Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2438-2446.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210298
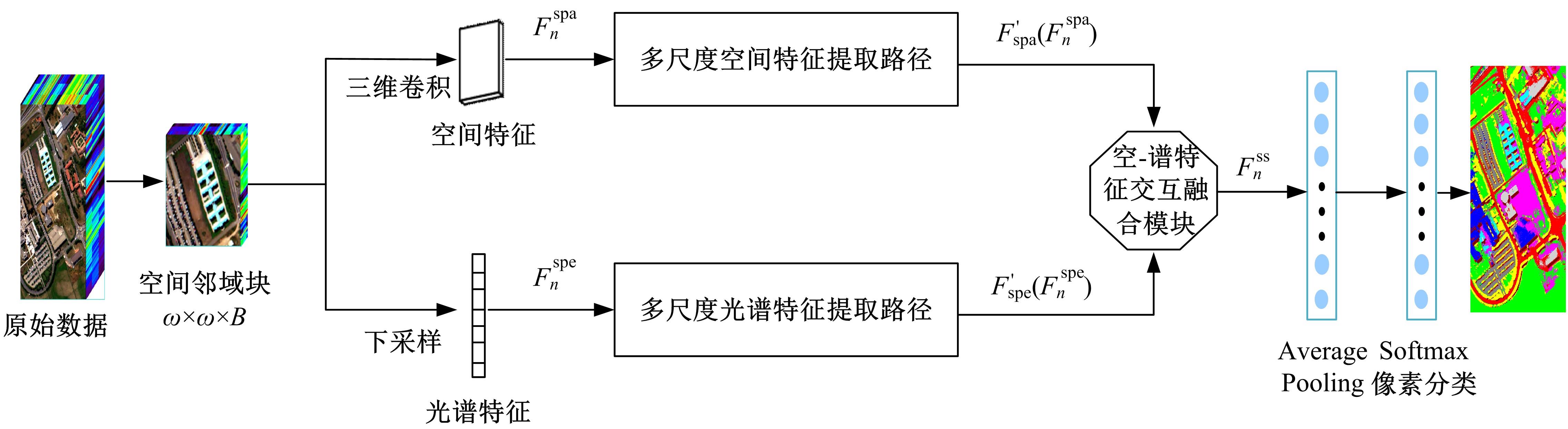
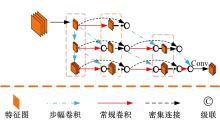
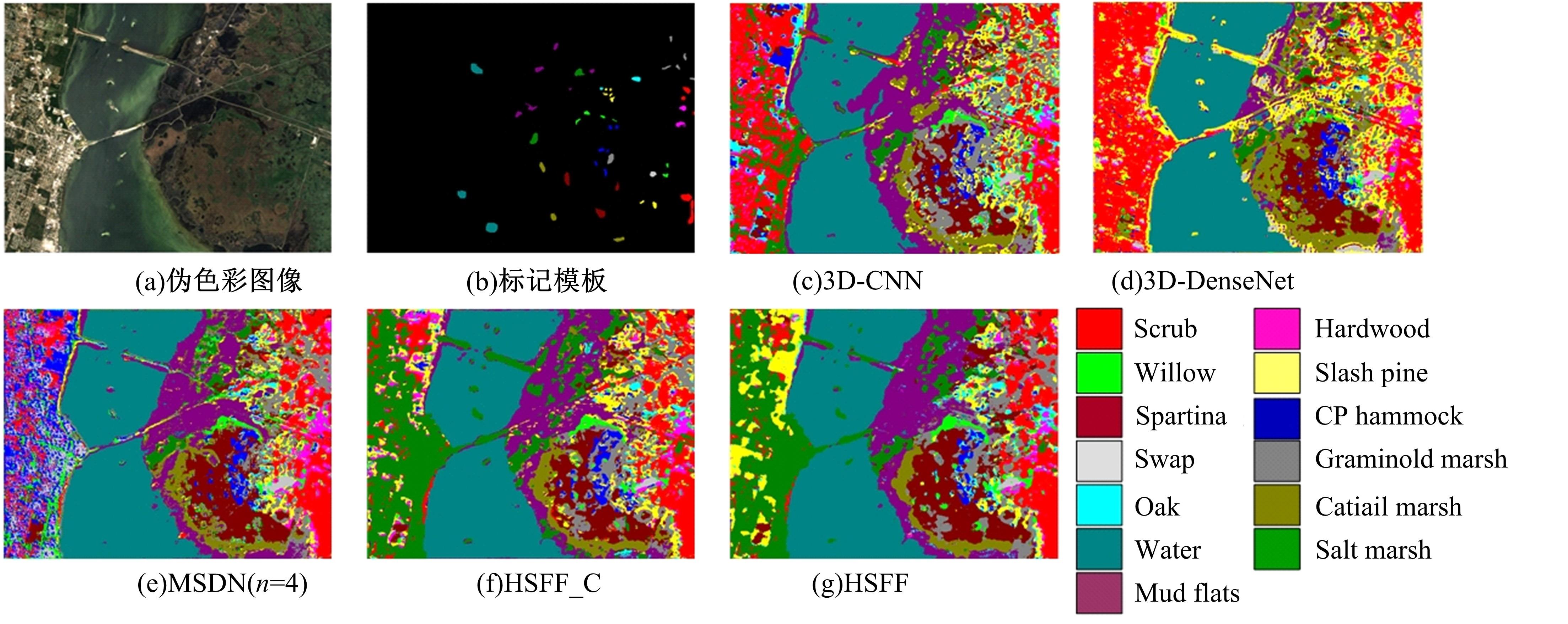
Hyperspectral image classification based on hierarchical spatial-spectral fusion network
Ning OUYANG( ),Zu-feng LI,Le-ping LIN(
),Zu-feng LI,Le-ping LIN( )
)
- School of Information and Communication,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
CLC Number:
- TP753
| 1 | Li W, Prasad S, Flower J E, et al. Locality-preserving dimensionality reduction and classification for hyperspectral image analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing,2012,50(4):1185-1198. |
| 2 | Li W, Chen C, Su H J, et al. Local binary patterns and extreme learning machine for hyperspectral imagery classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoence & Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 3681-3693. |
| 3 | Huang K, Li S, Kang X, et al. Spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification based on KNN[J]. Sensing and Imaging, 2016, 17(1):1-13. |
| 4 | 闫敬文, 陈宏达, 刘蕾. 高光谱图像分类的研究进展[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(3): 680-693. |
| Yan Jing-wen, Chen Hong-da, Liu Lei. Overiew of hyperspectral image classification[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 680-693. | |
| 5 | Zhang H, Li Y, Zhang Y, et al. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery using a dual-channel convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(5):438-447. |
| 6 | Ouyang N, Zhu T, Lin L P. Convolutional neural network trained by joint loss for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 16(3): 457-461. |
| 7 | Qing Y, Liu W. Hyperspectral image classification based on multi-scale residual network with attention mechanism[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(3):No.335. |
| 8 | Zhu M H, Jiao L C, Liu F, et al. Residual spectral–spatial attention network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59(1): 449-462. |
| 9 | 欧阳宁, 朱婷, 林乐平. 基于空-谱融合网络的高光谱图像分类方法[J].计算机应用, 2018, 38(7): 1888-1892. |
| Ouyang Ning, Zhu Ting, Lin Le-ping. Spatial-spetral fusion network for hyperspectral image classification method[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(7): 1888-1892. | |
| 10 | Roy S K, Krishna G, Dubey S R, et al. HybridSN: exploring 3D-2D CNN feature hierarchy for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(2): 277-281. |
| 11 | Li Y, Zhang H K, Shen Q. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(1): 67-87. |
| 12 | Zhang C, Li G, Du S, et al. Three-dimensional densely connected convolutional network for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2019, 13(1):No.16519. |
| 13 | Zhang C J, Li G D, Du S H, et al. Multi-scale dense networks for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9201-9222. |
| 14 | Wang W, Dou S, Jiang Z, et al. A fast dense spectral-spatial convolution network framework for hyperspectral images classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): No.1068. |
| 15 | Zhu M H, Jiao L C, Liu F, et al. Residual spectral–spatial attention network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59(1): 449-462. |
