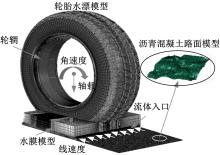
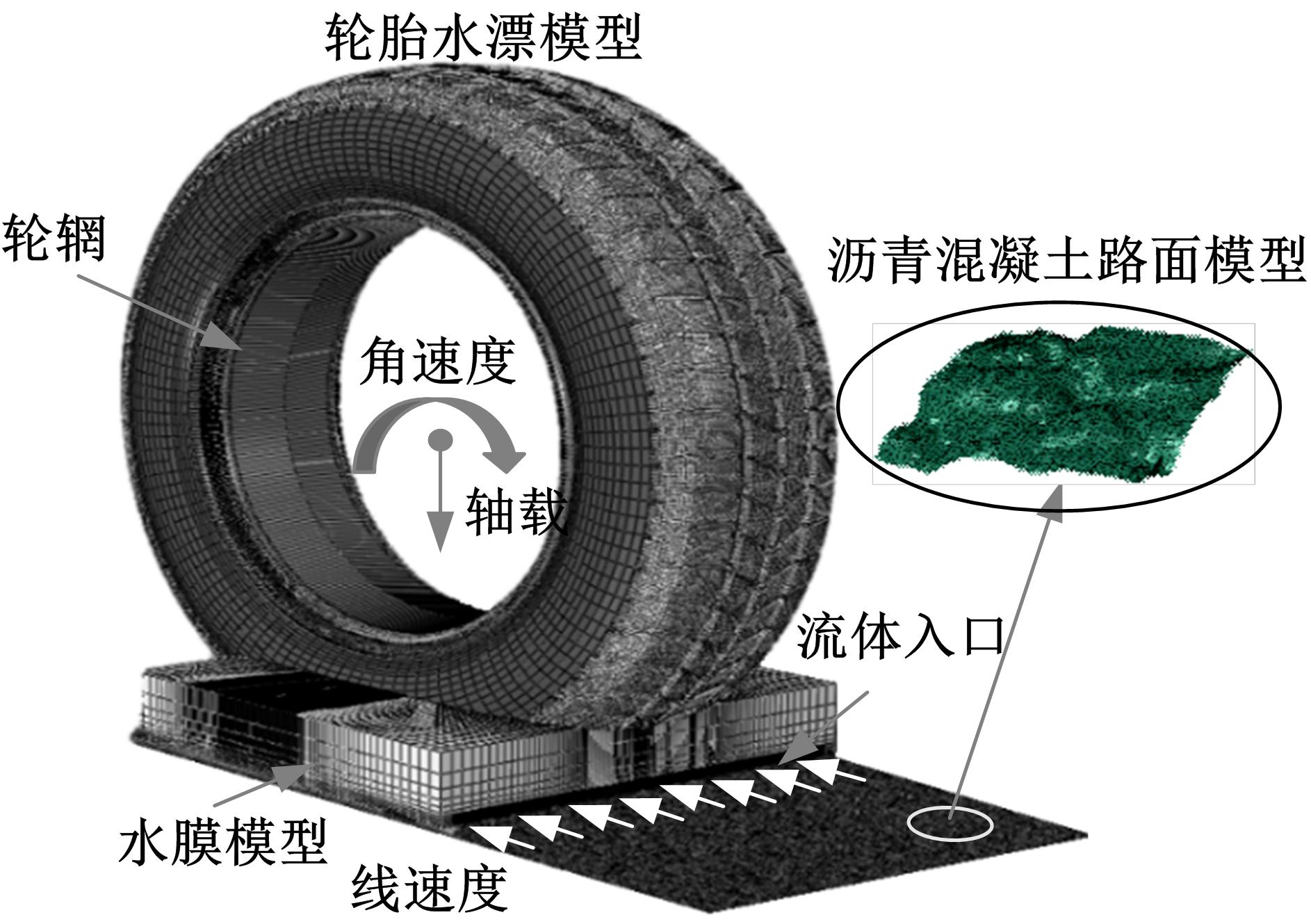
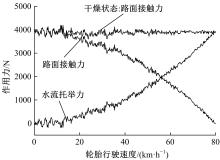
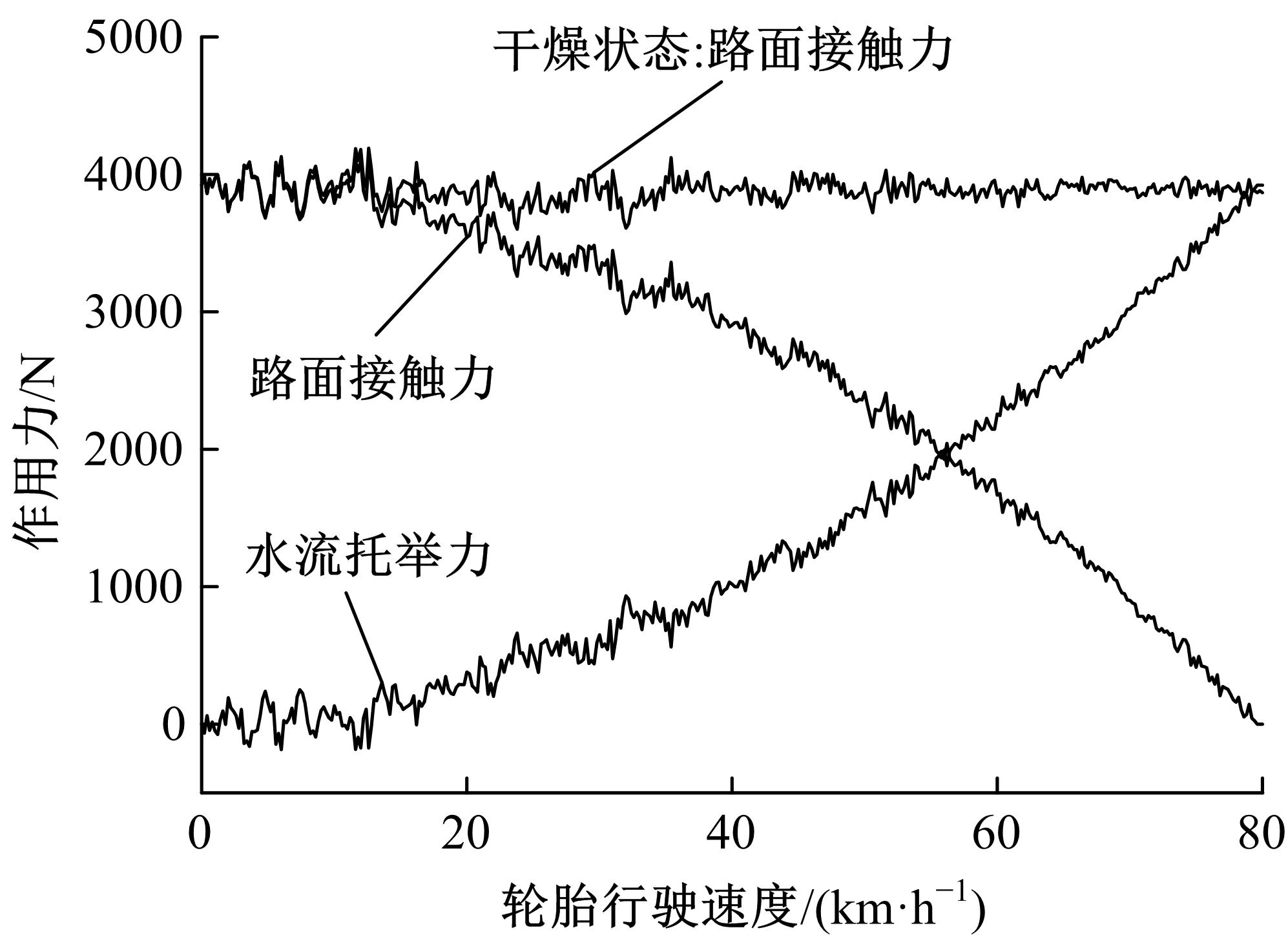
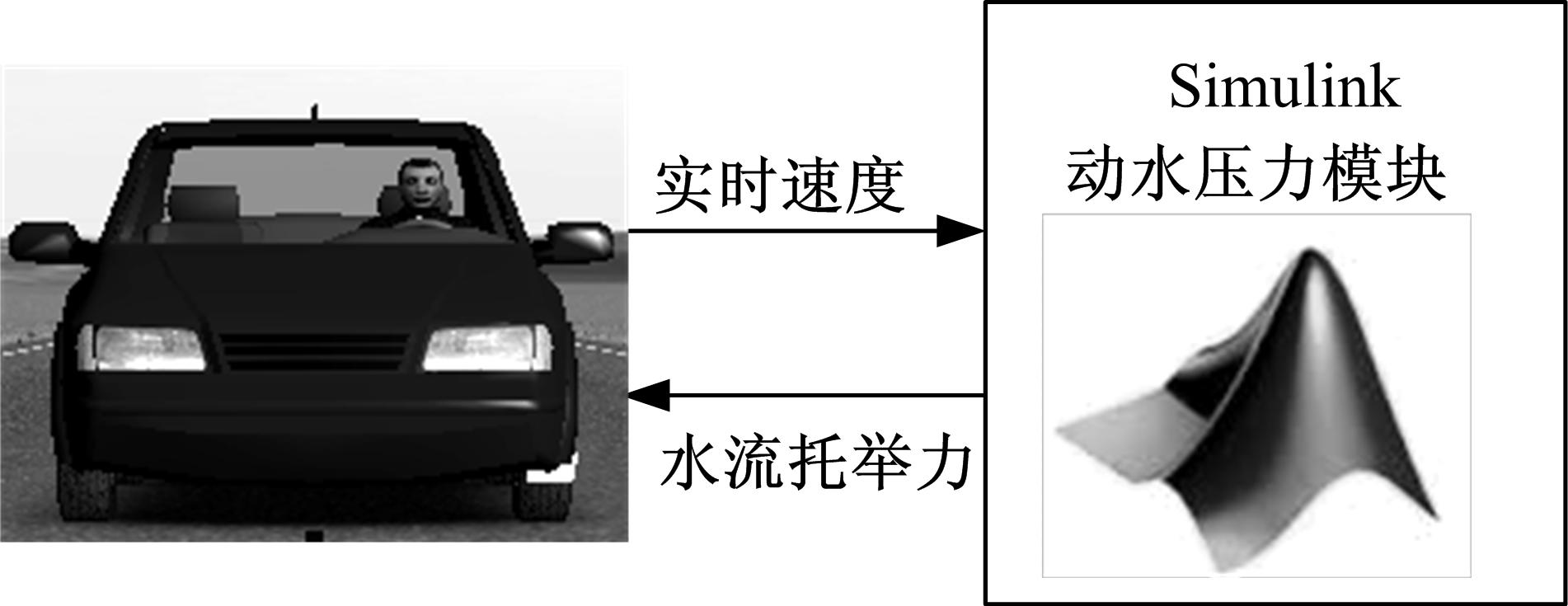
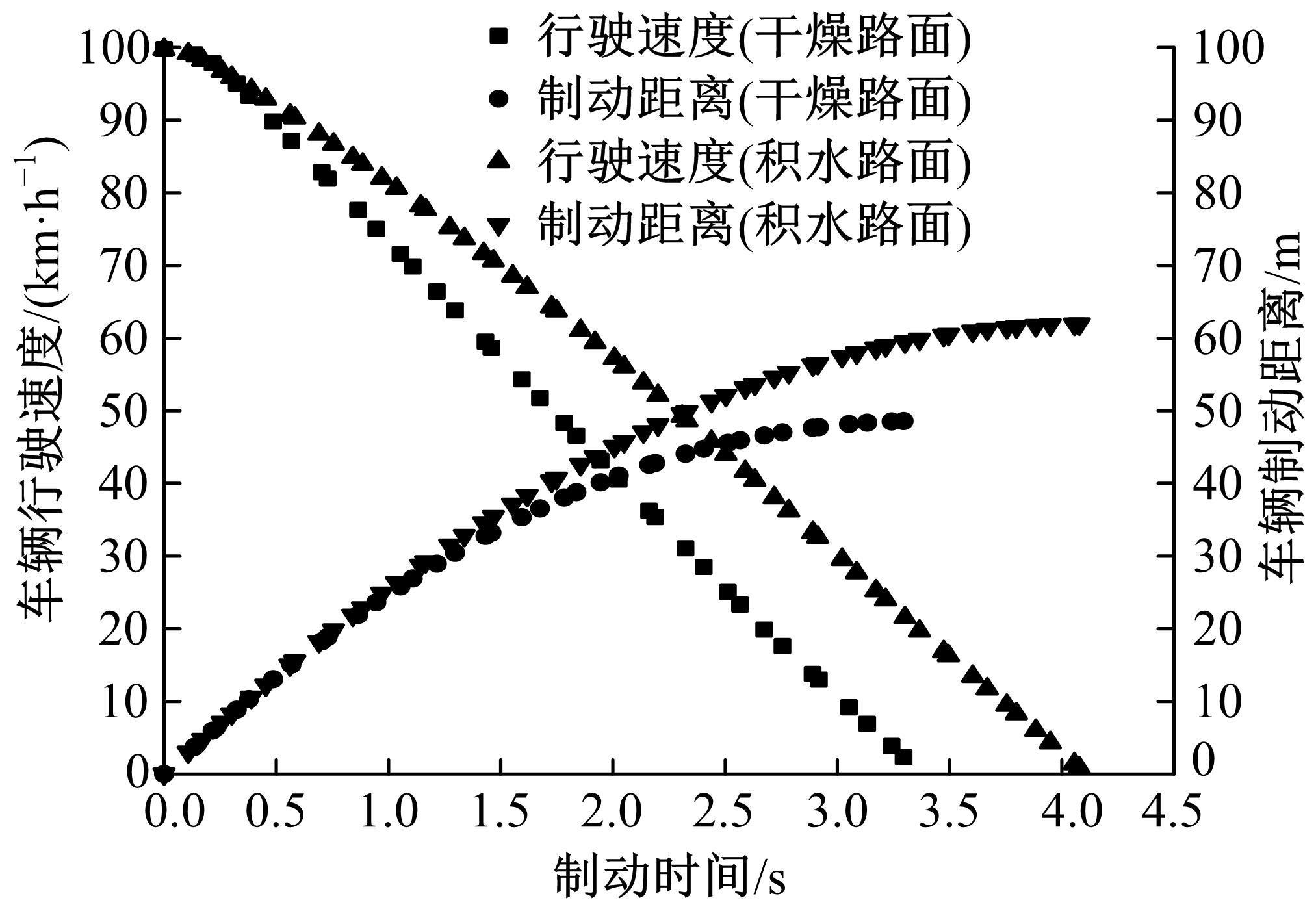
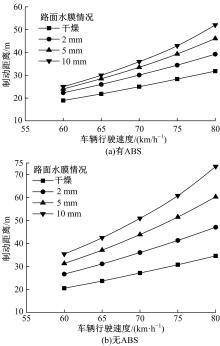
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 757-765.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171082
Previous Articles Next Articles
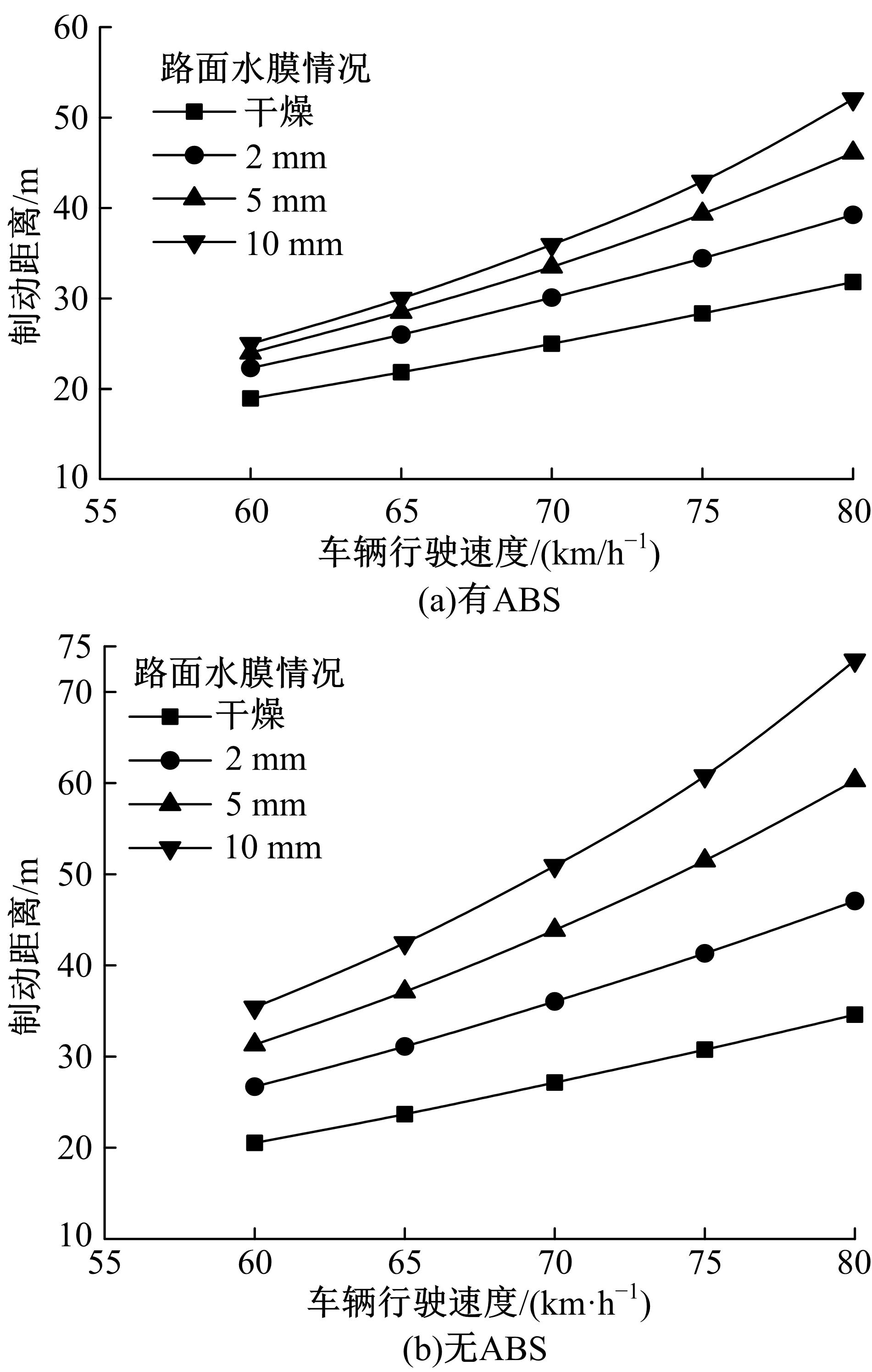
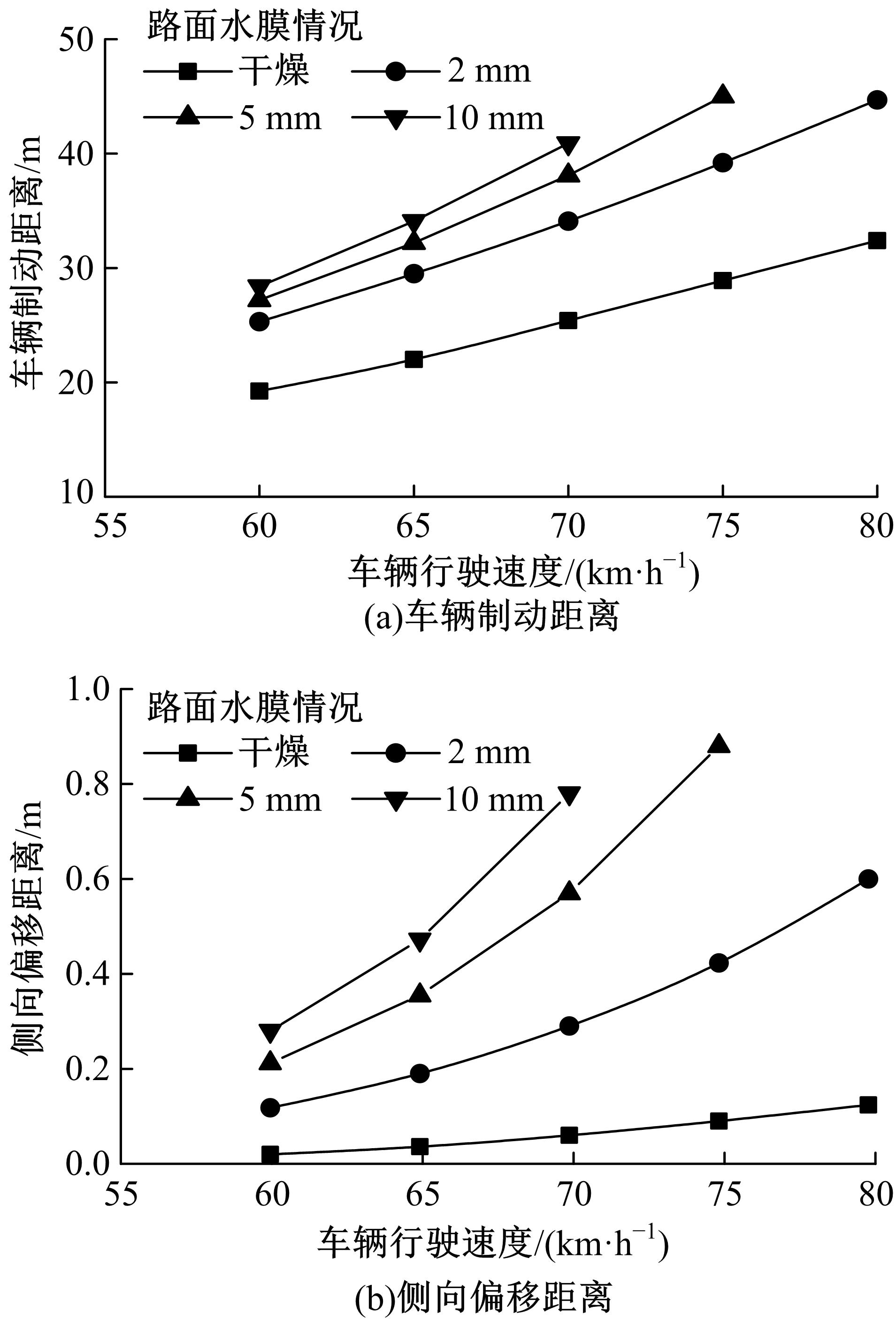
Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory
Xiao⁃ming HUANG1( ),Qing⁃qing CAO1,Xiu⁃yu LIU1,Jia⁃ying CHEN1,Xing⁃lin ZHOU2
),Qing⁃qing CAO1,Xiu⁃yu LIU1,Jia⁃ying CHEN1,Xing⁃lin ZHOU2
- 1. School of Transportation, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2. School of Automobile and Traffic Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
CLC Number:
- U416.217
| 1 | HorneW B, JoynerU T. Pneumatic tire hydroplaning and some effects on vehicle performance[R]. Hampton, Virginia, USA: Langley Research Center, 1965: 1⁃28. |
