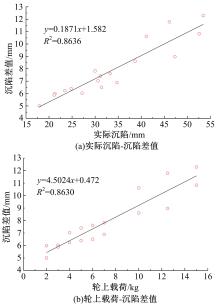
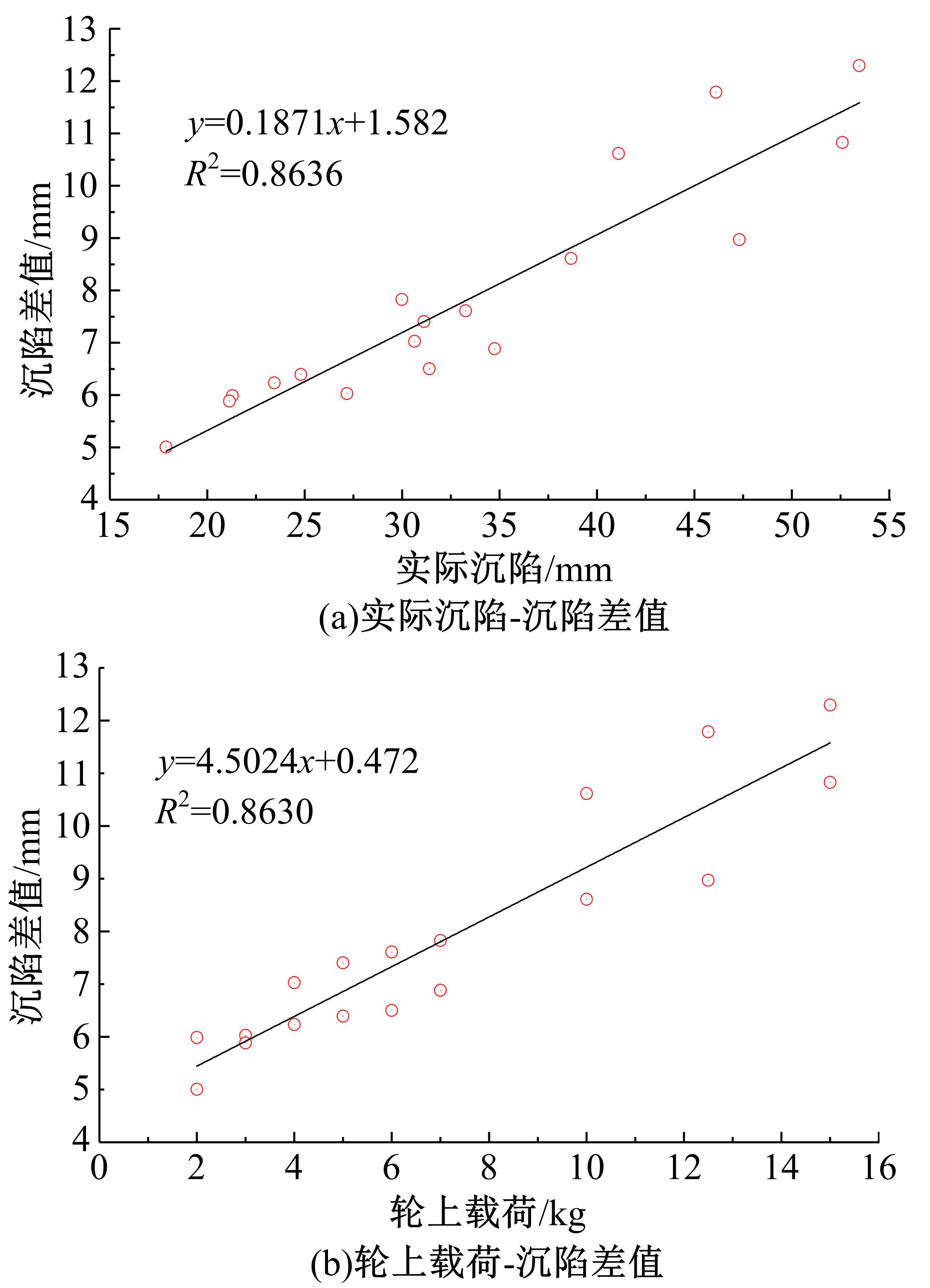
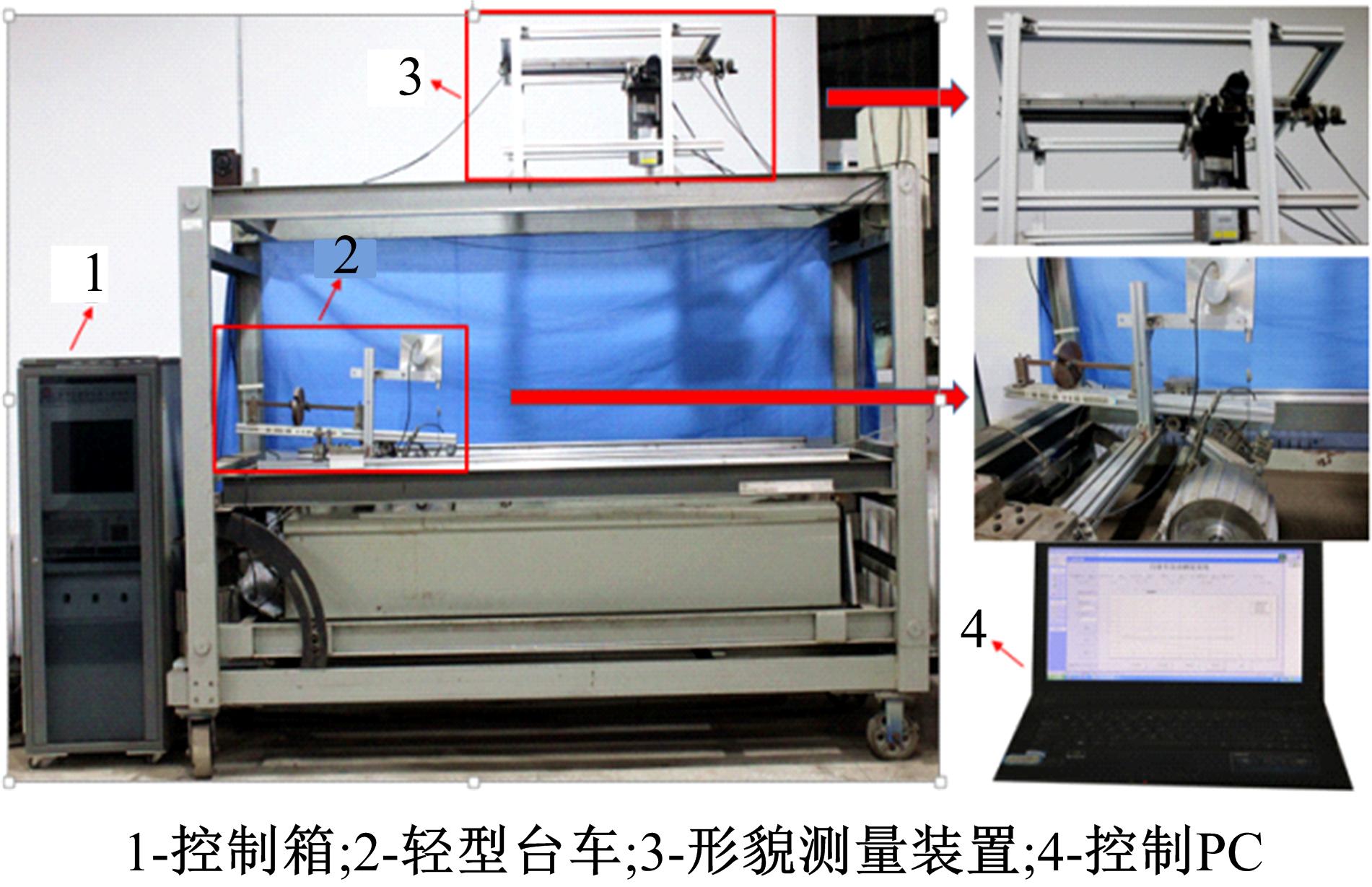
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1836-1843.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180904
Previous Articles Next Articles
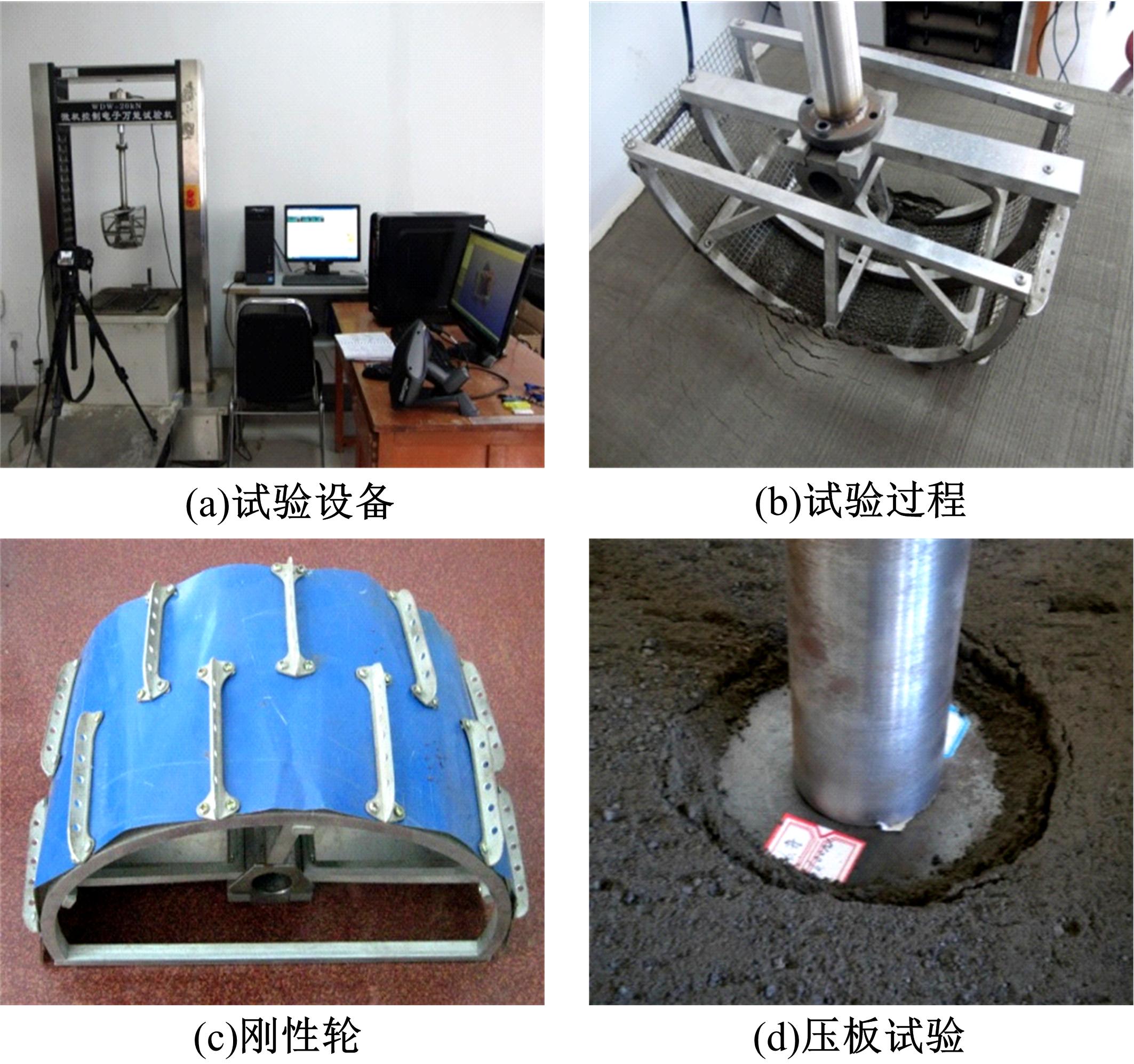
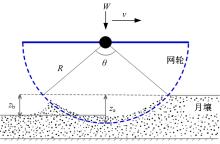
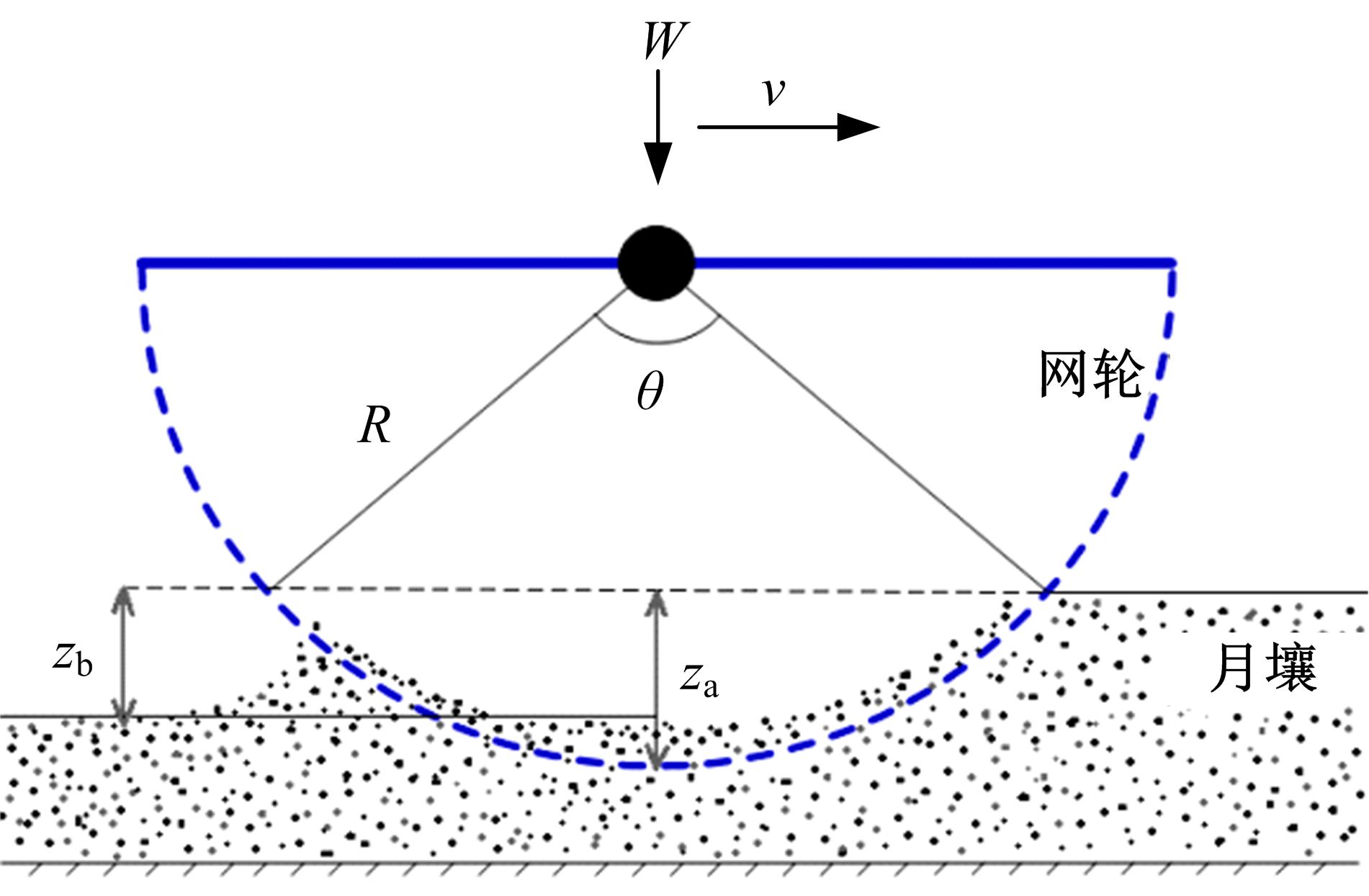
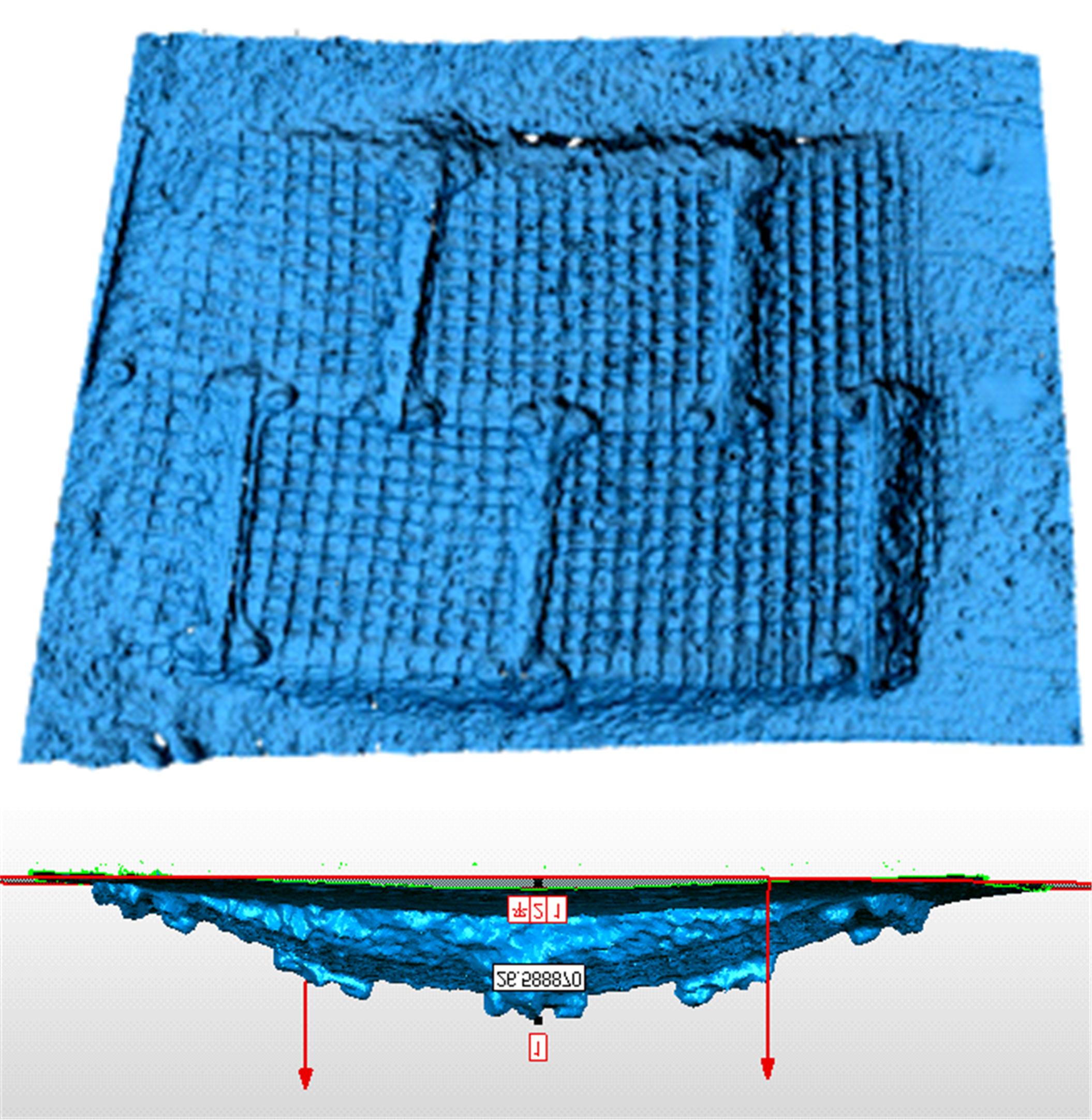
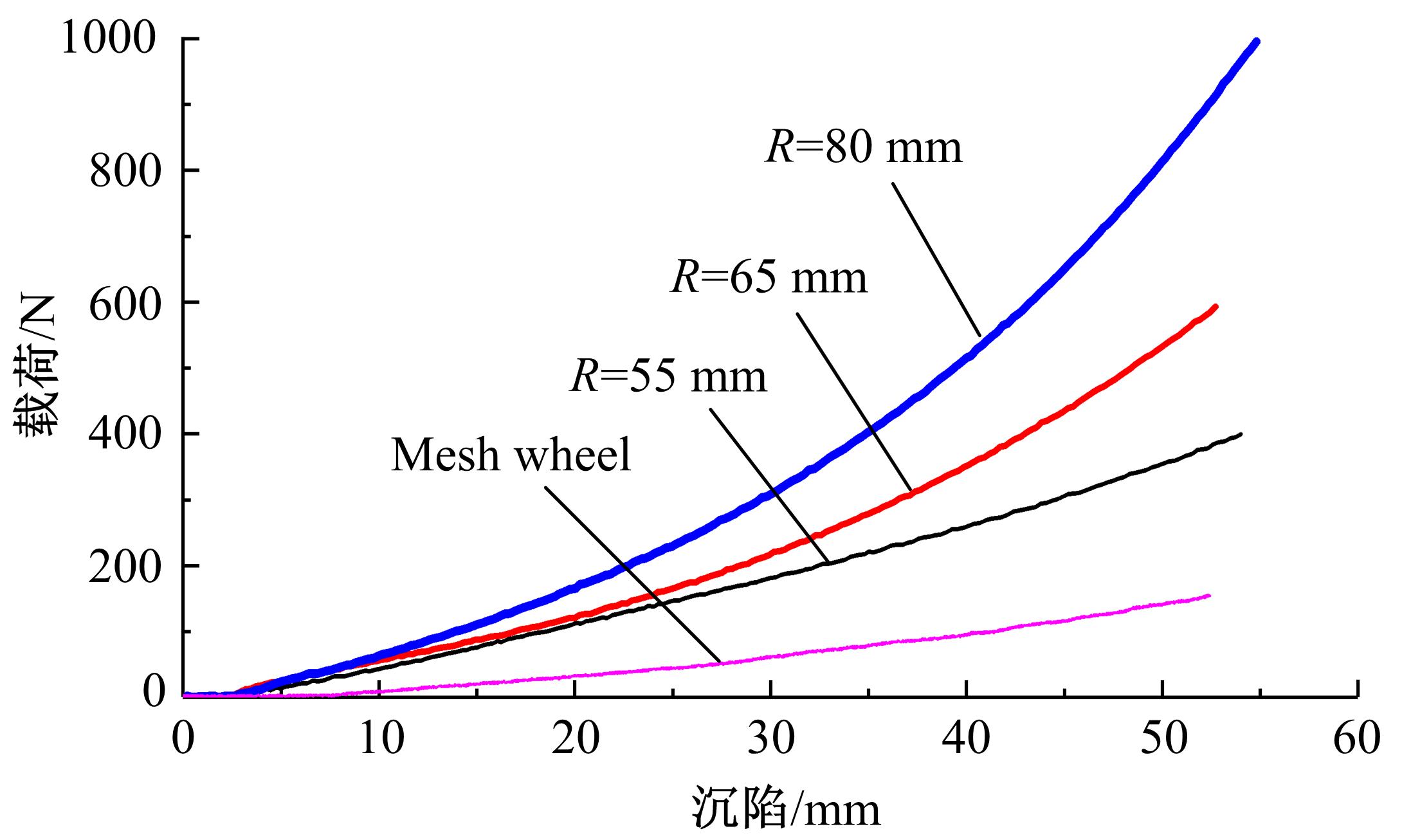
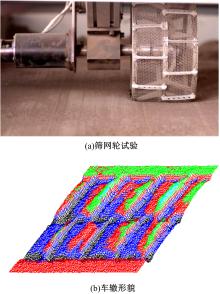
