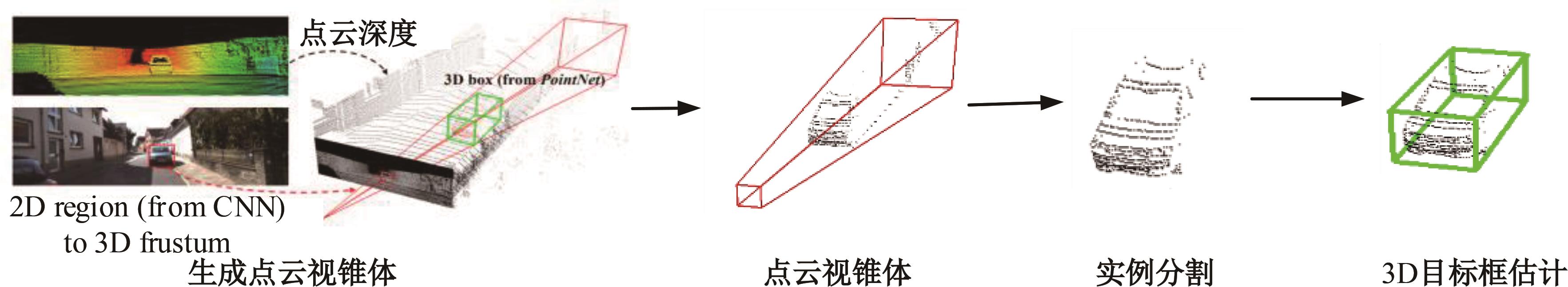
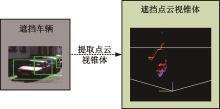
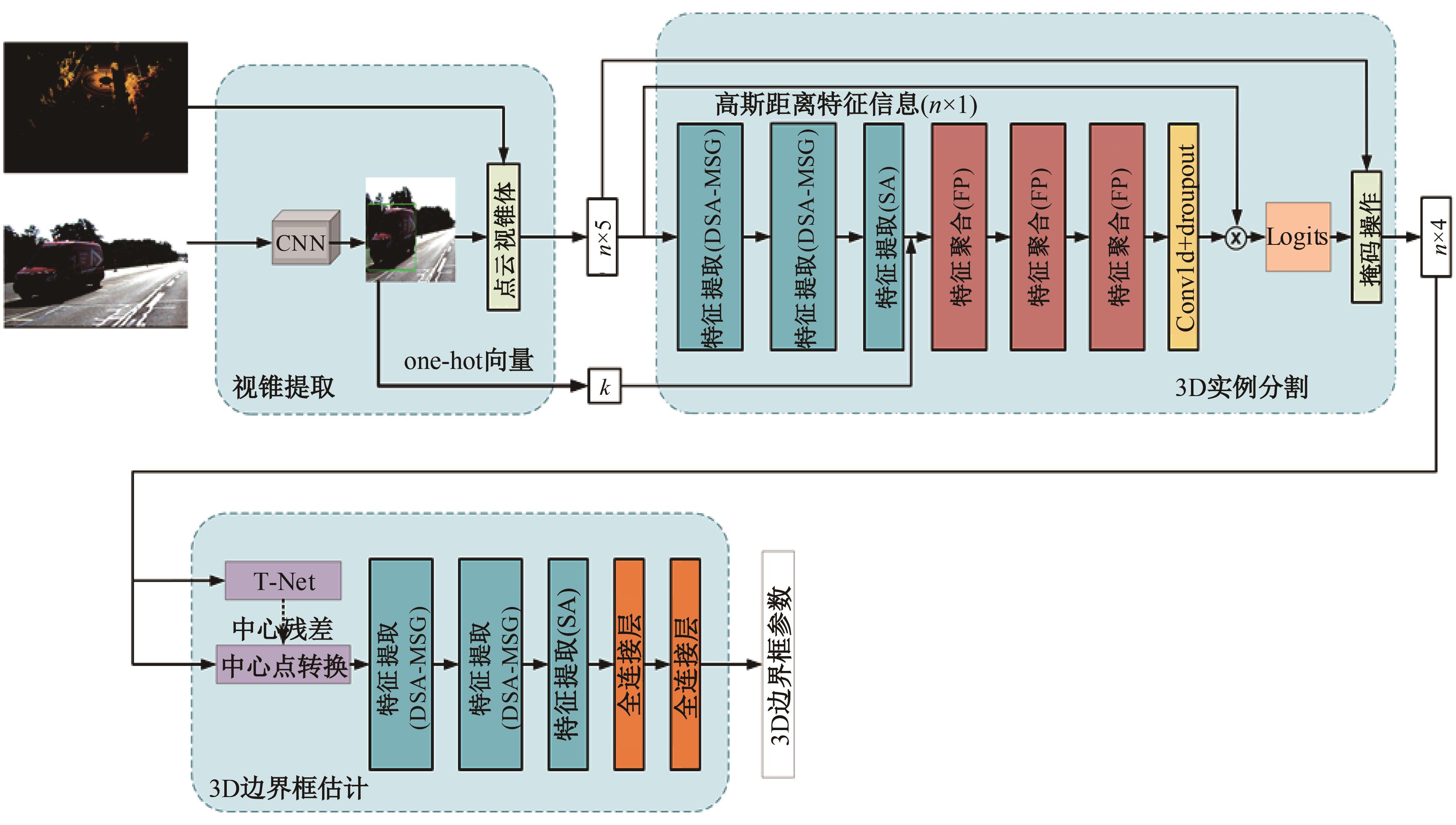
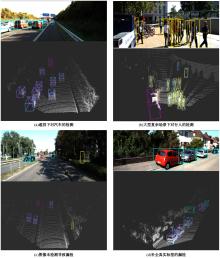
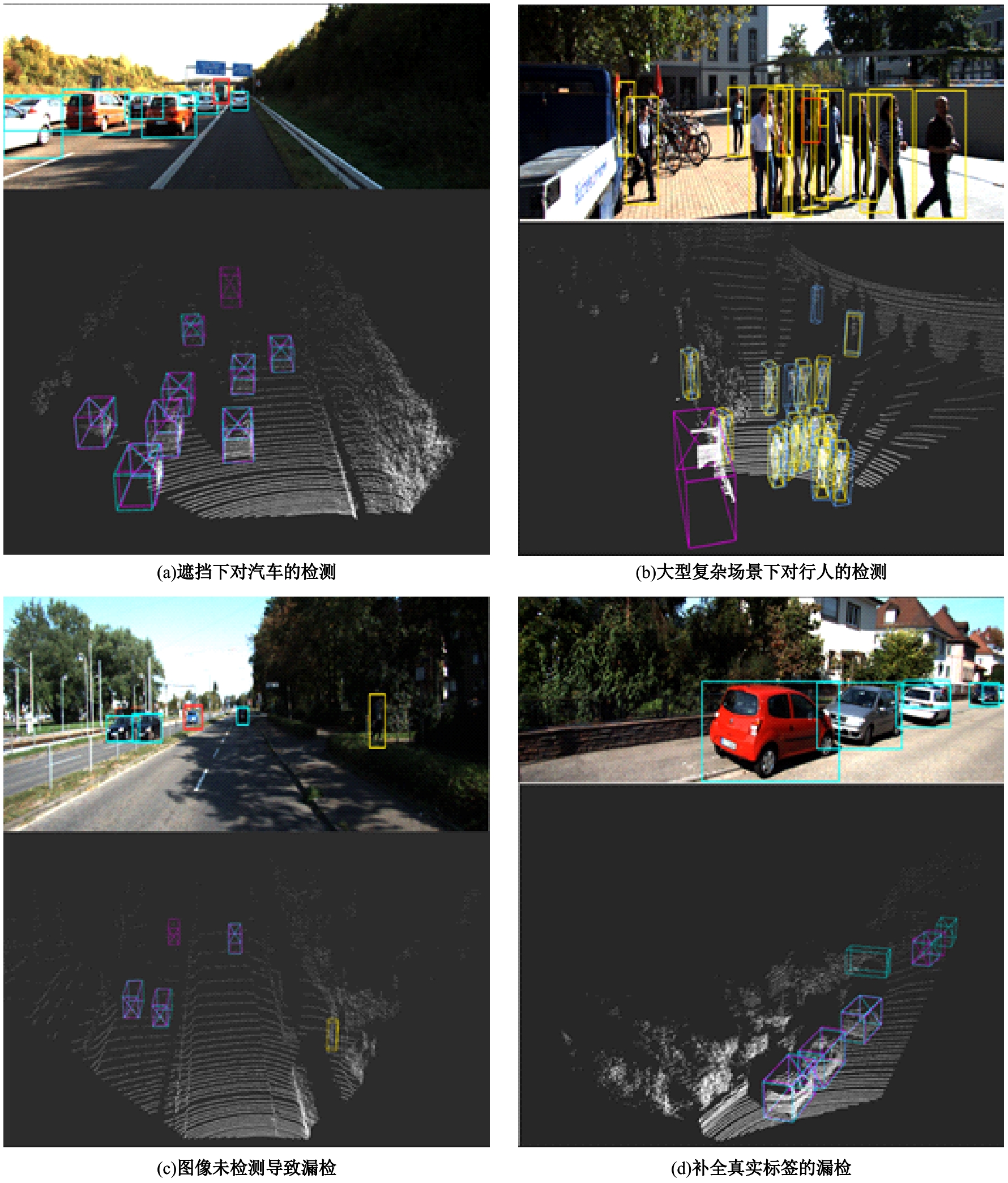
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3589-3600.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230105
Previous Articles Next Articles
3D object detection algorithm fusing dense connectivity and Gaussian distance
Xin CHENG1,2( ),Sheng-xian LIU1,Jing-mei ZHOU3(
),Sheng-xian LIU1,Jing-mei ZHOU3( ),Zhou ZHOU1,Xiang-mo ZHAO1
),Zhou ZHOU1,Xiang-mo ZHAO1
- 1.School of Information Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710018,China
2.Traffic Management Research Institute of the Ministry of Public Security,Wuxi 214151,China
3.School of Electronics and Control Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710018,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Cheng X, Zhou J M, Liu P Y, et al. 3D vehicle object tracking algorithm based on bounding box similarity measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(12): 15844-15854. |
| 2 | Cheng X, Zhou J M, Song J C, et al. A highway traffic image enhancement algorithm based on improved GAN in complex weather conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(8): 8716-8726. |
| 3 | Yurtsever E, Lambert J, Carballo A, et al. A survey of autonomous driving: common practices and emerging technologies[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 58443-58469. |
| 4 | Cui Y D, Chen R, Chu W B, et al. Deep learning for image and point cloud fusion in autonomous driving: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 722-739. |
| 5 | Zhou Y, Tuzel O. VoxelNet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4490-4499. |
| 6 | Lang A H, Vora S, Caesar H, et al. PointPillars: fast encoders for object detection from point clouds [C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12697-12705. |
| 7 | Yan Y, Mao Y X, Li B. SECOND: sparsely embedded convolutional detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3337. |
