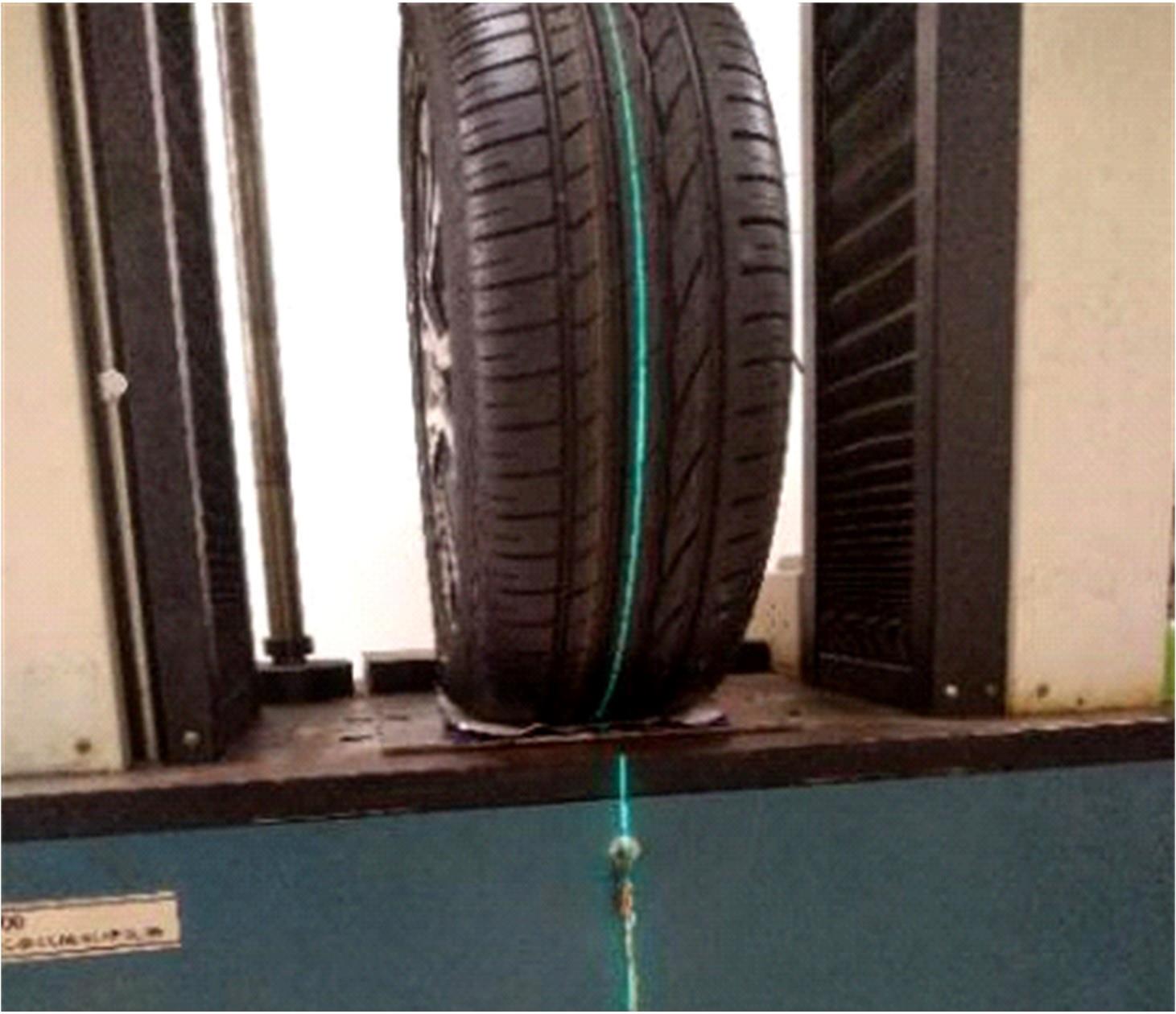
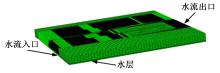
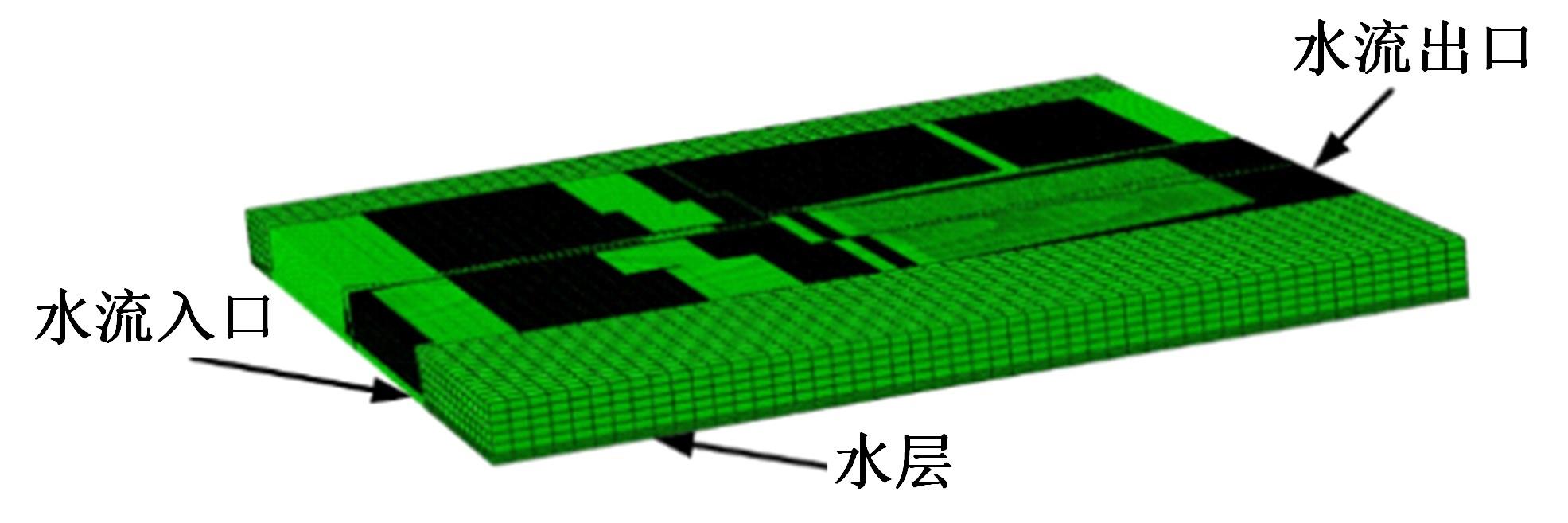
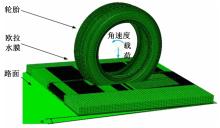
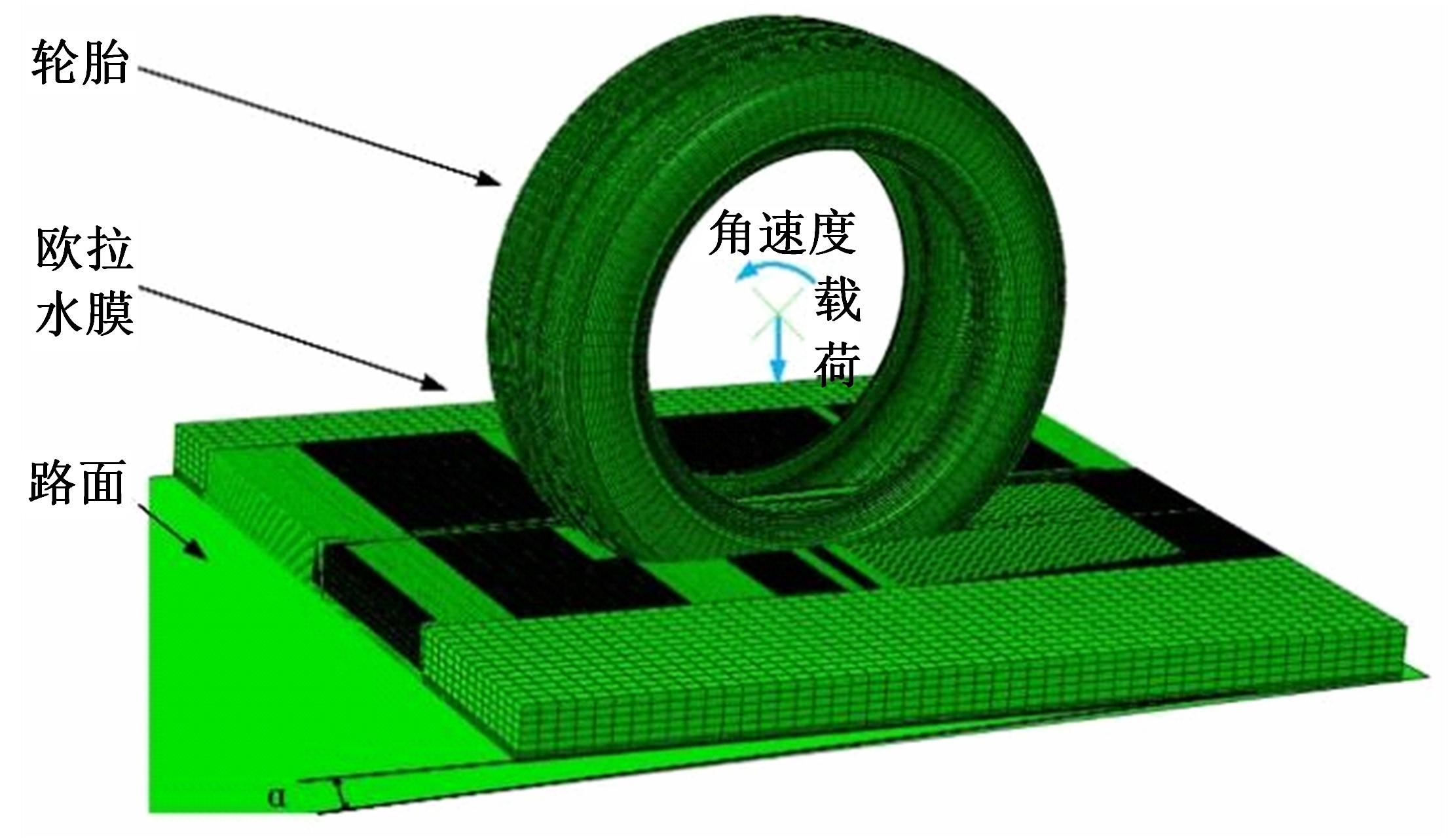
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1501-1511.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220951
Tire grounding mechanical model on wet roads
Cong-zhen LIU1( ),Gao CHEN1,Hong-zhu LIU1,Qiang MA1,Cheng-wei XU1,Hui MENG1,Guo-lin WANG2
),Gao CHEN1,Hong-zhu LIU1,Qiang MA1,Cheng-wei XU1,Hui MENG1,Guo-lin WANG2
- 1.School of Transportation and Vehicle Engineering,Shandong University of Technology,Zibo 255022,China
2.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
CLC Number:
- U463.341
| 1 | Dolwichai P, Limtragool J. The effect of tire treads shape to stick-slip phenomenon in frictional contact[C]∥The 20th Conference of MENETT, Nakorn Ratchasima, Thailand, 2006: 18-20. |
| 2 | El-Sayegh Z, El-Gindy M. Cornering characteristics of a truck tire on wet surface using finite element analysis and smoothed-particle hydrodynamics[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2018, 6(4): 1567-1576. |
| 3 | El-Sayegh Z, El-Gindy M. Sensitivity analysis of truck tyre hydroplaning speed using FEA-SPH model[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Systems Modelling and Testing, 2017, 12(1/2): 143-161. |
| 4 | Jeong J Y, Jeong H Y. Hydroplaning simulation of a tire in thin water using fem and an estimation method and its application to skid number estimation[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2013, 14(2): 325-331. |
