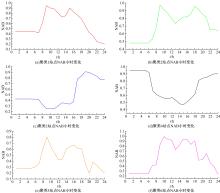
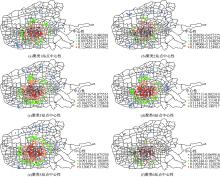
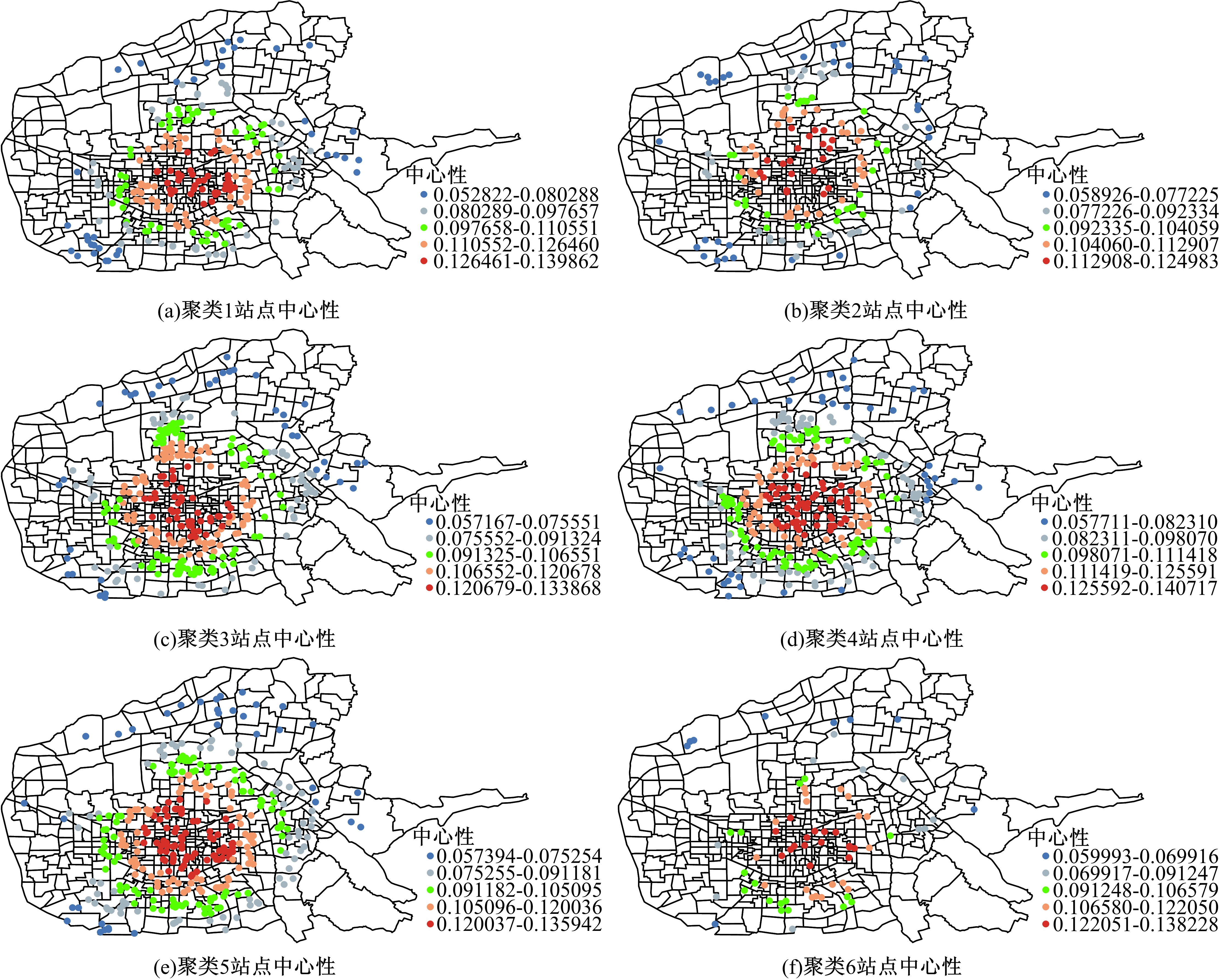
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 531-540.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191153
Forecast of urban public bicycle traffic demand by station classification
Cai-hua ZHU( ),Xiao-li SUN,Yan LI(
),Xiao-li SUN,Yan LI( )
)
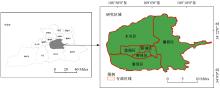
- College of Transportation Engineering,Chang′an University,Xi′an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| 1 | 周素红, 杨利军. 交通与土地利用一体化规划管理[J]. 规划师, 2005, 21(8): 14-19. |
| Zhou Su-hong, Yang Li-jun. Planning and management for integration of traffic and land utilization and case study[J]. Planners, 2005, 21(8): 14-19. | |
| 2 | 孔祥夫, 杨家文. 土地利用视角下的轨道站点客流预测——以深圳市为例[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(12): 2074-2083. |
| Kong Xiang-fu, Yang Jia-wen. A new method for forecasting station-level transit ridership from land-use perspective from land-use perspective: the case of Shenzhen city[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 2074-2083. | |
| 3 | 马新卫, 季彦婕, 金雨川, 等. 基于时空地理加权回归的共享单车需求影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1344-1354. |
| Ma Xin-wei, Ji Yan-jie, Jin Yu-chuan, et al. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in dockless bikeshare usage demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1344-1354. | |
| 4 | 田恬, 谷达华, 牛德利, 等. 城市土地利用与城市交通协调关系评价——以重庆市主城区为例[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 41(7): 96-104. |
| Tian Tian, Gu Da-hua, Niu De-li, et al. Evaluation of the coordination relationship between urban land use and urban transport: a case study of Chongqing's main district[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 41(7): 96-104. | |