| 8 | Deng J J, Shi S S, Li P W, et al. Voxel R-CNN: towards high performance voxel-based 3D object detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(2): 1201-1209. |
| 9 | Li B. 3D fully convolutional network for vehicle detection in point cloud[C]∥2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 1513-1518. |
| 10 | 程鑫, 王宏飞, 周经美, 等. 基于体素柱形的激光雷达点云车辆目标检测算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(3): 247-260. |
| Cheng Xin, Wang Hong-fei, Zhou Jing-mei, et al. Vehicle detection algorithm based on voxel pillars from lidar point clouds[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(3): 247-260. | |
| 11 | Qi C R, Su H, Mo K, et al. PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77-85. |
| 12 | Qi C R, Yi L, Su H, et al. PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105 - 5114 . |
| 13 | Shi S S, Wang X G, Li H S. PointRCNN: 3D object proposal generation and detection from point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 770-779. |
| 14 | Yang Z T, Sun Y A, Liu S, et al. 3DSSD: point-based 3D single stage object detector[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11040-11048. |
| 15 | Yang Z T, Sun Y A, Liu S, et al. STD: sparse-to-dense 3D object detector for point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1951-1960. |
| 16 | Shi W J, Rajkumar R. Point-GNN: graph neural network for 3D object detection in a point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle,USA, 2020: 1711-1719. |
| 17 | Yin T W, Zhou X Y, Krahenbuhl P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 11784-11793. |
| 18 | Chen X Z, Ma H M, Wan J, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1907-1915. |
| 19 | Ku J, Mozifian M, Lee J, et al. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation[C]∥2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: No.8594049. |
| 20 | Qi C R, Liu W, Wu C X, et al. Frustum PointNets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 918-927. |