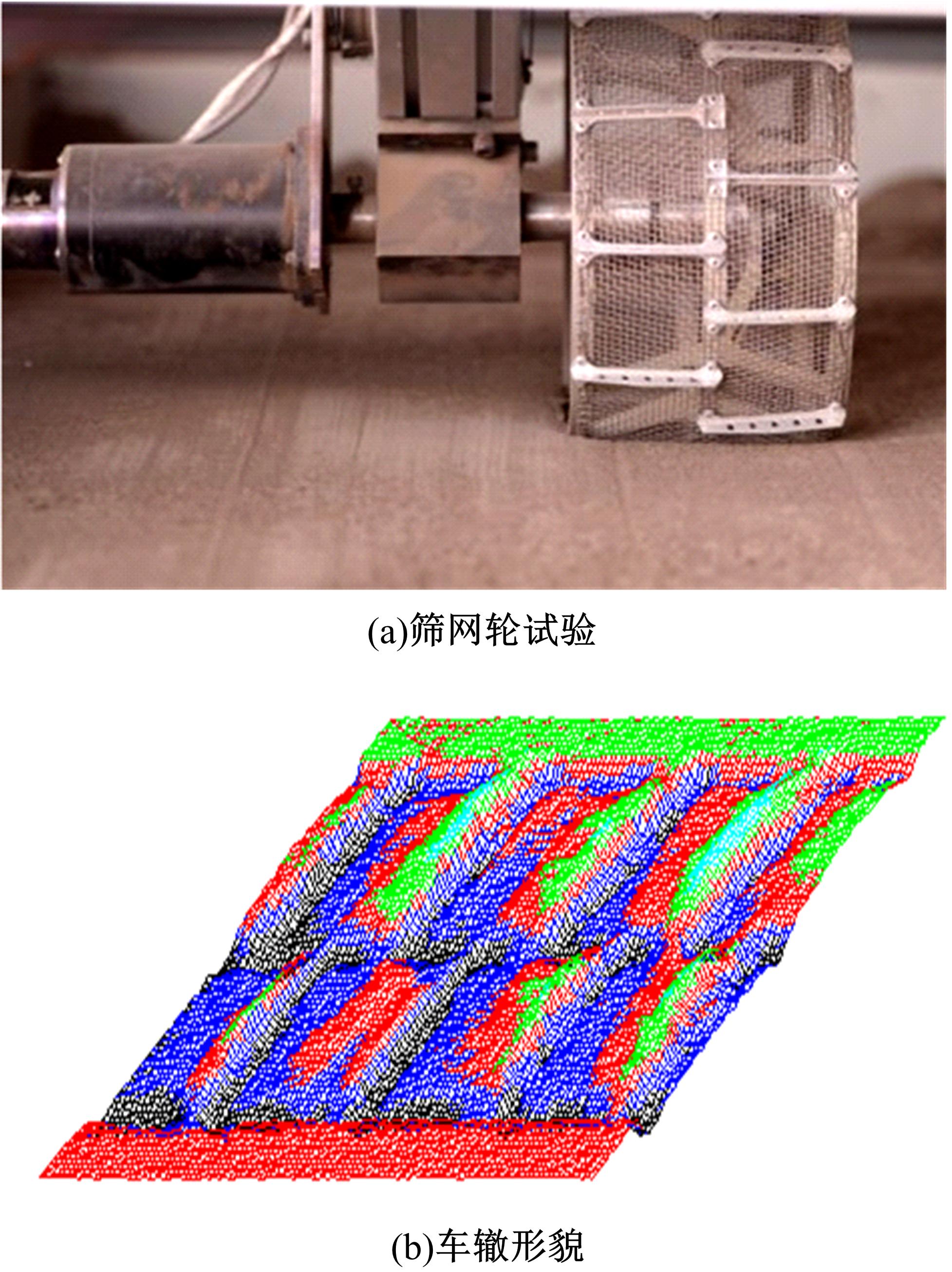
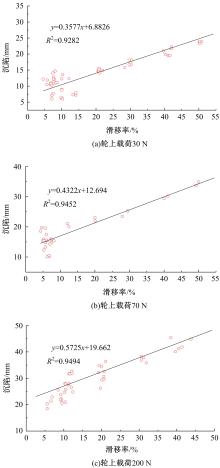
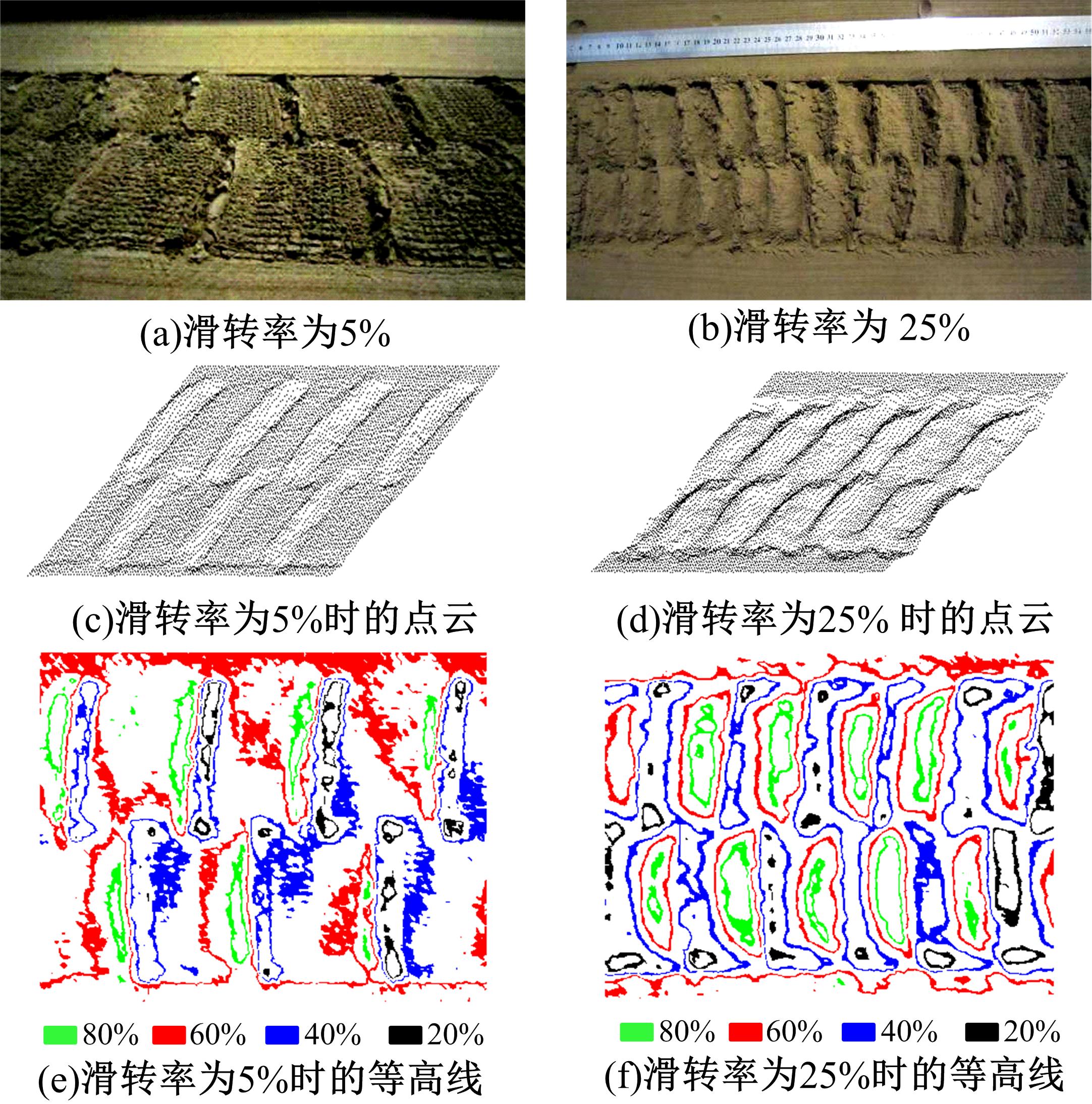
Experiment on pressure⁃sinkage for mesh wheels of CE⁃3lunar rover on lunar regolith
Bai-chao CHEN1( ),Meng ZOU2(
),Meng ZOU2( ),Zhao-long DANG1,Han HUANG2,Yang JIA1,Rui-yang SHI2,Jian-qiao LI2
),Zhao-long DANG1,Han HUANG2,Yang JIA1,Rui-yang SHI2,Jian-qiao LI2
- 1. Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering, China Academy of Space Technology, Beijing 100094, China