| 5 | Bullock C, Brereton F, Bailey S. The economic contribution of public bike-share to the sustainability and efficient functioning of cities[J]. Sustainable cities and society, 2017, 28(9): 76-87. |
| 6 | Wagner T. Regional traffic impacts of logistics-related land use[J]. Transport Policy, 2010, 17(4): 224-229. |
| 7 | 吴韬, 张梦莹. 基于GIS的轨道交通沿线土地发展演变研究[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2019, 32(3): 39-45. |
| Wu Tao, Zhang Meng-ying. Land development and evolution along rail transit based on GIS[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2019, 32(3): 39-45. | |
| 8 | 唐炉亮, 陈西, 杨雪, 等. 基于城市用地的公共自行车骑行量建模[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(1): 150-158. |
| Tang Lu-liang, Chen Xi, Yang Xue, et al. Public bicycle usage modeling based on urban land use[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(1): 150-158. | |
| 9 | Wang F, Chen H, Zhu C, et al. Estimating driving fatigue at a plateau area with frequent and rapid altitude change[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(22): 1-16. |
| 10 | Ermagun A, Lindsey G, Loh T H. Bicycle, pedestrian, and mixed-mode trail traffic: a performance assessment of demand models[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2018, 177(4): 92-102. |
| 11 | 朱从坤, 韩晓玉, 何承韡. 基于城市轨道交通接驳的公共自行车租赁点规模确定方法[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2018, 21(9): 23-25, 31. |
| Zhu Cong-kun, Han Xiao-yu, He Cheng-wei. On the scale of public bicycle rental point based on rail transit connection mode[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2018, 21(9): 23-25, 31. | |
| 12 | Li Y, Wang F, Ke H, et al. A driver's physiology sensor-based driving risk prediction method for lane-changing process using hidden Markov model[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 1-21. |
