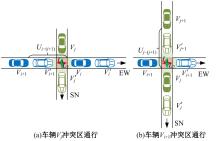
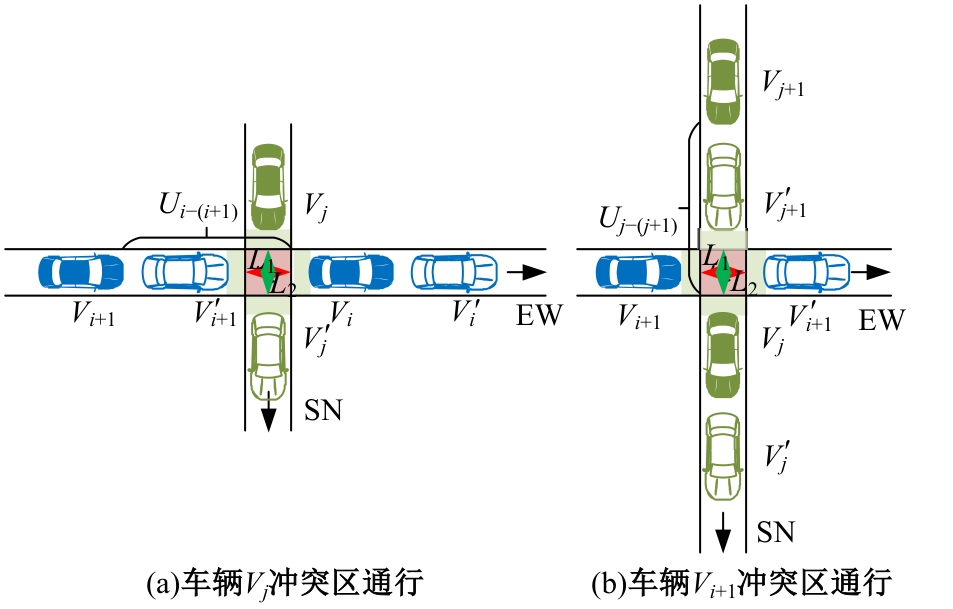
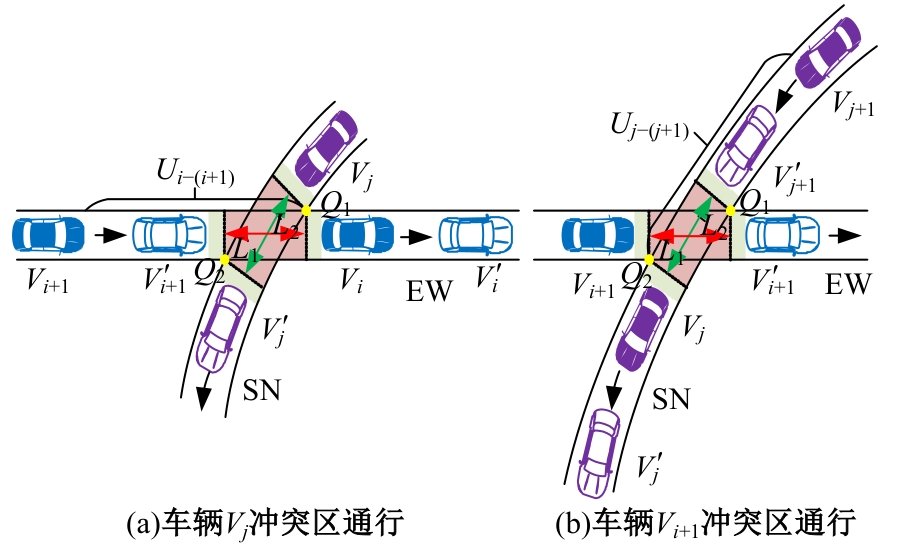
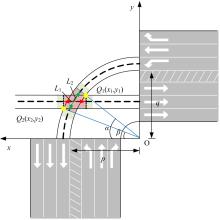
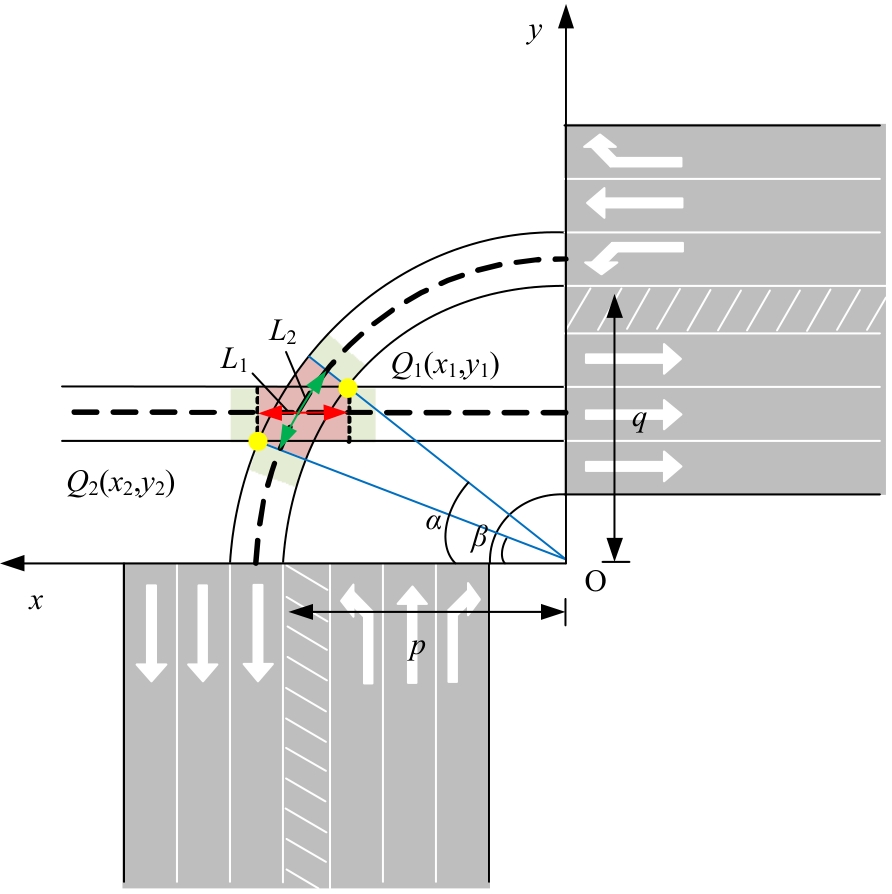
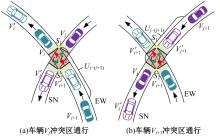
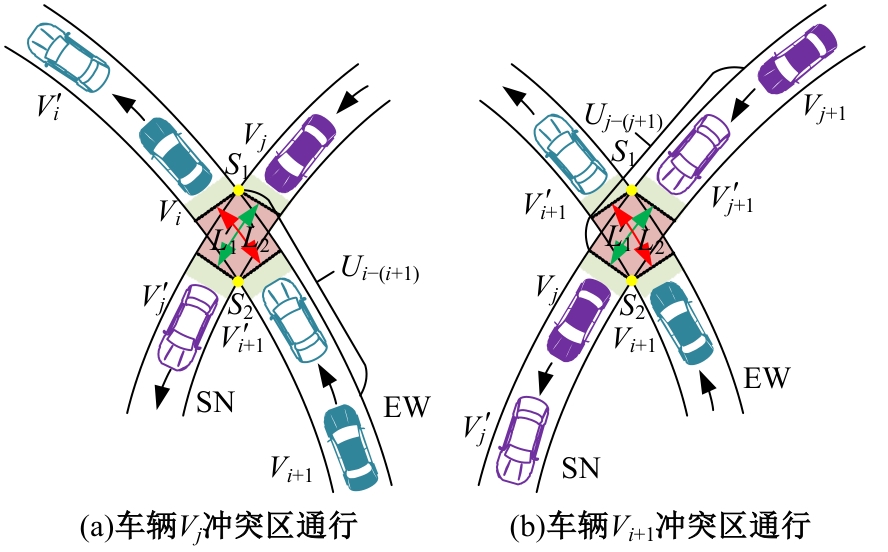
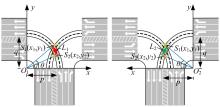
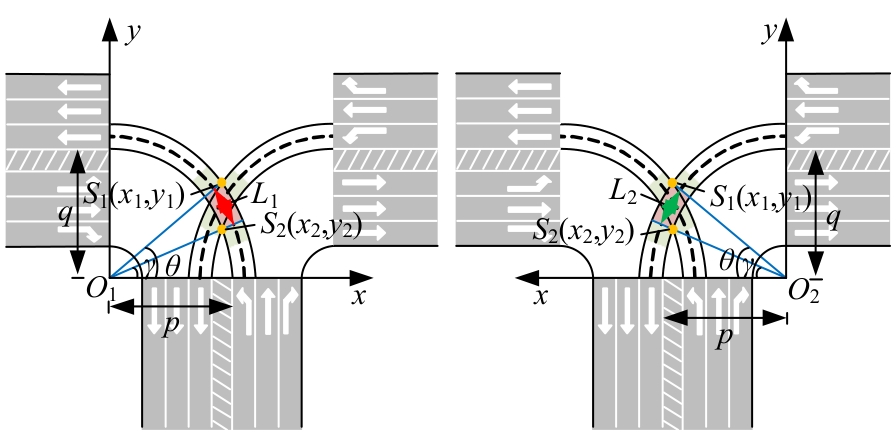
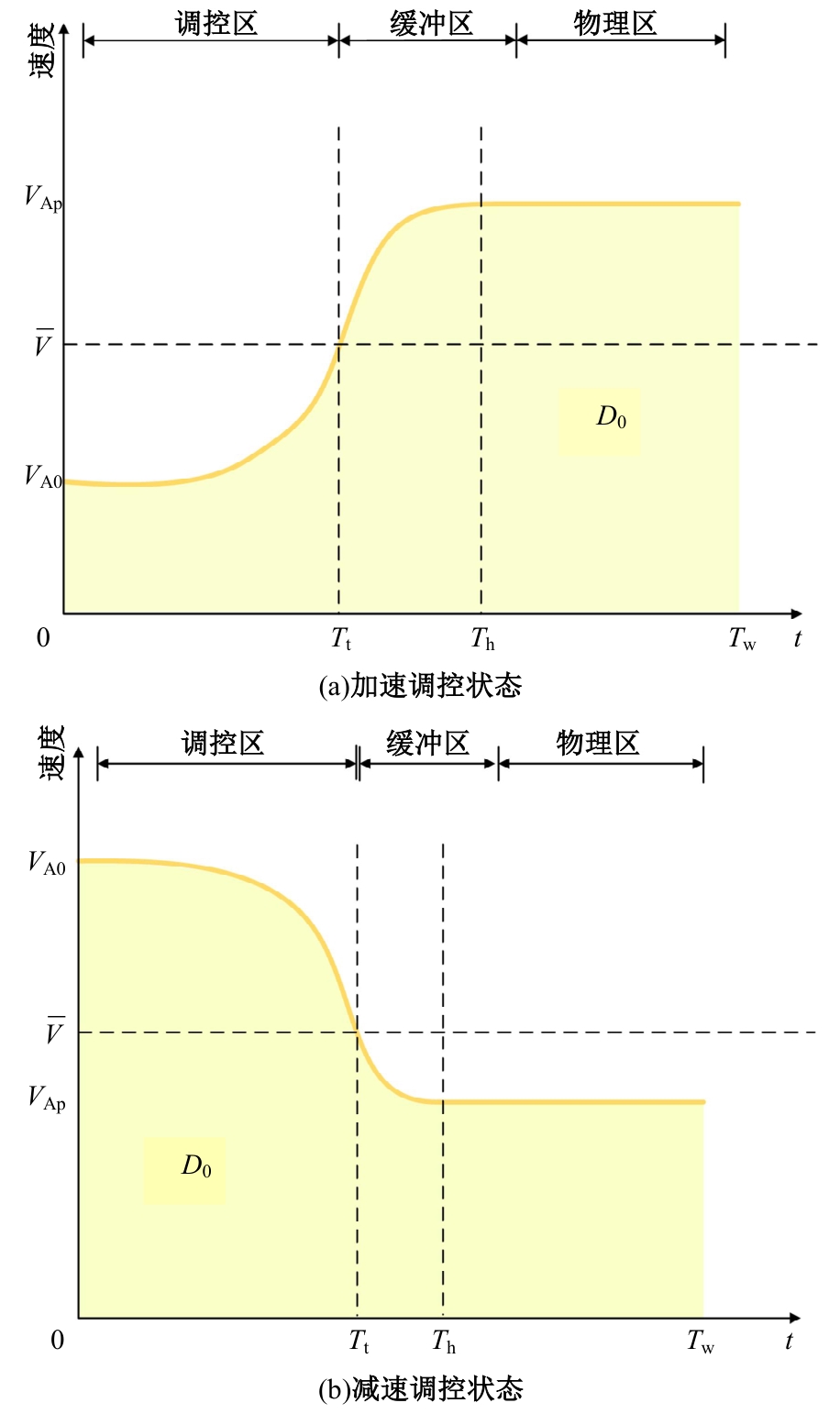
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1948-1962.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221102
Previous Articles Next Articles
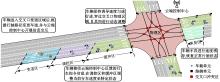
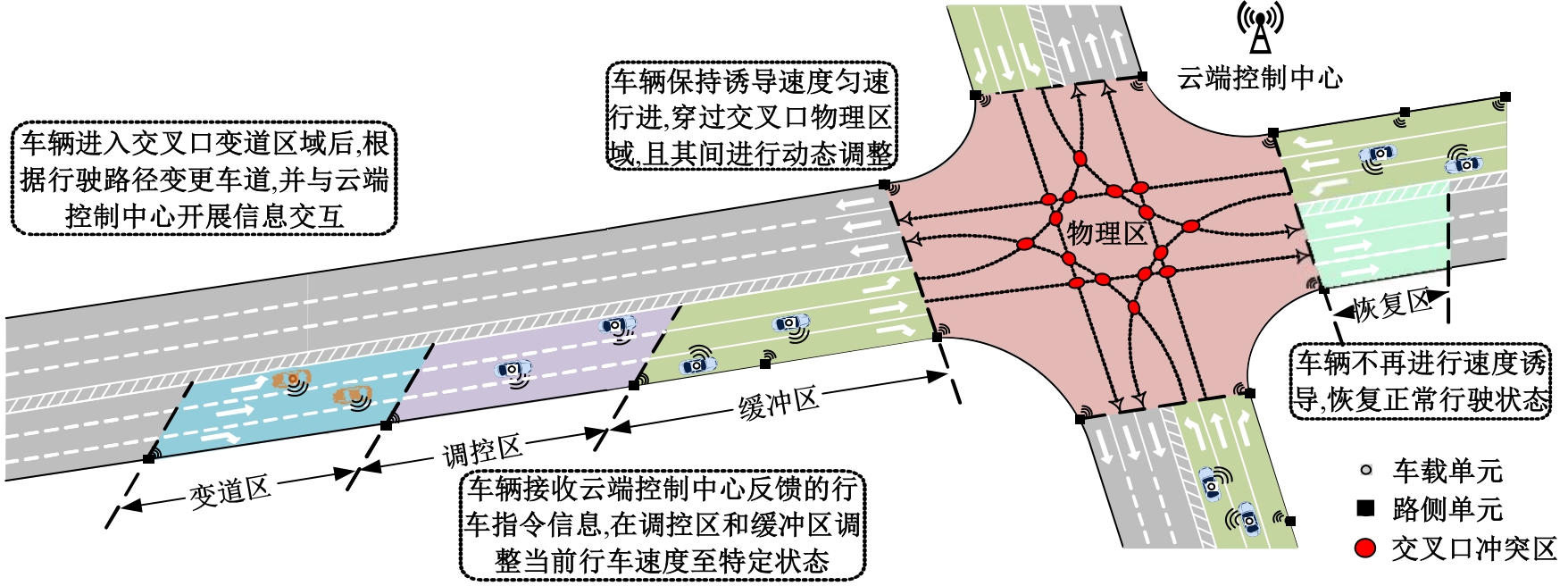
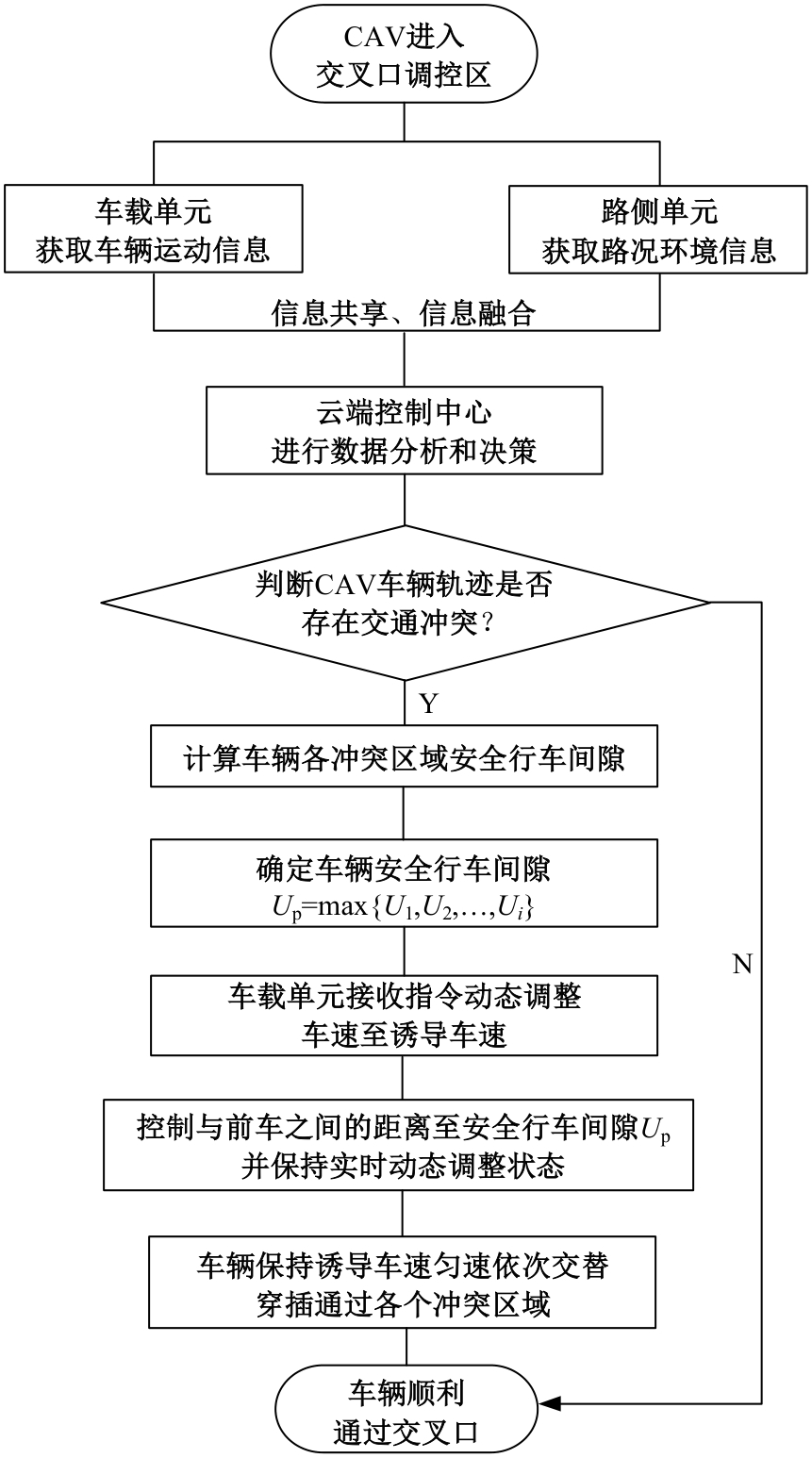
Strategies for controlling vehicle movements at signal⁃free intersections in intelligent networked environment
Fu-quan PAN1( ),Yuan-zheng NIU1,Li-xia ZHANG2,Jin-shun YANG1,Xiu-feng CHEN1,De-qi CHEN1
),Yuan-zheng NIU1,Li-xia ZHANG2,Jin-shun YANG1,Xiu-feng CHEN1,De-qi CHEN1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Qingdao University of Technology,Qingdao 266520,China
