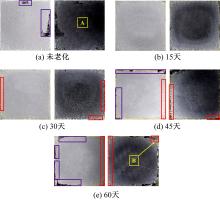
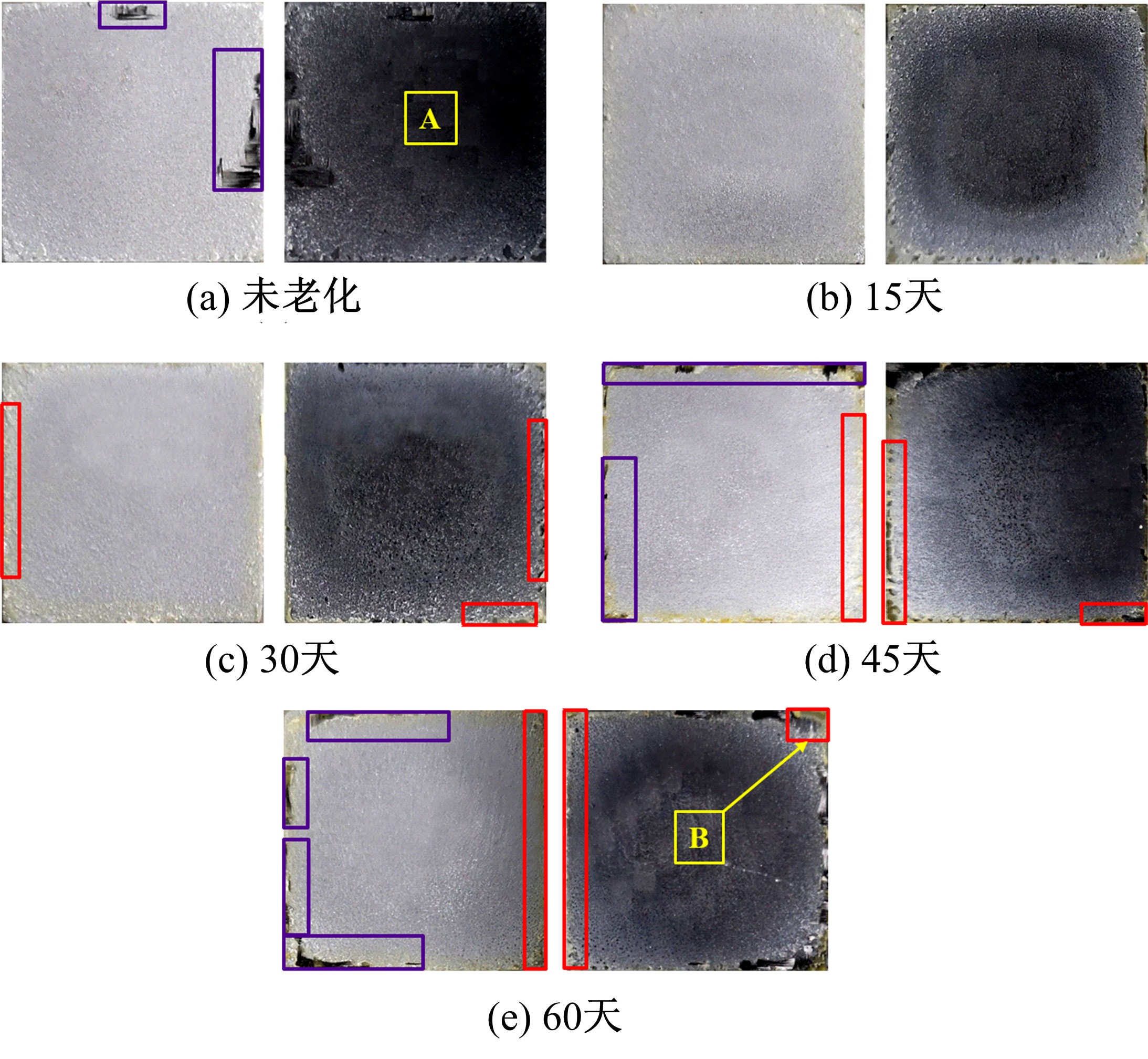
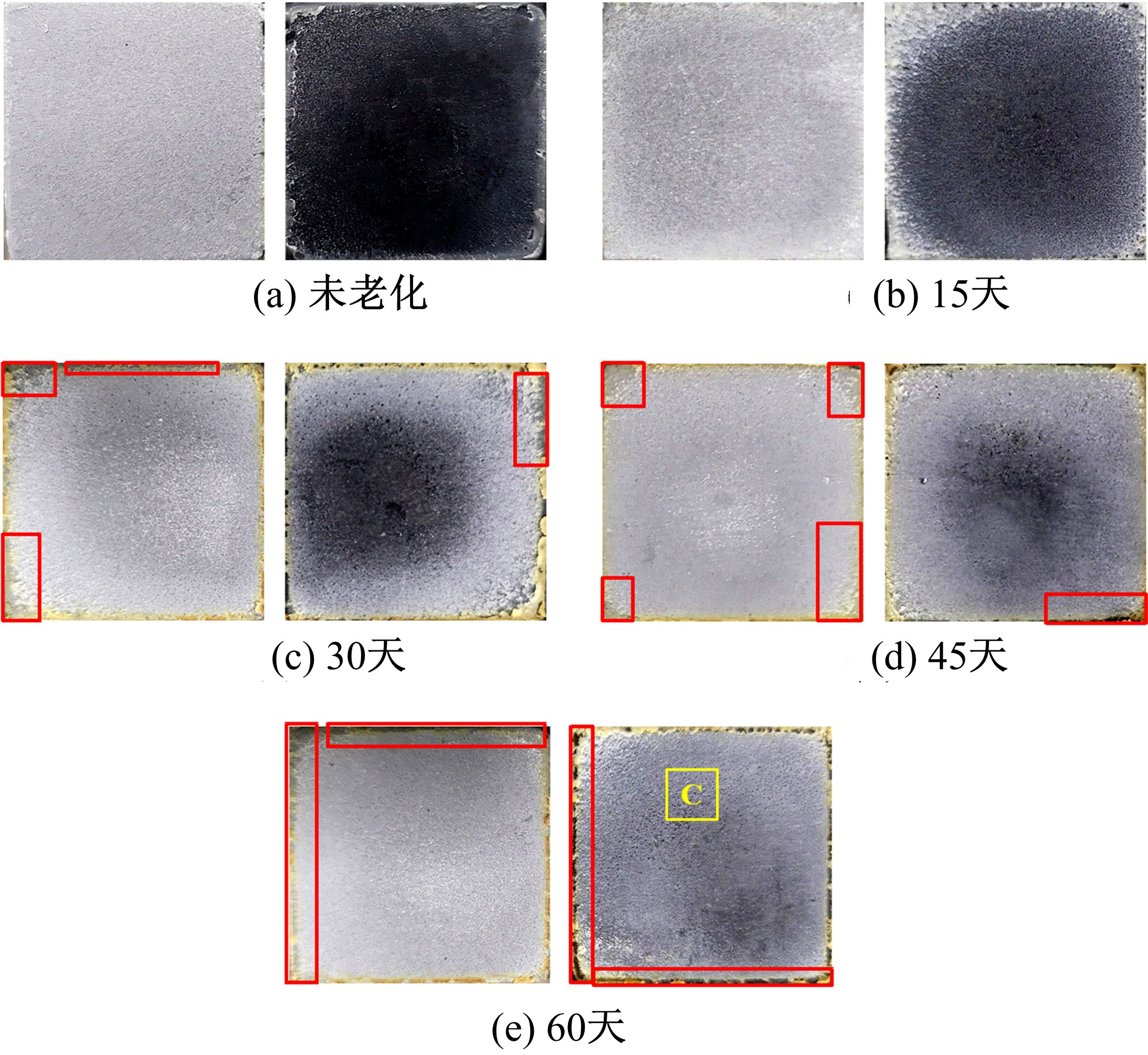
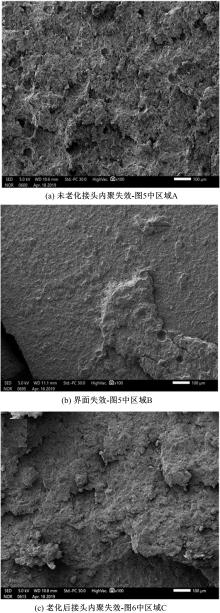
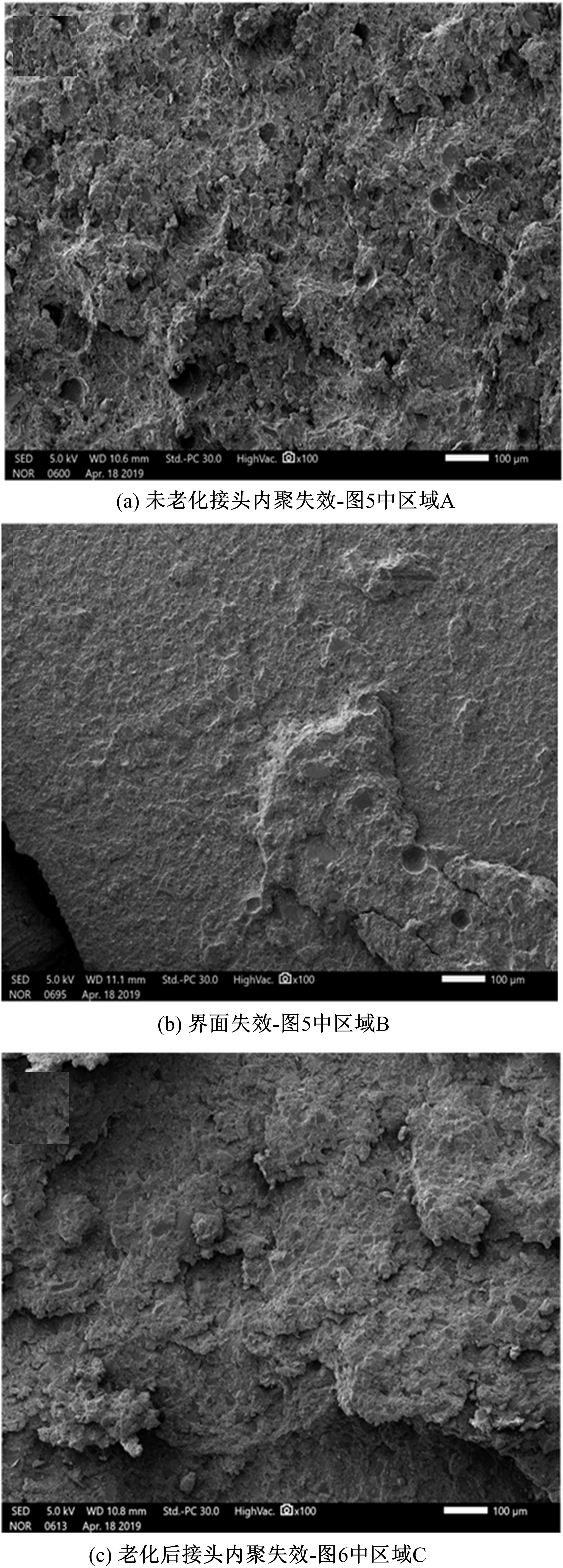
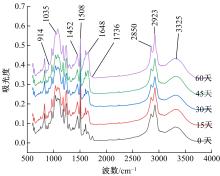
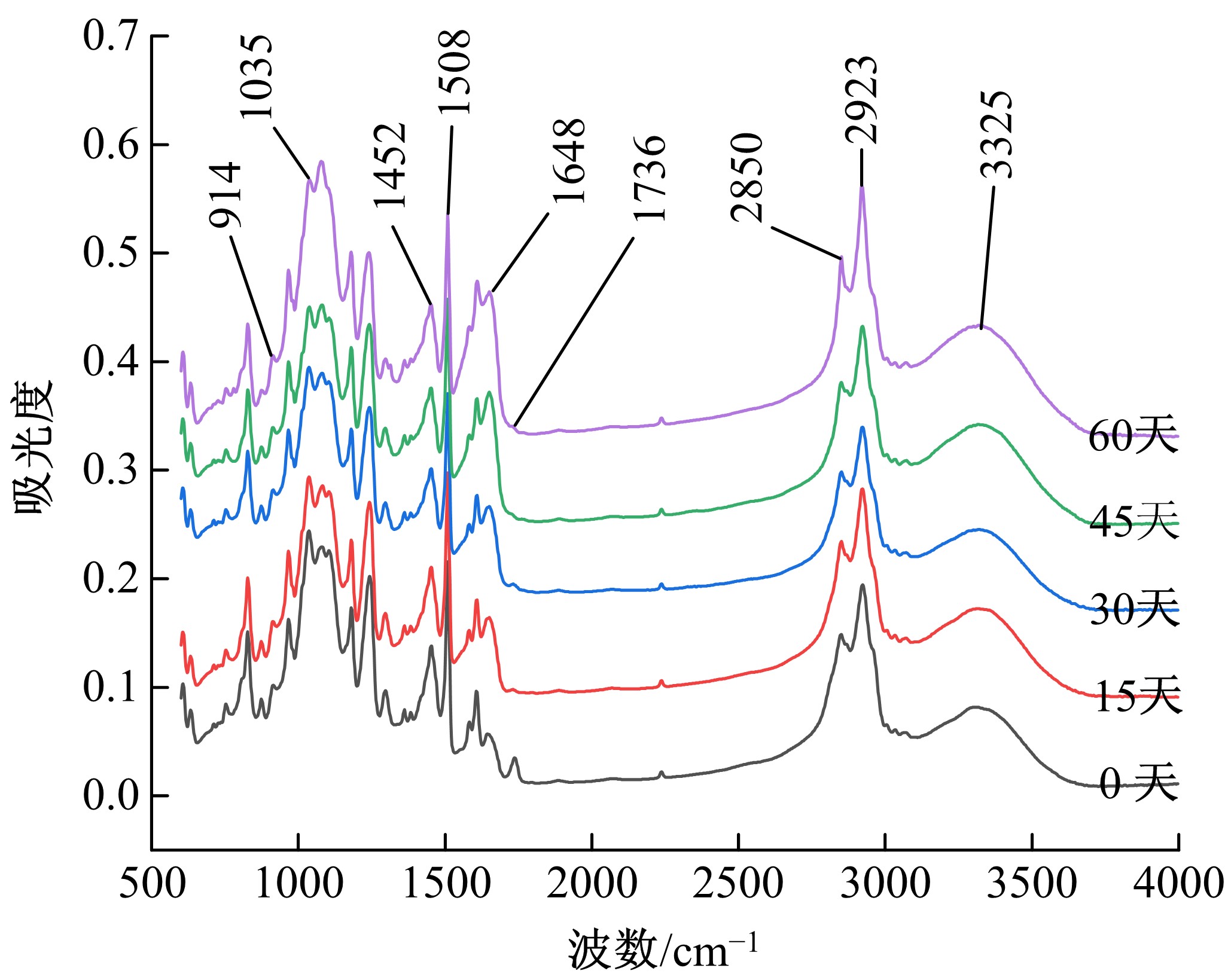
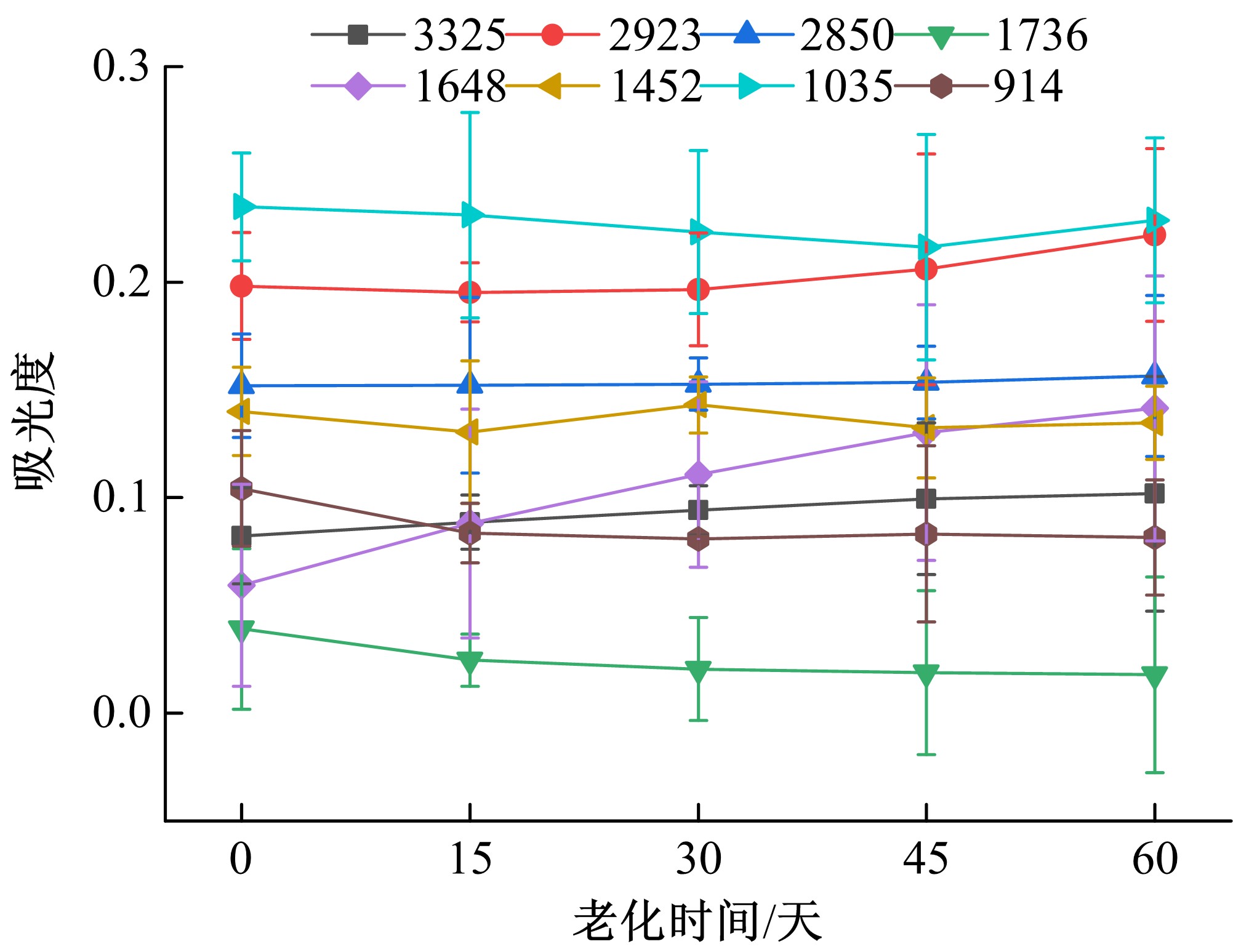
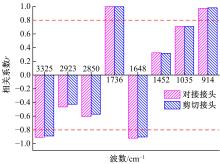
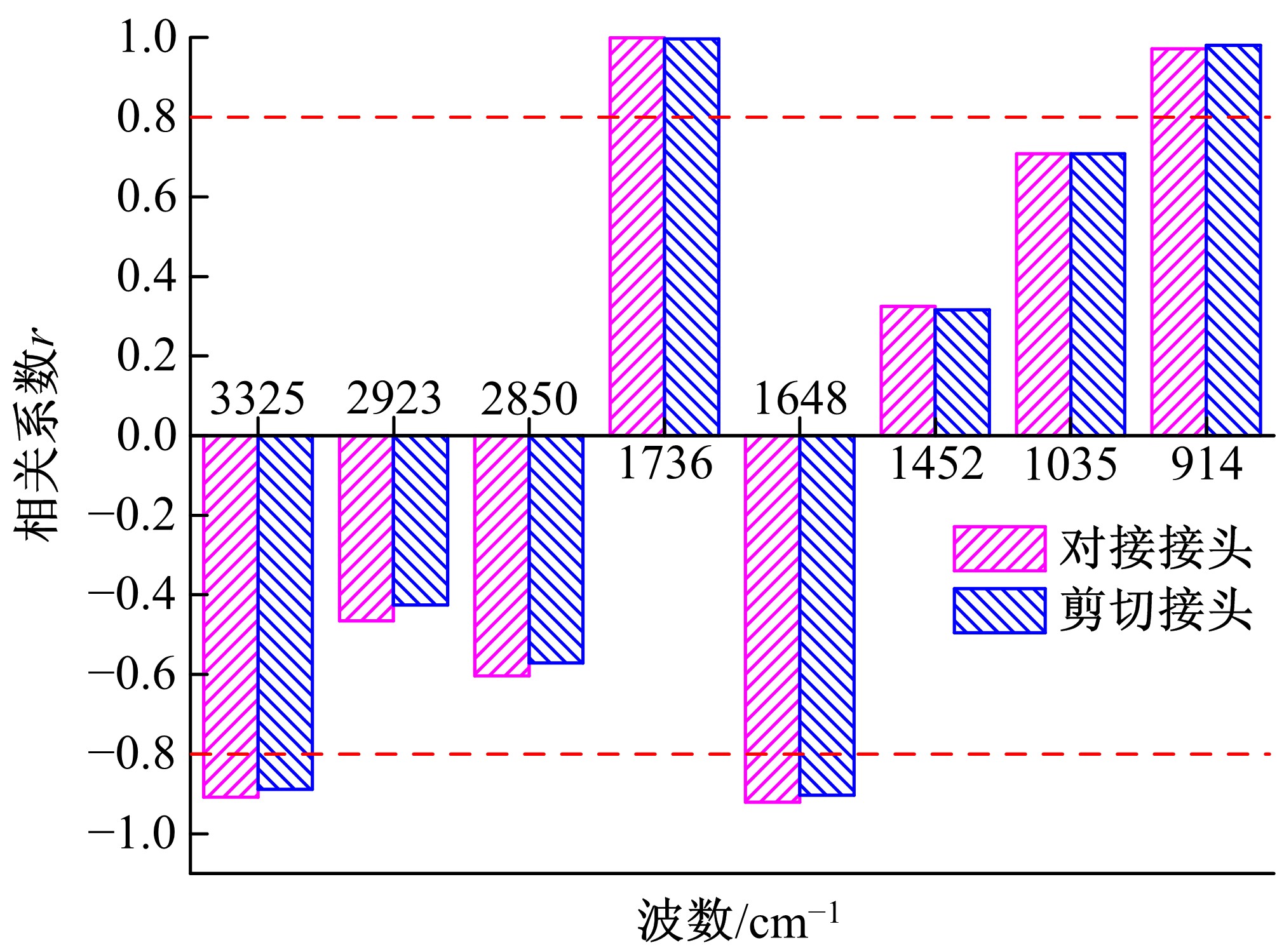
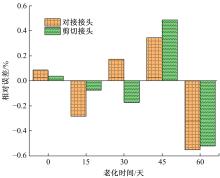
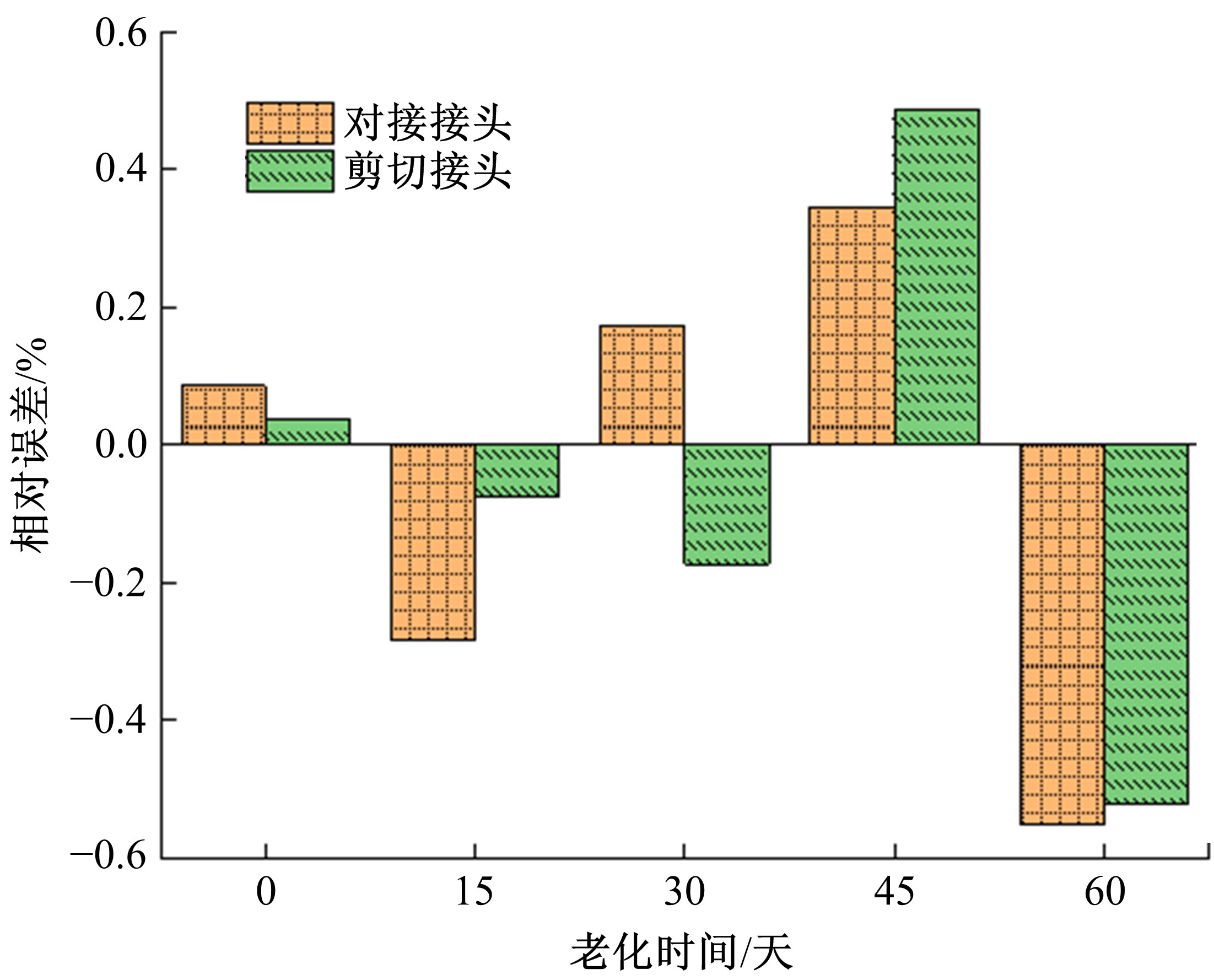
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 139-146.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191063
