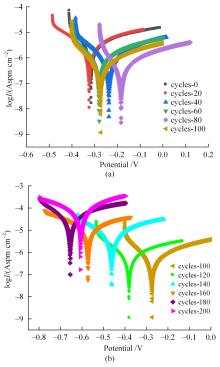
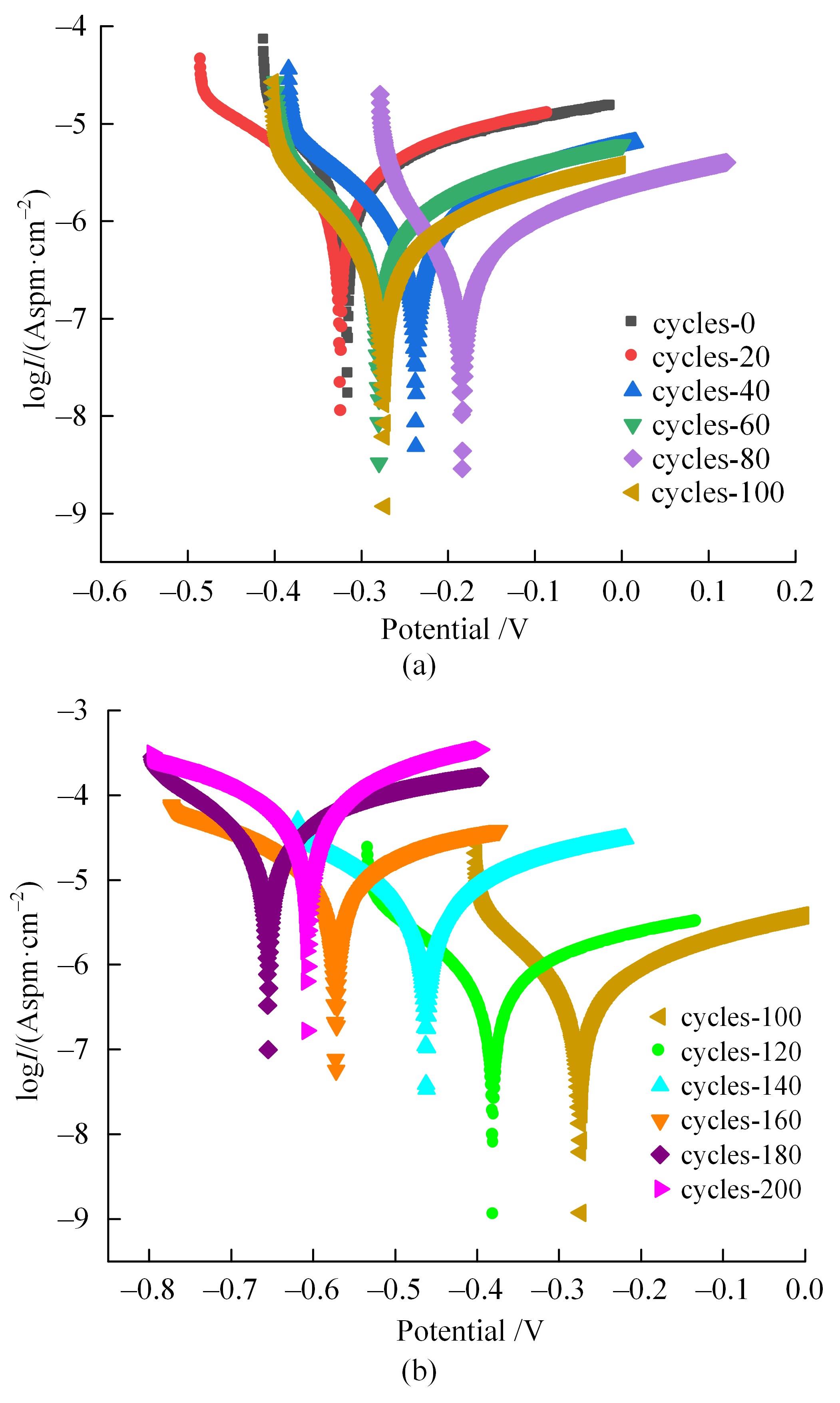
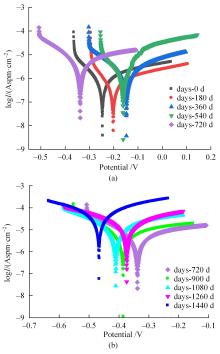
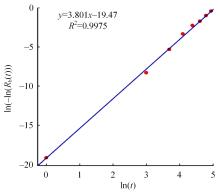
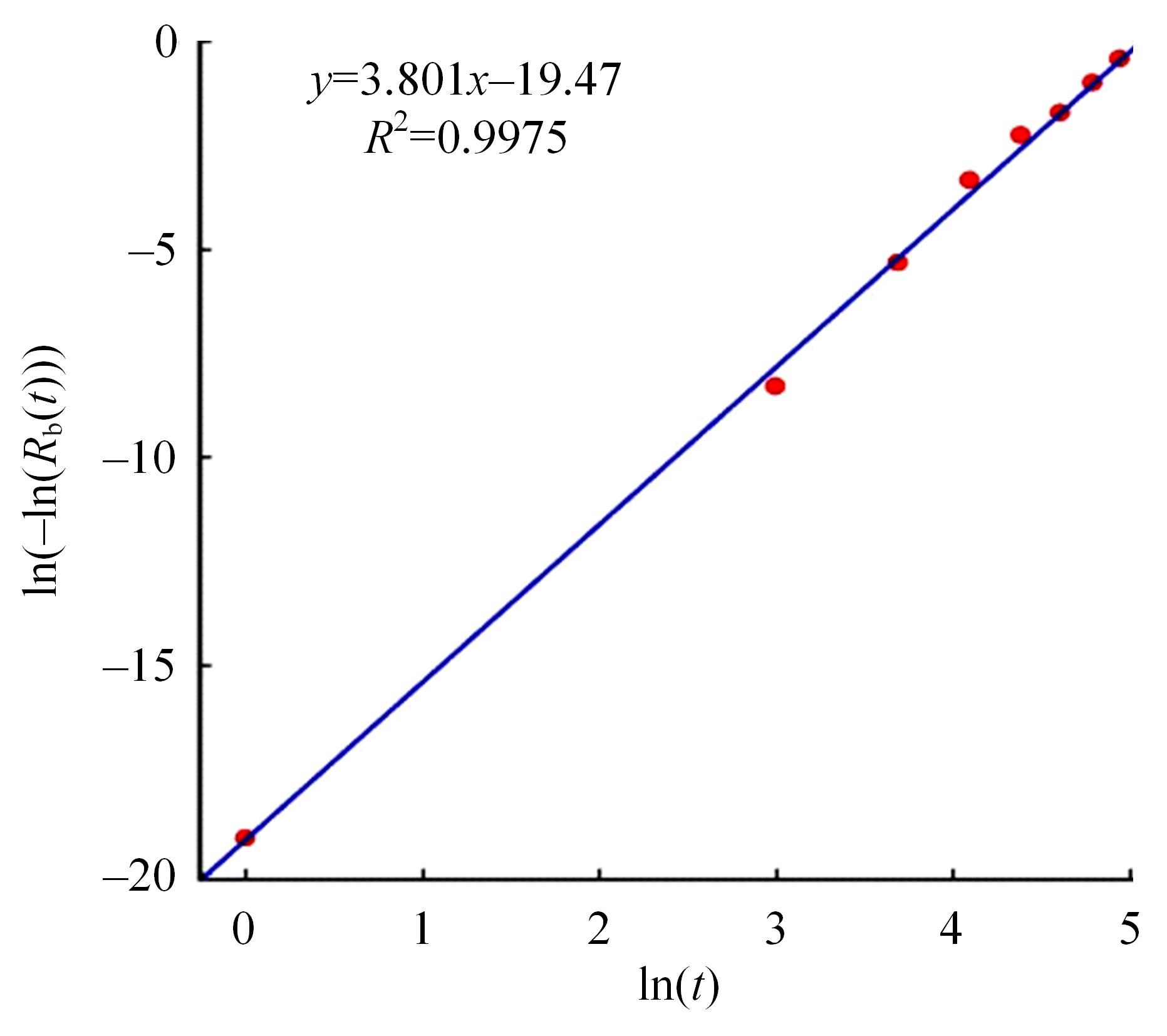
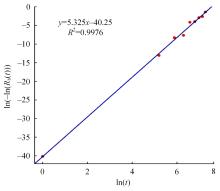
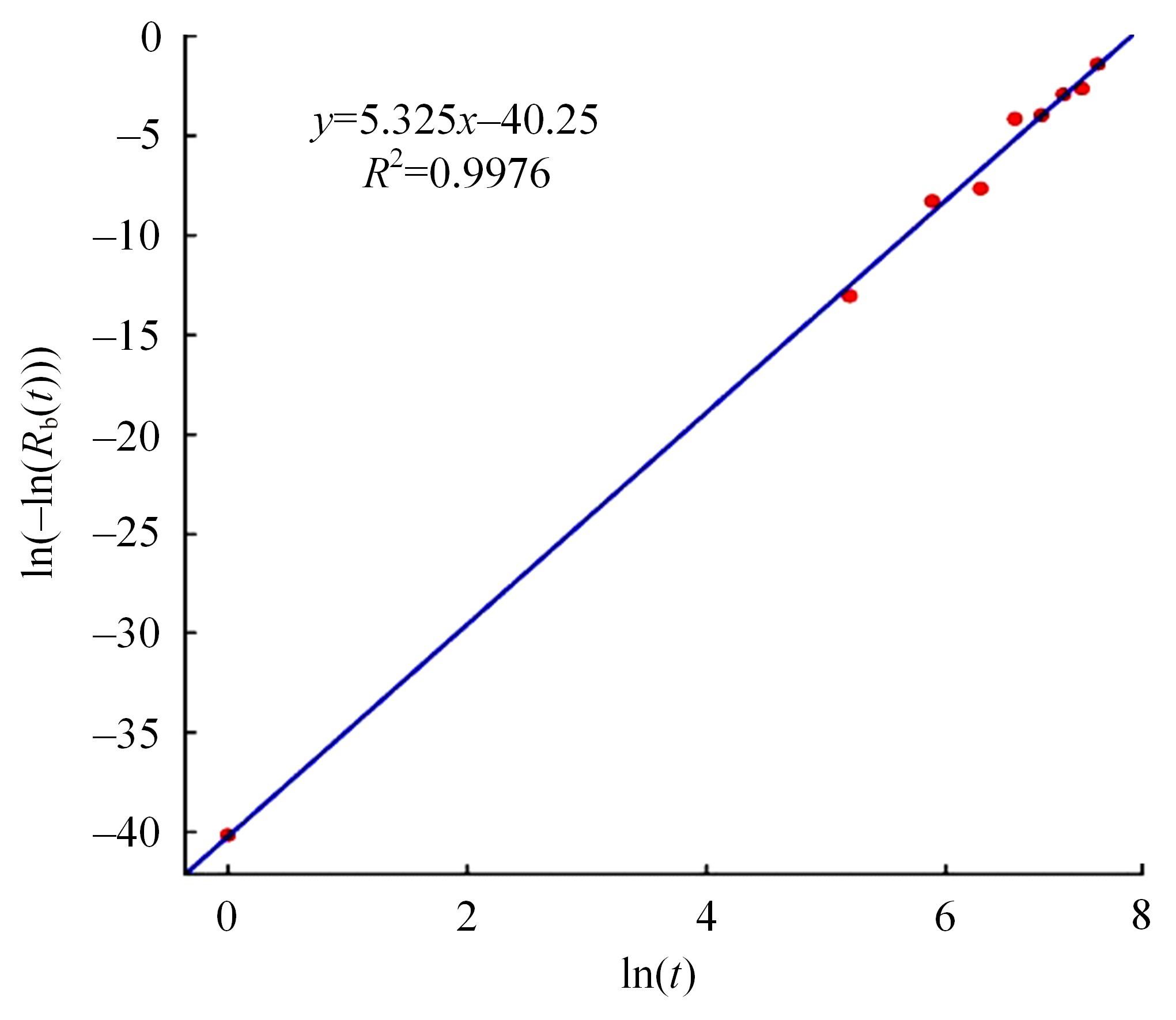
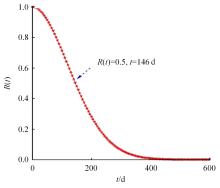
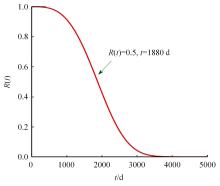
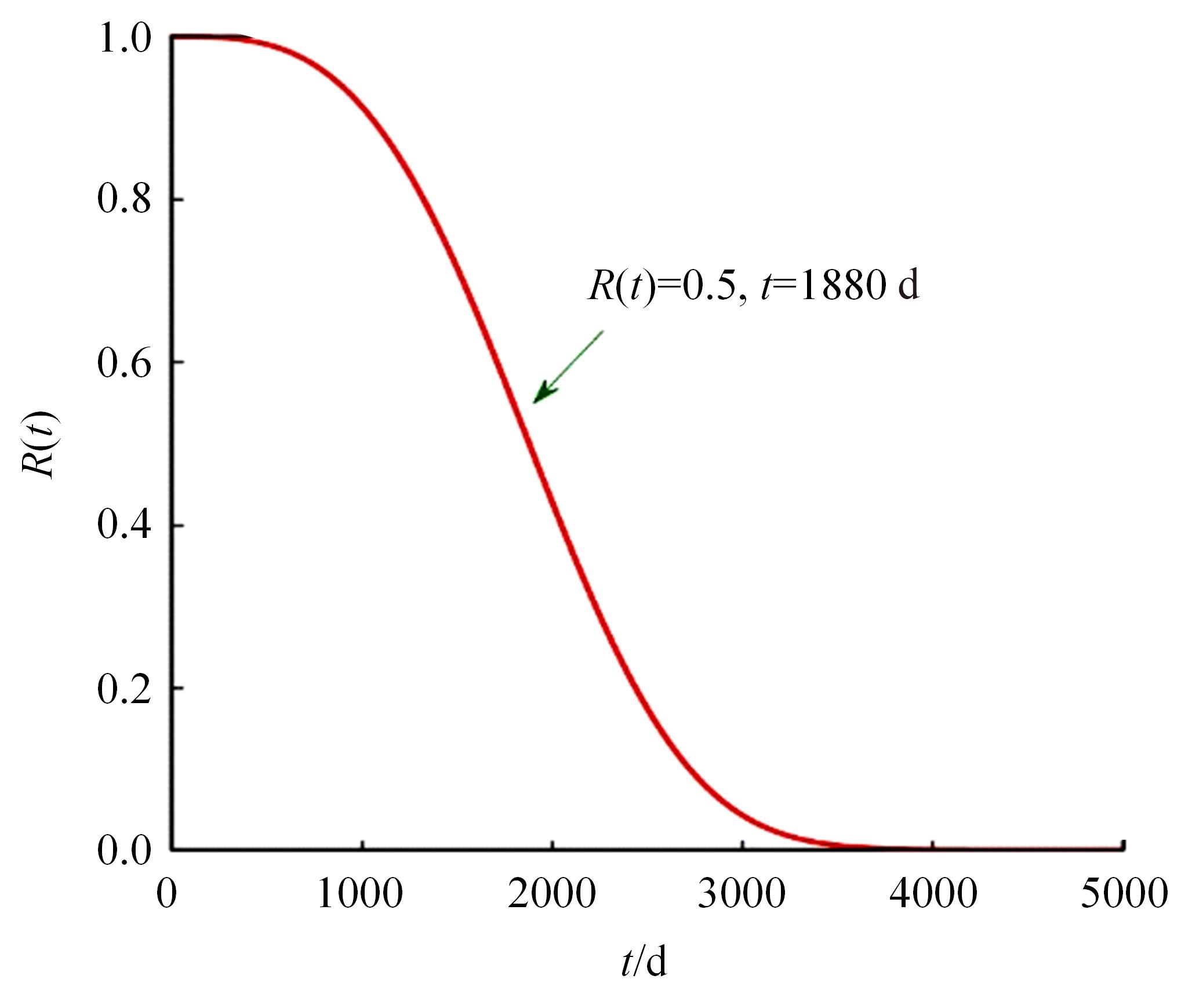
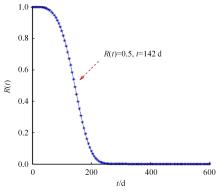
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 494-505.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220414
Corrosion deterioration and equivalent relationship between natural exposure and salt spray accelerated environment of reinforced concrete
Qiong FENG1( ),Hao-zheng TIAN1,Hong-xia QIAO1,2(
),Hao-zheng TIAN1,Hong-xia QIAO1,2( ),Teng-fei NIAN1,Wen-wen HAN1
),Teng-fei NIAN1,Wen-wen HAN1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Western Ministry of Civil Engineering Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering Research Center,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
CLC Number:
- TU528.1
| 1 | 余波,毋铭,詹雷颖. 混凝土中钢筋的腐蚀速率模型及电化学参数分析[J]. 混凝土, 2015(8): 20-25. |
| Yu Bo, Wu Ming, Zhan Lei-ying. Corrosion rate model and electrochemical parameters analysis of reinforcing steel in concrete[J]. Concrete, 2015(8): 20-25. | |
