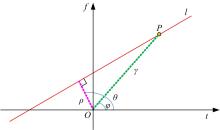
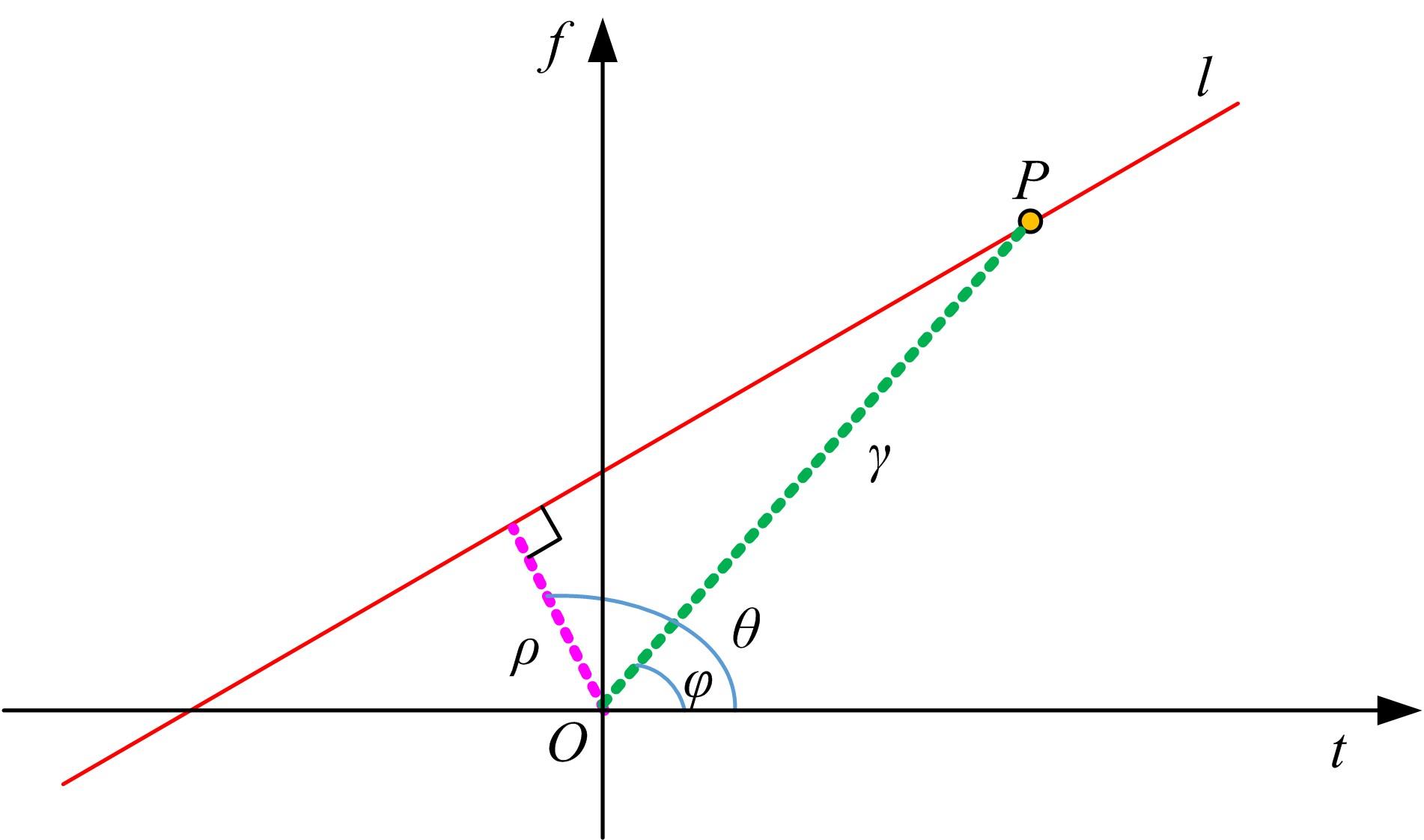
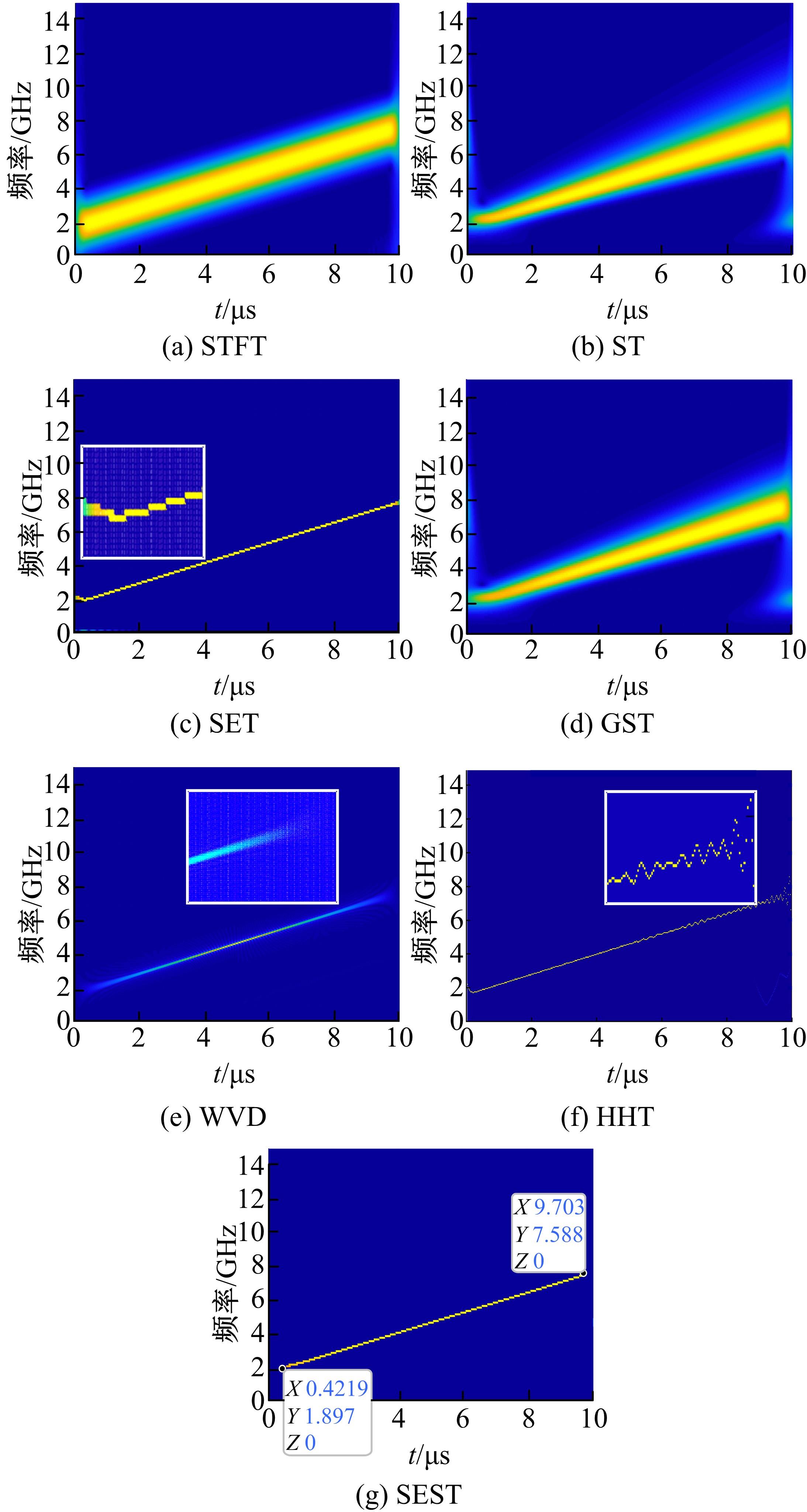
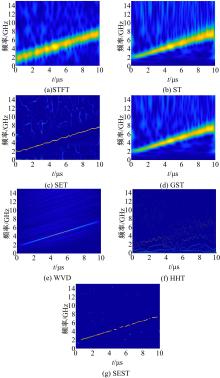
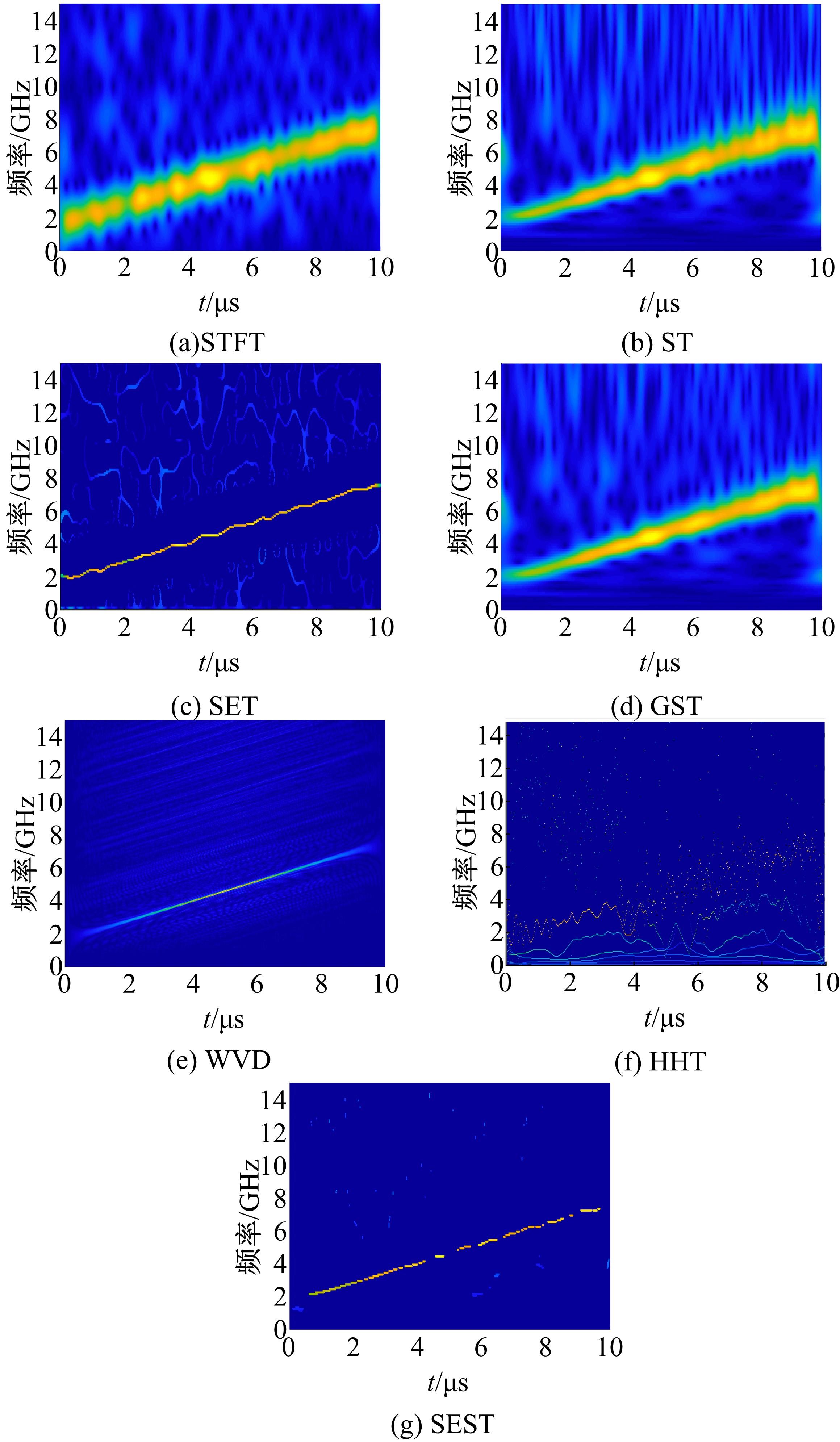
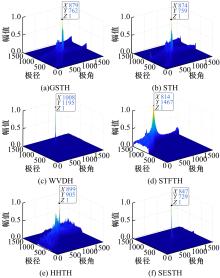
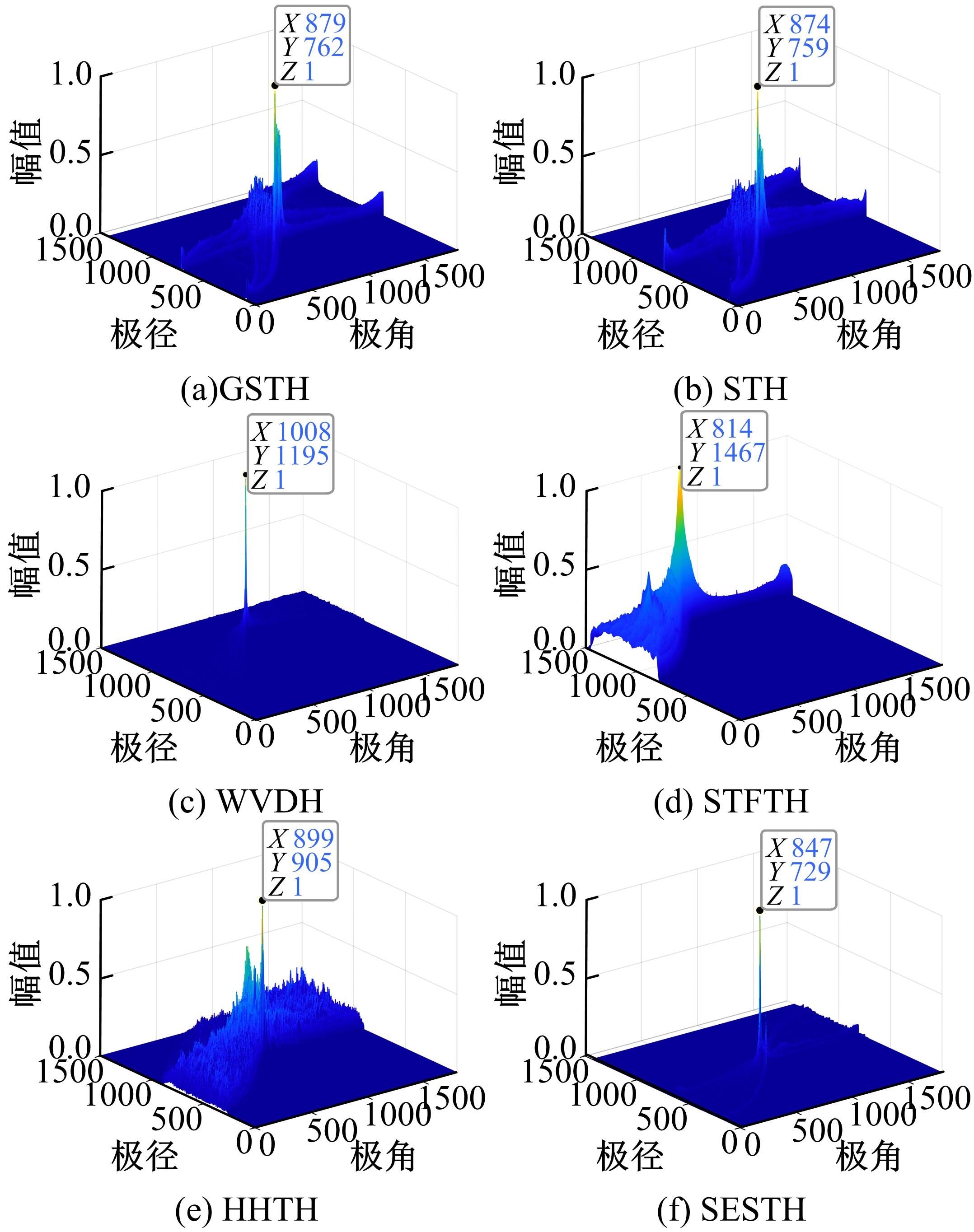
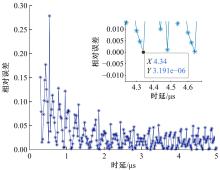
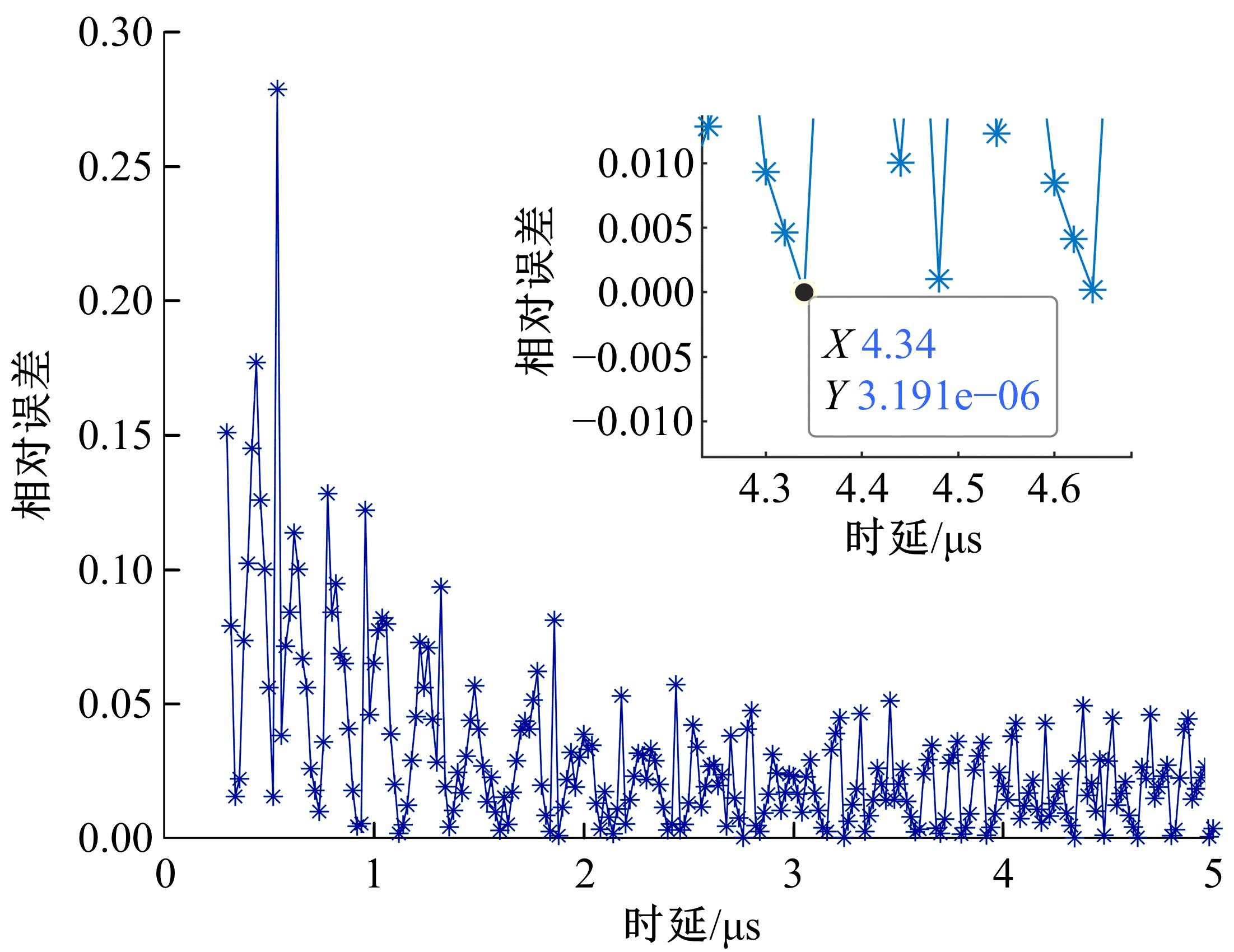
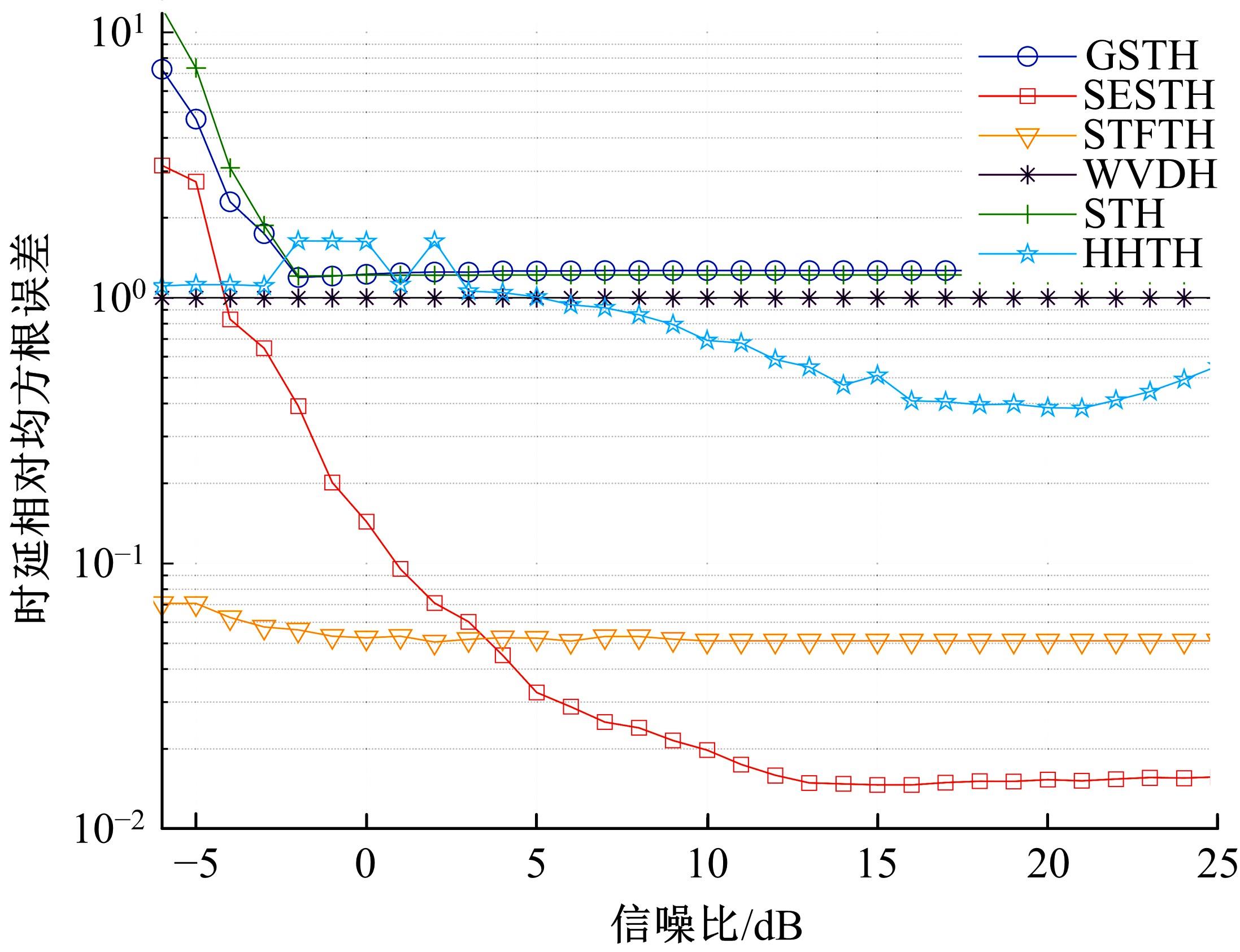
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 950-958.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211034
Time delay estimation of linear frequency-modulated continuous-wave lidar signals via SESTH
Xue-mei LI1,2( ),Chun-yang WANG1,3(
),Chun-yang WANG1,3( ),Xue-lian LIU3,Da XIE1
),Xue-lian LIU3,Da XIE1
- 1.School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Mechanical and Control Engineering,Baicheng Normal University,Baicheng 137000,China
