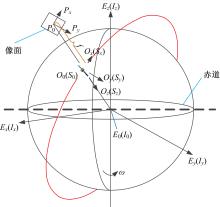
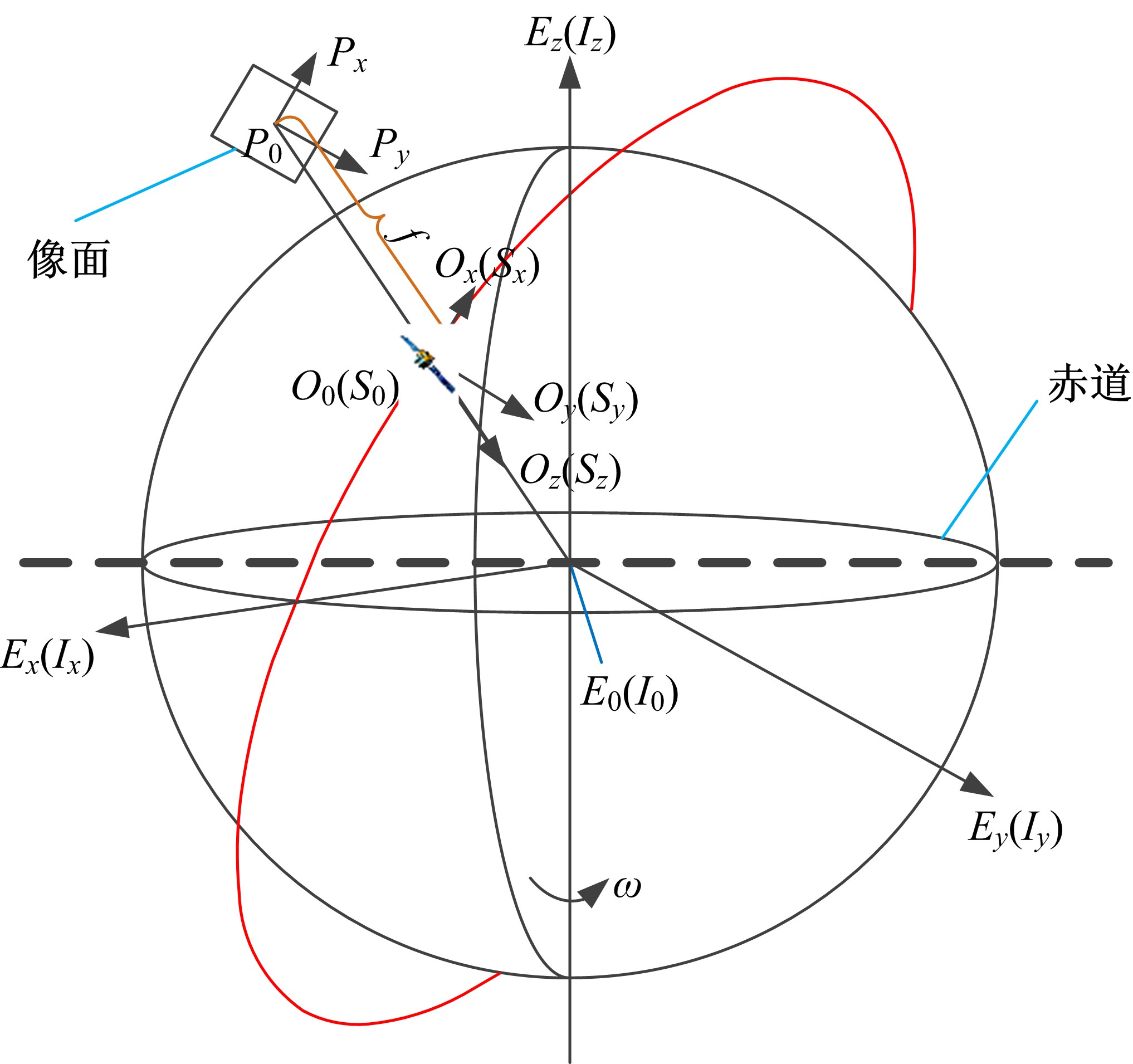
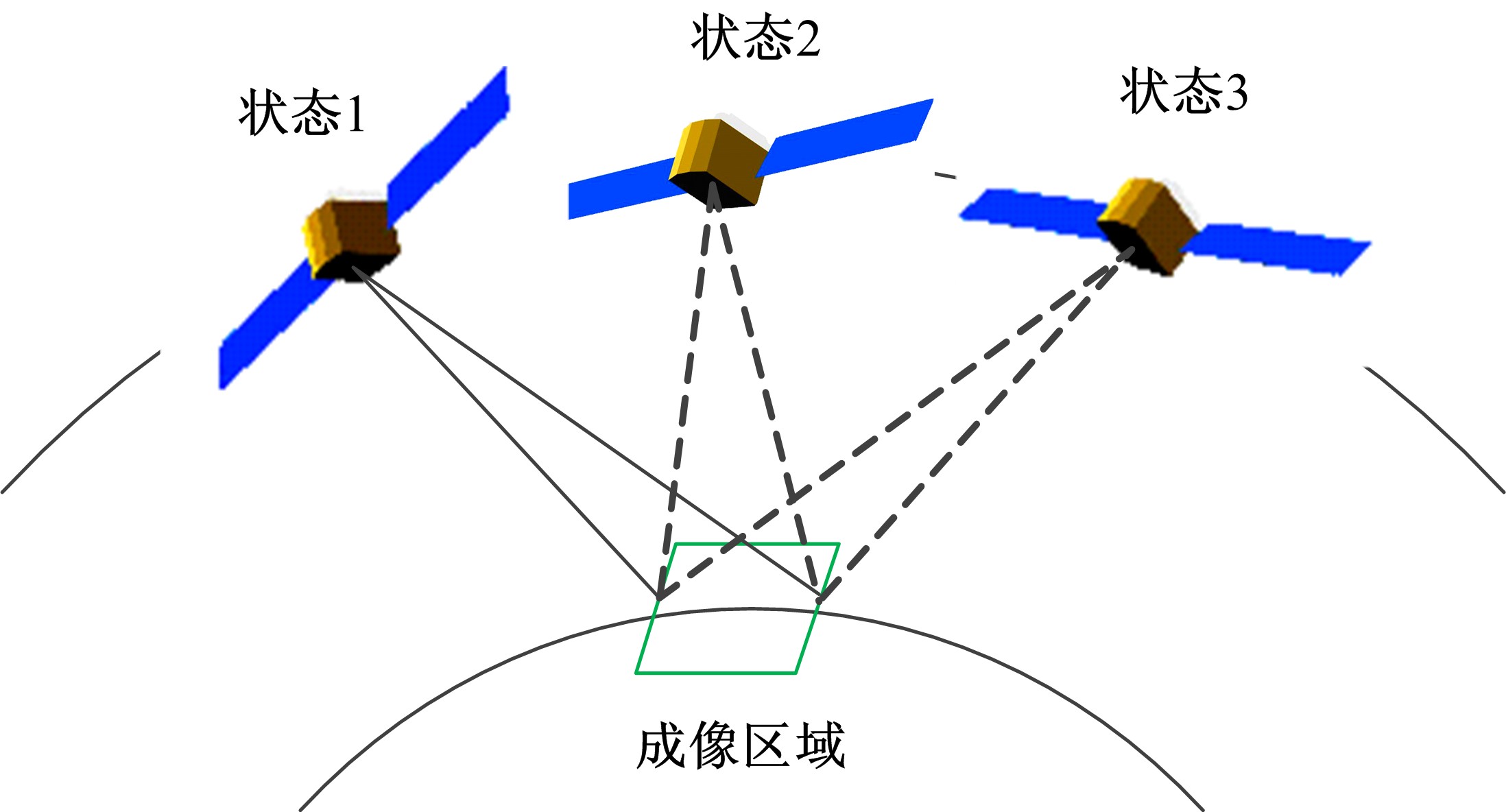
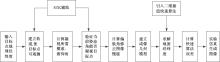
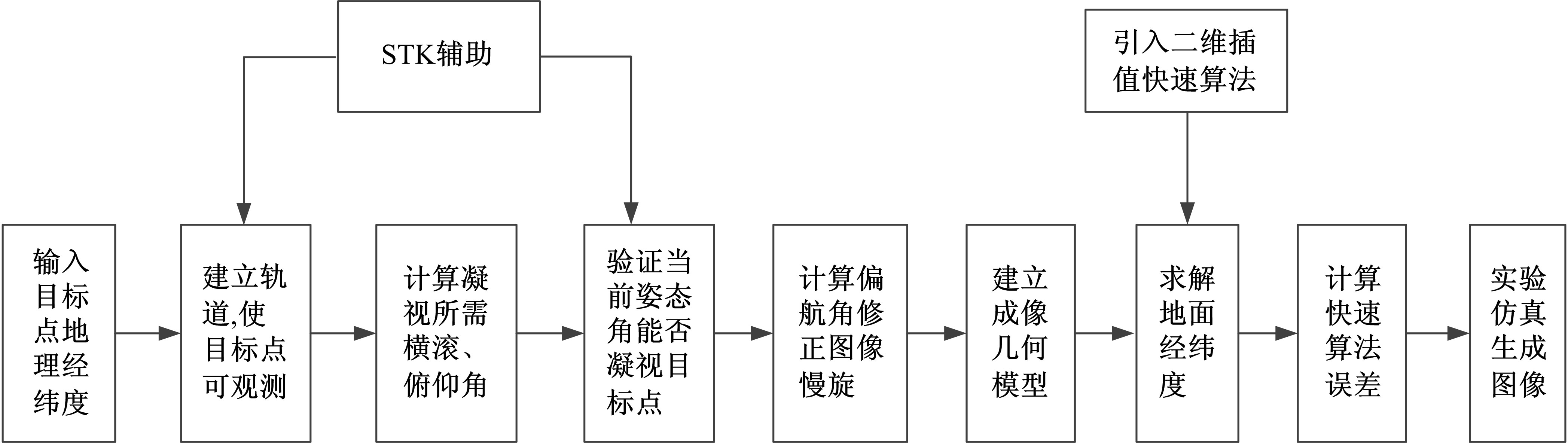
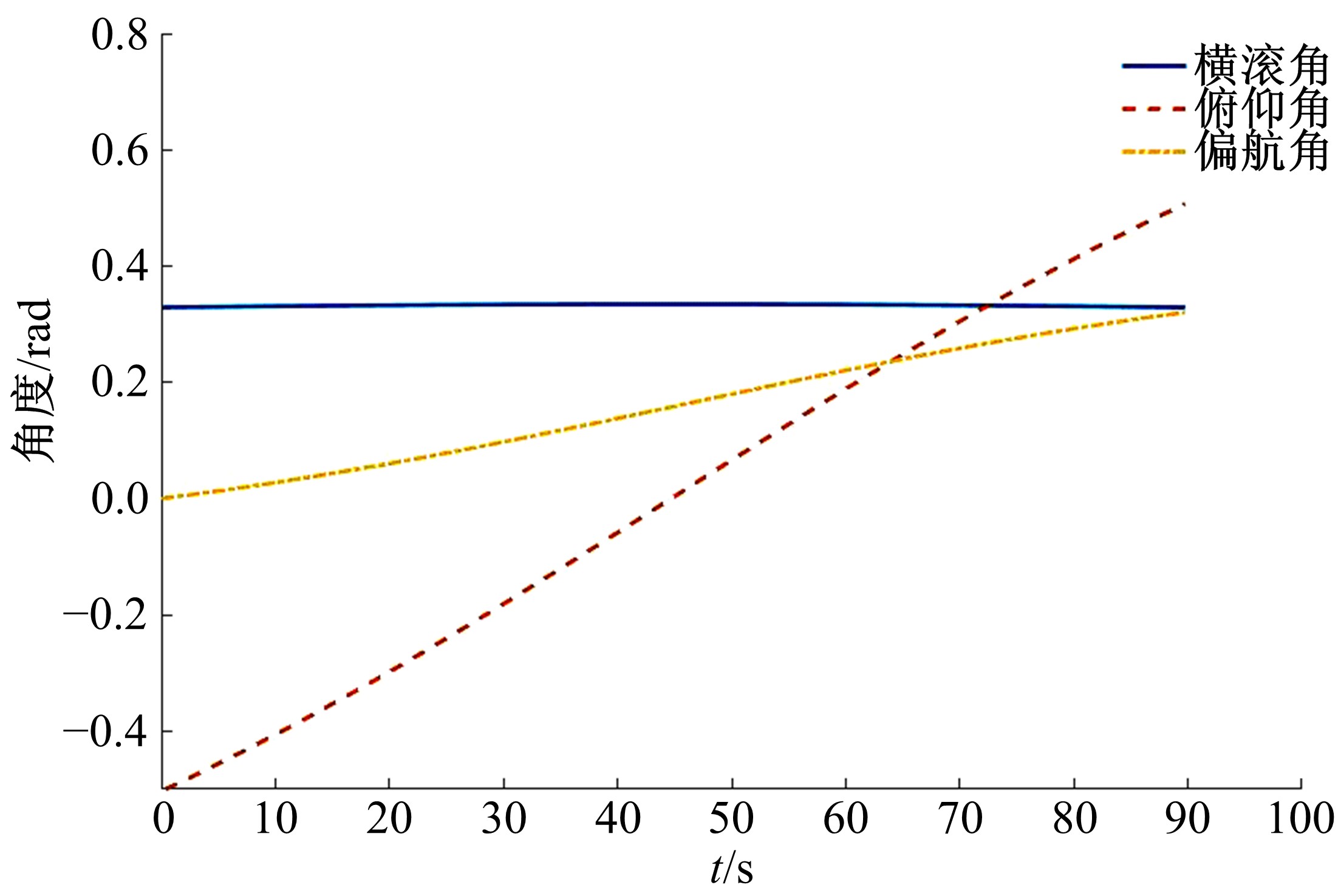
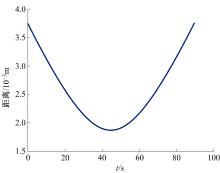
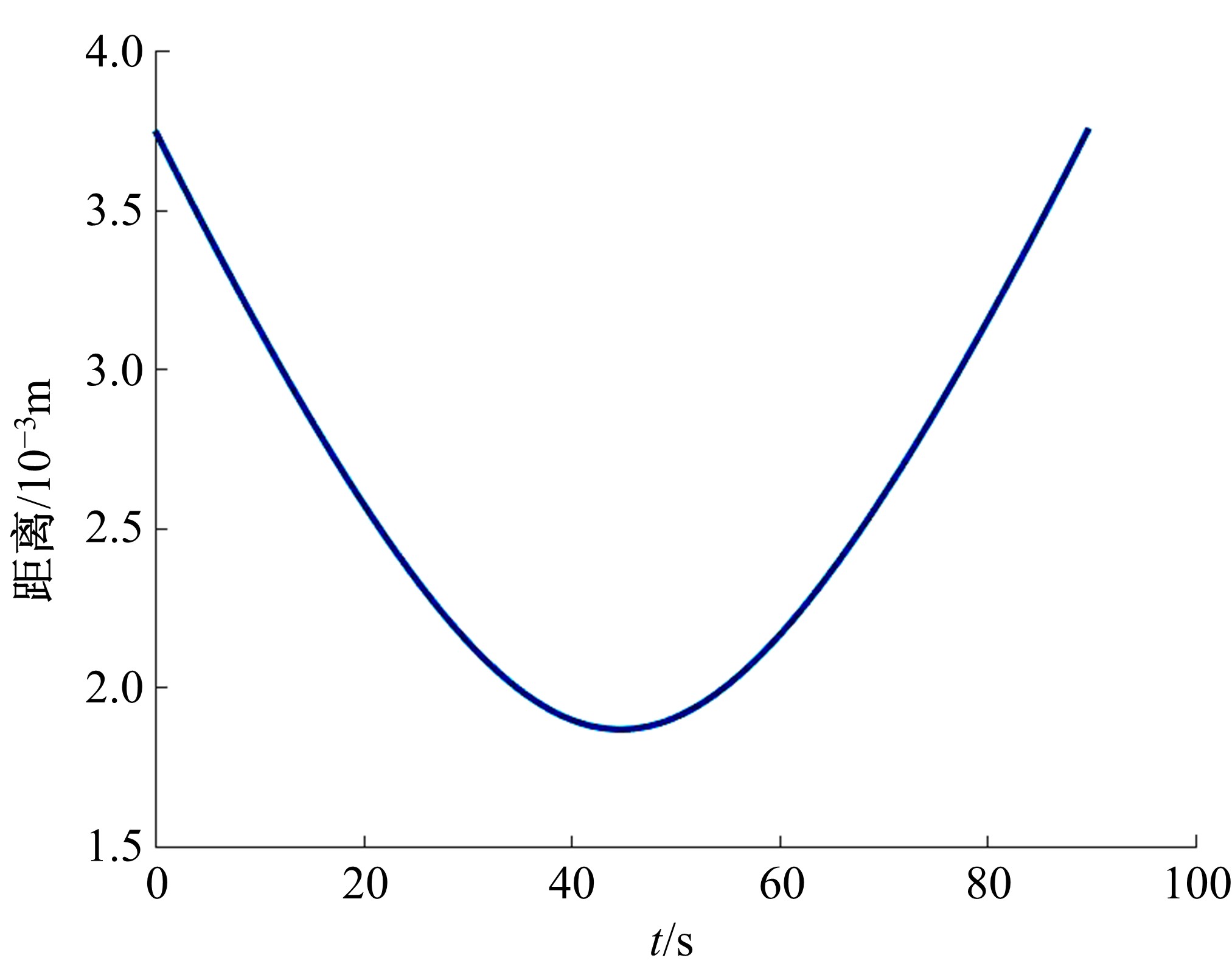
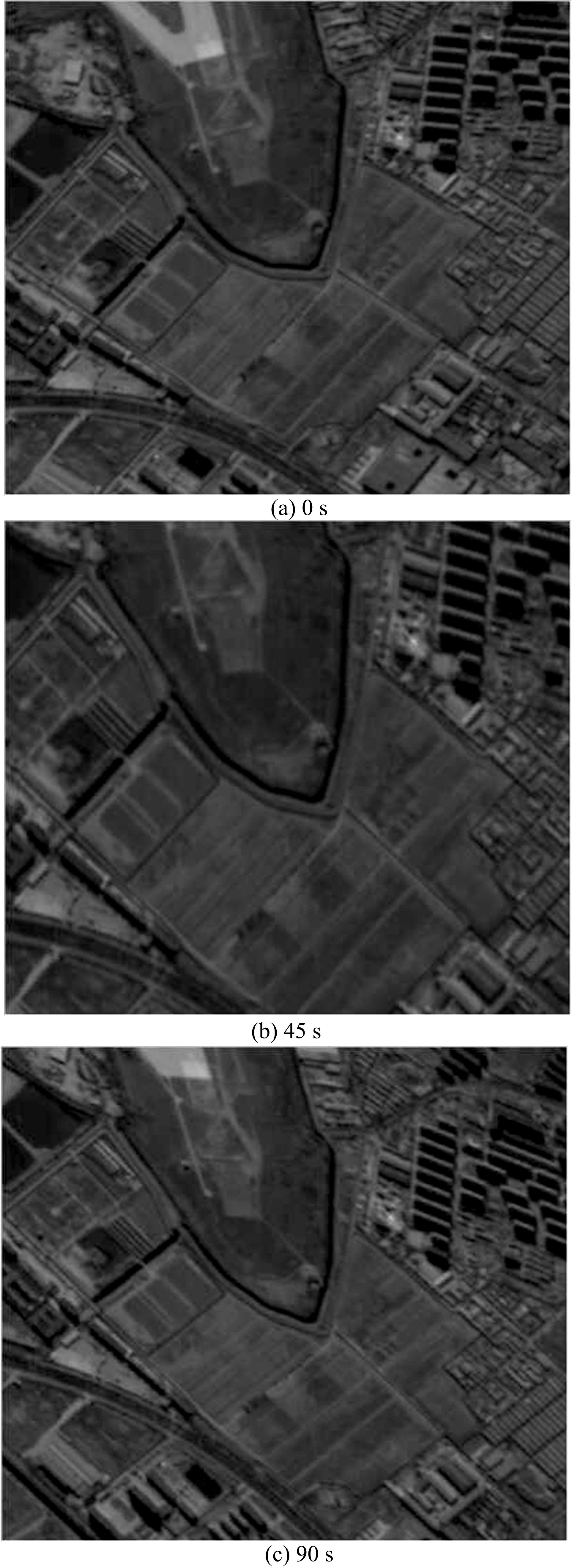
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 340-348.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190885
Attitude planning and fast simulation method for staring imaging of optical remote sensing satellite
Liu ZHANG1( ),Xiao-han ZHANG1,Qing-xing YUE2,Nian LIU3,Kai-peng SUN4,Jie SUN4,Guo-wei FAN1(
),Xiao-han ZHANG1,Qing-xing YUE2,Nian LIU3,Kai-peng SUN4,Jie SUN4,Guo-wei FAN1( )
)
- 1.College of Instrument and Electrical Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Land Satellite Remote Sensing Application Center,Ministry of Natural Resources,Beijing 100048,China
3.Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunications Technology,Chinese People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force,Beijing 100094,China
4.Shanghai Institute of Satellite Engineering,Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology,Shanghai 201109,China