| 2 | 刘军,邢锋. 盐雾环境下氯离子在混凝土中的扩散[J]. 深圳大学学报: 理工版, 2010, 27(2): 192-198. |
| Liu Jun, Xing Feng. Diffusion of chloride ions in concrete under salt spray environment[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University (Science and Technology Edition), 2010, 27(2): 192-198. | |
| 3 | 关博文,杨涛,於德美,等. 干湿循环作用下钢筋混凝土氯离子侵蚀与寿命预测[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(10): 152-157. |
| Guan Bo-wen, Yang Tao, Yu De-mei, et al. Prediction of chloride ion erosion and lifetime of reinforced concrete under the action of dry and wet cycles[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(10): 152-157. | |
| 4 | 张云升,黄冉,杨永敢,等. 杂散电流-盐卤耦合作用下钢筋混凝土腐蚀行为[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(3): 449-455. |
| Zhang Yun-sheng, Huang Ran, Yang Yong-gan, et al. Corrosion behavior of reinforced concrete under the action of stray current-salt brine coupling[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2017, 20(3): 449-455. | |
| 5 | 宿晓萍, 王清. 复合盐浸-冻融-干湿多因素作用下的混凝土腐蚀破坏[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(1): 112 -120. |
| Su Xiao-ping, Wang Qing. Corrosion damage of concrete under multi-salt soaking, freezing-thawing and dry-wet cycles[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(1): 112 -120. | |