| 5 | Ong G P, Fwa T F. Mechanistic interpretation of braking distance specifications and pavement friction requirements[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2010, 2155(1): 145-157. |
| 6 | Fwa T F, Anupam K, Ong G P. Relative effectiveness of grooves in tire and pavement for reducing vehicle hydroplaning risk[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2010, 2155(1): 73-81. |
| 7 | 陈磊,周海超,潘公宇. 轮胎花纹凹坑非光滑表面对抗滑水性能的影响分析[J]. 现代制造工程, 2019, 19(1): 23-31. |
| Chen Lei, Zhou Hai-chao, Pan Gong-yu. Influence analysis of bionic pit non-smooth surface pattern on tire hydroplaning performance[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2019, (1): 23-31. | |
| 8 | 杨建,王国林,周海超,等. 仿生非光滑花纹沟对轮胎抗滑水性能的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 43(2): 21-25. |
| Yang Jian, Wang Guo-lin, Zhou Hai-chao, et al. Study on influence of bionic non-smooth pattern groove on tire anti-hydroplaning performance[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 21-25. | |
| 9 | Zhou H C, Zhai H H, Ding Y M, et al. Numerical investigation of passive control flow to improve tire hydroplaning performance using a V-riblet non-smooth surface[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 9(11): 1-13. |
| 10 | 黄晓明,刘修宇,曹青青,等. 积水路面轮胎部分滑水数值模拟[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(9): 113-121. |
| Huang Xiao-ming, Liu Xiu-yu, Cao Qing-qing, et al. Numerical simulation of tire partial hydroplaning on flooded pavement[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(9): 113-121. | |
| 11 | 季天剑,黄晓明,刘清泉. 部分滑水对路面附着系数的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2003, 3(4): 10-12. |
| Ji Tian-jian, Huang Xiao-ming, Liu Qing-quan. Part hydroplaning effect on pavement friction coefficient[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2003, 3(4): 10-12. | |