CLC Number:
- V416
| 1 | 付凯林, 杨芳, 黄敏, 等. 低轨道视频卫星任务模式的研究与应用[C]∥北京力学会第21届学术年会暨北京振动工程学会第22届学术年会,北京, 2015: 17-22. |
| 2 | 袁益琴, 何国金, 江威, 等. 遥感视频卫星应用展望[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2018, 30(3): 1-8. |
| Yuan Yi-qin, He Guo-jin, Jiang Wei, et. al. Application of earth observation system of video satellite[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2018, 30(3): 1-8. | |
| 3 | 王握文, 刘小兵. 我首颗视频成像体制微卫星"天拓二号"发射成功[N/OL]. 光明日报, 2014: 09009. |
| 4 | 邹维荣, 宗兆盾. 中国成功发射一颗米级高清动态视频卫星[EB/OL]. [2015-10-10]. |
| 5 | 詹桓. 珠海-1遥感微纳卫星星座首批星——欧比特视频卫星-1A、1B成功发射[J]. 国际太空, 2017(6): 14-15. |
| Zhan Huan. The first two satellites OVS-1A/1B of Zhuhai-1 remote-sensing micro/nano satellites constellation launched successfully[J]. Space International, 2017(6): 14-15. | |
| 6 | 孙伟健, 林军, 阮宁娟, 等. 国外光学遥感成像系统仿真软件发展综述与思考[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2010, 31(3): 70-75. |
| Sun Wei-jian, Lin Jun, Ruan Ning-juan, et al. Summarization and consideration of oversea's simulation software development for optical remote sensing system[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(3): 70-75. | |