| 6 | 涂永明,吕志涛. 应力状态下混凝土结构的盐雾侵蚀试验研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2004, 34(5): 1-3. |
| Tu Yong-ming, Lv Zhi-tao. Experimental study on salt spray erosion of concrete structures under stress condition [J]. Industrial Construction, 2004, 34(5): 1-3. | |
| 7 | 王元站,周海锋. 盐雾环境下受荷混凝土中氯离子扩散试验[J]. 材料科学与工程, 2013, 31(5): 645-650. |
| Wang Yuan-zhan, Zhou Hai-feng. Chloride ion diffusion test in salt spray loaded concrete[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2013, 31(5): 645-650. | |
| 8 | 李林,丁士君,李镜培,等. 不同环境条件下混凝土构件氯离子侵蚀试验[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48(12): 28-33. |
| Li Lin, Ding Shi-jun, Li Jing-pei, et al. Experiments on chloride ion erosion of concrete members under different environmental conditions[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016, 48(12): 28-33. | |
| 9 | Maslehuddin M, Alzaharni M M, Aldulaijan S U, et al. Effect of steel manufacturing process and atmospheric corrosion on the corrosion-resistance of steel bars in concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2002, 24(1): 151-158. |
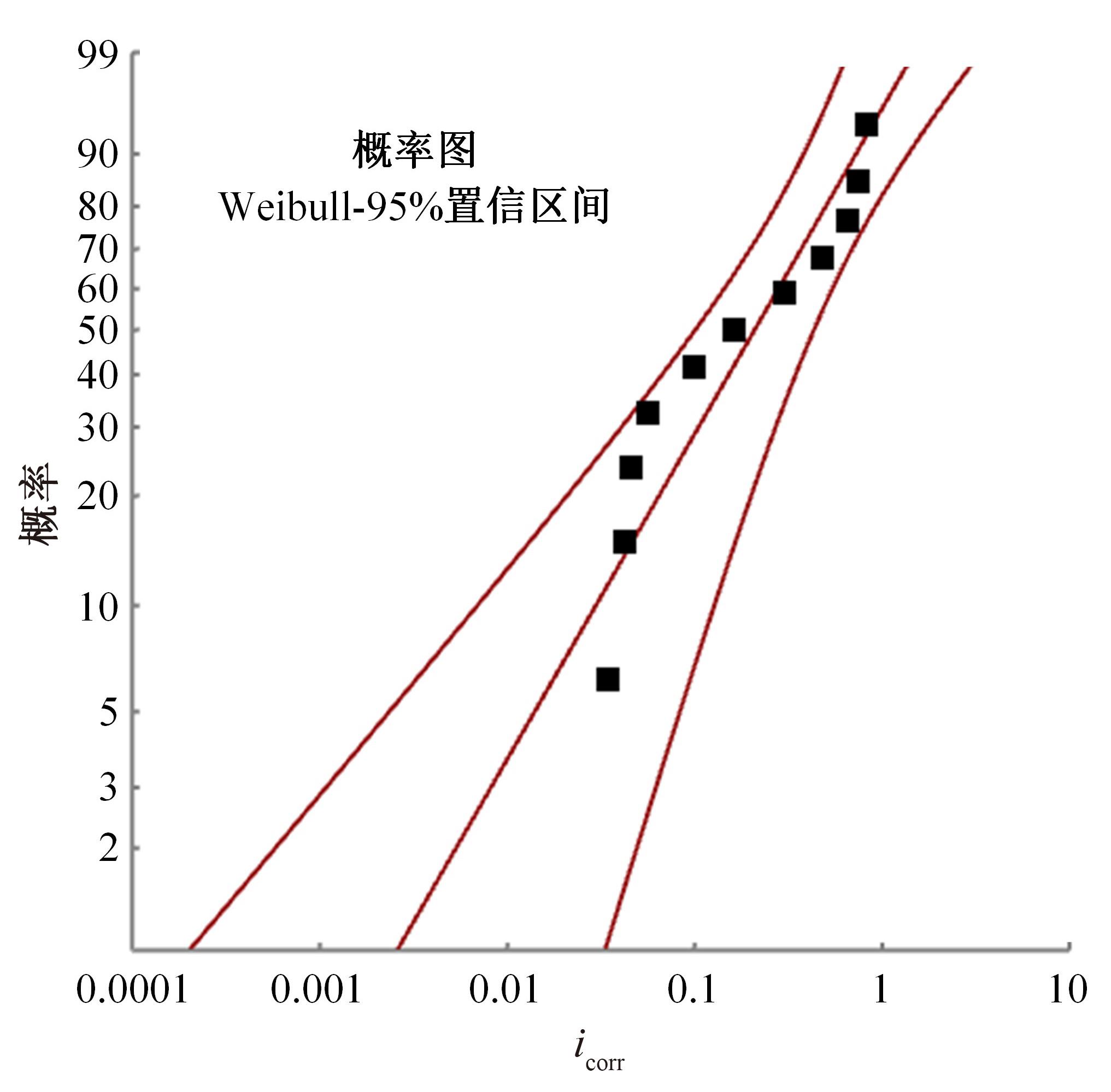
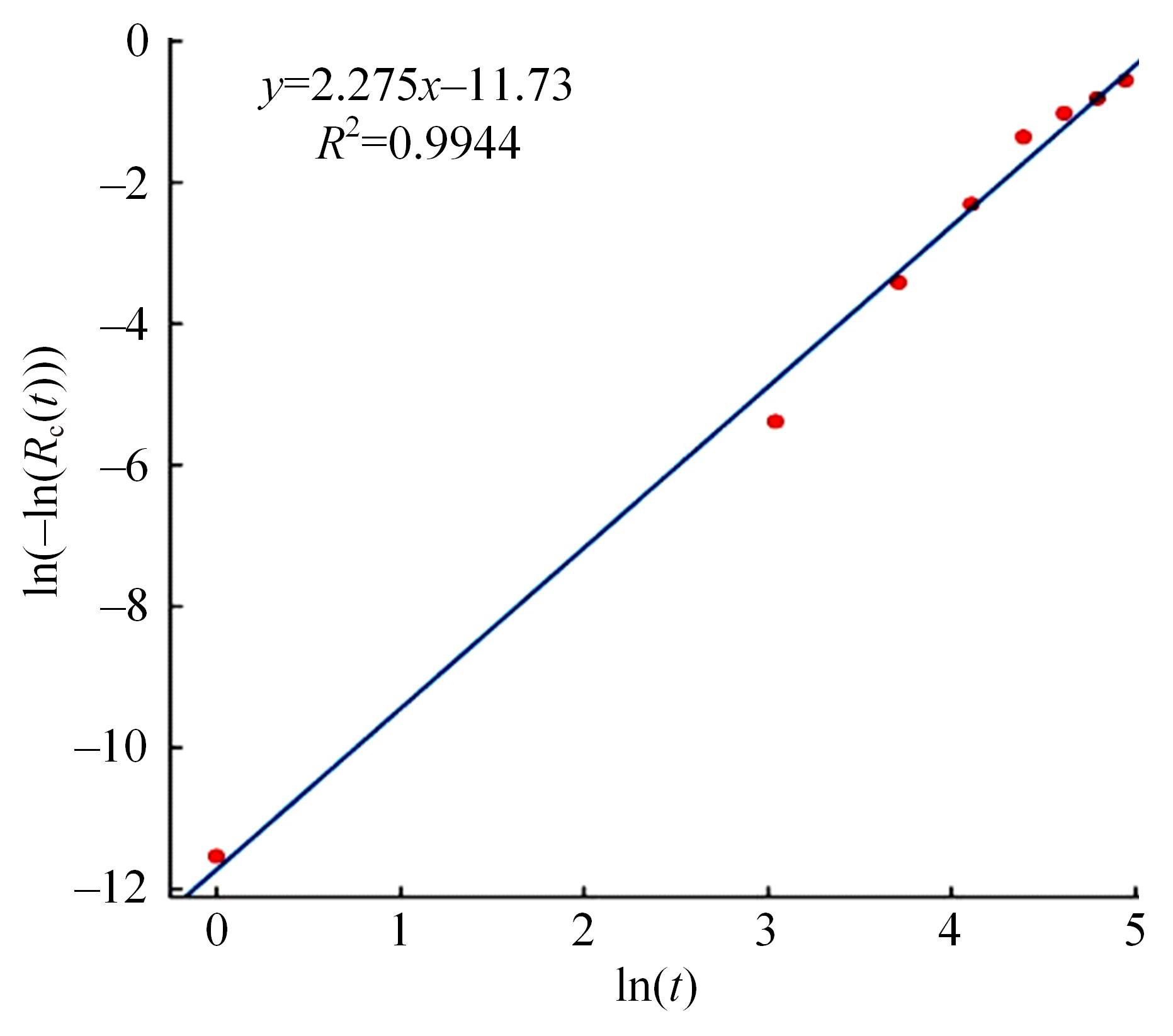
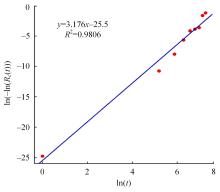