| 13 | Cardozo O D, García-Palomares J C, Gutiérrez J. Application of geographically weighted regression to the direct forecasting of transit ridership at station-level[J]. Applied Geography, 2012, 34(12): 548-558. |
| 14 | Chan S, Miranda-Moreno L. A station-level ridership model for the metro network in Montreal, Quebec[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2013, 40(3): 254-262. |
| 15 | 朱亚迪, 陈峰, 王子甲, 等. 基于概率图模型的乘客出行链提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 60-65. |
| Zhu Ya-di, Chen Feng, Wang Zi-jia, et al. Passengers′trip chains extraction method based on probabilistic graph model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 60-65. | |
| 16 | Vanderwaart C, Attanucci J P, Salvucci F P. Applications of inferred origins, destinations, and interchanges in bus service planning[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2017, 26(52): 70-77. |
| 17 | 吕铃, 彭雅丽, 曾欣怡, 等. 公共自行车复杂网络可达性指标潜力评价模型[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2018, 40(1): 175-183. |
| Lv Ling, Peng Ya-li, Zeng Xin-yi, et al. An accessibility index potential evaluation model for the complex network of public bicycles[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2018, 40(1): 175-183. | |
| 18 | Seriani S, Fernandez R. Planning guidelines for metro-bus interchanges by means of a pedestrian microsimulation model[J]. Transportation Planning and Technology, 2015, 38(5): 569-583. |
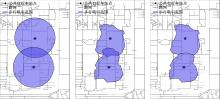
| 19 | 蒋源, 陈小鸿, 徐晓敏, 等. 公共自行车接驳轨道交通服务范围研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(): 94-102. |
| Jiang Yuan, Chen Xiao-hong, Xu Xiao-min, et al. Exploring The catchment area of public bike connecting to subway[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(Sup.1): 94-102. | |
