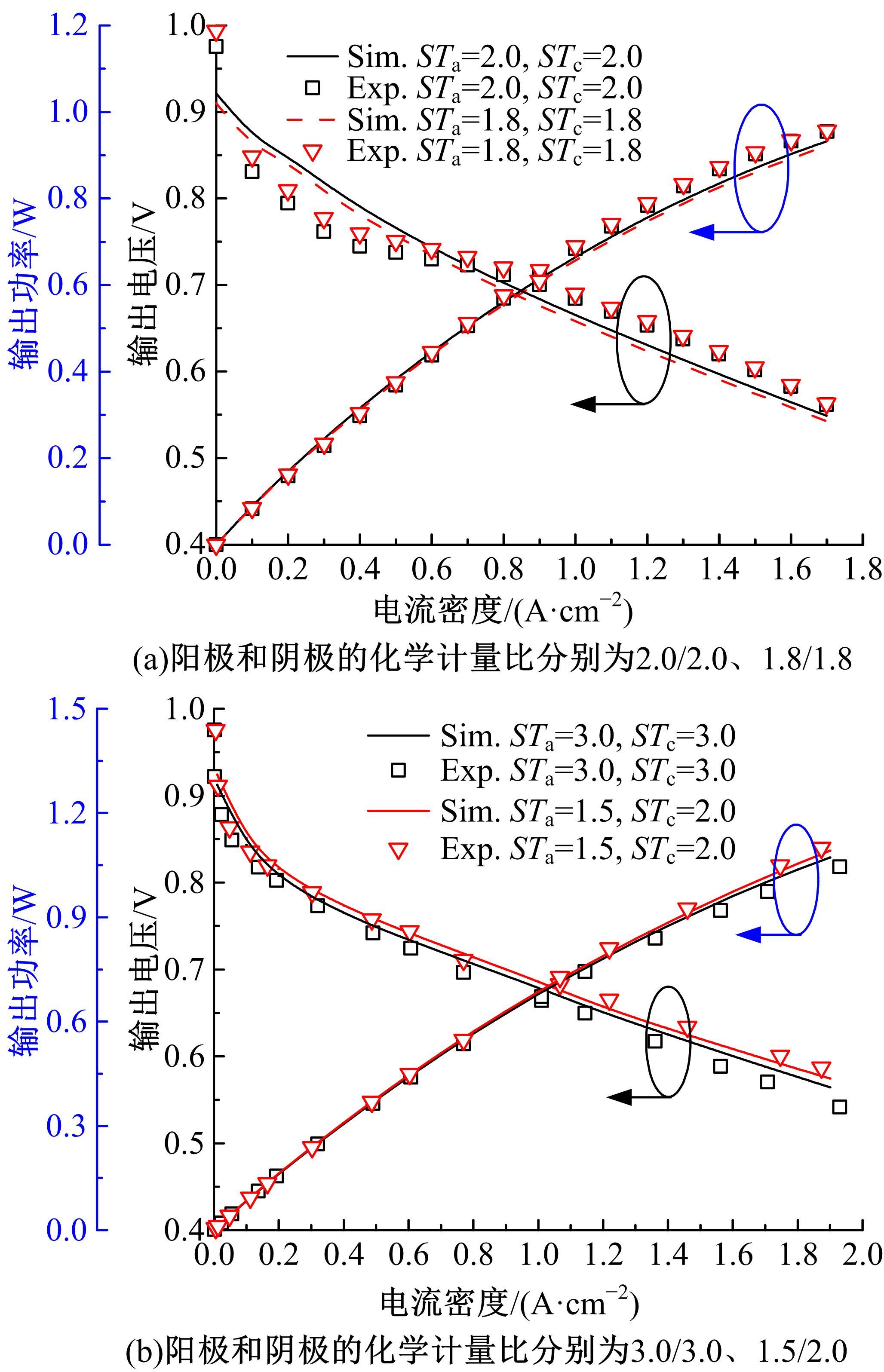
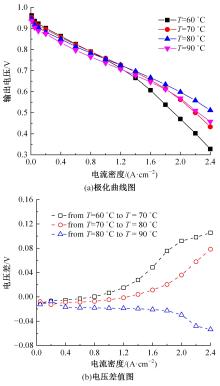
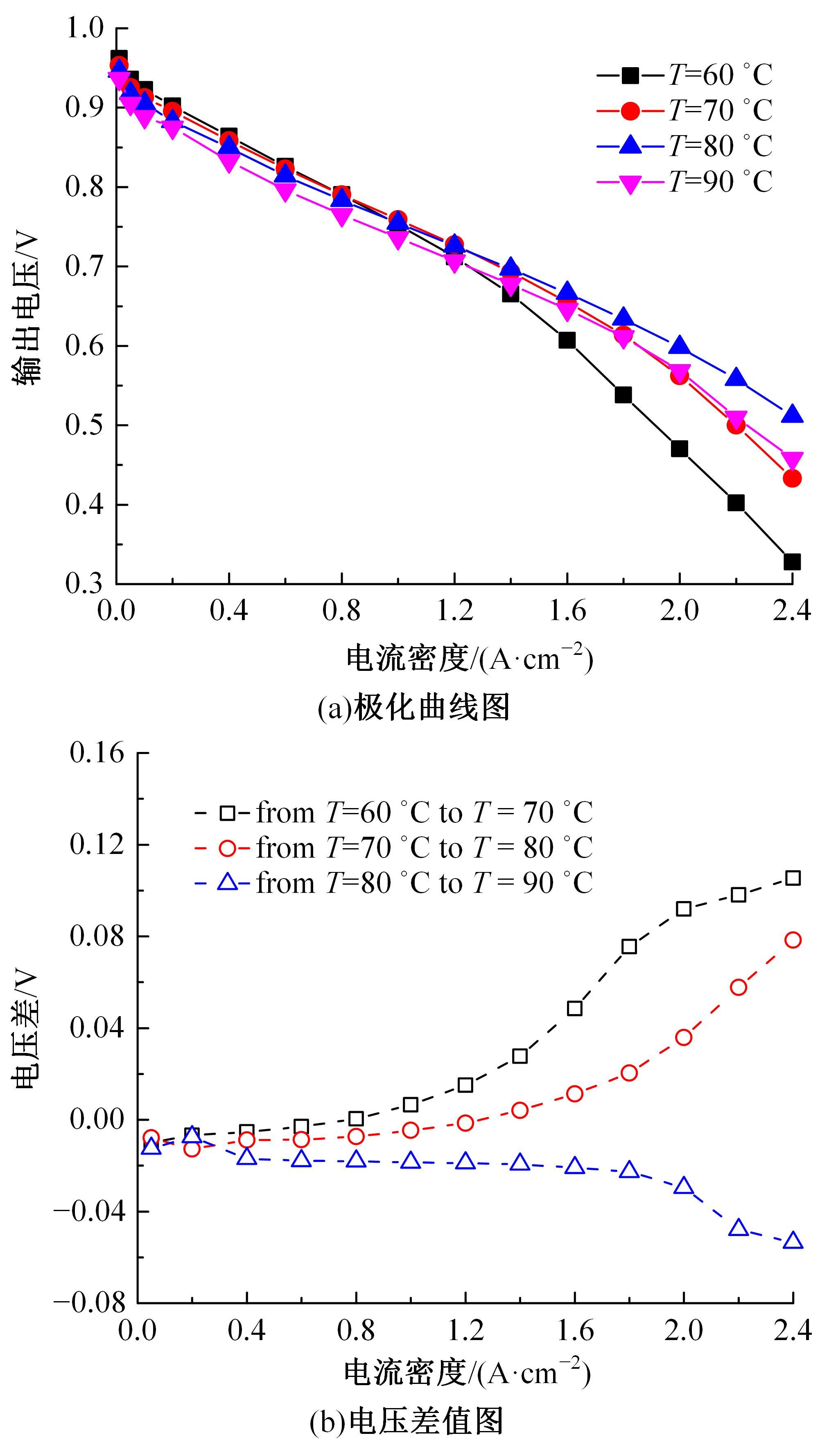
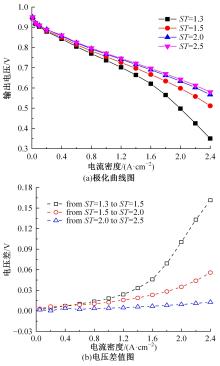
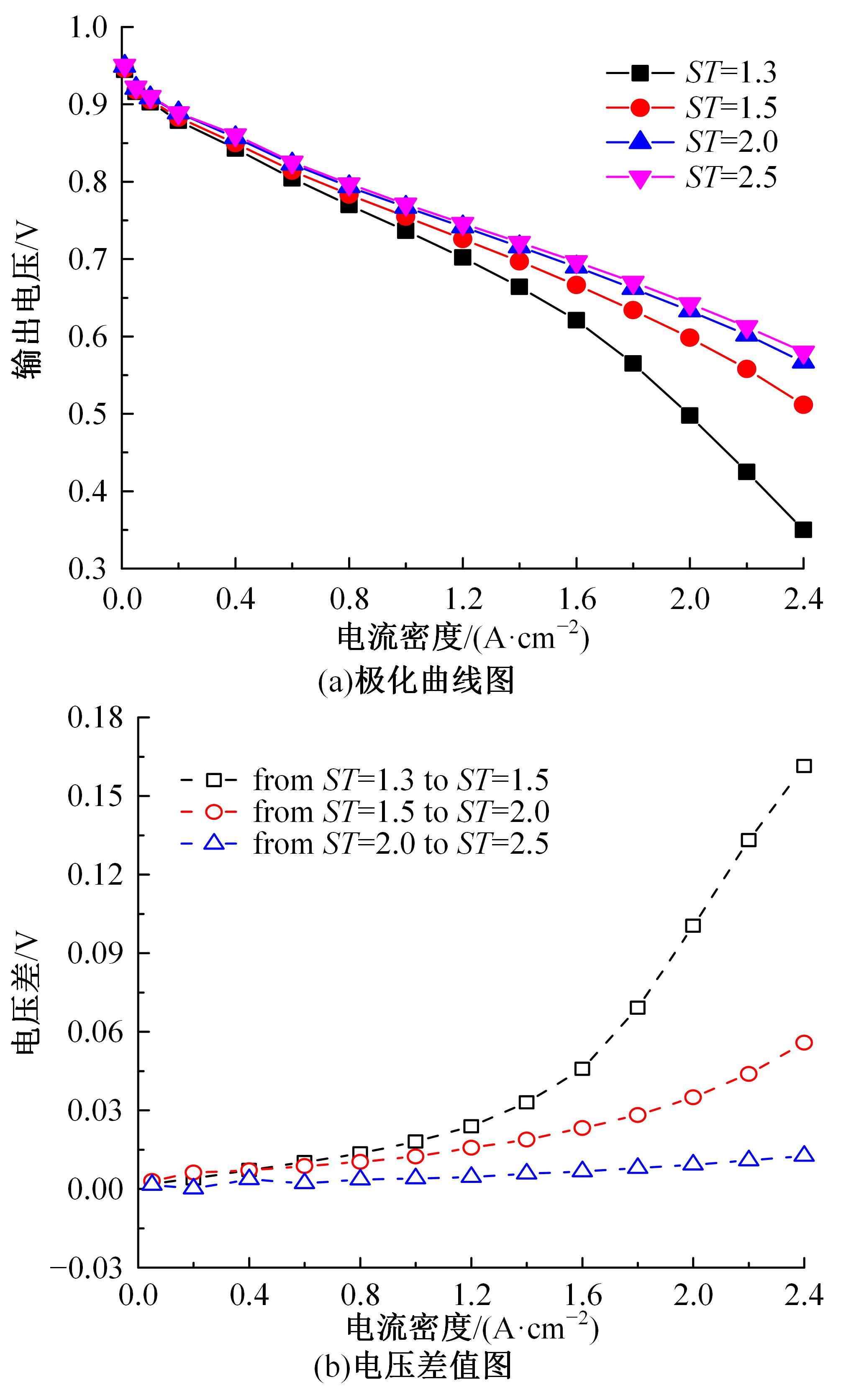
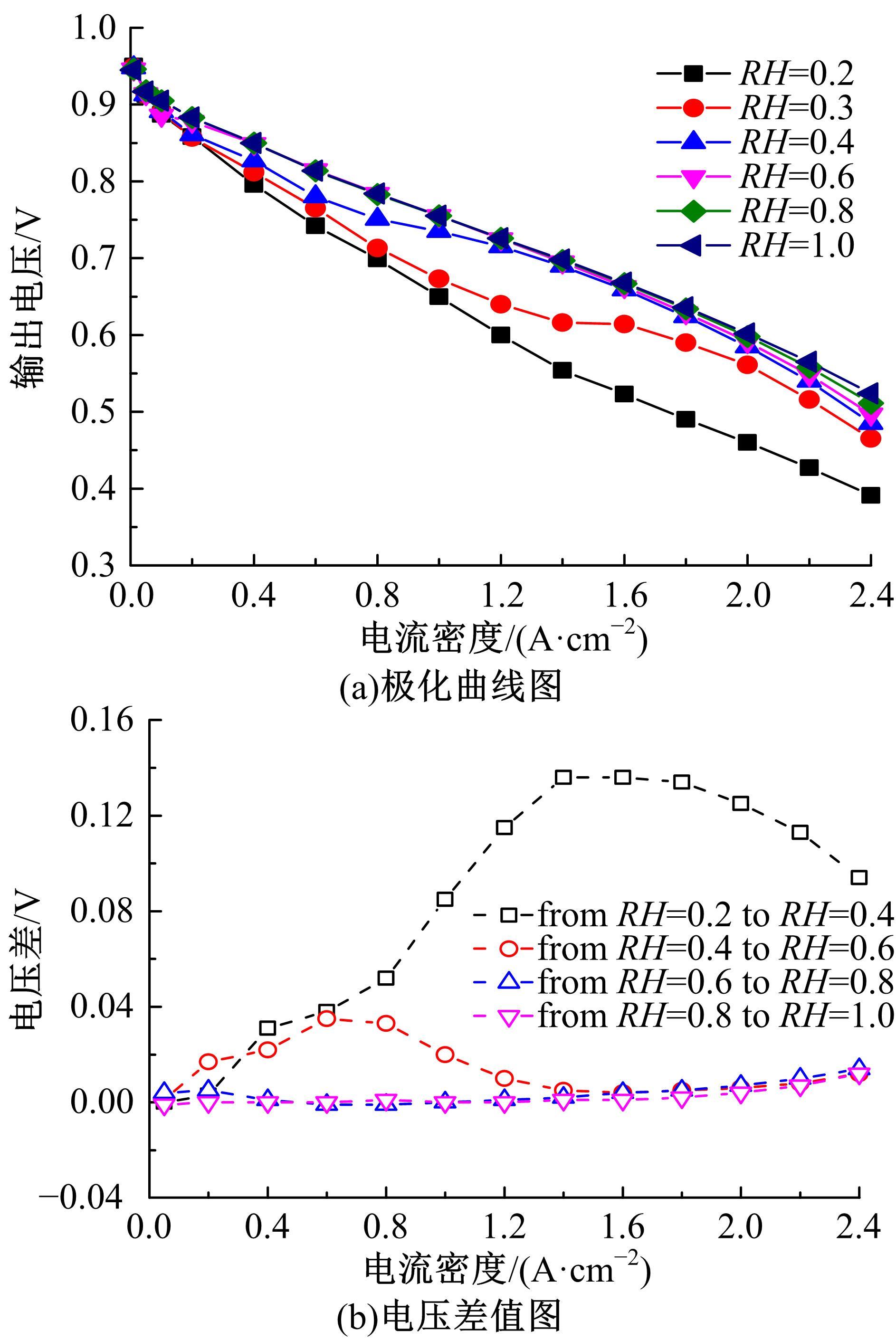
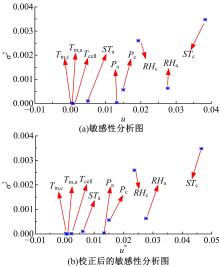
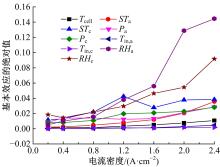
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 1971-1981.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220355
Sensitivity analysis of operating parameters for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Zi-rong YANG1,2( ),Yan LI1,3,Xue-feng JI1,2,Fang LIU3,Dong HAO1,2(
),Yan LI1,3,Xue-feng JI1,2,Fang LIU3,Dong HAO1,2( )
)
- 1.CATARC New Energy Vehicle Test Center (Tianjin) Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300399,China
2.China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300399
3.School of Mechanical Engineering,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
CLC Number:
- TM911.42
| 1 | 高帷韬, 雷一杰, 张勋, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池研究进展[J].化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. |
| Gao Wei-tao, Lei Yi-jie, Zhang Xun, et al. An overview of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. | |
| 2 | 侯中军, 江洪春, 王仁芳, 等. 轿车用燃料电池发动机示范应用稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(): 131-136. |
| Hou Zhong-jun, Jiang Hong-chun, Wang Ren-fang, et al. Performance stability of fuel cell engine applied in the fuel cell car demonstration[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(Sup.2): 131-136. | |
| 3 |
孙闫,夏长高,尹必峰,等. 燃料电池电动汽车的能量管理[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版. DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 |