3.Xi'an Key Laboratory of Active Photoelectric Imaging Detection Technology,Xi'an Technological University,Xi'an 710021,China
CLC Number:
- TN911.7
| 1 | Chimenti R V, Dierking M P, Powers P E, et al. Sparse frequency LFM ladar signals[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(10): 8302-8309. |
| 2 | Tsuchida H. Regression analysis of FMCW-LiDAR beat signals for non-linear chirp mitigation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(16): 914-916. |
| 3 | Sharma K K, Joshi S D. Time delay estimation using fractional Fourier transform[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 87(5): 853-865. |
| 4 | 宋杰, 唐小明, 何友. 脉冲制无源雷达动目标时延快速估计方法[J].电子科技大学学报, 2009, 38(6): 908-912, 978. |
| Song Jie, Tang Xiao-ming, He You. Fast method for time delay estimation of moving targets in passive pulse radar systems[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2009, 38(6): 908-912, 978. | |
| 5 | Riemensberger Johann, Lukashchuk Anton, Karpov Maxim, et al. Massively parallel coherent laser ranging using a soliton microcomb[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7807): 164-170. |
| 6 | Xu Zhong-yang, Zhang Hong-xiang, Chen Kai, et al. FMCW LiDAR using phase-diversity coherent detection to avoid signal aliasing[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2019, 31(22): 1822-1825. |
| 7 | Fardoost A, Vanani F G, Wen H, et al. Few-mode frequency-modulated LiDAR receivers[J]. Optics Letters, 2020,45(11): 3127-3130. |
| 8 | 戴延中, 李志舜. 基于Wigner-Ville分布的宽带回波到达时刻估计方法[J]. 声学学报, 2002, 27(1): 84-87. |
| Dai Yan-zhong, Li Zhi-shun. Time of arrival estimation of wide band echoes based on wignerville distribution[J]. Acta Acustica, 2002, 27(1): 84-87. | |
| 9 | 蒋忠进, 林君, 陈祖斌. 离散小波变换在Chirp信号检测与时延估计中的应用[J]. 自动化仪表, 2003, 43(2): 58-61. |
| Jiang Zhong-jin, Lin Jun, Chen Zu-bin. The application of discrete small wave transfer in chirp signal detection and delay estimation[J]. Process Automation Instrumentation, 2003, 43(2): 58-61. | |