| 20 | Chen Q, Sun T. A model for the layout of bike stations in public bike-sharing systems[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2015, 49(8): 884-900. |
| 21 | Zhang Y, Thomas T, Brussel M, et al. Exploring the impact of built environment factors on the use of public bikes at bike stations: case study in Zhongshan, China[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2017, 58(16): 59-70. |
| 22 | 贾洪飞, 郭明雪, 罗清玉, 等. GPS数据下的城市路网关键路段识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Guo Ming-xue, Luo Qing-yu, et al. Identifying critical links of urban road networks based on GPS data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. | |
| 23 | Gutiérrez J, García-Palomares J C. Distance-measure impacts on the calculation of transport service areas using GIS[J]. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 2008, 35(3): 480-503. |
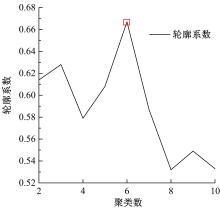
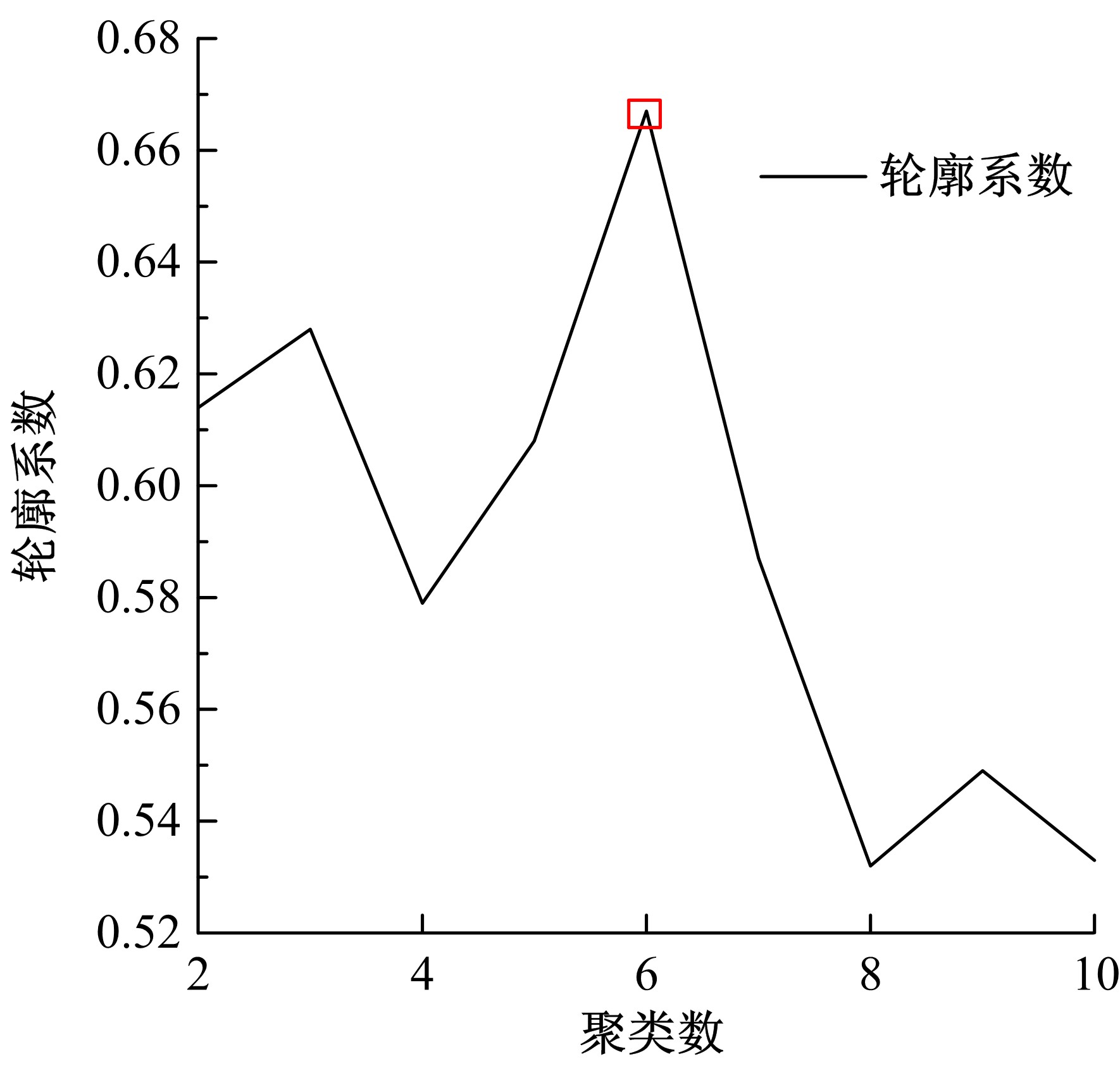
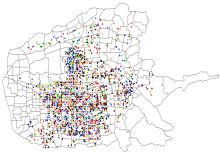
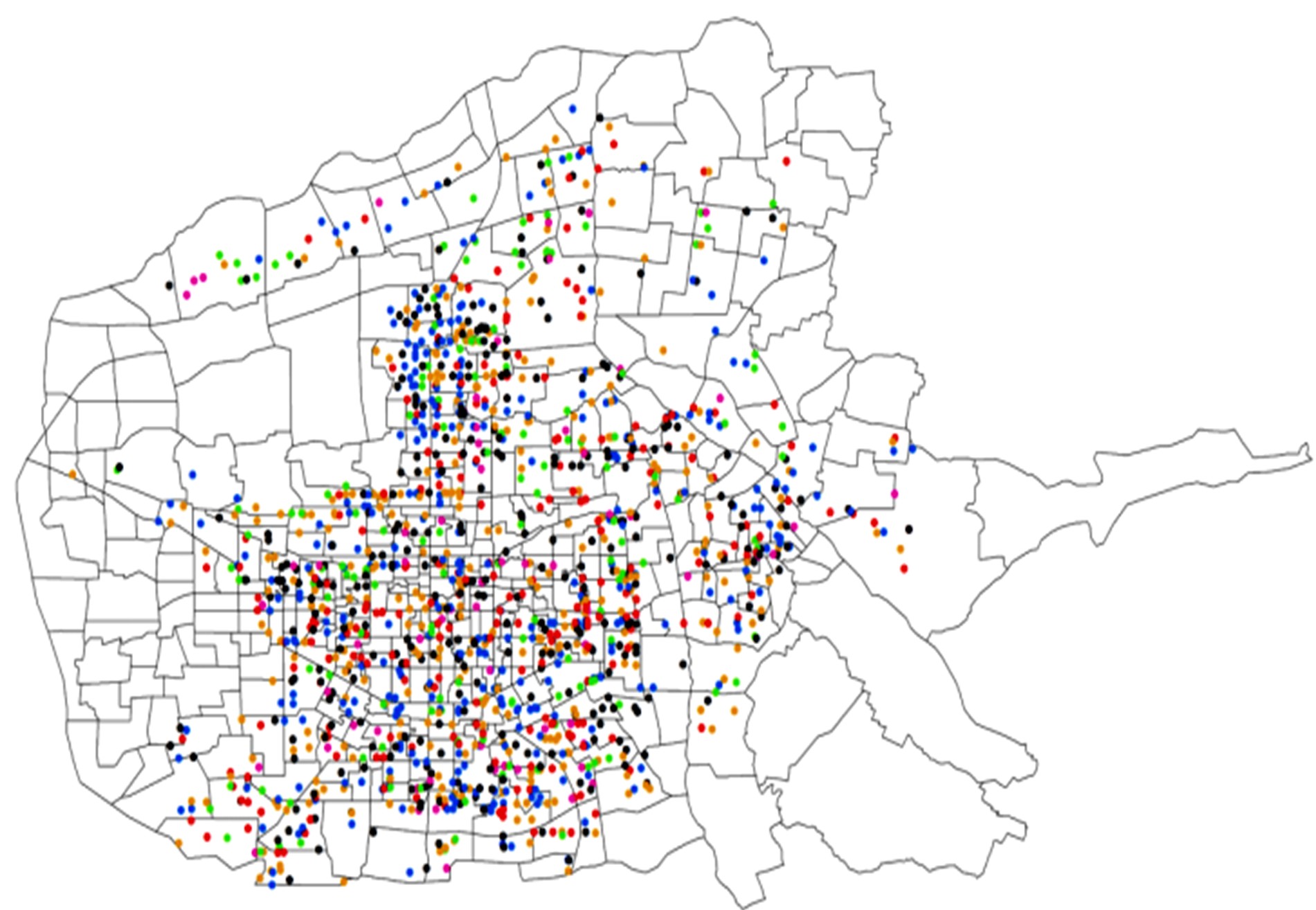
| 24 | 邵滢宇, 丁柏群. 基于聚类分析的地铁站点分类——以哈尔滨地铁1号线为例[J]. 森林工程, 2015, 31(3): 106-111, 116. |
| Shao Ying-yu, Ding Bai-qun. Metro stations classification based on clustering analysis——a case study of Harbin metro line 1[J]. Forest Engineering, 2015, 31(3): 106-111, 116. |
| [1] | Qing-yu LUO,Wan-li TIAN,Hong-fei JIA. Location and capacity model of electric vehicle charging station considering commuting demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| [2] | CHANG Shan,SONG Rui,HE Shi-wei,LI Hao-dong,YIN Wei-chuan. Recycling model of faulty bike sharing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1677-1684. |
