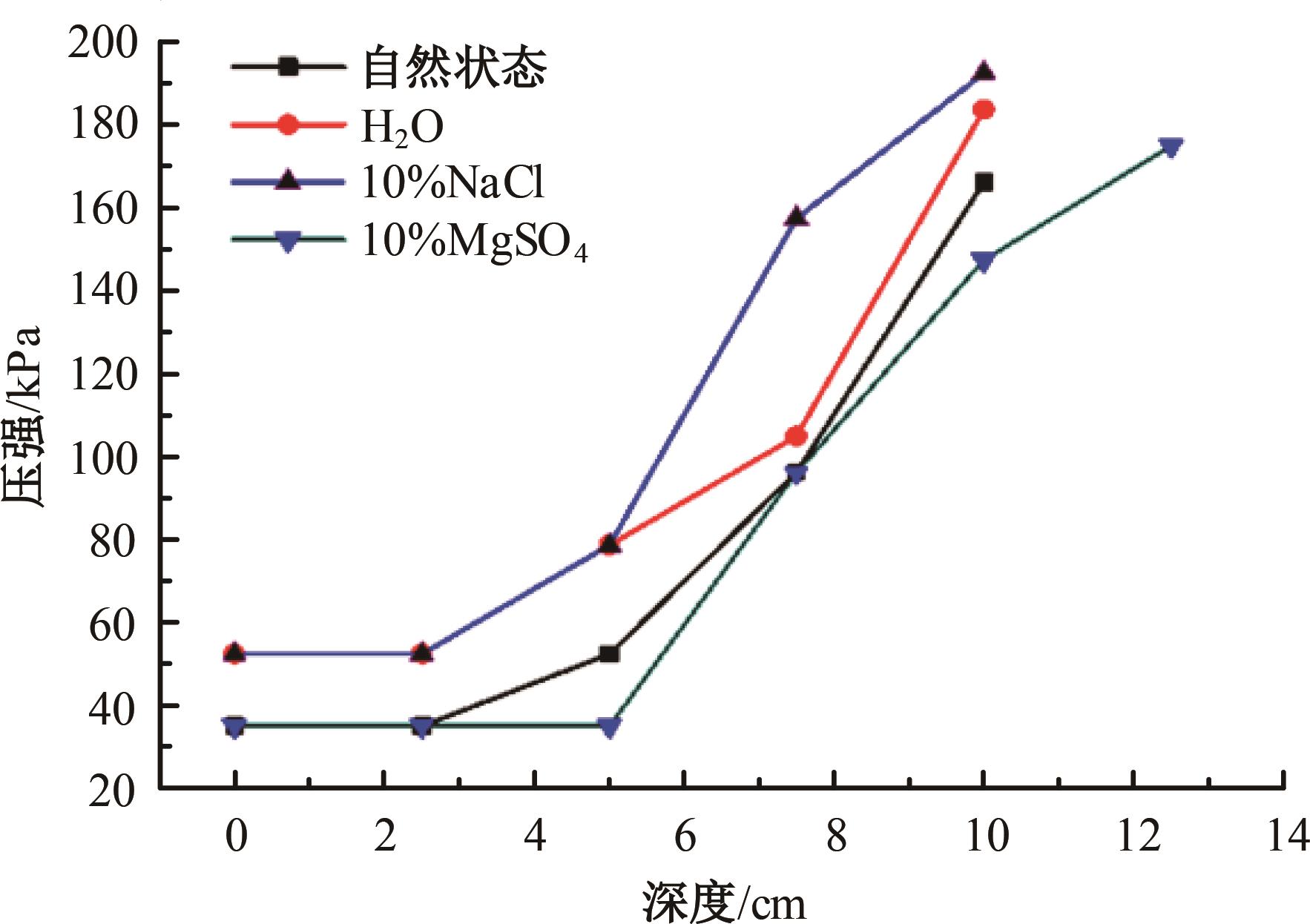
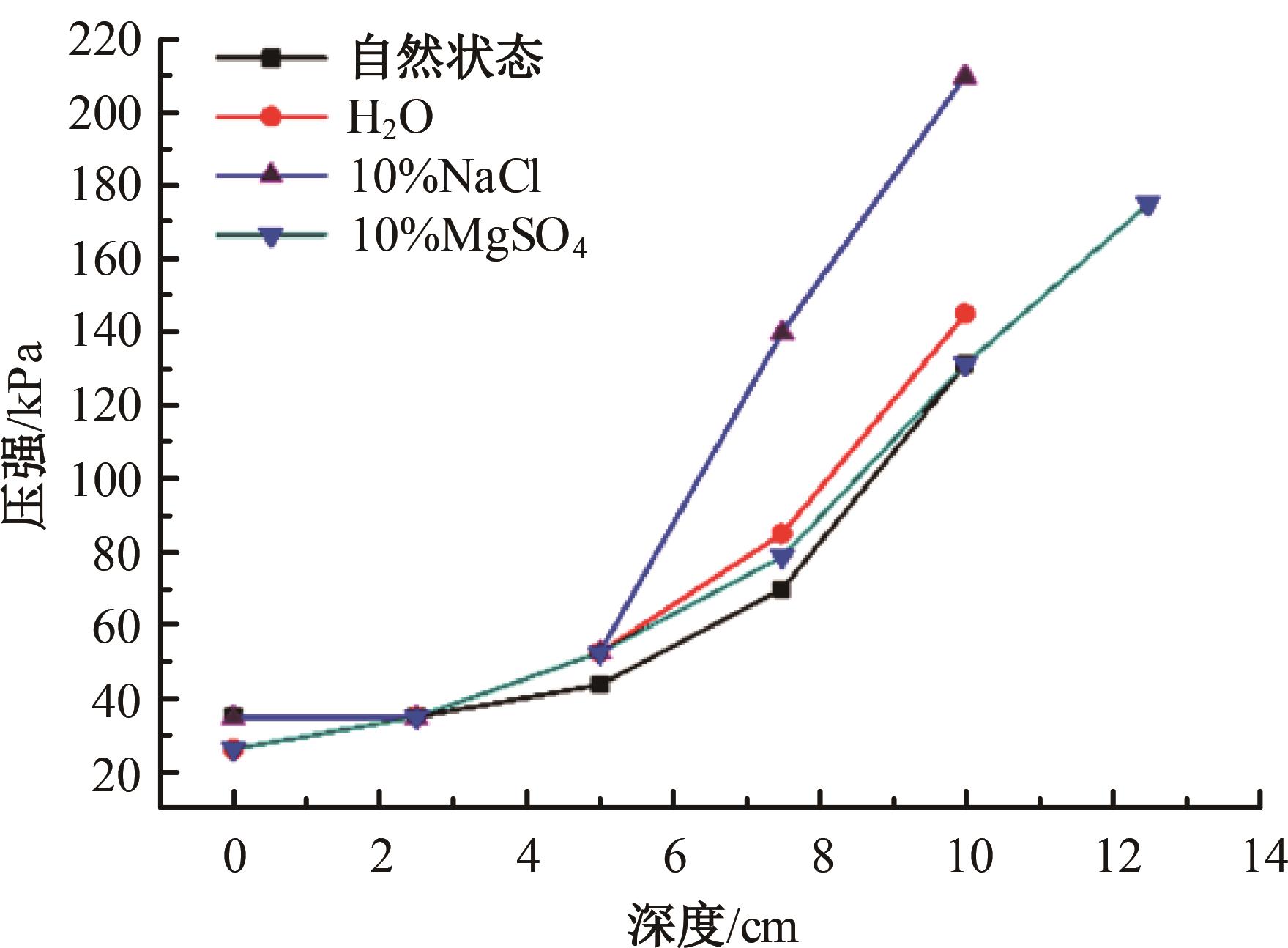
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (8): 2393-2400.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231159
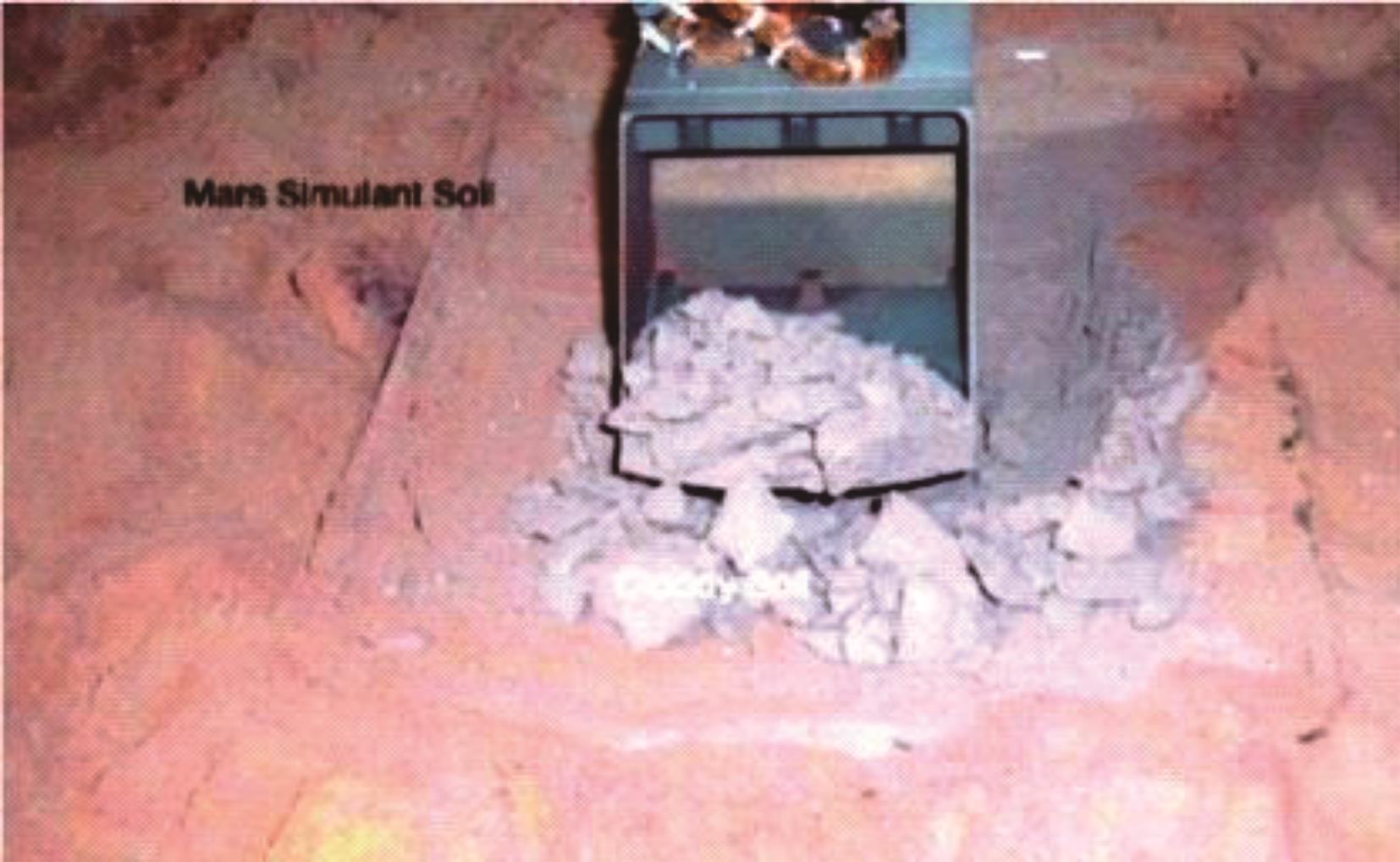
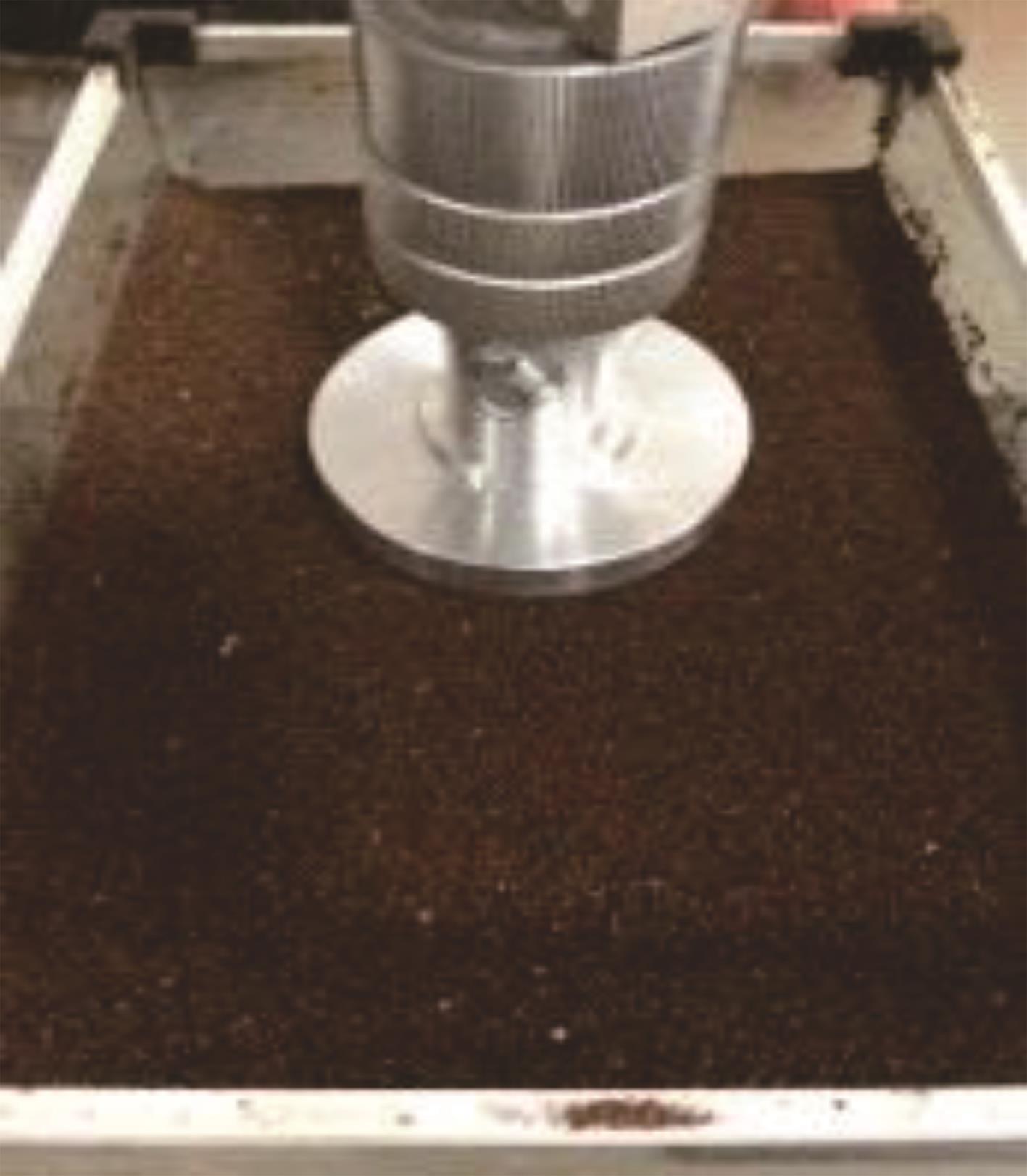
Experimental on mechanical properties of simulated Mars soil crust and its crusting
Zhao-long DANG1( ),Meng ZOU2,Jia-feng SONG2,Bai-chao CHEN1,Yan SHEN2,Ying-chun QI2(
),Meng ZOU2,Jia-feng SONG2,Bai-chao CHEN1,Yan SHEN2,Ying-chun QI2( )
)
- 1.Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering,CAST,Beijing 100094,China
2.Key Lab. for Bionics Engineering of Education Ministry,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- V476.4