| 10 | 陆侃, 卓永宁. UWB CHIRP信号的多径时延频域提取方法[J]. 通信技术, 2010, 43(12): 15-17. |
| Lu Kan, Zhou Yong-ning. Extraction of multipath time delay in frequency domain to UWB chirp signal[J]. Communications Technology, 2010, 43(12):15-17. | |
| 11 | Yu Ge, Sheng-chun Piao, Han Xiao. Fractional fourier transform-based detection and delay time estimation of moving target in strong reverberation environment[J]. IET Radar Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(9): 1367-1372 . |
| 12 | 曲杨, 王春晖, 高洁, 等. 基于连续线性调频激光器的测距方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(6): 1779-1783. |
| Qu Yang, Wang Chun-hui, Gao Jie, et al. Ranging measurement based on linear frequency modulated continuous laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(6): 1779-1783. | |
| 13 | 漆翔宇, 刘会杰, 马天鸣. 基于Morlet小波的LFM雷达信号到达时间估计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2017, 25(24): 59-64. |
| Qi Xiang-yu, Liu Hui-jie, Ma Tian-ming. Arrival time estimation of LFM radar signals based on Morlet wavelets transform[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2017, 25(24): 59-64. | |
| 14 | Ren Jia-qi, Dai Xu-chu, Li Hui. Repeater jamming suppression technology based on HHT[C]∥IEEE Radar Conference,Philadelphia, USA, 2016. |
| 15 | Stockwell R G, Mansinha L, Lowe R P. Localization of the complex spectrum: the S transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(4): 998-1001. |
| 16 | Xin Yu, Hao Hong, Li Jun. Time-varying system identification by enhanced empirical wavelet transform based on synchroextracting transform[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 196: No. 10931313. |
| 17 | Lim S, Lee S. Hough transform based ego-velocity estimation in automotive radar system[J]. Electronics Letters, 2021, 57(2): 80-82. |
