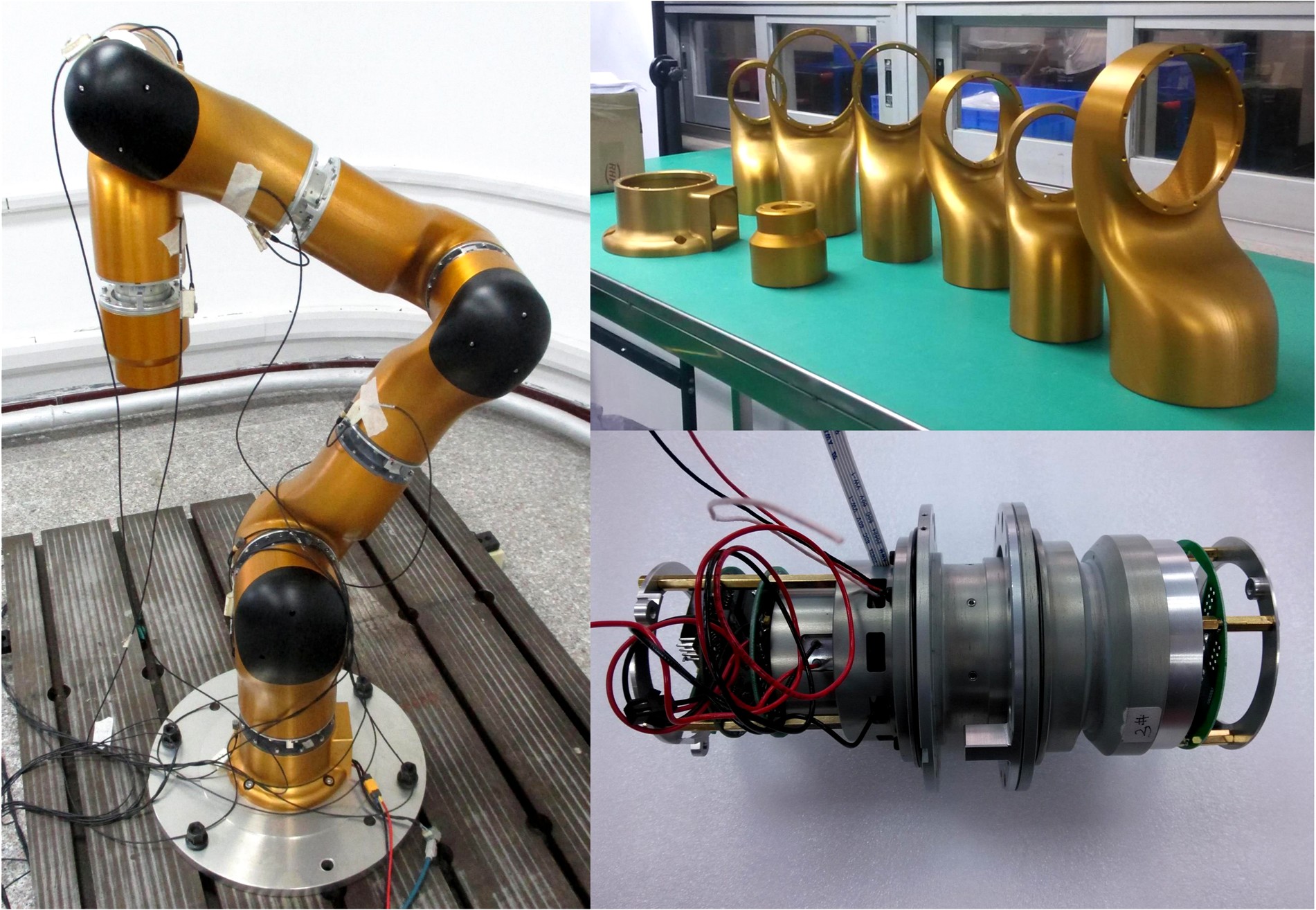
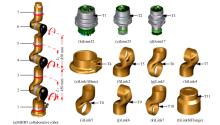
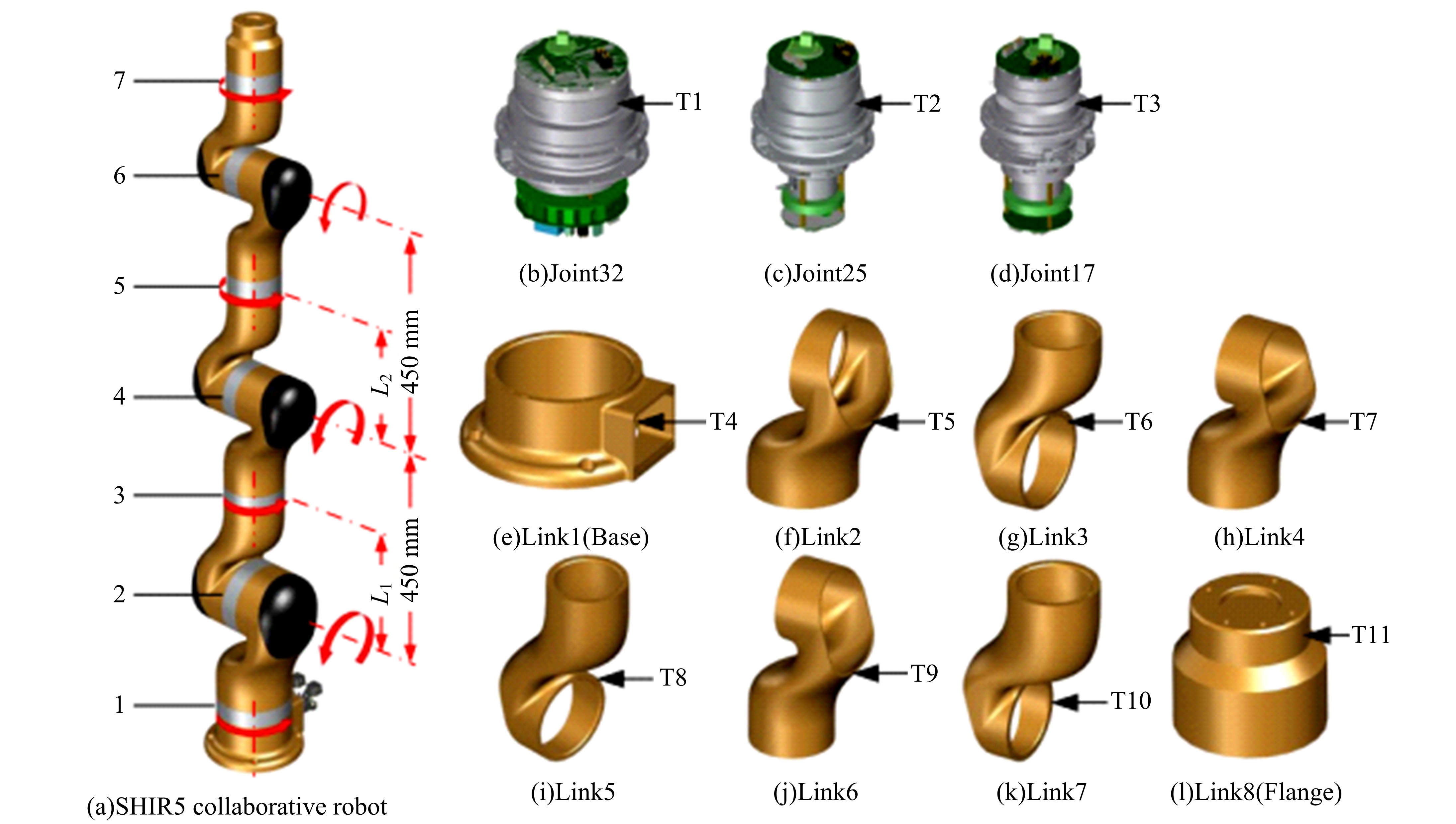
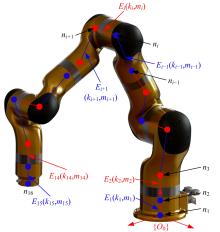
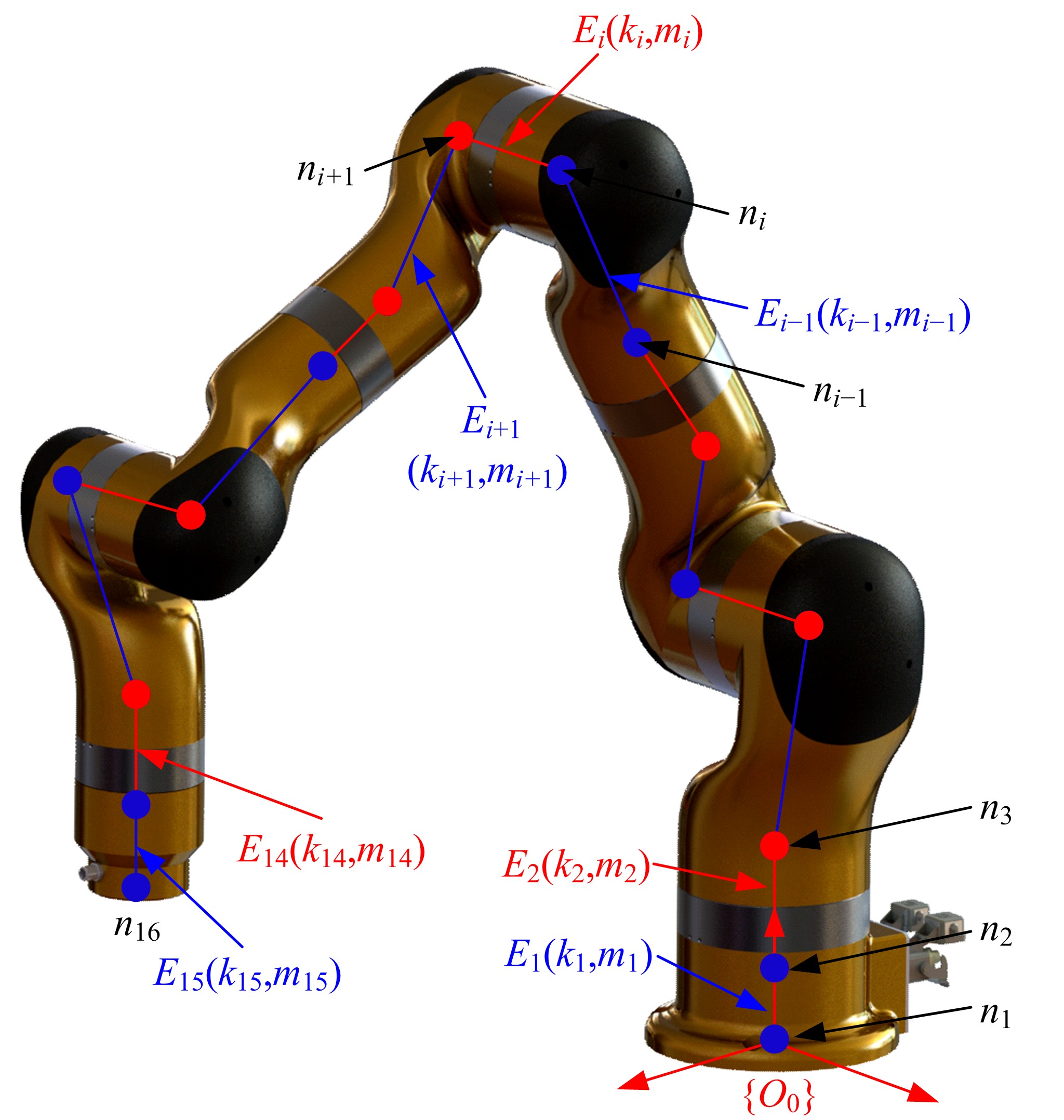
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 370-378.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190838
Global structural optimization design of collaborative robots using orthogonal design
Ming-wei HU1,2,3( ),Hong-guang WANG1,2(
),Hong-guang WANG1,2( ),Xin-an PAN1,2
),Xin-an PAN1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Robotics,Shenyang Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenyang 110016,China
2.Institutes for Robotics and Intelligent Manufacturing,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenyang 110169,China
3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
CLC Number:
- TP241
| 1 | ―2:2011. Robots and robotic devices—Safety requirements for industrial robots part 2: robot systems and integration[S]. |
| 2 | Alici G, Shirinzadeh B. Enhanced stiffness modeling, identification and characterization for robot manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(4): 554-564. |
| 3 | 胡明伟, 王洪光, 潘新安, 等. 一种协作型机器人运动性能分析与仿真[J]. 智能系统学报, 2017, 12(1): 75-81. |
| Hu Ming-wei,Wang Hong-guang,Pan Xin-an, et al. Analysis and simulation on kinematics performance of a collaborative robot[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2017, 12(1): 75-81. | |
| 4 | 刘延杰, 吴明月, 王刚, 等. 硅片传输机器人手臂结构优化设计方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(1): 1-9. |
| Liu Yan-jie, Wu Ming-yue, Wang Gang, et al. Method for structural optimization design of wafer handling robot arms[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(1): 1-9. | |