2. Key Laboratory of Bionics Engineering, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- V416
|
| [1] | Xin CHEN,Xin-jian RUAN,Ming LI,Ning WANG,Jia-ning WANG,Kai-xuan PAN. Application of modified discrete scheme based onlarge eddy simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1756-1763. |
| [2] | Ren HE,Kun TU. Electromagnetic brake with changed⁃temperature air gap width [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1777-1785. |
| [3] | Li-qiang JIN, Duan-yang TIAN, Hao TIAN, Meng-meng LIU. Brake force assistant technology for vehicle electronicstability control system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1764-1776. |
| [4] | Jie LI, Wen-cui GUO, Qi ZHAO, Sheng-feng GU. Road roughness identification based on vehicle responses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1810-1817. |
| [5] | Xin GUAN,Hao JIN,Chun-guang DUAN,Ping-ping LU. Estimation of lateral slope of vehicle driving road [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. |
| [6] | Yang WANG,Zhan⁃shuai SONG,Kong⁃hui GUO,Ye ZHUANG. Measurement of inertial parameters of rotating inertia rig [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1795-1801. |
| [7] | Qiao-bin LIU,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Lian-meng LUO,Zhi-yong SU,Kai-jun HUANG. Parameter estimation of mixed reliability model based on kernel density optimal grouping and gravity search algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1818-1825. |
| [8] | Wei-min ZHUANG,Yang LIU,Peng-yue WANG,Hong-da SHI,Ji-shuan XU. Simulation on peeling failure of self⁃piercing riveted joints insteel and aluminum alloy