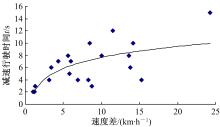
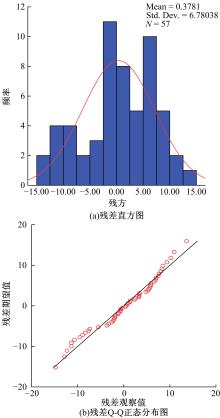
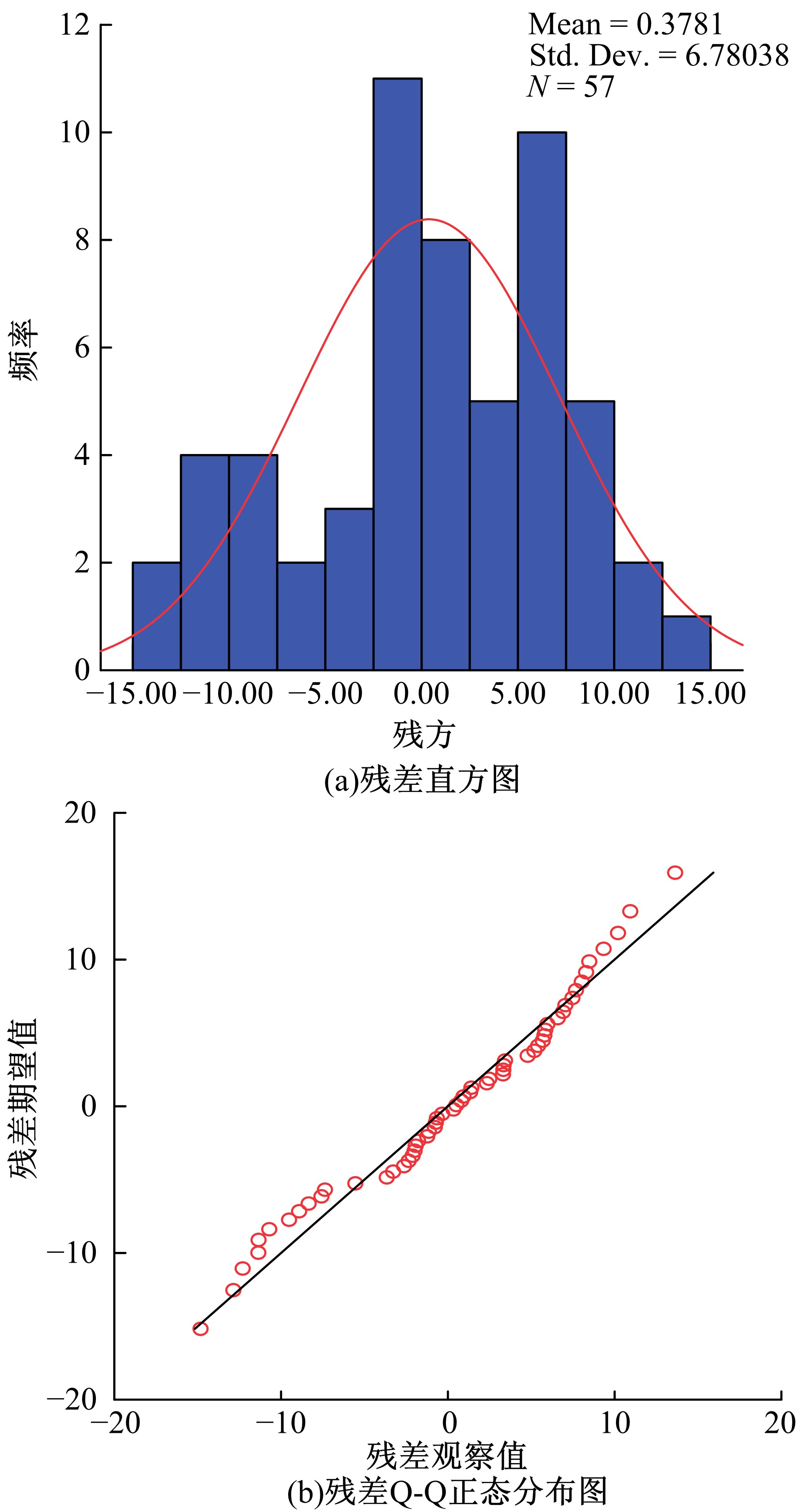
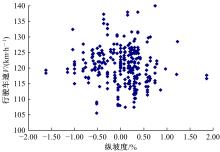
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 575-582.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200032
Modeling and analysis of road speed micro model in long straight line section of desert
Fang WANG( ),Jia HU,Sheng JING,Wei CHENG,Xiao-ying HE,Xiao-guang LI
),Jia HU,Sheng JING,Wei CHENG,Xiao-ying HE,Xiao-guang LI
- School of Civil Engineering and Hydraulic Engineering,Ningxia University,Yinchuan 750021,China
CLC Number:
- U41