| 7 | 武晓雯. 敏捷卫星姿态机动规划方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学自动化学院, 2016. |
| Wu Xiao-wen. Research on attitude maneuvering planning method of agile satellite[D]. Harbin: School of Automation, Harbin Engineering University, 2016. | |
| 8 | 魏静波. 视频小卫星姿态控制技术研究[D]. 长沙:国防科学技术大学航空学院, 2012. |
| Wei Jing-bo. Attitude control technology of a small video satellite[D]. Changsha: School of Aeronautics, University of Defense Science and Technology, 2012. | |
| 9 | 赵学敏, 马文坡, 刘兆军. 低轨卫星面阵凝视成像技术研究[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2007, 28(2): 10-14. |
| Zhao Xue-min, Ma Wen-po, Liu Zhao-jun. Study on area array staring imaging technology for LEO satellite[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2007, 28(2): 10-14. | |
| 10 | 江万寿, 张剑清, 张祖勋. 三线阵CCD卫星影像的模拟研究[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2002, 27(4): 414-419. |
| Jiang Wan-shou, Zhang Jian-qing, Zhang Zu-xun. Simulation study of three-line array CCD satellite imagery [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2002, 27(4): 414-419. | |
| 11 | 王刚, 禹秉熙. 基于图像仿真的对地遥感过程科学可视化研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2002, 14(6): 756-760. |
