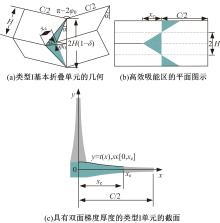
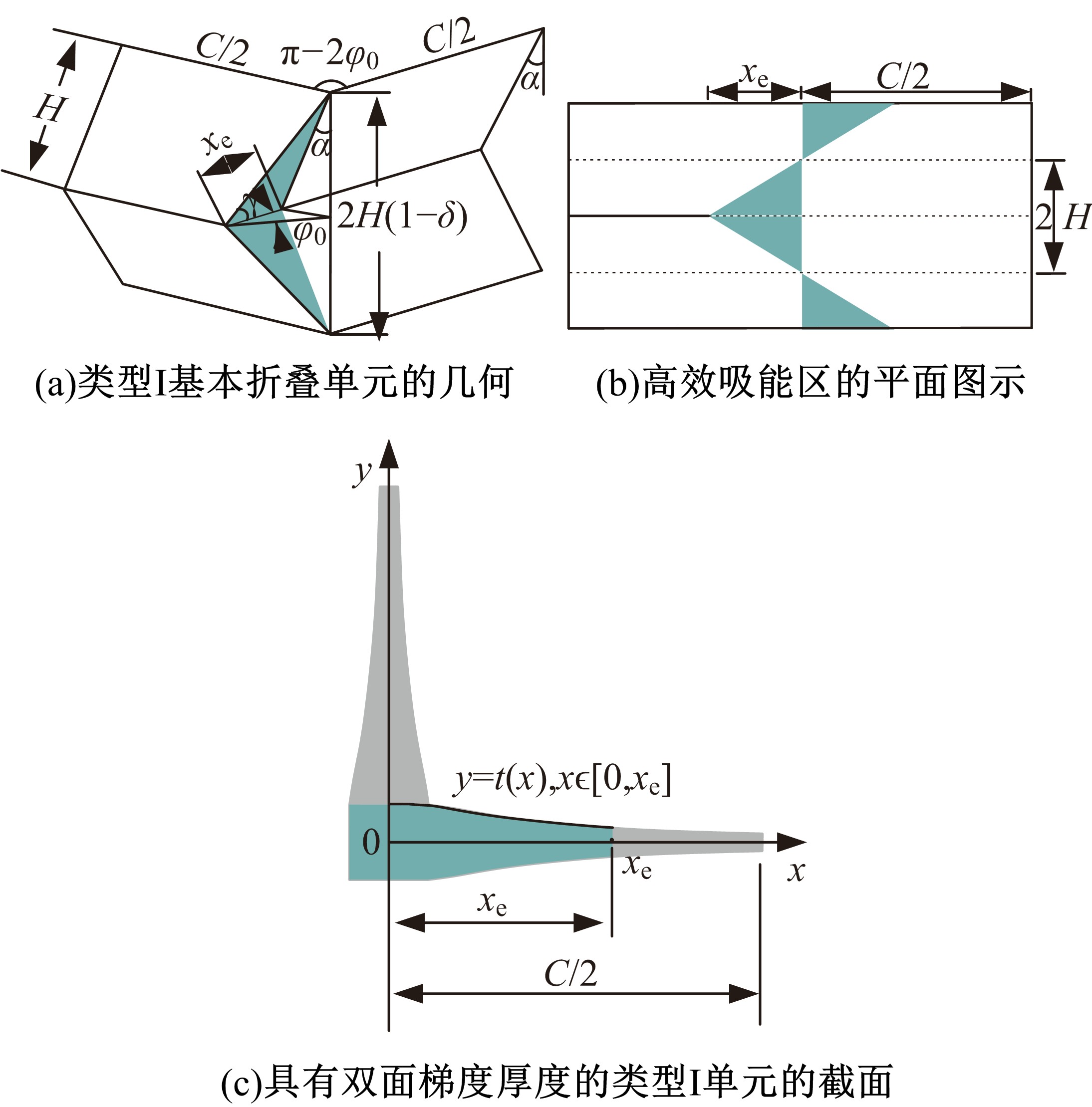
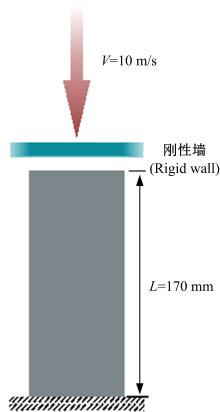
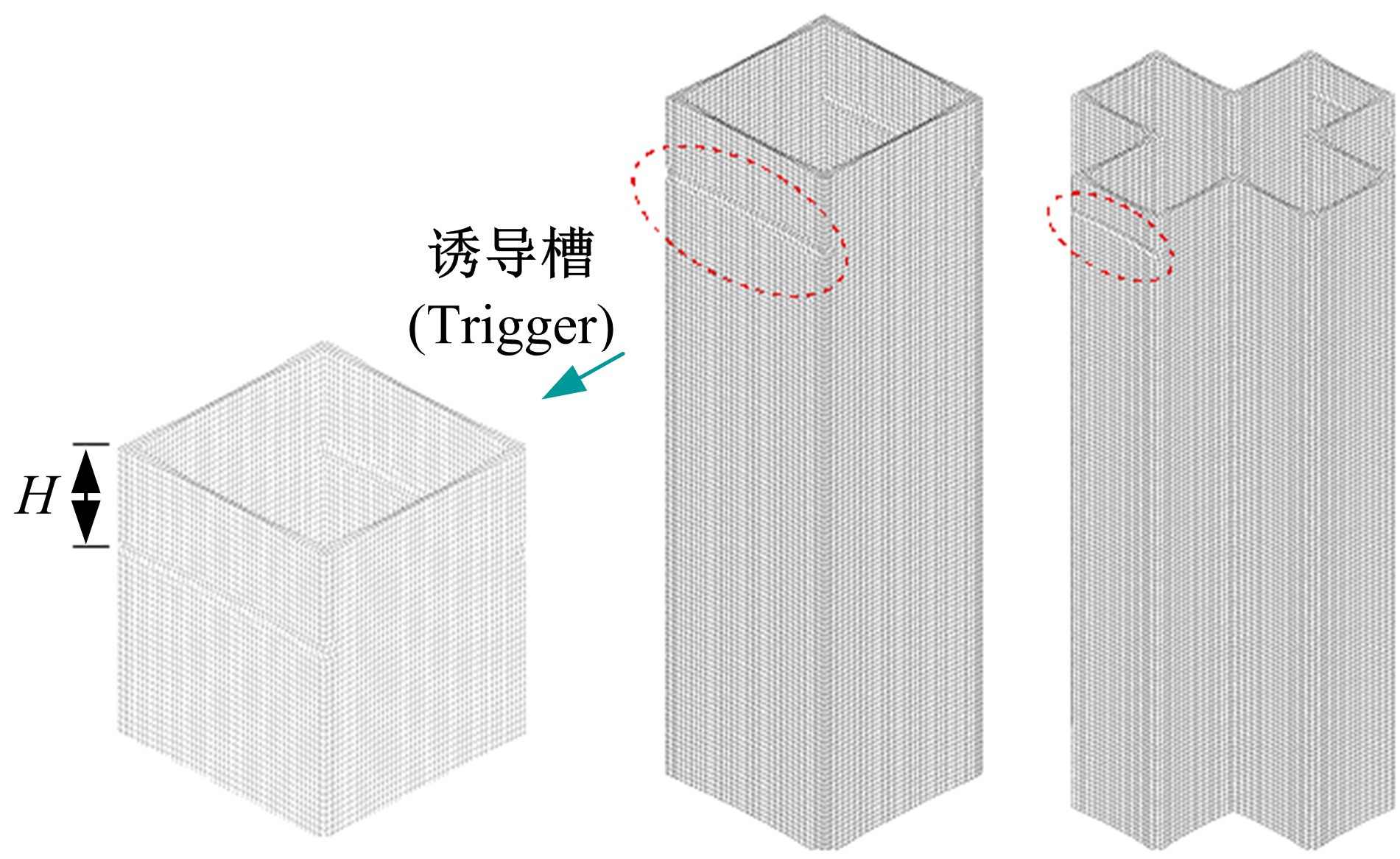
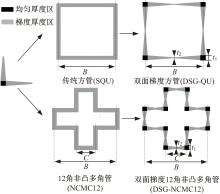
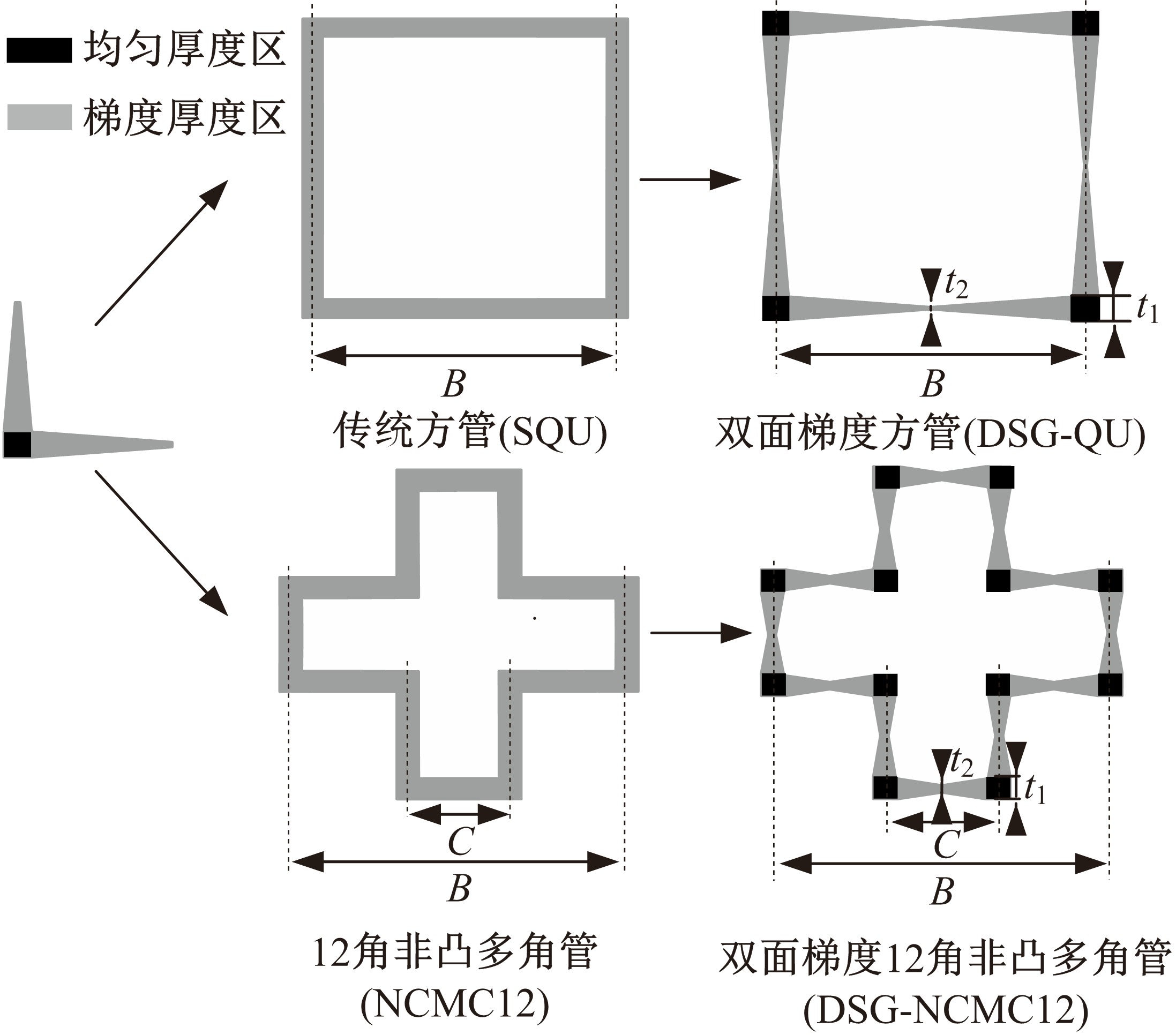
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1584-1592.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190272
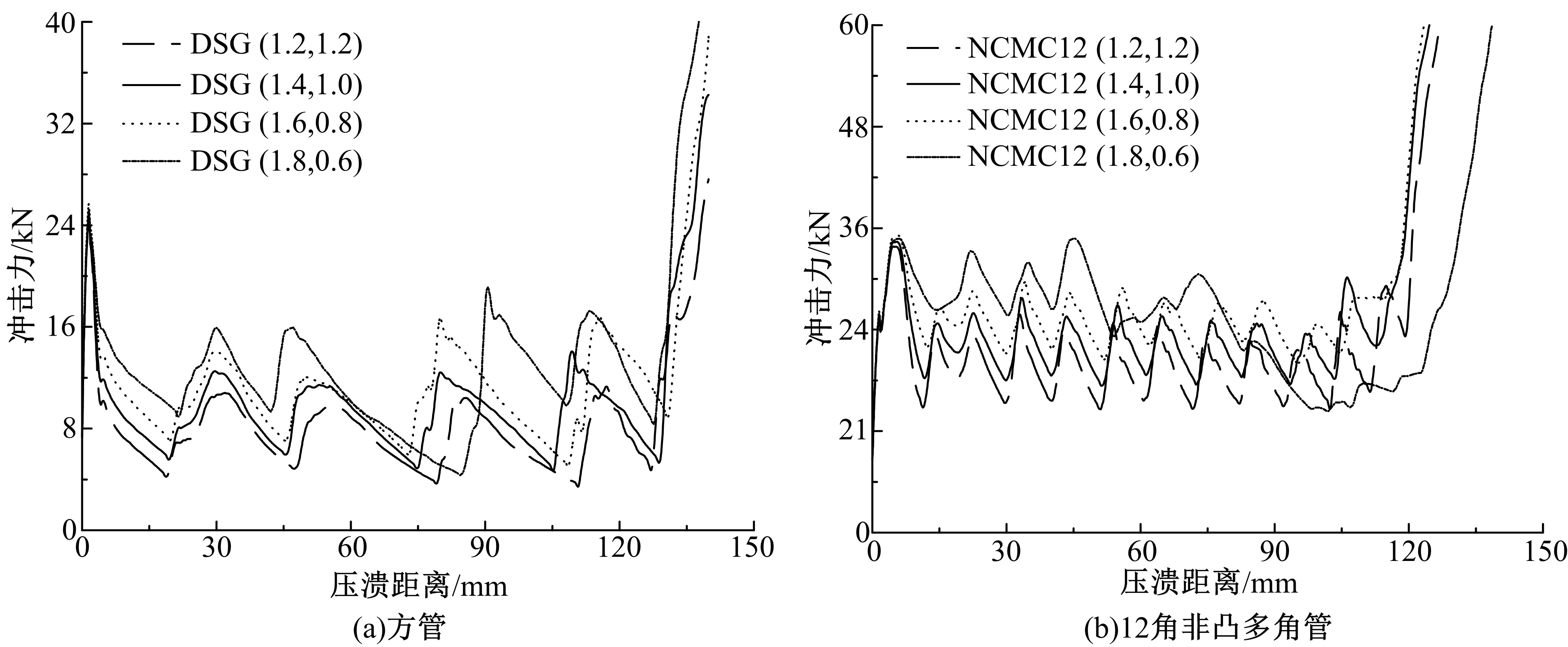
Energy absorption properties of multi-corner thin-walled columns with double surface gradients
Jun-xian ZHOU1( ),Rui-xian QIN1,Bing-zhi CHEN2(
),Rui-xian QIN1,Bing-zhi CHEN2( )
)
- 1. College of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116021, China
2. College of Locomotive and Vehicle Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116021, China
CLC Number:
- O342
| 1 | Lu G X , Yu T . Energy absorption of structures and materials[C]∥Woodhead Publishing Series in Metals and Surface Engineering. Cambridge: CRC Press, 2003: 385-400. |
| 2 | Abramowicz W . Thin-walled structures as impact energy absorbers[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2003, 41(2): 91-107. |