| 10 | 徐存东,张鹏,连海东,等. 基于Weibull分布的灌区混凝土建筑物寿命预测[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(5): 1483-1490. |
| Xu Cun-dong, Zhang Peng, Lian Hai-dong, et al. Life prediction of concrete buildings in irrigation areas based on Weibull distribution[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(5): 1483-1490. | |
| 11 | 赵文帅. 考虑材料属性二次Weibull分布的混凝土细观模型[D]. 济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2021. |
| Zhao Wen-shuai. Concrete mesoscopic model considering the quadratic weibull distribution of material pr-operties[D]. Ji'nan: School of Civil Engineering, Shandong University, 2021. | |
| 12 | 宋鲁光,孙伟,高建明.干湿循环条件下矿渣混凝土氯离子表观扩散系数的影响因素研究[J]. 混凝土, 2015(11): 4-11. |
| Song Lu-guang, Sun Wei, Gao Jian-ming. Study on the factors influencing the apparent diffusion coefficient of chloride ions in slag concrete under dry and wet cycle conditions[J]. Concrete, 2015(11): 4-11. | |
| 13 | Qin H L, Zhang H, Sun D T. Corrosion behavior of the friction-stirwelded joints of 2A14-T6 aluminu-m alloy[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015, 22(6): 627-638. |
| 14 | 蒋仁言. 威布尔模型族-特性、参数估计和应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. |
| 15 | Weibull W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1951, 18(3): 293-297. |
| 16 | 茆诗松,汤银才,王玲玲. 可靠性统计[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008. |