| 1 | 裴玉龙, 马骥. 道路交通事故道路条件成因分析及预防对策研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2003(4): 77-82. |
| Pei Yu-long,Ma Ji. Research on countermeasures for road condition causes of traffic accidents[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2003(4): 77-82. | |
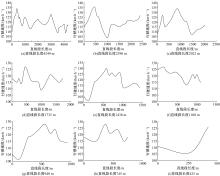
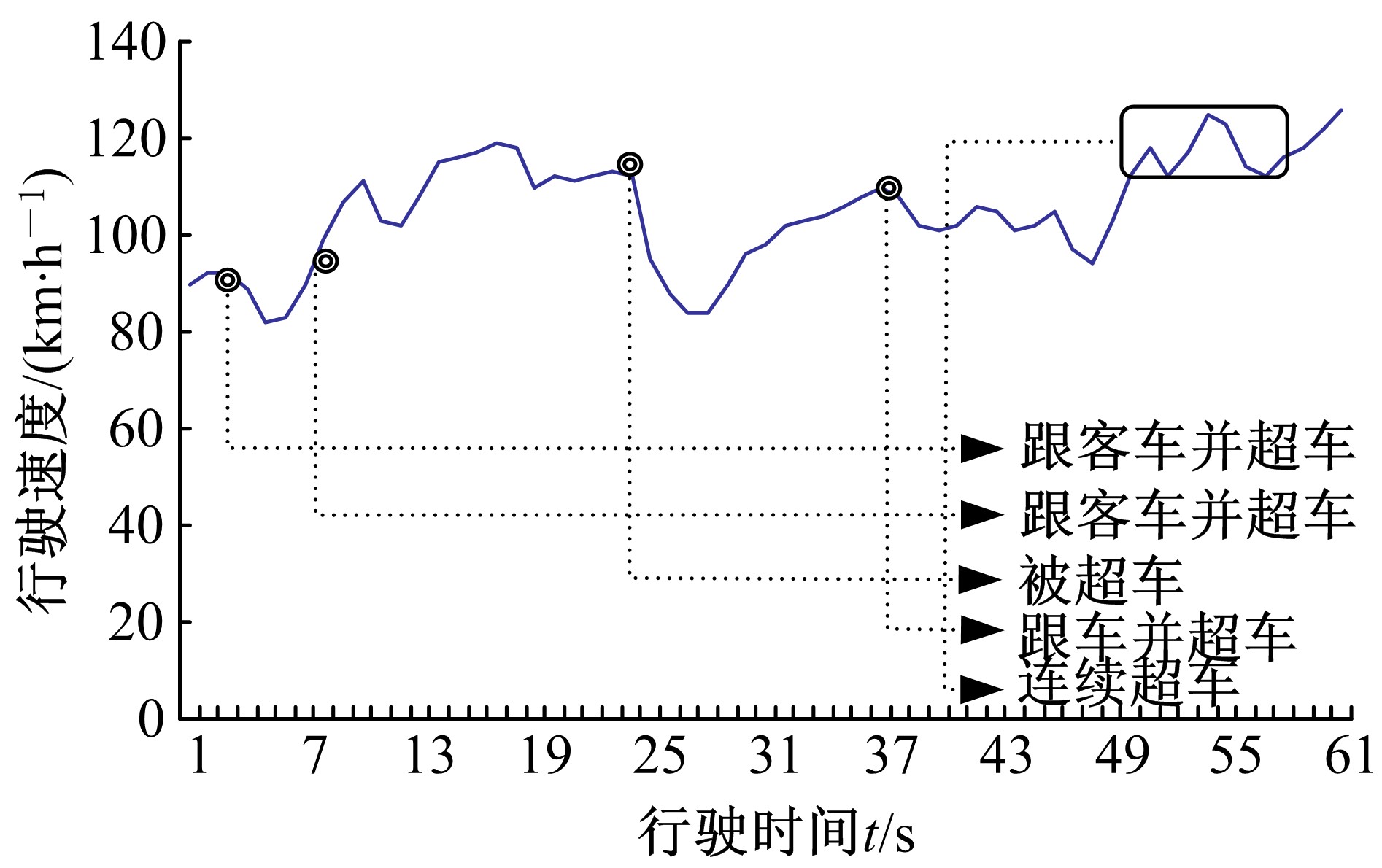
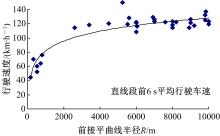
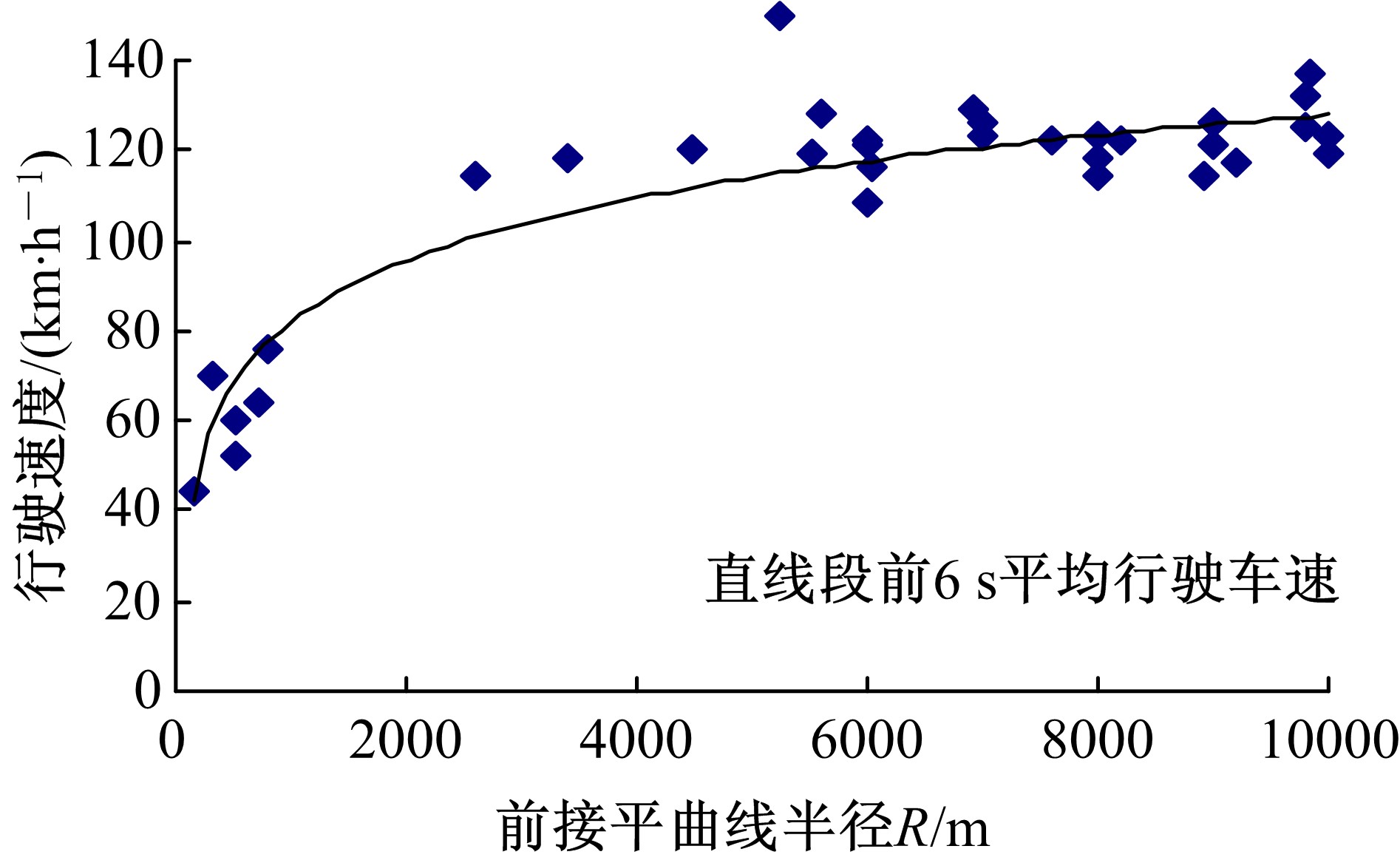
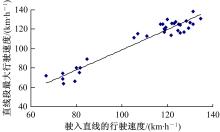
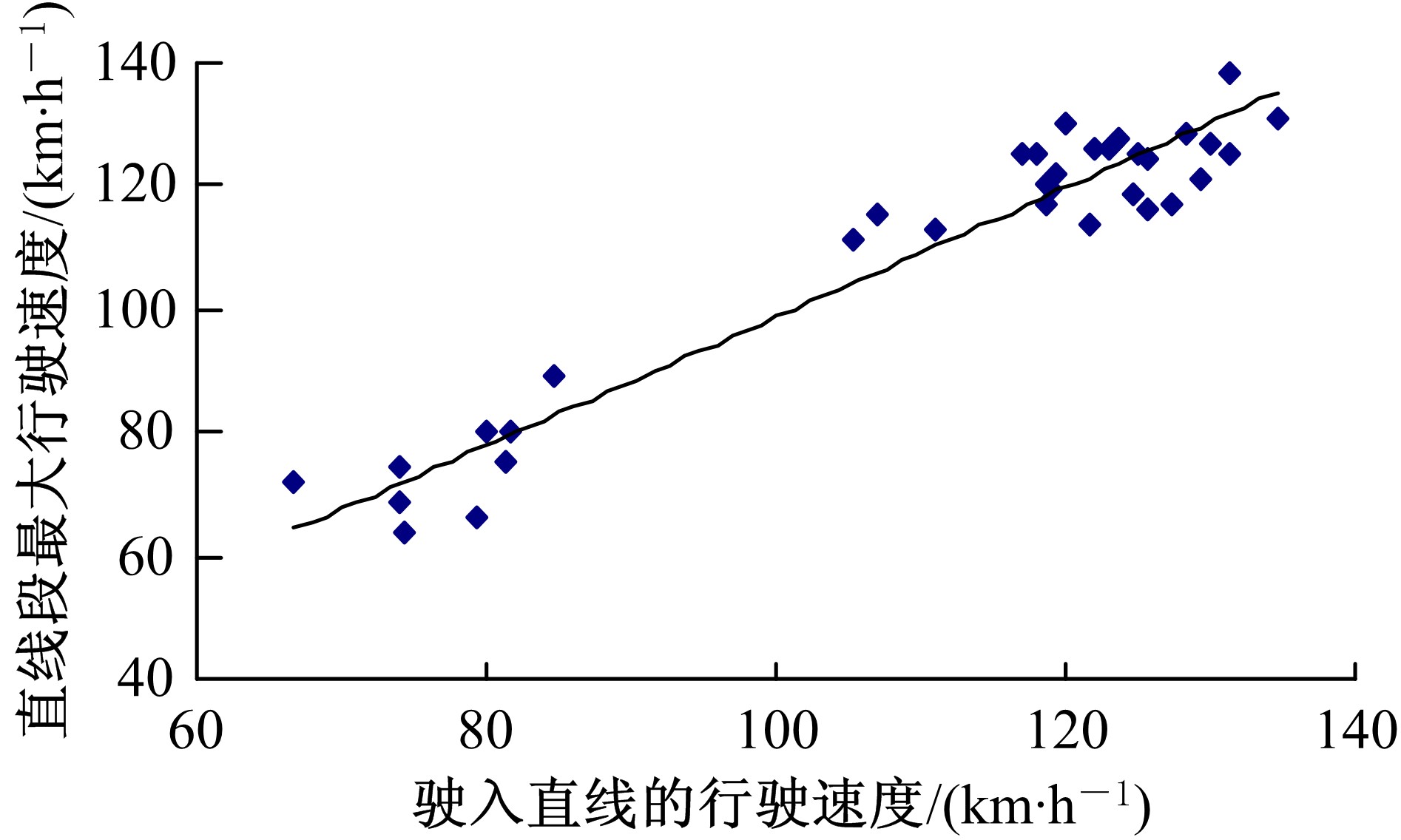
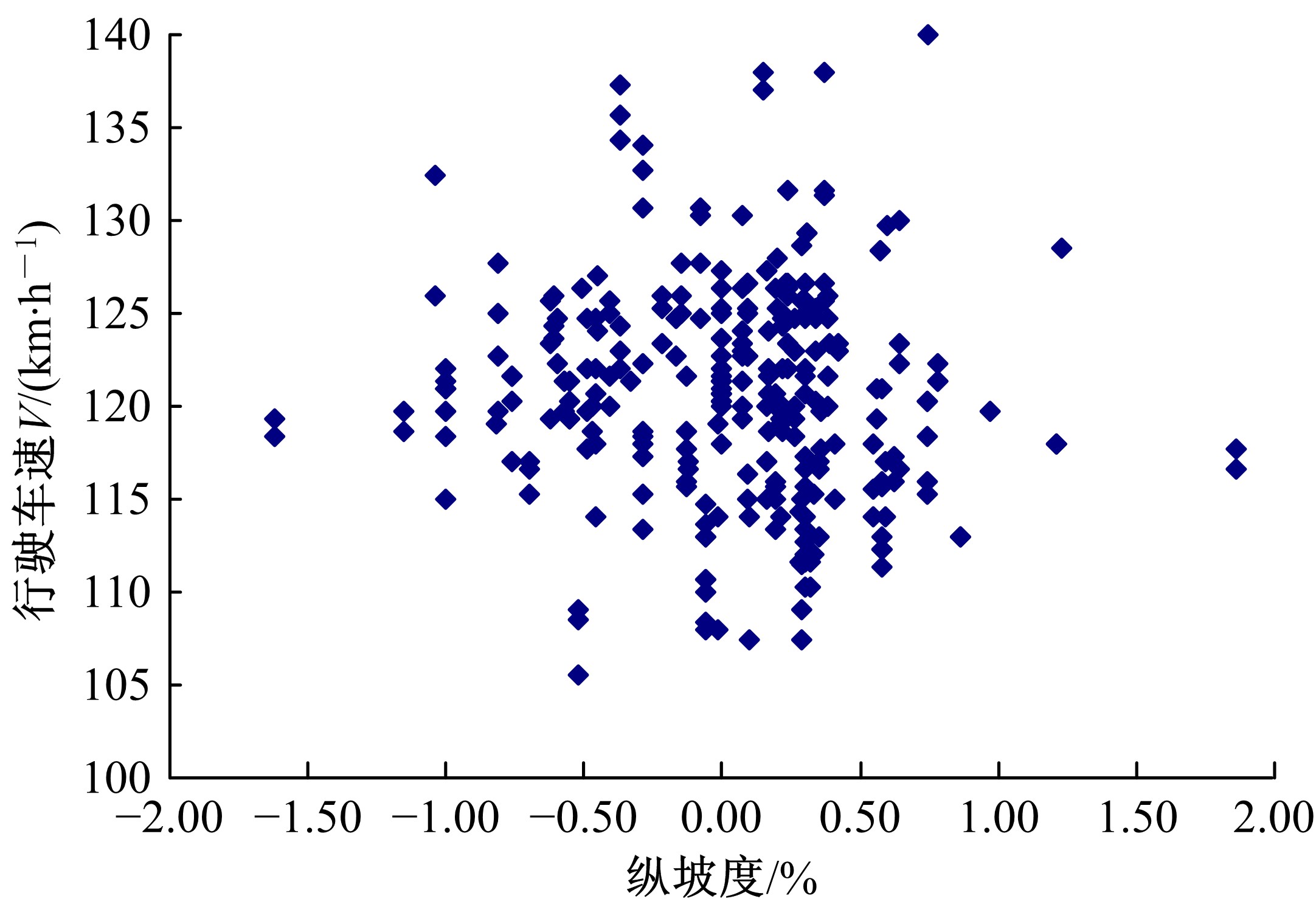
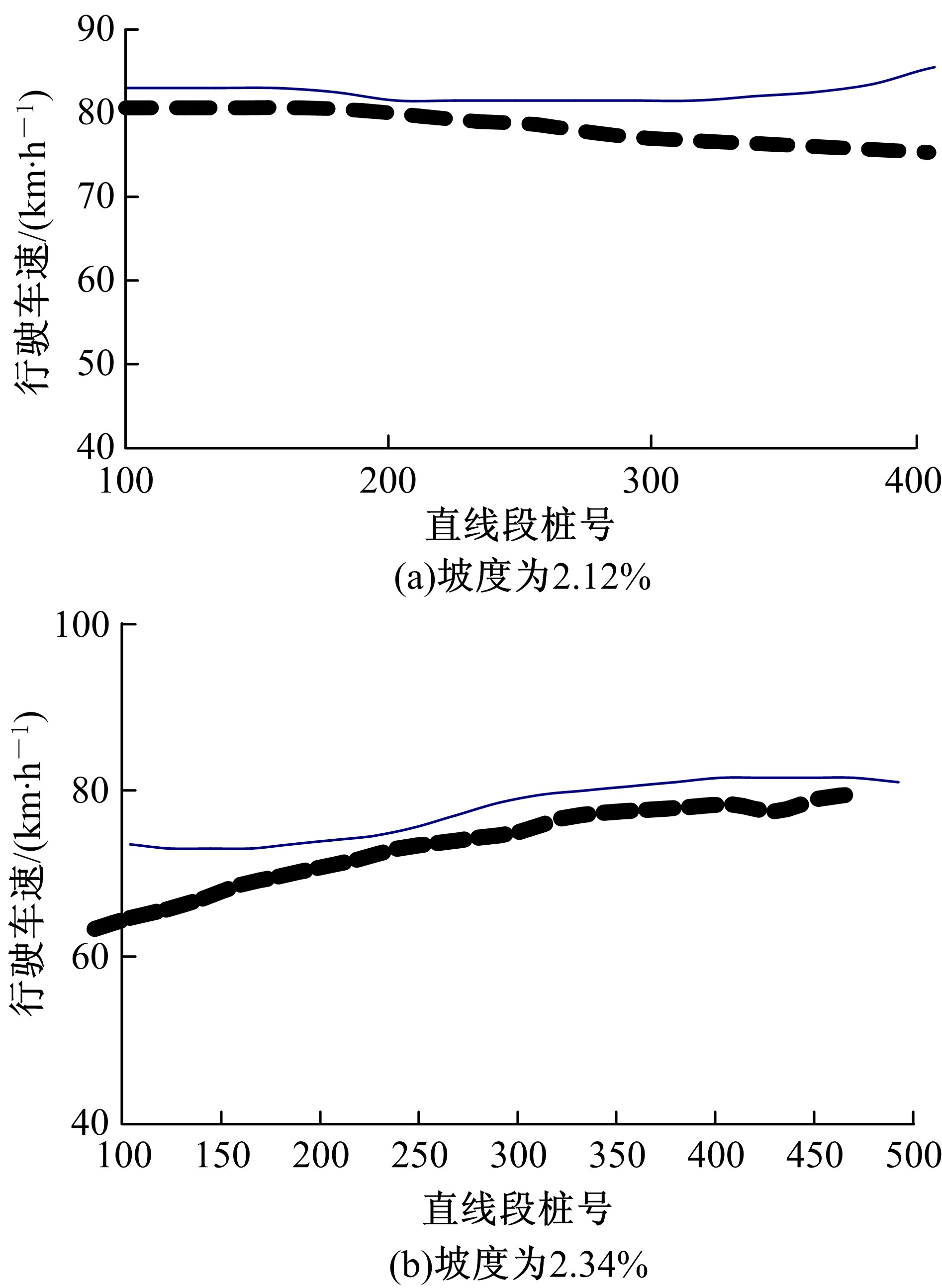
