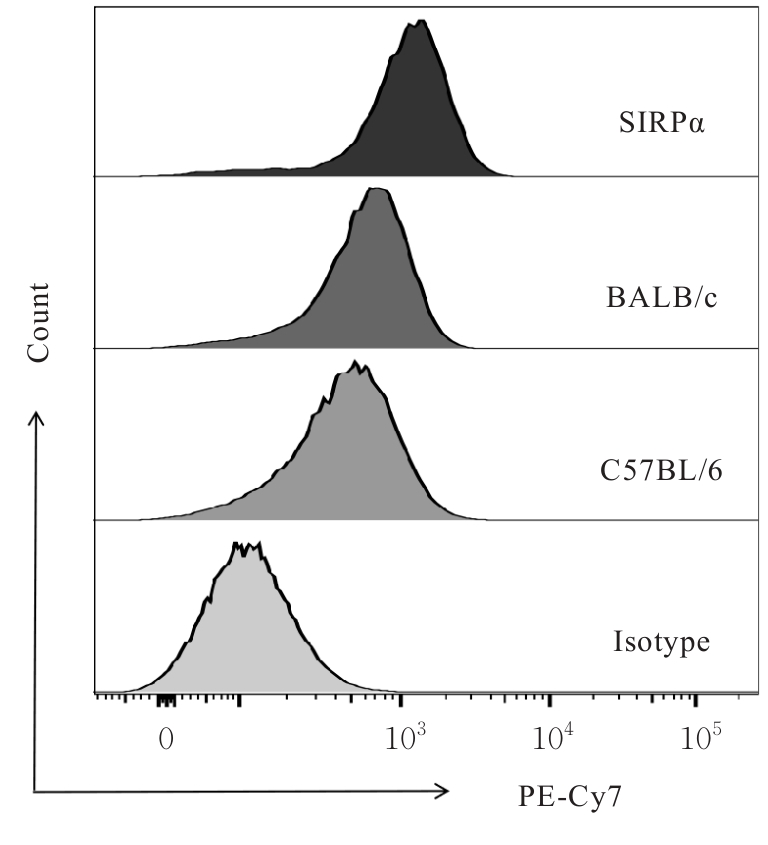
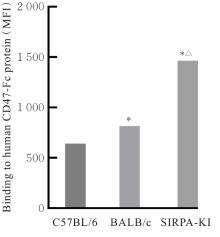
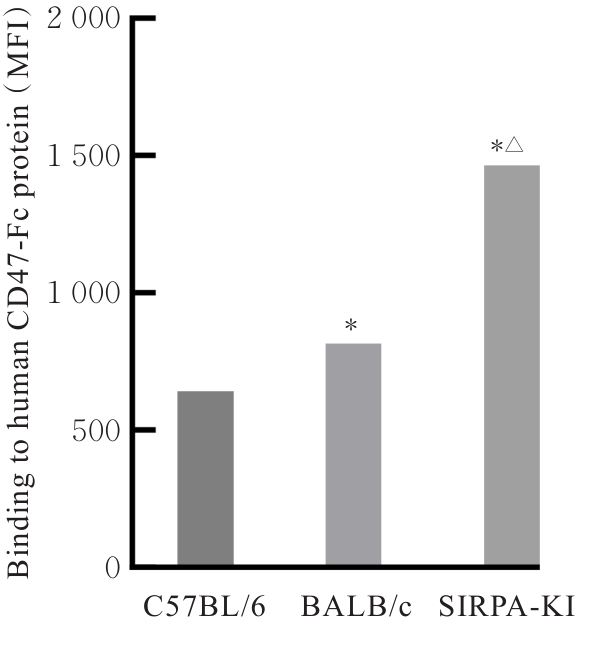
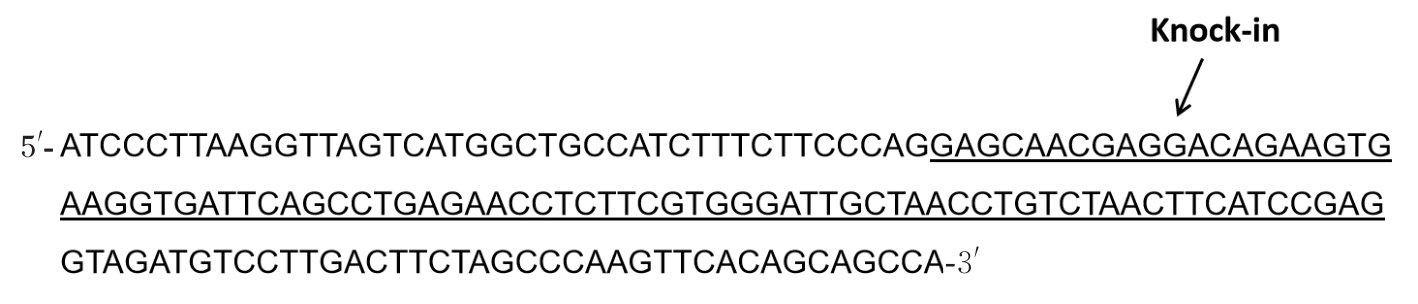| [1] |
BREHM M A, SHULTZ L D, GREINER D L. Humanized mouse models to study human diseases[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2010, 17(2): 120-125.