| 1 | 吴伟仁, 刘旺旺, 唐玉华, 等. 深空探测几项关键技术及发展趋势[J]. 国际太空, 2013, 420(12): 45-51. |
| Wu Wei-ren, Liu Wang-wang, Tang Yu-hua, et al. Development trends of deep space exploration and several key technologies[J]. Space Exploration, 2013, 420(12): 45-51. | |
| 2 | 李超, 董治宝, 吕萍, 等. 火星沙丘地貌的形态学窥究[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(1): 80-90. |
| Li Chao, Dong Zhi-bao, Ping Lyu, et al. A morphological insight into the Martian dune geomorphology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(1): 80-90. | |
| 3 | Wong J Y. Terr Mechanics and Off-road Vehicles[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1989. |
| 4 | Greeley R, Squyres S W, Arvidson R E, et al. Wind-related processes detected by the spirit rover at gusev crater, mars[J]. Science, 2004, 305: 810-813. |
| 5 | Hannan M, Rickman D, Chavers G, et al. Flight testing of guidance, navigation and control systems on the mighty eagle robotic lander test bed[C]∥ AIAA SciTech 2015, Kissimmee, USA, 2015: 20150002955. |
| 6 | Yuan B, Wang C, Zou M, et al. Experimental study on the durability of China's Mars rover's mobility system[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 34(5): 0001292. |
| 7 | Team R. Characterization of the martian surface deposits by the Mars pathfinder rover, sojourner[J]. Science, 1997, 278: 1765-1768. |
| 8 | Sheehan W, Bell J. Discovering Mars: a history of observation and exploration of the red planet[J]. University of Arizona Press, 2021, 2: 102307. |