| 12 | 董斌. 部分滑水条件下高速公路车辆行驶安全性研究[D].重庆: 重庆交通大学土木建筑学院, 2011. |
| Dong Bin. Study of safety drive on expressway under partly hydroplaning[D]. Chongqing: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2011. | |
| 13 | Fiala E. Seitenkraefte am rollenden Luftreifen[J]. Verein Deutscher Ingenieure, 1954, 96(29): 973-979. |
| 14 | 刘青,郭孔辉,陈秉聪. 轮胎刷子模型分析Ⅰ.稳态侧偏刷子模型[J]. 农业机械学报, 2000, 31(1): 19-22. |
| Liu Qing, Guo Kong-hui, Chen Bing-cong. Review of tire brush models I. Steady state cornering brush models[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2000, 31(1): 19-22. | |
| 15 | 郭孔辉. 汽车轮胎动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. |
| 16 | 郭孔辉,李宁,庄晔. 轮胎侧向力影响因素试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2011, 42(12): 1-5. |
| Guo Kong-hui, Li Ning, Zhuang Ye. Test on factors of tire lateral force[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(12): 1-5. | |
| 17 | Horne W B, Joyner U T. Pneumatic tire hydroplaning and some effects on vehicle performance[J]. SAE Transactions, 1966, 74: 623-650. |
| 18 | Horne W B, Yager T J, Ivey D L. Recent studies to investigate effects of tire footprint aspect ratio on dynamic hydroplaning speed[J]. ASTM Special Technical Publication, 1986, 929: 26-46. |
| 19 | Gim G, Nikravesh P E. An analytical model of pneumatic tyres for vehicle dynamic simulations. Part 1: pure slips[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 1990, 11(6): 589-618. |
| 20 | Gim G. An analytical model of pneumatic tyres for vehicle dynamic simulations. Part 2: comprehensive slips[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design of Vehicle Design, 1991, 12(1): 19-39. |