2.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,Qingdao University of Technology,Qingdao 266520,China
CLC Number:
- U491.2
| [1] | Zhong G, Zhang J, Yin T T, et al. A cooperative management strategy designed for unsignalized intersections under a connected vehicle environment[J]. Coat International Conference of Transportation Professionals, 2015, 2015: 233-245. |
| [2] | 胡永辉, 金旭峰, 王亦兵, 等. 智能网联混行动力异构交通流生态驾驶[J].中国公路学报, 2022, 35(3): 15-27. |
| Hu Yong-hui, Jin Xu-feng, Wang Yi-bing, et al. Intelligent networked hybrid mobility for heterogeneous traffic flow eco-driving[J]. Chinese Journal of Highways, 2022, 35(3): 15-27. | |
| [3] | Lee J, Park B. Development and evaluation of a cooperative vehicle intersection control algorithm under the connected vehicles environment[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation System, 2012, 13(1): 81-90. |
| [4] | 张游, 潘福全, 张丽霞, 等. 车路协同环境下智能交叉口车速控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(6): 1057-1064. |
| Zhang You, Pan Fu-quan, Zhang Li-xia,et al. Intelligent intersection speed control in a vehicle-road cooperative environment[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2022, 39(6): 1057-1064. | |
| [5] | 潘福全, 张游, 张丽霞, 等. 车路协同下基于间隙理论的交叉口智能控制策略[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 41(1): 44-52. |
| Pan Fu-quan, Zhang You, Zhang Li-xia, et al. Intelligent control strategy of intersection based on gap theory under vehicle-road cooperation[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 41(1): 44-52. | |
| [6] | Chen W, Liu Y. Gap-based automated vehicular speed guidance towards eco-driving at an unsignalized intersection[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2017, 2017(3): 1-22. |
| [7] | Chai L G, Cai B G, Wei S G, et al. Connected and autonomous vehicles coordinating approach at intersection based on space-time slot[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2018, 14(10): 929-951. |
| [8] | 刘显贵, 王晖年, 洪经纬, 等. 网联环境下信号交叉口车速控制策略及优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(2): 82-90. |
| Liu Xian-gui, Wang Hui-nian, Hong Jing-wei, et al. Signal intersection speed control strategy and optimization in a network-linked environment[J]. Transportation Systems Engineering and Information, 2021, 21(2): 82-90. | |