| 17 | Erdogdu Ş, Bremner T W, Kondratova I L. Accelerated testing of plain and epoxy-coated reinforcement in simulated seawater and chloride solutions[J]. Cement Concrete Research, 2001, 31(6): 861-867. |
| 18 | Santhanam M, Cohen M D, Olek J. Mechanism of sulfate attack: a fresh look-Part 1. summary of experi-mental results[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(6): 915-921. |
| 19 | Alamoudi O S, Maslehuddin M. The effect of chloride and sulfate ions on reinforcement corrosion[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1993, 23(1): 139-146. |
| 20 | 王甲春,阎培渝. 海洋环境下钢筋混凝土中钢筋锈蚀的概率[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(2): 352-357. |
| Wang Jia-chun, Yan Pei-yu. Probabilistic analysis of rebar rust in concrete under marine environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(2): 352-357. | |
| 21 | 王鹏辉,乔宏霞,冯琼,等. 氯氧镁涂层钢筋混凝土两重因素耦合作用下的耐久性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 191-201. |
| Wang Peng-hui, Qiao Hong-xia, Feng Qiong, et al. Durability model of magnesium oxychloride-coated reinforced concrete under the two coupling factors[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 191-201. | |
| 22 | 张俊喜,易博,林德源,等. 盐渍土环境下钢筋混凝土腐蚀的电化学研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2016, 19(2): 390-396. |