| 5 | Hegde G S, Vinod M S, Shankar A, et al. Optimum dynamic design of flexible robotic manipulator[J]. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 2009, 5(4): 315-325. |
| 6 | Kim B J, Yun D K, Lee S H, et al. Topology optimization of industrial robots for system-level stiffness maximization by using part-level metamodels[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 54(4): 1061-1071. |
| 7 | Zhou L, Bai S. A new approach to design of a lightweight anthropomorphic arm for service applications[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2015, 7(3): 1-12. |
| 8 | Luo H, Fu J, Wang P, et al. Design optimization of the ram structure of friction stir welding robot[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2019: 1-11. |
| 9 | 田野, 陈晓鹏, 贾东永, 等. 仿人机器人轻型高刚性手臂设计及运动学分析[J]. 机器人, 2011, 33(3): 332-339. |
| Tian Ye, Chen Xiao-peng, Jia Dong-yong, et al. Design and kinematic analysis of a light weight and high stiffness manipulator for humanoid robots[J]. Robot, 2011, 33(3): 332-339. | |
| 10 | Ning K P, Li D B, He F, et al. Research on the structural optimization design of ER300 palletizing robot[J]. The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7(1): 1405-1414. |
| 11 | Nezhadali V. Multi-objective optimization of Industrial robots[D]. Linköping: Linköping University, 2015. |
| 12 | Yin H, Huang S, He M, et al. A unified design for lightweight robotic arms based on unified description of structure and drive trains[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2017, 14(4): 1-14. |
| 13 | Saravanan R, Ramabalan S, Ebenezer N G, et al. Evolutionary bi-criteria optimum design of robots based on task specifications[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 41(3): 386-406. |