| 2 | 王芳, 李晓光, 郭慧, 等. 基于驾驶员视觉兴趣区的沙漠草原公路曲线间直线段线形指标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 114-120. |
| Wang Fang,Li Xiao-guang,Guo Hui,et al.Optimization of straight segment index between highway curves of desert grassland based on driver's visual interest region[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 114-120. | |
| 4 | 裴玉龙, 程国柱. 高速公路车速离散性与交通事故的关系及车速管理研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2004(1): 74-79. |
| Pei Yu-long, Cheng Guo-zhu. Research on the relationship between speed dispersion and traffic accidents and speed management of expressway[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2004(1): 74-79. | |
| 5 | 阎莹. 高速公路运行车速预测模型及其应用研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学交通运输工程学院, 2009. |
| Yan Ying. Research on the prediction model of Expressway speed and its application[D]. Shanghai: School of Transportation Engineering, Tongji University, 2009. | |
| 6 | Fu X S. Prediction model of theoretical operating speed based on combination alignment of cross and vertical section[J]. Journal of Chang Pan University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 30(3): 24-27. |
| 7 | . 公路项目安全评价规范[S].. |
| 8 | Misaghi P, Hassan Y. Modeling operating speed and speed differential on two-lane rural roads[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2005, 131(6): 408-417. |