| Zhang Jun-xi, Yi Bo, Lin De-yuan, et al. Electrochemical study of corrosion of reinforced concrete in saline soil environment[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2016, 19(2): 390-396. | |
| 23 | 李隽,高培伟,刘宏伟,等. 混凝土在浸泡和干湿循环作用下的抗氯盐侵蚀性能[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2017, 41(5): 666-670. |
| Li Jun, Gao Pei-wei, Liu Hong-wei, et al. Resistance of concrete to chloride salt erosion under immersion and wet and dry cycles[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology, 2017, 41(5): 666-670. |
| [1] | Er-gang XIONG,Zhong-wen GONG,Jia-ming LUO,Tuan-jie FAN. Experiment on cracks in reinforced concrete beams based on digital image correlation technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1094-1104. |
| [2] | Ya-zhen SUN,Zhi ZHENG,Wei-ming HUANG,Jin-chang WANG. Structural analysis of cement pavement with cracks based on state⁃space method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 188-196. |
| [3] | Yi-hong WANG,Qiao-luo TIAN,Guan-qi LAN,Sheng-fa YAO,Jian-xiong ZHANG,Xi LIU. Experimental research on the mechanical properties of concrete column reinforced with 630 MPa high⁃strength steel under large eccentric loading [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2626-2635. |