|
Sun Yan, Xia Chang-gao, Yin Bi-feng, et al. Energy management strategyof fuel cell electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition).DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210773 |
|
| 4 | Chen H C, Liu B, Zhang T, et al. Influencing sensitivities of critical operating parameters on PEMFC output performance and gas distribution quality under different electrical load conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 255: No. 113849. |
| 5 | Miansari M, Sedighi K, Amidpour M, et al. Experimental and thermodynamic approach on proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 190(2): 356-361. |
| 6 | Barakat E G, Abdel-Rahman A K, Ahmed M A, et al. An experimental study of operational parameters on the performance of PEMFCs[C]∥Asme International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition. British Columbia, Canada, 2010, 927-933. |
| 7 | Zhang Q, Lin R, Cui X, et al. Experimental study of variable operating parameters effects on overall PEMFC performance and spatial performance distribution[J]. Energy, 2016, 115(1): 550-560. |
| 8 | Liu Y F, Fan L, Pei P C, et al. Asymptotic analysis for the inlet relative humidity effects on the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 573-584. |
| 9 | Baschuk J, Li X G. Modelling of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with variable degrees of water flooding[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1/2): 181-196. |
| 10 | Mann R F, Amphlett J C, Hooper M, et al. Development and application of a generalised steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1/2): 173-180. |