| 3 | Abramowicz W , Jones N . Dynamic progressive buckling of circular and square tubes[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1986, 4(4): 243-270. |
| 4 | Langseth M , Hopperstad O S . Static and dynamic axial crushing of square thin-walled aluminium extrusions[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1996, 18(7/8): 949-968. |
| 5 | Langseth M , Hopperstad O S , Hanssen A G . Crash behaviour of thin-walled aluminium members[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 1998, 32(1): 127-150. |
| 6 | Abramowicz W , Jones N . Transition from initial global bending to progressive buckling of tubes loaded statically and dynamically[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1997, 19(5): 415-437. |
| 7 | Wierzbicki T , Abramowicz W . On the crushing mechanics of thin-walled structures[J]. J Appl Mech, 1983, 50(4): 727-734. |
| 8 | Abramowicz W , Jones N . Dynamic axial crushing of square tubes[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1984, 2(2): 179-208. |
| 9 | Santosa S P , Wierzbicki T , Hanssen A G , et al . Experimental and numerical studies of foam-filled sections[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2000, 24(5): 509-534. |
| 10 | Santosa S , Wierzbicki T . Crash behavior of box columns filled with aluminum honeycomb or foam[J]. Comput Struct, 1998, 68(4): 343-367. |
| 11 | Zhang X , Cheng G . A comparative study of energy absorption characteristics of foam-filled and multi-cell square columns[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2007, 34(11): 1739-1752. |
| 12 | Hanssen A G , Langseth M , Hopperstad O S . Static and dynamic crushing of square aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2000, 24(4): 347-383. |
| 13 | Hanssen A C , Langseth M , Hopperstad O S . Static and dynamic crushing of circular aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2000, 24(5): 475-507. |
| 14 | Tang Z , Liu S , Zhang Z . Energy absorption properties of non-convex multi-corner thin-walled columns[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2012, 51: 112-120. |