| [4] | Er-gang XIONG,Han XU,Ci TAN,Jing WANG,Ruo-yu DING. Shear strength of reinforced concrete beams based on elastoplastic stress field theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 259-267. |
| [5] | Qian-hui PU,Jing-wen LIU,Gang-yun ZHAO,Meng YAN,Xiao-bin LI. Theoretical analysis of bearing capacity of concrete eccentric compressive column reinforced by HTRCS [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 606-612. |
| [6] | Ning⁃hui LIANG,Qing⁃xu MIAO,Xin⁃rong LIU,Ji⁃fei DAI,Zu⁃liang ZHONG. Determination of fracture toughness and softening traction⁃separation law of polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1144-1152. |
| [7] | Tian⁃lai YU,Hai⁃sheng LI,Wei HUANG,Si⁃jia WANG. Shear strengthening of reinforced concrete beam with prestressed steel wire ropes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [8] | DAI Yan, NIE Shao-feng, ZHOU Tian-hua. Finite element analysis of hysteretic behavior of square steel tube confined steel reinforced concrete column steel frame ring beam joint [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| [9] | YU Tian-lai, LIU Xing-guo, YAO Shuang, Muhammad Mansour. Fatigue performance of RC beams strengthened with externally prestressed CFRP tendons [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1867-1873. |
| [10] | GUO Jun-ping, DENG Zong-cai, LU Hai-bo, LIN Jin-song. Experiment on shear behavior of reinforced concrete beams strengthened with prestressed high strength steel wire mesh [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 968-977. |
| [11] | WANG Jia-chun, YAN Pei-yu. Probabilistic analysis of rebar rust in concrete under marine environment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 352-357. |
| [12] | ZHONG Chun-ling, LI Na, MENG Guang-wei. Temperature effect on mechanical behaviors of continuously reinforced concrete pavement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 68-73. |
| [13] | LIU Han-bing, ZHENG Ji-guang, ZOU Pin-de. Calculation on bearing capacity of eccentric compression reinforced concrete short column with circular combined-section [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 159-163. |
| [14] | MENG Song-He, GAO Hui-Ting, SUN Li-An, SHI Hong-Jun. Effect of silica fumeslag on performance of polypropylene fiber concrete [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 214-0217. |
| [15] | BO Ming-Yuan, YAO Ji-Tao. Reliability of reinforced concrete structural element [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 218-0221. |
|
||