| 14 | Zhu Y, Qiu J, Tani J. Simultaneous optimization of a two-link flexible robot arm[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2015, 18(1): 29-38. |
| 15 | Alessandro C, Rosario S. Elastodynamic optimization of a 3T1R parallel manipulator[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2014, 73: 184-196. |
| 16 | Zhang L, Song Y. Optimal design of the Delta robot based on dynamics[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 2011, 43(9): 336-341. |
| 17 | Wang X, Zhang D, Zhao C, et al. Optimal design of lightweight serial robots by integrating topology optimization and parametric system optimization[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019, 132: 48-65. |
| 18 | Hu M W, Wang H G, Pan X A, et al. Research on elastic deformation modeling of collaborative robots[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Macau, China, 2017: 2462-2467. |
| 19 | 王新敏. ANSYS结构动力分析与应用[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2014. |
| 20 | Slamani M, Nubiola A, Bonev I A, et al. Assessment of the positioning performance of an industrial robot[J]. Industrial Robot——an International Journal, 2012, 39(1): 57-68. |
| 21 | Hu M W, Wang H G, Pan X A, et al. Optimal synthesis of pose repeatability for collaborative robots based on the ISO 9283 standard[J]. Industrial Robot, 2019, 46(6): 812-818. |
| [1] | Chun-ling ZHONG,Dong LIANG,Yun-long ZHANG,Jing WANG. Calculation of natural vibration frequency of simply supported beam strengthened by external prestressing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1884-1890. |
| [2] | WANG Xiu-gang, SU Jian, CAO Xiao-ning, LIN Hui-ying, ZHANG Yi-rui, YANG Xiao-min. Experiment on natural vibration characteristics of suspension based on simulation of semi-vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1583-1590. |