|
| [2] |
ITO R, TAKAHASHI T, KATANO I, et al. Current advances in humanized mouse models[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2012, 9(3): 208-214.
|
| [3] |
GREINER D L, HESSELTON R A, SHULTZ L D. SCID mouse models of human stem cell engraftment[J]. Stem Cells, 1998, 16(3): 166-177.
|
| [4] |
SHULTZ L D, BANUELOS S, LYONS B, et al. NOD/LtSz-Rag1nullPfpnull mice: a new model system with increased levels of human peripheral leukocyte and hematopoietic stem-cell engraftment[J]. Transplantation, 2003, 76(7): 1036-1042.
|
| [5] |
ROH Y J, GONG J E, KIM J E, et al. Comparison of immunophenotypes between Rag2 knockout mice derived from two different sources[J]. Lab Anim Res, 2023, 39(1): 2.
|
| [6] |
ITO M, HIRAMATSU H, KOBAYASHI K, et al. NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse: an excellent recipient mouse model for engraftment of human cells[J]. Blood, 2002, 100(9): 3175-3182.
|
| [7] |
BAXTER A G, COOKE A. Complement lytic activity has no role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice[J]. Diabetes, 1993, 42(11): 1574-1578.
|
| [8] |
LOGTENBERG M E W, SCHEEREN F A, SCHUMACHER T N. The CD47-SIRPα immune checkpoint[J]. Immunity, 2020, 52(5): 742-752.
|
| [9] |
MORRISSEY M A, KERN N, VALE R D. CD47 ligation repositions the inhibitory receptor SIRPA to suppress integrin activation and phagocytosis[J]. Immunity, 2020, 53(2): 290-302.
|
| [10] |
TAKENAKA K, PRASOLAVA T K, WANG J C Y, et al. Polymorphism in Sirpa modulates engraftment of human hematopoietic stem cells[J]. Nat Immunol, 2007, 8(12): 1313-1323.
|
| [11] |
GUTIERREZ-BARBOSA H, MEDINA-MORENO S, PERDOMO-CELIS F, et al. A comparison of lymphoid and myeloid cells derived from human hematopoietic stem cells xenografted into NOD-derived mouse strains[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(6): 1548.
|
| [12] |
IWAMOTO C, TAKENAKA K, URATA S, et al. The BALB/c-specific polymorphic SIRPA enhances its affinity for human CD47, inhibiting phagocytosis against human cells to promote xenogeneic engraftment[J]. Exp Hematol, 2014, 42(3): 163-171.e1.
|
| [13] |
BREHM M A, CUTHBERT A, YANG C X, et al. Parameters for establishing humanized mouse models to study human immunity: analysis of human hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in three immunodeficient strains of mice bearing the IL2 rgamma(null) mutation[J]. Clin Immunol, 2010, 135(1): 84-98.
|
| [14] |
YAMAUCHI T, TAKENAKA K, URATA S, et al. Polymorphic Sirpa is the genetic determinant for NOD-based mouse lines to achieve efficient human cell engraftment[J]. Blood, 2013, 121(8): 1316-1325.
|
| [15] |
MA Y W, ZHANG L F, HUANG X X. Genome modification by CRISPR/Cas9[J]. FEBS J, 2014, 281(23): 5186-5193.
|
| [16] |
LOPEZ-LASTRA S, MASSE-RANSON G, FIQUET O, et al. A functional DC cross talk promotes human ILC homeostasis in humanized mice[J]. Blood Adv, 2017, 1(10): 601-614.
|
| [17] |
SHULTZ L D, SCHWEITZER P A, CHRISTIANSON S W, et al. Multiple defects in innate and adaptive immunologic function in NOD/LtSz-scid mice[J]. J Immunol, 1995, 154(1): 180-191.
|
| [18] |
邹波, 杨娉婷. 嵌合抗原受体T细胞疗法在自身免疫性疾病中的应用[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(6): 466-471.
|
| [19] |
CHEN J, ZHONG M C, GUO H J, et al. SLAMF7 is critical for phagocytosis of haematopoietic tumour cells via Mac-1 integrin[J]. Nature, 2017, 544(7651): 493-497.
|
| [20] |
JIA X, YAN B J, TIAN X Q, et al. CD47/SIRPα pathway mediates cancer immune escape and immunotherapy[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(13): 3281-3287.
|
| [21] |
LEGRAND N, HUNTINGTON N D, NAGASAWA M, et al. Functional CD47/signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP(alpha)) interaction is required for optimal human T- and natural killer- (NK) cell homeostasis in vivo [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(32): 13224-13229.
|
| [22] |
JINNOUCHI F, YAMAUCHI T, YURINO A, et al. A human SIRPA knock-in xenograft mouse model to study human hematopoietic and cancer stem cells[J]. Blood, 2020, 135(19): 1661-1672.
|
 )
)