| 15 | Liu S , Tong Z , Tang Z , et al . Bionic design modification of non-convex multi-corner thin-walled columns for improving energy absorption through adding bulkheads[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2015, 88: 70-81. |
| 16 | Zhang X , Huh H . Crushing analysis of polygonal columns and angle elements[J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2010, 37(4): 441-451. |
| 17 | Yamashita M , Gotoh M , Sawairi Y . Axial crush of hollow cylindrical structures with various polygonal cross-sections: numerical simulation and experiment[J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2003, 140(1-3): 59-64. |
| 18 | Godat A , Legeron F , Bazonga D . Stability investigation of local buckling behavior of tubular polygon columns under concentric compression[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2012, 53: 131-140. |
| 19 | Zhang X , Zhang H . Experimental and numerical investigation on crush resistance of polygonal columns and angle elements[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2012, 57: 25-36. |
| 20 | Zhang X , Wen Z , Zhang H . Axial crushing and optimal design of square tubes with graded thickness[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2014, 84: 263-274. |
| 21 | Abramowicz W , Wierzbicki T , Axial crushing of multicorner sheet metal columns [J]. J Appl Mech Trans ASME, 1989, 56(1): 113-120. |
| 22 | Ma J , Hou D , Chen Y , et al . Quasi-static axial crushing of thin-walled tubes with a kite-shape rigid origami pattern: numerical simulation[J]. Thin Wall Struct, 2016, 100: 38-47. |
| [1] | ZOU Meng, YU Yong-jun, ZHANG Rong-rong, WEI Can-gang, WANG Hui-xia. Simulation analysis of energy-absorption properties of thin-wall tube based on horn structure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1863-1868. |
| [2] | YU Xiang-Jun, WANG Guo-Qiang, WANG Ji-Xin, TANG Xiao-Bo, HU Ji. Dynamic response of rollover prevention system for wheel loader [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(05): 1262-1267. |
|
||