Residual strength prediction of adhesive CFRP-aluminum alloy adhesively bonded joint based on FTIR analysis
Wen-long MU1,2( ),Jing-xin NA1(
),Jing-xin NA1( ),Wei TAN1,Guang-bin WANG1,Hao SHEN1,Jian-ze LUAN1
),Wei TAN1,Guang-bin WANG1,Hao SHEN1,Jian-ze LUAN1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Mechnical and Electrical Engineering,Henan Agricultural University,Zhengzhou 450002,China
CLC Number:
- U463.82
| 1 | 胡志清, 郑会会, 徐亚男, 等. 表面微沟槽对Al/CFRP胶结性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(1): 229-235. |
| Hu Zhi-qing, Zheng Hui-hui, Xu Ya-na, et al. Effect of Al surface with micro/macro grooves on AI/CFRP adhesive-bonded joints[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(1): 229-235. | |
| 2 | Budhe S, Banea M D, Barros S D, et al. An updated review of adhesively bonded joints in composite materials[J]. International Journal of Adhesion & Adhesives, 2017, 72: 30-42. |
| 3 | Mu W, Qin G, Na J, et al. Effect of alternating load on the residual strength of environmentally aged adhesively bonded CFRP-aluminum alloy joints[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 168: 87-97. |
| 4 | Viana G, Costa M, Banea M D, et al. A review on the temperature and moisture degradation of adhesive joints[J]. Journal of Materials: Design and Applications, 2017, 231(5): 488-501. |
| 5 | Lin Y C, Chen X, Zhang H J, et al. Effects of hygrothermal aging on epoxy-based anisotropic conductive film[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60(24): 2958-2963. |
| 6 | Xiao G Z, Shanahan M E R. Irreversible effects of hygrothermal aging on DGEBA/DDA epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1998, 69(2): 363-369. |