| Wang Gang, Yu Bing-xi. Study on scientific visualization of earth remote sensing based on imagery simulation[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2002, 14(6): 756-760. | |
| 12 | 薛高雄, 廖瑛, 杜鑫. 卫星对空间目标的凝视仿真[C]∥第18届中国系统仿真技术及其应用学术年会,兰州,2017: 138-141. |
| 13 | 刘一良, 肖倩, 马灵霞, 等. 考虑卫星综合运动的凝视成像仿真及质量评估方法及装置[P]. 中国:CN105136164B, 2019-04-05. |
| 14 | 杨秀彬, 林星辰. 低轨凝视卫星动态跟踪对成像的影响分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(): 203-208. |
| Yang Xiu-bin, Lin Xing-chen. Analysis of influence of LEO staring satellite dynamic tracking on imaging[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(Sup.1): 203-208. | |
| 15 | 汪志良. 基于数字地球的遥感卫星对地成像仿真研究[D]. 西安:西安电子科技大学电子工程学院, 2014. |
| Wang Zhi-liang. Imaging simulation of remote-sensing satellite based on digital earth[D]. Xi'an:School of Electronic Eengineering, Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2014. | |
| 16 | 曹平, 章文毅, 马广彬. 遥感卫星成像模型研究及仿真[J]. 遥感信息, 2014, 29(3): 62-66, 81. |
| Cao Ping, Zhang Wen-yi, Ma Guang-bin. Imaging model of remote sensing satellite and its simulation[J]. Remate Sensing Information, 2014, 29(3): 62-66, 81. | |
| 17 | 阮宁娟, 庄绪霞, 李妥妥, 等. 空间光学遥感系统全链路仿真与分析[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2013, 34(6): 36-43. |
