Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2573-2580.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221082
Previous Articles Next Articles
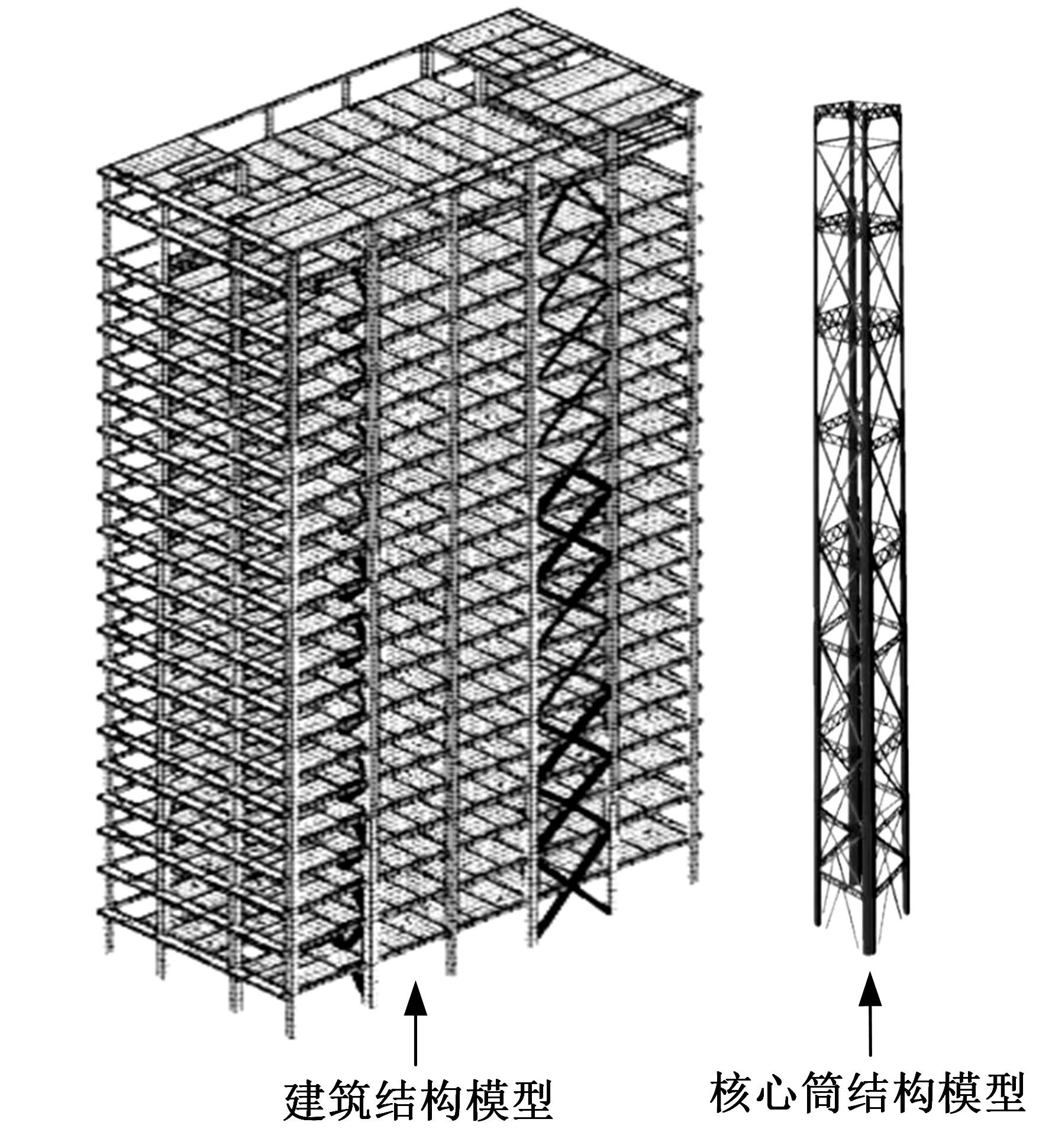
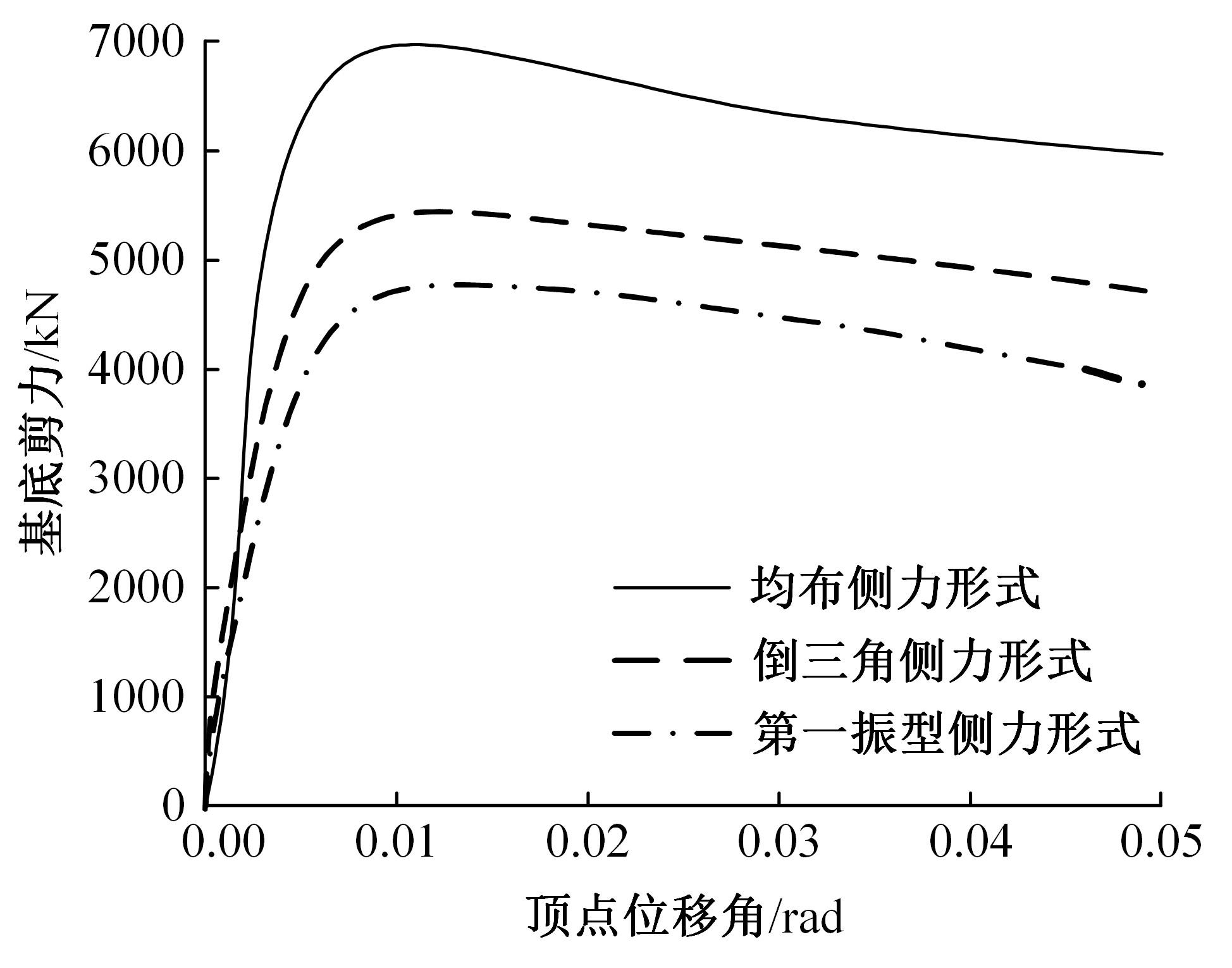
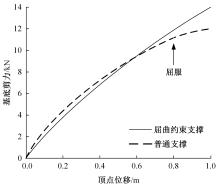
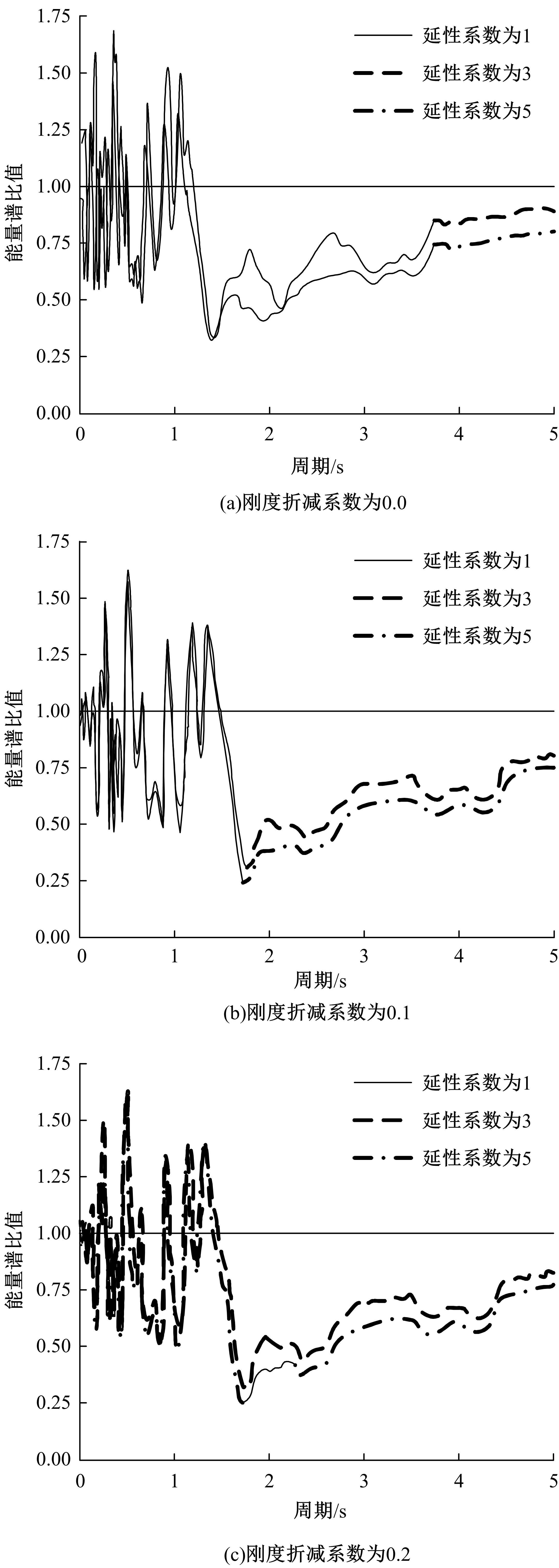
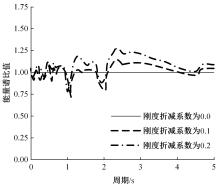
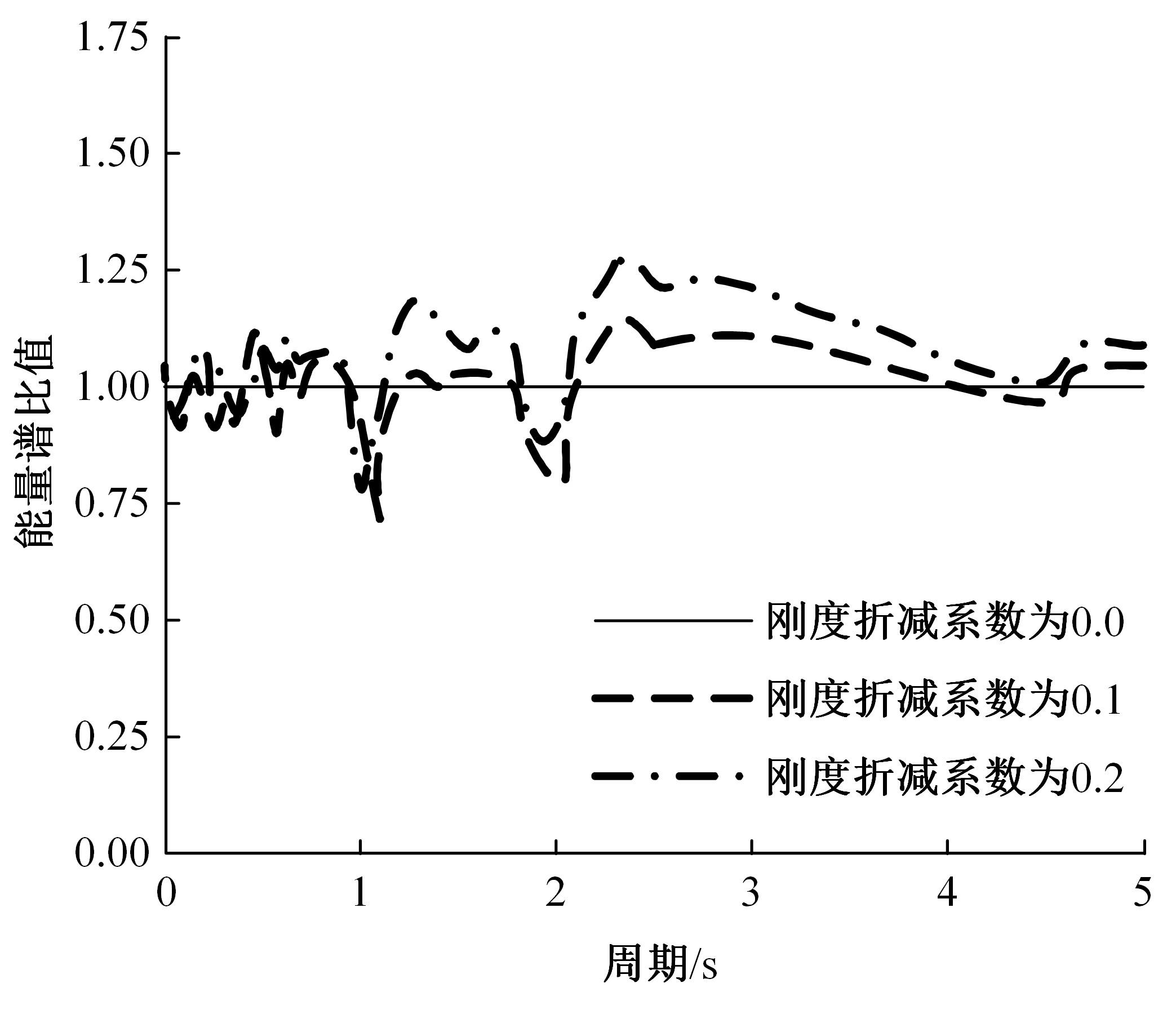
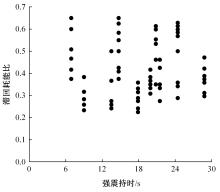
Seismic performance simulation of high⁃rise concrete core tube based on static nappe analysis algorithm
Ming LEI( ),Si-yang YIN,De-ling WANG,Ji-cheng ZHANG(
),Si-yang YIN,De-ling WANG,Ji-cheng ZHANG( ),Shi-wei LU
),Shi-wei LU
- School of Urban Construction,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
CLC Number:
- TU971
| 1 | 郭天祥. 基于大震动力弹塑性分析的某超高层混合结构抗震设计[J]. 建筑结构, 2020, 50(16): 64-70. |
| Guo Tian-xiang. Seismic design of a super high-rise hybrid structure based on dynamic elastoplastic analysis under rare earthquake[J]. Building Structure, 2020, 50(16): 64-70. | |
| 2 | 李永梅, 王浩, 彭凌云, 等. 填充墙钢筋混凝土框架结构基于位移的改进抗震设计方法[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2019, 40(6): 125-132. |