| [9] | Mahyar A, Mehdi N, Oliver G. Optimal traffic control at smart intersections: automated network fundamental diagram[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2019, 137: 2-18. |
| [10] | Zhang Y, Cassandras C G. Decentralized optimal control of connected automated vehicles at signal-free intersections including comfort-constrained turns and safety guarantees[J]. Automatica, 2019, 109: No.108563. |
| [11] | 常玉林, 张成祥, 张鹏, 等. 车联网环境下基于间隙优化的无信号交叉口车速控制方法[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2021, 35(3): 10-17, 60. |
| Chang Yu-lin, Zhang Cheng-xiang, Zhang Peng, et al. A gap optimization-based speed control method for signal-free intersections in a connected vehicle environment[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Sciences), 2021, 35(3): 10-17, 60. | |
| [12] | 潘福全, 张丽霞, 陆键, 等. 接入管理技术在公路交叉口安全改善中的运用[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2011, 37(2): 237-242. |
| Pan Fu-quan, Zhang Li-xia, Lu Jian, et al. The application of access management technology in highway intersection safety improvement[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2011, 37(2): 237-242. | |
| [13] | Milanés V, Shladover S E, Spring J, et al. Cooperative adaptive cruise control in real traffic situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 15(1): 296-305. |
| [14] | Milanés V, Shladover S E. Modeling cooperative and autonomous adaptive cruise control dynamic responses using experimental data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 48: 285-300. |
| [15] | Xiao L, Wang M, Schakel W, et al. Unravelling effects of cooperative adaptive cruise control deactivation on traffic flow characteristics at merging bottlenecks[J]. Transportation Research Part C: emerging technologies, 2018, 96: 380-397. |
| [16] | Wu X, Freese D, Cabrera A, et al. Electric vehicles' energy consumption measurement and estimation[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2015, 34: 52-67. |
| [17] | Altan O D, Wu G, Barth M J, et al. GlidePath: eco-friendly automated approach and departure at signalized intersections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2017, 2(4): 266-277. |
| [18] | 张健, 吴坤润, 杨敏, 等. 智能网联环境下交叉口双环自适应控制模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| Zhang Jian, Wu Kun-run, Yang Min, et al. Dual-loop adaptive control model for intersections in an intelligent network link environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. | |
| [19] | Stevanovic J, Stevanovic A, Martin P T, et al. Stochastic optimization of traffic control and transit priority settings in VISSIM[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2008, 16(3): 332-349. |
| [20] | Mahmassani H S. 50th Anniversary invited article—autonomous vehicles and connected vehicle systems: flow and operations considerations[J]. Transportation Science, 2016, 50(4): 1140-1162. |
| [1] | ZHANG Jian-Rui, XU Xiu-Min, LI Kang, LIU Jiang-Wei, QIN Ke-Yin, YIN Bao-Zhi, ZHANG Peng. SCR urea dosing control strategy to meet China IV [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 128-0132. |
| [2] |
Liang Chun-yan,Wang Chun-guang,Shen Zhan,Wang Dian-hai .
Calculation method of travel time of rightturn vehicle at motorand nonmotorvehicle mixed traffic intersection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(05): 1053-1057. |
|