| 2 | GroggerH, WeissM. Calculation of the three⁃dimensional free surface flow around an automobile tire[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 1996, 24(1): 39⁃49. |
| 3 | OngG P, FwaT F. A mechanistic interpretation of braking distance specifications and pavement friction requirements[J]. Transportation Research Record:Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2010, 2155: 145⁃157. |
| 4 | FwaT F, PasinduH R, OngG P. Critical rut depth for pavement maintenance based on vehicle skidding and hydroplaning consideration[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 423⁃429. |
| 5 | JuF, FwaT F, OngG P. Evaluating wet weather driving benefits of grooved pavements[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research & Technology, 2013, 6(4): 287⁃293. |
| 6 | PasinduH R, FwaT F. Improving wet⁃weather runway performance using trapezoidal grooving design[J]. Transportation in Developing Economies, 2015, 1(1): 1⁃10. |
| 7 | ZhouHai⁃chao, WangGuo⁃lin, DingYang⁃min, et al. Effect of friction model and tire maneuvering on tire⁃pavement contact stress[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015, 2015: 632647. |
| 8 | ZhuS, LiuX, CaoQ, et al. Numerical study of tire hydroplaning based on power spectrum of asphalt pavement and kinetic friction coefficient[J/OL].[2017-10-28].http:∥downloads.hindawi.com/journals/amse/2017/5843061. |
| pdf. | |
| 9 | 刘修宇, 曹青青, 朱晟泽, 等. 沥青混凝土路面轮胎临界滑水速度数值模拟[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 47(5): 1020⁃1025. |
| LiuXiu⁃yu, CaoQing⁃qing, ZhuSheng⁃ze, et al. Numerical simulation of tire critical hydroplaning speed on asphalt pavement [J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2017,47(5): 1020⁃1025. | |
| 10 | 黄晓明,刘修宇,曹青青,等. 积水路面轮胎部分滑水数值模拟[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(9): 113⁃121. |
| HuangXiao⁃ming, LiuXiu⁃yu, CaoQing⁃qing, et al. Numerical simulation of tire partial hydroplaning on flooded pavement[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 45(9): 113⁃121. | |
| 11 | PerssonB N J. Theory of rubber friction and contact mechanics[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2001, 115(8): 3840⁃3861. |
| 12 | 张敏, 郭鑫鑫, 张驰. 积水条件下考虑行车安全的车辙长度仿真分析[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2015, 27(4): 747⁃754. |