| 16 | Huang G, Chen D, Li T, et al. Multi-scale dense networks for resource efficient image classification[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1-14. |
| 17 | Chang Y H, Xu J T, Gao Z Y. Multi-scale dense attention network for stereo matching[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(11):1881-1892. |
| 18 | Lu J, Yang J W, Batra D, et al. Hierarchical question-image co-attention for visual question answering[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 289-297. |
| 19 | Ma H Y, Li Y J, Ji X P, et al. MsCoa: multi-step co-attention model for multi-label classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 109635-109645. |
| 20 | Li M N, Tei K J, Fukazawa Y. An efficient adaptive attention neural network for social recommendation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 63595-63606. |
| [1] | Xiao-ying PAN,De WEI,Yi-zhe ZHAO. Detecetion of lung nodule based on mask R-CNN and contextual convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2419-2427. |
| [2] | Da-ke ZHOU,Chao ZHANG,Xin YANG. Self-supervised 3D face reconstruction based on multi-scale feature fusion and dual attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [3] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Dong-sheng HUO,Jie WANG,Xiao-ning LI. Image classification of insect pests based on saliency detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [4] | WANG Sheng-sheng, GUO Xu, ZHANG Jia-chen, WANG Guang-yao, ZHAO Xin. Shape recognition algorithm based on fusion of global and local properties [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1627-1632. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hao, LIU Hai-ming, WU Chun-guo, ZHANG Yan-mei, ZHAO Tian-ming, LI Shou-tao. Detection method of vehicle in highway green toll lane based on multi-feature fusion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 271-276. |
| [6] | YANG Xin,LIU Jia,ZHOU Peng-yu,ZHOU Da-ke. Adaptive particle filter for object tracking based on fusing multiple features [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 533-539. |
| [7] | WU Di, CAO Jie. Multi-feature fusion face recognition based on KRWDA algorithm under smart environment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 439-443. |
| [8] | WANG Xin-ying, LIU Gang, GU Fang-ming, XIAO Wei. Heterogeneous feature fusion method based on semantic and shape for 3D model retrieval [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 359-363. |
| [9] | QU Zhi-guo, WANG Ping, GAO Ying-hui, WANG Peng, SHEN Zhen-kang, LI Jiang. Edge detection based on feature fusion of USAN area [J]. , 2012, (03): 759-765. |
| [10] | CHEN Mian-Shu, FU Ping, LI Yong, ZHANG Hui. Image feature fusion based on scope similarity scores minimization [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 365-0368. |
| [11] | WANG Ying, LI Wen-Hui. Highprecision video flame detection algorithm base on multifeature fusion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 769-0775. |
| [12] | SHANG Fei, MA Jun-Xiao, YAO Li, TIAN Di, QIU Chun-Ling. Multifeature fusion based method for monitoring working status of instruments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 545-0548. |
| [13] | ZHENG Ya-yu,TIAN Xiang,CHEN Yao-wu. Visual attention model based on fussion of spatiotemporal features [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(06): 1625-1630. |
|
||