| Li Yong-mei, Wang Hao, Peng Ling-yun, et al. Advanced displacement-based seismic design method of reinforced concrete frame structures with infill wall[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2019, 40(6): 125-132. | |
| 3 | 倪茜, 张斌, 李锦锦. 基于静力弹塑法方法的碳纤维加固框架结构抗震性能分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2020, 50(2): 104-108, 112. |
| Ni Qian, Zhang Bin, Li Jin-jin.Seismic performance analysis of carbon fiber reinforced frame structures based on static elastic-plastic method[J].Industrial Construction, 2020, 50(2): 104-108, 112. | |
| 4 | 卢啸. 钢筋混凝土框架核心筒结构地震韧性评价[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2021, 42(5): 55-63. |
| Lu Xiao. Seismic resilience evaluation of reinforced concrete frame core tube structure[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2021, 42(5): 55-63. | |
| 5 | 寇俊敏, 苍雁飞. 建筑框架-核心筒结构静力弹塑性参数优化[J]. 计算机仿真, 2020, 37(9): 189-193. |
| Kou Jun-min, Cang Yan-fei. Optimization of static elastoplastic parameters of frame core tube structure[J]. Computer Simulation, 2020, 37(9): 189-193. | |
| 6 | 贺星新, 朱金坤, 刘斌, 等. 吴江某超高层塔楼结构抗震设计与分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2021, 51(): 676-682. |
| He Xing-xin, Zhu Jin-kun, Liu Bin, et al. Seismic design and analysis of a super tall tower in Wujiang[J]. Building Structure, 2021, 51(Sup.1): 676-682. | |
| 7 | 肖从真, 李建辉, 陆宜倩, 等. C100高强混凝土框架-核心筒高层建筑结构抗震性能研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2021, 37(3): 1-7. |
| Xiao Cong-zhen, Li Jian-hui, Lu Yi-qian, et al. Research on seismic performance of frame-core tube high-rise building structure with C100 high-strength concrete[J]. Building Science, 2021, 37(3): 1-7. | |
| 8 | 曲扬, 罗永峰, 黄青隆, 等. 格构拱结构动力响应评估的改进模态推覆分析法[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 47(1): 1-8. |
| Qu Yang, Luo Yong-feng, Huang Qing-long, et al. An improved modal pushover analysis procedure for estimating seismic responses of latticed arch[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2019, 47(1): 1-8. | |
| 9 | 郝润霞, 王谋庭, 贾硕, 等. 基于拟力法的框架结构静力推覆分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(5): 1028-1035. |