| Ruan Ning-juan, Zhuang Xu-xia, Li Tuo-tuo, et al. End to end simulation and analysis of space optical remote sensing system[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(6): 36-43. | |
| 18 | 马晓珊, 孟新, 杨震, 等. 光学遥感成像系统全链路仿真框架研究[J]. 量子电子学报, 2012, 29(4): 392-399. |
| Ma Xiao-shan, Meng Xin, Yang Zhen, et al. Framework of entire image chains simulation for optical remote sensing images system[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2012, 29(4): 392-399. | |
| 19 | 黄晓敏. 机载光学遥感成像物理特性建模与仿真[D]. 西安:西安电子科技大学电子与通信工程学院, 2014. |
| Huang Xiao-min. The physics modeling and simulation of airborne optical remote sensing imaging[D]. Xi'an:School of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2014. | |
| 20 | Cui K, Xiang J, Zhang Y. Mission planning optimization of video satellite for ground multi-object staring imaging[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 61(6): 1476-1489. |
| 21 | 王家骐, 于平, 颜昌翔, 等. 航天光学遥感器像移速度矢计算数学模型[J]. 光学学报, 2004, 24(12): 1585-1589. |
| Wang Jia-qi, Yu Ping, Yan Chang-xiang, et.al. Space optical remote sensor image motion velocity vector computational modeling[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2004, 24(12): 1585-1589. | |
| 22 | 窦长勇, 岳昔娟. 轨道坐标系到地心固定坐标系的直接转换方法[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2016, 37(5): 86-94. |