| 18 | Yu Gang, Yu Ming-jin, Xu Chuan-yan. Synchroextracting transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(10): 8042-8054. |
| 19 | Baraniuk R G, Flandrin P, Janssen A J E M, et al. Measuring time-frequency information content using the Rényi entropies[J]. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 2001, 47(4): 1391-1409. |
| 20 | Wang Hong-wei, Fan Xiang-yu, Chen You, et al. Recognition method of LFM signals based GSTH transform[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(10): 2228-2234. |
| 21 | Niu Meng, Liu Guang-bin. Multi component LFM signal time frequency detection based on S-hough transform[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007, 27(3): 266-268. |
| 22 | Zhang Wei-ke, Cui Kai-bo, Wu Wei-wei, et al. DOA estimation of LFM signal based on single-source time-frequency points selection algorithm by using the Hough transform[J]. Radio Engineering, 2019, 27(1): 265-275. |
| 23 | Xu Fen-fei, Bao Qing-long, Chen Zeng-ping, et al. Parameter Estimation of multi-component lfm signals based on STFT+Hough transform and fractional Fourier transform[C]∥The 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Xi'an, China, 2018. |
| 24 | Yuan Ye, Mei Wen-bo. Chirp-Like Jammer excision in DSSS communication systems using combined hht spectrum and Hough transform[C]∥The 4th IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Systems for Communications, Shanghai, China, 2008. |
| 25 | Dong Yong-kang, Zhu Zong-da, Tian Xiao-ning, et al. Frequency-modulated continuous-wave LIDAR and 3D imaging by using linear frequency modulation based on injection locking[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(8): 2275-2280. |
| [1] | Hui-jing DOU,Gang DING,Jia GAO,Xiao LIANG. Wideband signal direction of arrival estimation based on compressed sensing theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2237-2245. |
| [2] | Xin-yu JIN,Mu-han XIE, SUN-Bin. Grain information compressed sensing based on semi-tensor product approach [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 379-385. |
| [3] | Li⁃min GUO,Xin CHEN,Tao CHEN. Radar signal modulation type recognition based on AlexNet model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 1000-1008. |
| [4] | YANG Wei,SHI Yao-wu. Broadband direction-arrival estimation of Chirp signal using fractional Fourier transform [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 818-821. |
| [5] | LI Jing, WANG Shuxun, WANG Fei. Parameter estimation of adaptive Chirp signal based on polynomial phase transform [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (4): 617-621. |
| [6] | AN Dexi, ZHOU Donghua. Robust adaptive smoothing algorithm for nonlinear stochastic systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (3): 433-438. |
|
||