| [3] | ZHANG Tian-xiao, LIU Xin-hui, ZHANG Nong. Vibration analysis of hydraulic relief valve [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 91-94. |
| [4] | LIU Han-bing, WANG Long-lin, TAN Guo-jin, CHENG Yong-chun, WU Chang-xia. Effect of prestress force on natural frequency of external prestressed simply supported steel beam [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 81-85. |
| [5] | HAN Zhi-Wu, LV You, DONG Li-Chun, ZHANG Jun-Qiu, NIU Shi-Chao, MA Rong-Feng, REN Lou-Quan. Modal analysis of gear with bionic surface morphology [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1604-1608. |
| [6] | JIN Wen-ming, LI Hua-jun, KOU Shu-qing, YANG Sheng-hua. Modal analysis of frame of cantilever NC assembling machine for assembled camshaft [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 319-0323. |
| [7] | ZHAO Shu-zhi,ZHAO Bei,ZHU Yong-gang. Choice model of trip mode and policy of public transport priority based on SP survey [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 187-0190. |
| [8] | Gao Feng;Huang He;Ren Lu-quan. Erosive wear resistance of Laudakin stoliczkana's ternary coupling and bionic experiments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(03): 586-0590. |
| [9] | LIU Han-bing, GONG Guo-qing, WEI Yuan. Improved r-and h-adaptive Finite Element Method Based on Perturbation and Element Energy Ratio [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2000, (3): 56-60. |
| [10] | SU Tie-jian, GUAN Ai-hua, MAI Li. Dynamic Analysis of Elastic Plate with Dispersing Pressure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2000, (3): 72-74. |
|
||