| 21 | Vora S, Lang A H, Helou B, et al. PointPainting: sequential fusion for 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 4604-4612. |
| 22 | Xu D F, Anguelov D, Jain A. PointFusion: deep sensor fusion for 3D bounding box estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 244-253. |
| 23 | Wang Z X, Jia K. Frustum ConvNet: sliding frustums to aggregate local point-wise features for amodal 3D object detection[C]∥2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 2019: 1742-1749. |
| 24 | Huang G, Liu Z, Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700-4708. |
| 25 | Geiger A, Lenz P, Stiller C, et al. Vision meets robotics: the KITTI dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231-1237. |
| 26 | Klokov R, Lempitsky V. Escape from cells: deep kd-networks for the recognition of 3D point cloud models[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 863-872. |
| 27 | Li J X, Chen B M, Lee G H. SO-Net: self-organizing network for point cloud analysis[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9397-9406. |
| 28 | Graham B, Engelcke M, Maaten L. 3D semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9224-9232. |
| [1] | Bo TAO,Fu-wu YAN,Zhi-shuai YIN,Dong-mei WU. 3D object detection based on high⁃precision map enhancement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [2] | Xue-mei LI,Chun-yang WANG,Xue-lian LIU,Da XIE. Time delay estimation of linear frequency-modulated continuous-wave lidar signals via SESTH [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 950-958. |
| [3] | Yi-cheng YU,Liang HU,Ling CHI,Jian-feng CHU. An anonymous authentication protocol for single⁃server architectures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 659-666. |
| [4] | Chang-fu ZONG,Long WEN,Lei HE. Object detection based on Euclidean clustering algorithm with 3D laser scanner [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [5] | PAN Hai-yang, LIU Shun-an, YAO Yong-ming. Depth information-basd autonomous aerial refueling [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1750-1756. |
|