| 11 | Bernardi D M. Water-balance calculations for solid-polymerelectrolyte fuel cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1990, 137(11): 3344-3350. |
| 12 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Jia Z W, et al. A comprehensive proton exchange membrane fuel cell system model integrating various auxiliary subsystems[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256: No. 113959. |
| 13 | Bao C, Bessler W G. Two-dimensional modeling of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell with long flow channel. Part I. Model development[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 922-934. |
| 14 | Jiao K, Li X G. Effect of surface dynamic wettability in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9095-9103. |
| 15 | Liao X, Liu K, Le J, et al. Extended affine arithmetic-based global sensitivity analysis for power flow with uncertainties[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 115: No. 105440. |
| 16 | Min C H, He Y L, Liu X L, et al. Parameter sensitivity examination and discussion of PEM fuel cell simulation model validation: part II: results of sensitivity analysis and validation of the model[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160(1): 374-385. |
| 17 | Laoun B, Naceur M W, Khellaf A, et al. Global sensitivity analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell model[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(22): 9521-9528. |
| 18 | Jiang Y, Yang Z R, Jiao K,et al. Sensitivity analysis of uncertain parameters based on an improved proton exchange membrane fuel cell analytical model[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2018, 164: 639-654. |
| 19 | 焦魁 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池水热管理[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2020. |
| 20 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Huo S, et al. Effect of membrane electrode assembly design on the cold start process of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(40): 25372-25387. |
| 21 | Huo S, Jiao K, Park J W. On the water transport behavior and phase transition mechanisms in cold start operation of PEM fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 233-234: 776-788. |
| 22 | Wu K C, Xie X, Wang B W, et al. Two-dimensional simulation of cold start processes for proton exchange membrane fuel cell with different hydrogen flow arrangements[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(35): 17795-17812. |
| 23 | Yao L, Peng J, Zhang J B, et al. Numerical investigation of cold-start behavior of polymer electrolyte fuel cells in the presence of super-cooled water[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(32): 15505-15520. |
| 24 | Gwak G H, Ko J H, Ju H. Numerical investigation of cold-start behavior of polymer-electrolyte fuel-cells from subzero to normal operating temperatures- effects of cell boundary and operating conditions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(36): 21927-21937. |
| 25 | Yang Z R, Du Q, Huo S, et al. Effect of membrane electrode assembly design on the cold start process of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(40): 25372-25387. |