dissimilar sheets [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1826-1835. |
| [9] | Fang-wu MA,Li-wei NI,Liang WU,Jia-hong NIE,Guang-jian XU. Position and attitude closed loop control of wheel⁃leggedall terrain mobile robot [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| [10] | Fang-wu MA,Lu HAN,Yang ZHOU,Shi-ying WANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi material optimal design of vehicle product using polylactic acid composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1385-1391. |
| [11] | Zhen-hai GAO,Tian-jun SUN,Lei HE. Causal reasoning decision⁃making for vehicle longitudinal automatic driving [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. |
| [12] | Bo ZHANG,Jian-wei ZHANG,Kong-hui GUO,Hai-tao DING,Hong-qing CHU. Current control of permanent magnet synchronous motor for road feeling simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1405-1413. |
| [13] | Peng-yu WANG,Shi-jie ZHAO,Tian-fei MA,Xiao-yong XIONG,Xin CHENG. Vehicle multi-sensor target tracking and fusion algorithm based on joint probabilistic data association [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1420-1427. |
| [14] | Xing-jun HU,Zheng HUI,Peng GUO,Yang-hui ZHANG,Jing-long ZHANG,Jing-yu WANG,Fei LIU. Characteristics of aerodynamics for an automobile by fluid-structure coupled method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1414-1419. |
| [15] | Xiao-jian HAN,Wei-qiang ZHAO,Li-jun CHEN,Hong-yu ZHENG,Yang LIU,Chang-fu ZONG. Local path planning of bus based on RS-RRT algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1428-1440. |
|