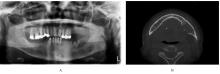
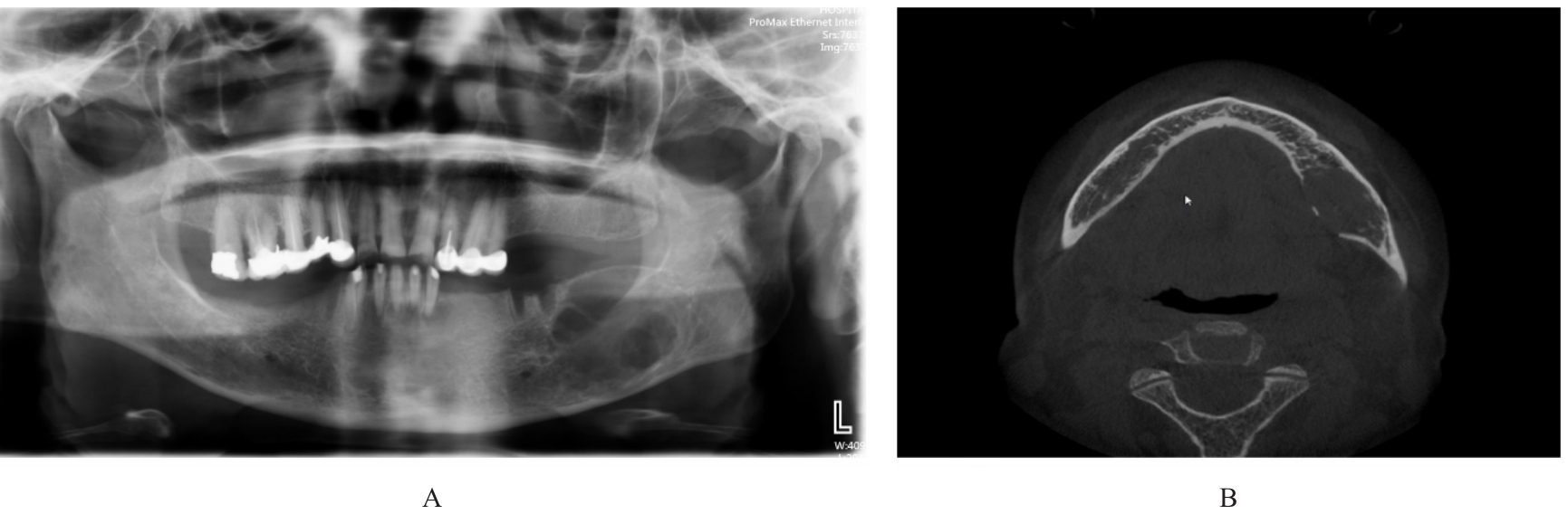
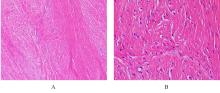
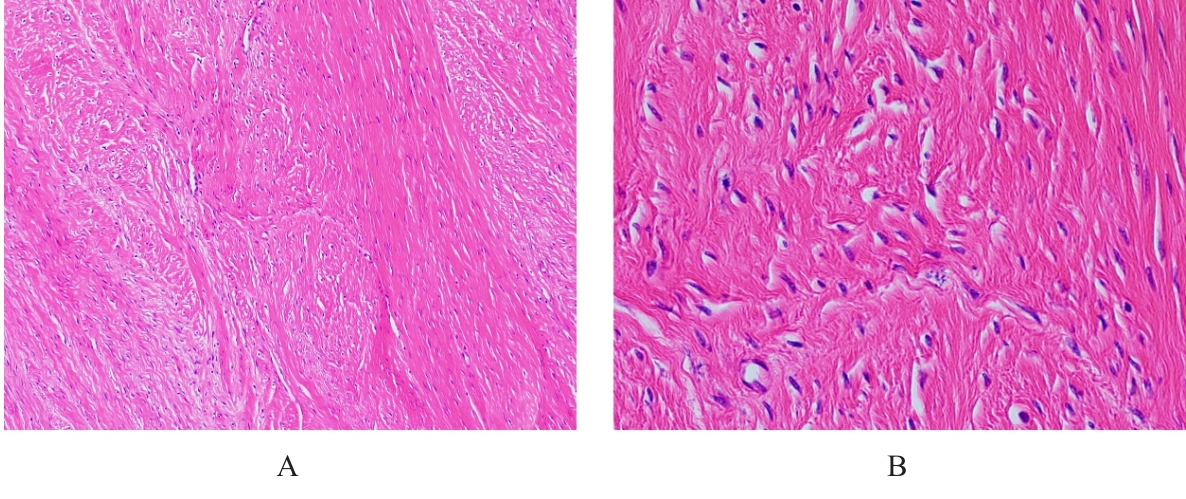
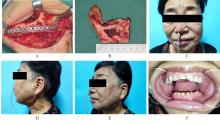
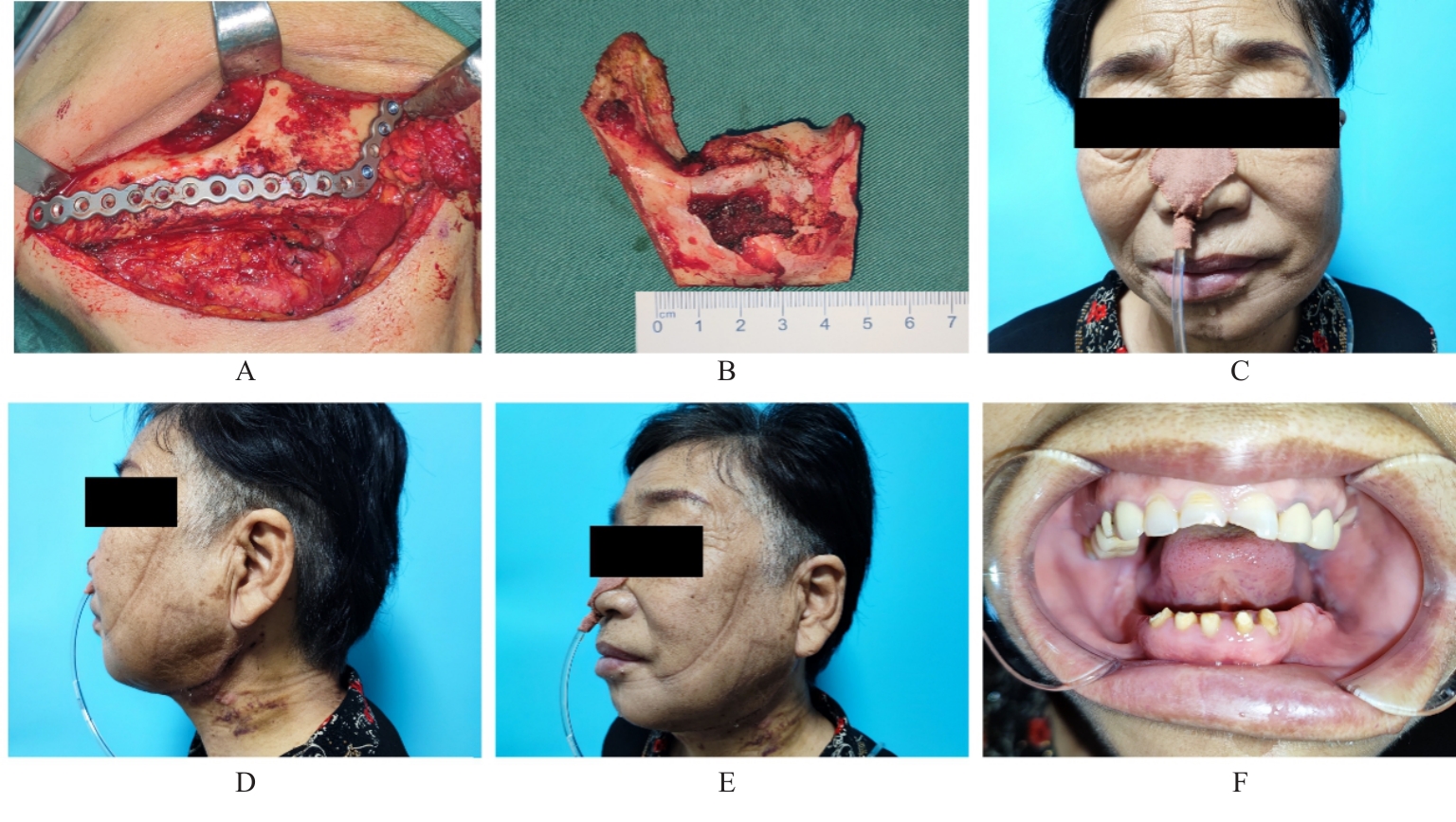
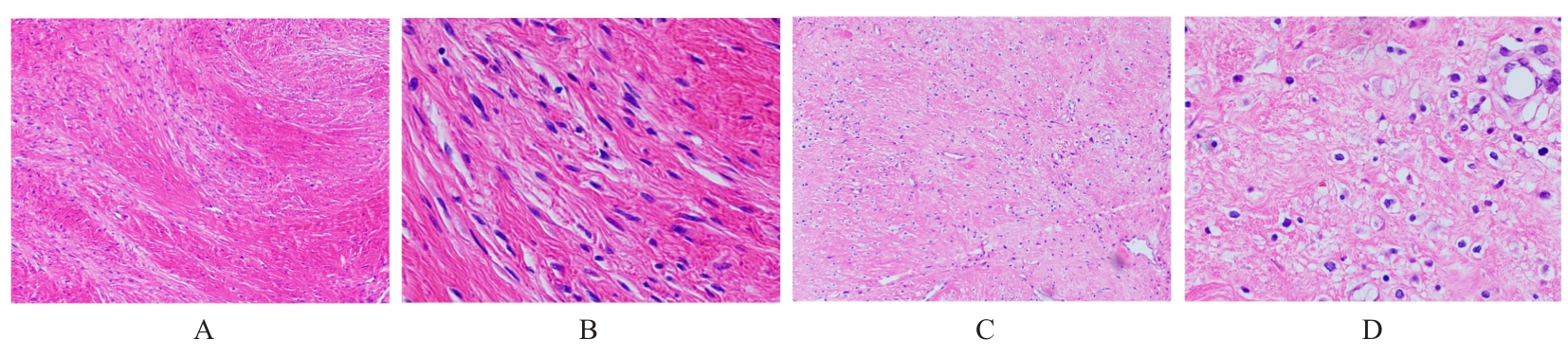
| [1] |
JAFFE H L. Tumors and tumorous conditions of the bones and joints[J]. Am J Med Sci, 1959, 238(1): 524.
|
| [2] |
GRIFFITH J G, IRBY W B. Desmoplastic fibroma report of a rare tumor of the oral structures[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1965, 20(2): 269-275.
|
| [3] |
LU Y K, LAN W, WU Q C, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma in a child: a 9-year follow-up case report[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2024, 25(1): 306.
|
| [4] |
FAHMY M D, GUPTA A, PADILLA R J, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma associated with tuberous sclerosis: case report and literature review[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2019, 128(2): e92-e99.
|
| [5] |
WANG X Y, GUAN W B, BAO L, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the pediatric cranium with CTNNB1 mutation: case report and literature review[J]. Childs Nerv Syst, 2024, 40(7): 2227-2233.
|
| [6] |
ALMEIDA LOUREIRO F J, NOGUEIRA W R, DUTRA M J, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the gnathic bones-a systematic review[J]. Oral Dis, 2025, 31(1): 32-38.
|
| [7] |
GAUTAM V K, GOEL P, AGRAWAL E, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of radius managed with non-vascularised fibular autograft - a case report[J]. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol, 2022, 27(4): 736-741.