| [3] | CAO Qian, LI Jun, LIU Yu, QU Da-wei. Construction of driving cycle based on Markov chain for passenger car in Changchun City [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| [4] | SUN Bao-feng, GAO Kun, SHEN Xiu-xiu, LIANG Ting. Location model of gas station for network expansion based on capacity balance and variable coverage radius [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 704-711. |
| [5] | SUN Lu, XU Jian, CUI Xiang-min. Panel data models for analysis and prediction of crash count [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1771-1778. |
| [6] | WANG Zhe, YANG Bai-ting, LIU Xin, LIU Qun, SONG Xian-min. Discriminant analysis of driving decisions based on fuzzy clustering [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. |
| [7] | LIU Shu-fen, MENG Dong-xue, WANG Xiao-yan. DBSCAN algorithm based on grid cell [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1135-1139. |
| [8] | LONG Xue-qin, GUAN Hong-zhi, QIN Huan-mei. Self-organization of hierarchies of urban roads based on efficiency and safety [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1222-1229. |
| [9] | WANG Jian-lin, YANG Yin-sheng, WANG Xue-ling. Evaluation of land use in Yellow river delta based on extension data mining [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 479-483. |
| [10] | LI Qi, JIANG Gui-yan, YANG Ju-fen. Automatic incident detection algorithms fusion method based on factor analysis and cluster analysis [J]. , 2012, 42(05): 1191-1197. |
| [11] | XU Liang,CHENG Guo-zhu. Setting minimum vehicle speed limit on freeway based on speed scattering and economic speed [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
| [12] |
Liu Bing-en,Juan Zhi-cai,Jia Hong-fei .
System dynamics model describing the relation between city landuse and traffic system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(增刊): 67-0070. |
|
||