| ZhangMin, GuoXin⁃xin, ZhangChi. Simulation analysis of rutting length based on driving safety under condition of road waterlogging[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2015, 27(4): 747⁃754. | |
| 13 | 徐进, 彭其渊, 邵毅明. 直线路段积水路面车辆事故产生机理分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2009, 22(1): 97⁃103. |
| XuJin, PengQi⁃yuan, ShaoYi⁃ming. Mechanism analysis of vehicle accident on surface gathered water in straight sections[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22(1): 97⁃103. | |
| 14 | PerssonB N J, TartaglinoU, AlbohrO, et al. Rubber friction on wet and dry road surfaces: the sealing effect[J]. Physical Review B, 2005, 71(3): 035428. |
| 15 | PerssonB N. Rubber friction and tire dynamics[J]. Journal of Physics⁃Condensed Matter, 2011, 23(1): 015003. |
| 16 | LorenzB, PerssonB N, FortunatoG, et al. Rubber friction for tire tread compound on road surfaces[J]. Journal of Physics⁃Condensed Matter, 2013, 25(9): 095007. |
| 17 | LorenzB, OhY R, NamS K, et al. Rubber friction on road surfaces: experiment and theory for low sliding speeds[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2015, 142(19): 194701. |
| 18 | 赵战利. 基于分形方法的沥青路面抗滑技术研究[D]. 西安:长安大学公路学院, 2005. |
| ZhaoZhan⁃li. Research on pavement skid resistance technique based on fractal methods[D]. Xi′an: Highway College, Chang′an University, 2005. | |
| 19 | HouY, HuangY, SunF, et al. Fractal analysis on asphalt mixture using a two⁃dimensional imaging technique[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 2016:8931295. |
| 20 | 冉茂平, 肖旺新, 周兴林, 等. 基于三维分形维数的沥青路面抗滑性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2016(2): 28⁃32. |
| RanMao⁃ping, XiaoWang⁃xin, ZhouXing⁃lin, et al. Research of skid resistance of asphalt pavement based on 3D fractal dimension[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2016(2): 28⁃32. | |
| 21 | 童申家, 谢祥兵, 赵大勇. 沥青路面纹理分布的分形描述及抗滑性能评价[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(2): 1⁃7. |
| TongShen⁃jia, XieXiang⁃bing, ZhaoDa⁃yong. Fractal description of texture distribution and evaluation of skid⁃resistance performance for asphalt pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(2): 1⁃7. | |
| 22 | PerssonB N J. On the fractal dimension of rough surfaces[J]. Tribology Letters, 2014, 54(1): 99⁃106. |