| Dou Chang-yong, Yue Xi-juan. Direct transformation from orbital to earth-centered earth-fixed reference frame[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2016, 37(5): 86-94. | |
| 23 | 刘洋, 易东云, 王正明. 地心惯性坐标系到质心轨道坐标系的坐标转换方法[J]. 航天控制, 2007, 25(2): 4-8. |
| Liu Yang, Yi Dong-yun, Wang Zheng-ming. Coordinate transformation methods from the inertial system to the centroid orbit system[J]. Aerospace Control, 2007, 25(2): 4-8. | |
| 24 | 雷伟伟, 张捍卫, 李凯. 岁差章动模型更新等因素对坐标转换的影响[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2016, 35(1): 53-62. |
| Lei Wei-wei, Zhang Han-wei, Li Kai. Effects of precession-nutation models update, polar motion, difference between UT1 and TT on coordinate transformation[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2016, 35(1): 53-62. | |
| 25 | 刘晓东, 王鹏, 林元, 等. 敏捷卫星对目标访问信息的计算方法[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2016, 42(5): 23-26. |
| Liu Xiao-dong, Wang Peng, Lin Yuan, et al. Calculation method for access information of agile satellite on target[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2016, 42(5): 23-26. | |
| 26 | Driben R, Konotop V V, Meier T. Precession and nutation dynamics of nonlinearly coupled non-coaxial three-dimensional matter wave vortices[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 22758. |
| 27 | 张方照, 许国昌, Barriot Jean-Pierre. 岁差章动极移对轨道根数的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(6): 2205-2211. |
| Zhang Fang-zhao,Xu Guo-chang,Barriot Jean-Pierre. Keplerian orbit elements induced by precession, nutation and polar motion[J]. Progress in Geophysics,34(6): 2205-2211. | |
| 28 | 梁健,张润宁,王大伟,等. 敏捷SAR卫星视频成像模式的姿态机动策略[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2019, 36(1): 125-130. |
| Liang Jian, Zhang Run-ning, Wang Da-wei, et al. Attitude maneuver strategy of video mode based on agile SAR satellite[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 36(1): 125-130. | |
| 29 | 陈闽, 张世杰, 张迎春. 基于反作用飞轮和磁力矩器的小卫星姿态联合控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2010, 40(4): 1155-1160. |
| Chen Min, Zhang Shi-jie, Zhang Ying-chun. Combined attitude control method of small satellite using reaction wheels and magnetorquers[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(4): 1155-1160. | |
| 30 | 张刘,金光. 输入受限空间飞行器大角度机动控制器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2010, 40(4): 1166-1170. |