| 7 | 牛一凡, 李璋琪, 朱晓峰. 全湿热场下碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料弯曲性能及寿命预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(1):104-112. |
| Niu Yi-fan, Li Zhang-qi, Zhu Xiao-feng. Flexural properties and life-time estimation of carbon fiber/epoxy composite under hygrothermal conditions[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(1):104-112. | |
| 8 | Liu S, Cheng X, Zhang Q, et al. An investigation of hygrothermal effects on adhesive materials and double lap shear joints of CFRP composite laminates[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 91: 431-440. |
| 9 | Viana G, Costa M, Banea M D, et al. Moisture and temperature degradation of double cantilever beam adhesive joints[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2017, 31(16): 1824-1838. |
| 10 | 张欢, 许文, 邹士文, 等. 环氧胶粘剂及其胶接界面热氧老化机理研究[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(12): 104-108. |
| Zhang Huan, Xu Wen, Zou Shi-wen, et al. Thermal-oxidative aging mechanism of epoxy adhesive and its interface[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(12): 104-108. | |
| 11 | Jana S, Zhong W H. FTIR study of ageing epoxy resin reinforced by reactive graphitic nanofibers[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2007, 106(5): 3555-3563. |
| 12 | Cherdoud‐Chihani A, Mouzali M, Abadie M J M. Study of crosslinking AMS/DGEBA system by FTIR[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1998, 69(6): 1167-1178. |
| 13 | Khan L A, Nesbitt A, Day R J. Hygrothermal degradation of 977-2A carbon/epoxy composite laminates cured in autoclave and Quickstep[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing, 2010, 41(8): 942-953. |
| 14 | 汪冬华. 多元统计分析与SPSS应用[M]. 上海:华东理工大学出版社, 2010. |
| 15 | 郇中丹, 黄海洋. 偏微分方程[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2013. |
| 16 | Liljedahl C D M, Crocombe A D, Wahab M A, et al. The effect of residual strains on the progressive damage modeling of environmentally degraded joints[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2005, 19(7): 525547. |
| [1] | NA Jing-xin,MU Wen-long,FAN Yi-sa,TAN Wei,YANG Jia-zhou. Effect of hygrothermal aging on steel-aluminum adhesive joints for automotive applications [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1653-1660. |
|
||