| Hao Run-xia, Wang Mou-ting, Jia Shuo, et al. Static pushover analysis of frame structure based on force analogy method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(5): 1028-1035. | |
| 10 | 陈安英, 朱光超, 完海鹰, 等. 斜交网格钢框架-混凝土核心筒结构施工变形控制数值模拟[J]. 工业建筑, 2021, 51(2): 76-82. |
| Chen An-ying, Zhu Guang-chao, Wan Hai-ying, et al.Numerical simulation of deformation control for a hybrid structure combined with diagrid structure and concrete core tube[J]. Industrial Construction, 2021, 51(2): 76-82. | |
| 11 | 吴轶, 林柱帆, 杨春, 等. 带高强混凝土钢板剪力墙的超高层框架-核心筒结构抗震性能研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2019, 49(8): 9-15. |
| Wu Yi, Lin Zhu-fan, Yang Chun, et al. Study on seismic performances of super high-rise frame-corewall structure with high strength concrete composite steel plate shear walls[J]. Building Structure, 2019, 49(8): 9-15. | |
| 12 | 李英民, 姜宝龙, 张梦玲, 等. 重庆高科太阳座大厦模型结构振动台试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2019, 40(3): 142-151. |
| Li Ying-min, Jiang Bao-long, Zhang Meng-ling, et al. Shaking table test on model structure of Chongqing Gaoke sun constellation mansion[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2019, 40(3): 142-151. | |
| 13 | 唐建余, 潘文, 董卫青, 等. 某超高层框架-钢筋混凝土核心筒结构减震案例分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2021, 47(7): 55-59. |
| Tang Jian-yu, Pan Wen, Dong Wei-qing, et al. Case study on seismic response of one super high rise frame reinforced concrete core tube structure[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 47(7): 55-59. | |
| 14 | 曾繁良, 黄炎生, 周靖. 钢管混凝土柱排架-核心筒结构抗震性能研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(12): 190-197. |
| Zeng Fan-liang, Huang Yan-sheng, Zhou Jing. A study on the seismic performance of concrete-filled steel tube column-steel shelf-concrete core tube structures[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(12): 190-197. | |
| 15 | 吴轶, 杨春, 王俊然, 等. 新型带耗能支撑-分散核心筒结构的抗震性能研究[J]. 工程抗震与加固改造, 2020, 42(5): 133-140, 147. |
| Wu Yi, Yang Chun, Wang Jun-ran, et al. Study on seismic performances of a new decentralized core tubes structure with energy dissipating braces[J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 2020, 42(5):133-140, 147. |
| No related articles found! |
|