| 9 | 蒋明镜, 戴永生, 张熇, 等. TJ-1 模拟月壤承载特性的现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(6): 1529-1535. |
| Jiang Ming-jing, Dai Yong-sheng, Zhang He, et al. Field experimental research on bearing properties of TJ-1 lunar soil simulant[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1529-1535. | |
| 10 | Hudson T L, Aharonson O. Diffusion barriers at Mars surface conditions: salt crusts, particle size mixtures, and dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113(9): 003026. |
| 11 | 薛龙,党兆龙,陈百超,等. 面向火星着陆器 缓冲试验的模拟火壤力学特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 176-186. |
| Xue Long, Dang Zhao-long, Chen Bai-chao, et al. Terra-mechanics of Mars soil for martian lander's landing tests[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 176-186. | |
| 12 | 李建桥,薛龙,邹猛,等.已有模拟火壤力学性质分析及新火星壤研制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2016, 46(1): 172-178. |
| Li Jian-qiao, Xue Long, Zou Meng, et al. Terra-mechanics characters and development of martian simulant regolith[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(1): 172-178. | |
| 13 | Westall F, Coates A J, Korablev O, et al. Habitability on early Mars and the search for biosignatures with the exomars rover[J]. Astrobiology, 2017, 17(6/7): 471-510. |
| 14 | Sullivan R, Anderson R, Biesiadecki J, et al. Cohesions, friction angles, and other physical properties of martian regolith from Mars exploration rover wheel trenches and wheel scuffs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2011, 116(2): 2010JE02006. |
| No related articles found! |
|