| Zhang Liu, Jin Guang. Large angle attitude maneuver control of spacecraft with bounded inputs[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(4): 1166-1170. | |
| 31 | 岳庆兴, 邱振戈, 张春玲, 等. 一种利用少量控制点的SPOT5地面点定位方法[J]. 遥感信息, 2008(2): 6-9. |
| Yue Qing-xing, Qiu Zhen-ge, Zhang Chun-ling, et al. A ground point positioning method of SPOT5 with a little control points[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2008(2): 6-9. | |
| 32 | 熊邦书, 吴铮, 俞华璟. 一种基于二维局部Lagrange插值的曲面重构算法[J]. 西安工程科技学院学报, 2003, 17(2): 138-141. |
| Xiong Bang-shu, Wu Zheng, Yu Hua-jing. A algorithm of surface reconstruction based on 2D local Lagrange interpolation[J]. Journal of Xi'an University Engineering Science and Technology, 2003, 17(2): 138-141. |
| [1] | Bao-feng YUAN,Cheng-en WANG,Meng ZOU,Ya-fang LIU,Yun-cheng LIN,Yang JIA,Bai-chao CHEN,Jing-fu JIN. Design active suspension system and creeping control strategy for mars rover of China [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 154-162. |
| [2] | Bai-chao CHEN,Meng ZOU,Zhao-long DANG,Han HUANG,Yang JIA,Rui-yang SHI,Jian-qiao LI. Experiment on pressure⁃sinkage for mesh wheels of CE⁃3lunar rover on lunar regolith [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. |
|
||