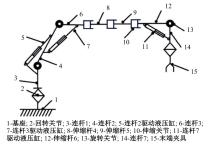
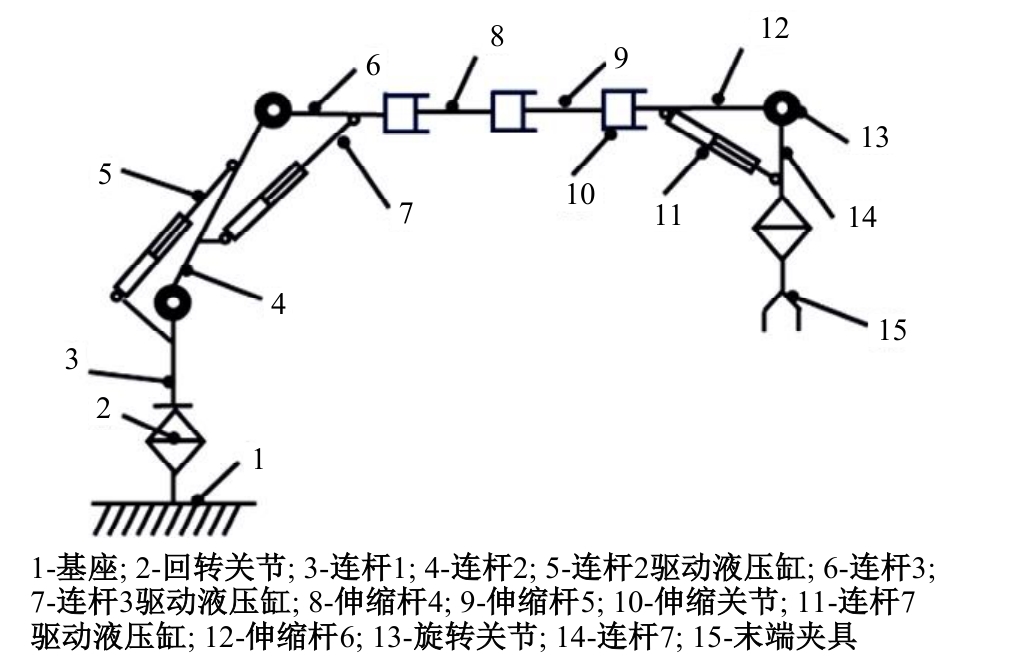
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1443-1452.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230656
Previous Articles Next Articles
Solving method on inverse kinematics of mobile loading missile manipulator by multi-population grey wolf optimization algorithm
Yun-feng HU1,2( ),Jia-min LI2,Zhi-guo TANG2(
),Jia-min LI2,Zhi-guo TANG2( )
)
- 1.National Key Laboratory of Automotive Chassis Integration and Bionics,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TP241
| [1] | 霍希建, 刘伊威, 姜力,等. 具有关节限位的7R仿人机械臂逆运动学优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(1): 213-220. |
| Huo Xi-jian, Liu Yi-wei, Jiang Li, et al. Inverse kinematics optimization of a 7R humanoid robot arm with joint limits [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition ), 2016, 46(1): 213-220. | |
| [2] | 石建平, 刘鹏, 陈冬云. 基于改进粒子群优化算法的冗余机械臂逆运动学求解[J]. 机械传动, 2021, 45(2): 69-75. |
| Shi Jian-ping, Liu Peng, Chen Dong-yun. Inverse kinematics of redundant manipulator based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2021, 45(2): 69-75. | |
| [3] | 冷舒, 吴克, 居鹤华. 机械臂运动学建模及解算方法综述[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(11): 1262-1273. |
| Leng Shu, Wu Ke, Ju He-hua, Kinematics modeling and calculating method of mechanical arm review [J]. Journal of Aerospace, 2019, 40(11): 1262-1273. | |
| [4] | Alkayyali M, Tutunji T A. PSO-based algorithm for inverse kinematics solution of robotic arm manipulators[C]∥20th International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM),IEEE, Wels, Austria, 2019: 1-6. |
| [5] | Ghosh A, Singh O, Ray A K. Inverse kinematic solution of a 7 DOF robotic manipulator using boundary restricted particle swarm optimization[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2022, 55(1): 101-105. |
| [6] | Liu Y, Xi J, Bai H, et al. A general robot inverse kinematics solution method based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 32341-32350. |
| [7] | Gao R. Inverse kinematics solution of robotics based on neural network algorithms[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2020, 11(12): 6199-6209. |
| [8] | Nguyen T, Bui T, Pham H. Using proposed optimization algorithm for solving inverse kinematics of human upper limb applying in rehabilitation robotic[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(1): 679-705. |
| [9] | Ahmed E S, Elhosseini M A, Haikal A Y. A new ABC variant for solving inverse kinematics problem in 5 DOF robot arm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 73: 24-38. |
| [10] | 杨凯, 黄晋英. 一种8自由度空间机械臂运动学及工作空间分析[J]. 机械传动, 2021, 45(3): 147-152. |
| Yang Kai, Huang Jin-ying. Kinematics and workspace analysis of a 8-DOF space manipulator[J]. Mechanical Transmission, 2021, 45(3): 147-152. | |
| [11] | 张清松, 段帅臣, 夏热. 基于Matlab的拟人机械臂工作空间分析及仿真[J]. 机械传动, 2020, 44(12): 99-105. |
| Zhang Qing-song, Duan Shuai-chen, Xia Re. Workspace analysis and simulation of anthropomorphic robotic arm based on Matlab[J]. Mechanical Transmission, 2020, 44(12): 99-105. | |
| [12] | Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S M, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| [13] | 张晓凤, 王秀英. 灰狼优化算法研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(3): 30-38. |
| Zhang Xiao-feng, Wang Xiu-ying, Review of grey wolf optimization algorithm[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(3): 30-38. | |
| [14] | Rezaei F, Safavi H R, Abd Elaziz M, et al. An enhanced grey wolf optimizer with a velocity-aided global search mechanism[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(3):No.351. |
| [1] | LIU Han-bing, WU Chun-li, CHENG Yong-chun. Sensor placement on bridge structure based on genetic algorithms with different fitness functions [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 51-56. |
|