| 26 | Wang B, Wu K, Yang Z, et al. A quasi-2D transient model of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with anode recirculation[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2018, 171: 1463-1475. |
| 27 | Abdollahzadeh M, Ribeirinha P, Boaventura M, et al. Three-dimensional modeling of PEMFC with contaminated anode fuel[J]. Energy, 2018, 152: 939-959. |
| 28 | Morris M D. Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments[J]. Technometrics, 1991, 33(2): 161-174. |
| 29 | Xia Z F, Chen H C, Zhang T, et al. Effect of channel-rib width ratio and relative humidity on performance of a single serpentine PEMFC based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(26):13076-13086. |
| 30 | Najmi A, Anyanwu I S, Xie X, et al. Experimental investigation and optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using different flow fields[J]. Energy, 2021, 217: No. 119313. |
| 31 | Yang T, Sheu B, Ghalambaz M, et al. Effects of operating parameters and load mode on dynamic cell performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(2): 2474-2487. |
| 32 | Jiao K, Li X G. Water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Progress in Energy & Combustion Science, 2011, 37(3): 221-291. |
| 33 | Yin L Z, Qi L, Chen W R, et al. Experimental analysis of optimal performance for a 5 kW PEMFC system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5499-5506. |
| [1] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [2] | WANG Zeng-hui, HUANG Dong-yan, LI Zhuo-shi, JIA Hong-lei, WAN Bao-cheng. Universal the blade the broken stubble power consumption influence of the working parameters of the rotary tiller broken stubble [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 122-125. |
|
||