| 10 | 范振宇, 张剑飞. 公路运行车速测算模型的研究和标定[J]. 中国公路学报, 2002(1): 107-109. |
| Fan Zhen-yu, Zhang Jian-fei. Research and calibration of highway running speed measurement model[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2002(1): 107-109. | |
| 11 | Wang F, Hu J. Modeling and analysis of drivers' visually interesting area[J]. Advance in Transportation Studies: An Iinternational Journal, 2018(3): 43-50. |
| 12 | 白辂韬. 基于线形条件的高速公路运行速度预测及控制研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学建筑工程学院, 2013. |
| Bai Jian-tao. Study on prediction and control of expressway running speed based on linear conditions [D]. Tianjin: School of Civil Engineering, Tianjin University, 2013. | |
| 13 | 高振海, 李扬, 张慧, 等. 不同车速下驾驶员变换车道前视行为特征规律[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(5): 1385-1390. |
| Gao Zhen-hai, Li Yang, Zhang Hui, et al. Driver's forward-looking behavior analysis during lane change under different speed[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(5): 1385-1390. |
| [1] | NA Jing-xin, BAI Shuang, LIU Hai-peng, YAN Ya-kun. Effects of drawbead corner radius and metal flow direction on drawbead restraining force [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1402-1407. |
| [2] | XU Liang,CHENG Guo-zhu. Setting minimum vehicle speed limit on freeway based on speed scattering and economic speed [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
| [3] | GUI Hai-Lin, WANG Jin-Song, WANG Yun-Peng, E Wen-Juan, GAO Lei. Vehicle fuel consumption model based on urban road operations [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(05): 1146-1150. |
| [4] | LI Xia,SHAO Chun-fu,CAO Peng . Economy level and freight model utilizing quick Kmeans cluster method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(05): 1040-1043. |
|
||