|
| [8] |
SAID-AL-NAIEF N, FERNANDES R, LOUIS P, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the jaw: a case report and review of literature[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2006, 101(1): 82-94.
|
| [9] |
SFEROPOULOS N K. Periosteal desmoplastic fibroma of the tibia in a 3-year-old child[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2015, 25(8): 1233-1238.
|
| [10] |
NISHA S, CHETANA C, RANJINI K, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the Mandible with unusual histopathological features[J]. Indian J Pathol Microbiol, 2021, 64(3): 548-552.
|
| [11] |
SINGH B P, ABDUL HALIM S, YAHAYA S, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the phalanx of the hand: a rare case report[J]. Case Rep Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 478-483.
|
| [12] |
SIDDIQUI H K, KHAN S A, AIJAZ A, et al. Unraveling the challenges in the diagnosis and management of desmoplastic fibroma of the mandible-a case report[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2024, 24(1): 256.
|
| [13] |
AJARRAG S, TORCHON M C. Distal phalanx desmoplastic fibroma of the hallux: a unique case mimicking a glomus tumor[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2025, 26(1): 98.
|
| [14] |
KARIMI A, DERAKHSHAN S, MORADZADEH KHIAVI M, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the jaws: a case series and review of literature[J]. Iran J Pathol, 2020, 15(2): 134-143.
|
| [15] |
RAZAVIPOUR M, AKHLAGHI H, ABDOLLAHI A. Overcoming diagnostic challenges in desmoplastic fibroma of the scapula: a rare case report[J]. Oxf Med Case Reports, 2023, 2023(8): omad057.
|
| [16] |
KALIA V, KAUR S, VASHISHT D. Gnathic desmoplastic fibroma mimicking a dentigerous cyst: a case report[J]. J Maxillofac Oral Surg, 2015, 14(): 150-153.
|
| [17] |
IWAI S, MATSUMOTO K, SAKUDA M. Desmoplastic fibroma of the mandible mimicking osteogenic sarcoma: report of a case[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1996, 54(11): 1370-1373.
|
| [18] |
SUMMA A, CERASTI D, CRISI G, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the mandible: usefulness of CT and MR imaging in diagnosis and treatment. a case report[J]. Neuroradiol J, 2010, 23(1): 109-113.
|
| [19] |
KAHRAMAN D, KARAKOYUNLU B, KARAGECE U, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the jaw bones: a series of twenty-two cases[J]. J Bone Oncol, 2021, 26: 100333.
|
| [20] |
MOHAMED S. Desmoplastic fibroma of the mandible[J]. Open Access J Transl Med Res, 2017, 1(1): 69-73.
|
| [21] |
RONEN S, KO J S, RUBIN B P, et al. Superficial low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma[J]. J Cutan Pathol, 2023, 50(2): 147-154.
|
| [22] |
WOODS T R, COHEN D M, ISLAM M N, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the mandible: a series of three cases and review of literature[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2015, 9(2): 196-204.
|
| [23] |
RAGIPOGLU D, DUDECK A, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M, et al. The role of mast cells in bone metabolism and bone disorders[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 163.
|
| [24] |
TANWAR Y S, KHARBANDA Y, RASTOGI R, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of bone: a case series and review of literature[J]. Indian J Surg Oncol, 2018, 9(4): 585-591.
|
| [25] |
RUAN M, ZHANG Z, WANG L Z, et al. Oral and maxillofacial desmoid-type fibromatoses in an eastern Chinese population: a report of 20 cases[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2011, 111(3): 340-345.
|
| [26] |
YIN H B, ZHANG D, WU Z P, et al. Desmoplastic fibroma of the spine: a series of 12 cases and outcomes[J]. Spine J, 2014, 14(8): 1622-1628.
|
| [27] |
HANNAM A G, STAVNESS I K, LLOYD J E, et al. A comparison of simulated jaw dynamics in models of segmental mandibular resection versus resection with alloplastic reconstruction[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2010, 104(3): 191-198.
|
 ),李佳2(
),李佳2( )
)
 ),Jia LI2(
),Jia LI2( )
)