| 21 | 周海超,陈磊,翟辉辉,等. 基于CFD的轮胎滑水及其性能影响因素分析[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 36(1): 110-116. |
| Zhou Hai-chao, Chen Lei, Zhai Hui-hui, et al. Research on flow field and influencing factors of tire hydroplaning based on CFD method[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2017, 36(1): 110-116. | |
| 22 | 张丽霞,郑超艺,杨朝会,等. 湿滑路面汽车轮胎滑水性能影响因素仿真[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(30): 12589-12595. |
| Zhang Li-xia, Zheng Chao-yi, Yang Chao-hui, et al. Simulation on factors affecting hydroplaning performance of vehicle tire on wet pavement[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(30): 12589-12595. | |
| 23 | 庄楚强,何春雄. 应用数理统计基础[M]. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2006. |
| 24 | 王婷婷. 严寒地区居民用能行为对住宅能耗影响的偏相关分析[J]. 建筑与文化, 2021, 18(10): 195-197. |
| Wang Ting-ting. Partial correlation analysis of the influence of residents' energy-using behavior on energy consumption in severe cold region[J]. Architecture and Culture, 2021, 18(10): 195-197. |
| [1] | Xiao⁃ming HUANG,Qing⁃qing CAO,Xiu⁃yu LIU,Jia⁃ying CHEN,Xing⁃lin ZHOU. Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [2] | ZHENG Xue-lian, LI Xian-sheng, REN Yuan-yuan, YANG Meng. Rollover stability analysis of tank vehicle impacted by transient liquid sloshing [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 625-630. |
| [3] | LIU Yu-mei,SU Jian,CAO Xiao-ning,XIONG Wei,SONG Xue-zhong. Study on fault diagnosis methods for automobile suspensions based on fuzzy mathematics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 220-0224. |
|
||