| 23 | JohannessonP, RychlikI. Laplace processes for describing road profiles[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2013, 66: 464⁃473. |
| 24 | JTJ—05995.公路路基路面现场测试规程[S]. |
| 25 | 郭孔辉. Unitire统一轮胎模型[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(12): 90⁃99. |
| GuoKong⁃hui. UniTire: unified tire model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(12): 90⁃99. |
| [1] | Jing WANG,Xiang LYU,Xiao⁃long QU,Chun⁃ling ZHONG,Yun⁃long ZHANG. Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [2] | LI Yi,LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun. Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [3] | ZANG Guo-shuai, SUN Li-jun. Method based on inertial point for setting depth to rigid layer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | NIAN Teng-fei, LI Ping, LIN Mei. Micro-morphology and gray entropy analysis of asphalt characteristics functional groups and rheological parameters under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [5] | GONG Ya-feng, SHEN Yang-fan, TAN Guo-jin, HAN Chun-peng, HE Yu-long. Unconfined compressive strength of fiber soil with different porosity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [6] | CHENG Yong-chun, BI Hai-peng, MA Gui-rong, GONG Ya-feng, TIAN Zhen-hong, LYU Ze-hua, XU Zhi-shu. Pavement performance of nano materials-basalt fiber compound modified asphalt binder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [7] | JI Wen-yu, LI Wang-wang, GUO Min-long, WANG Jue. Experimentation and calculation methods of prestressed RPC-NC composite beam deflection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yang-peng, WEI Hai-bin, JIA Jiang-kun, CHEN Zhao. Numerical evaluation on application of roadbed with composite cold resistance layer inseasonal frozen area [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [9] | MA Ye, NI Ying-sheng, XU Dong, DIAO Bo. External prestressed strengthening based on analysis of spatial grid model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [10] | LUO Rong, ZENG Zhe, ZHANG De-run, FENG Guang-le, DONG Hua-jun. Moisture stability evaluation of asphalt mixture based on film pressure model of Wilhelmy plate method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1753-1759. |
| [11] | NI Ying-sheng, MA Ye, XU Dong, LI Jin-kai. Space mesh analysis method for shear lag effect of cable-stayed bridge with corrugated steel webs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
| [12] | ZHENG Chuan-feng, MA Zhuang, GUO Xue-dong, ZHANG Ting, LYU Dan, Qin Yong. Coupling effect of the macro and micro characteristics of mineral powder on the low-temperature performance of asphalt mortar [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1465-1471. |
| [13] | YU Tian-lai, ZHENG Bin-shuang, LI Hai-sheng, TANG Ze-rui, ZHAO Yun-peng. Analyses of defects and causes of steel-plastic compound reinforced retaining wall [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1082-1093. |
| [14] | CAI Yang, FU Wei, TAO Ze-feng, CHEN Kang-wei. Influence analysis of geotextile on reducing traffic induced reflective cracking using extended finite element model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 765-770. |
| [15] | LIU Han-bing, ZHANG Hu-zhu, WANG Jing. Effect of dehydration on shear strength properties of compacted clayey soil [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 446-451. |
|
||