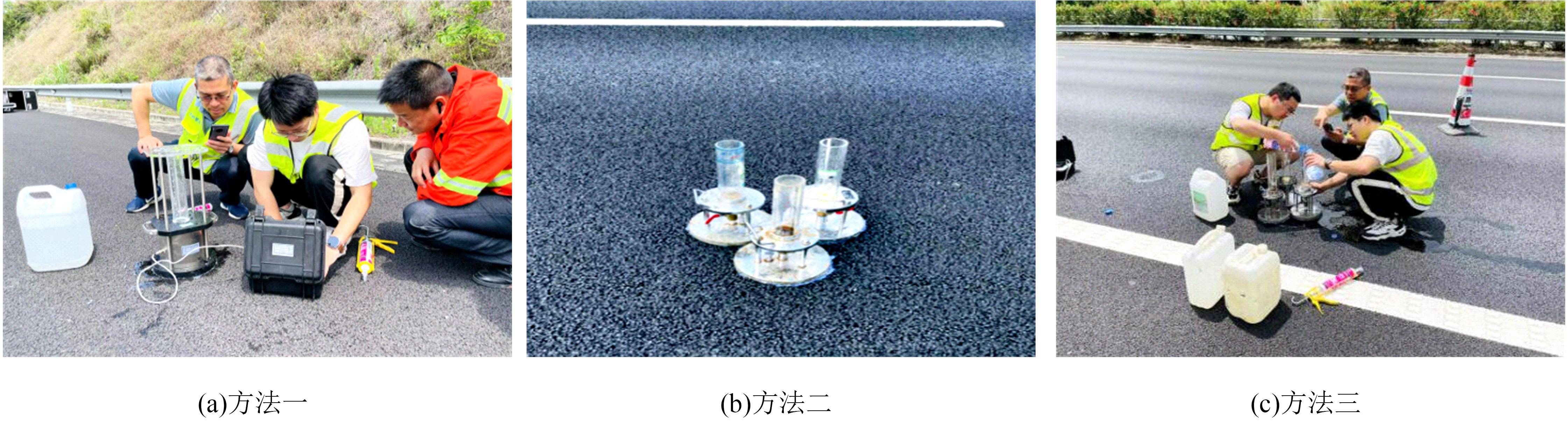
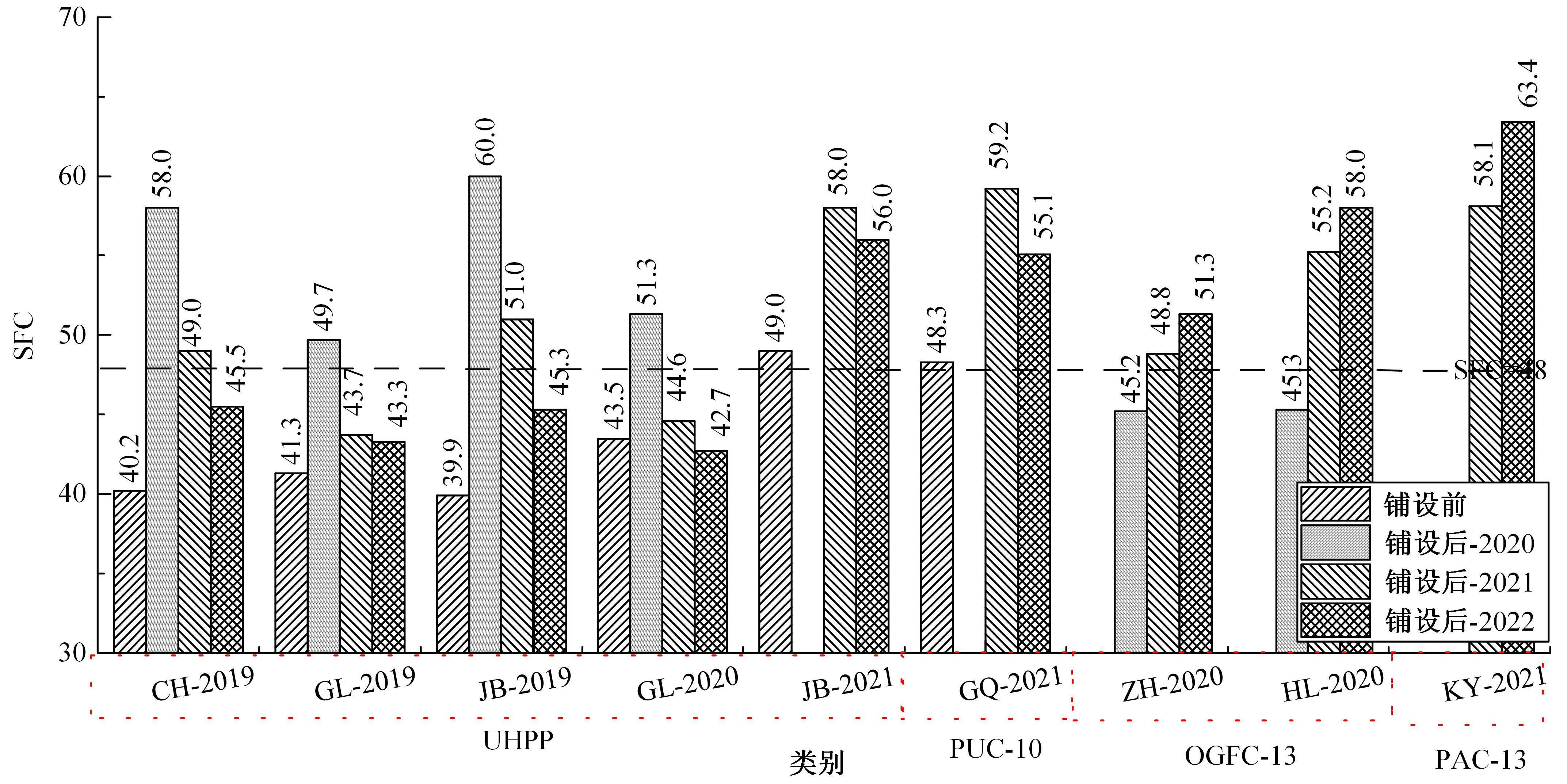
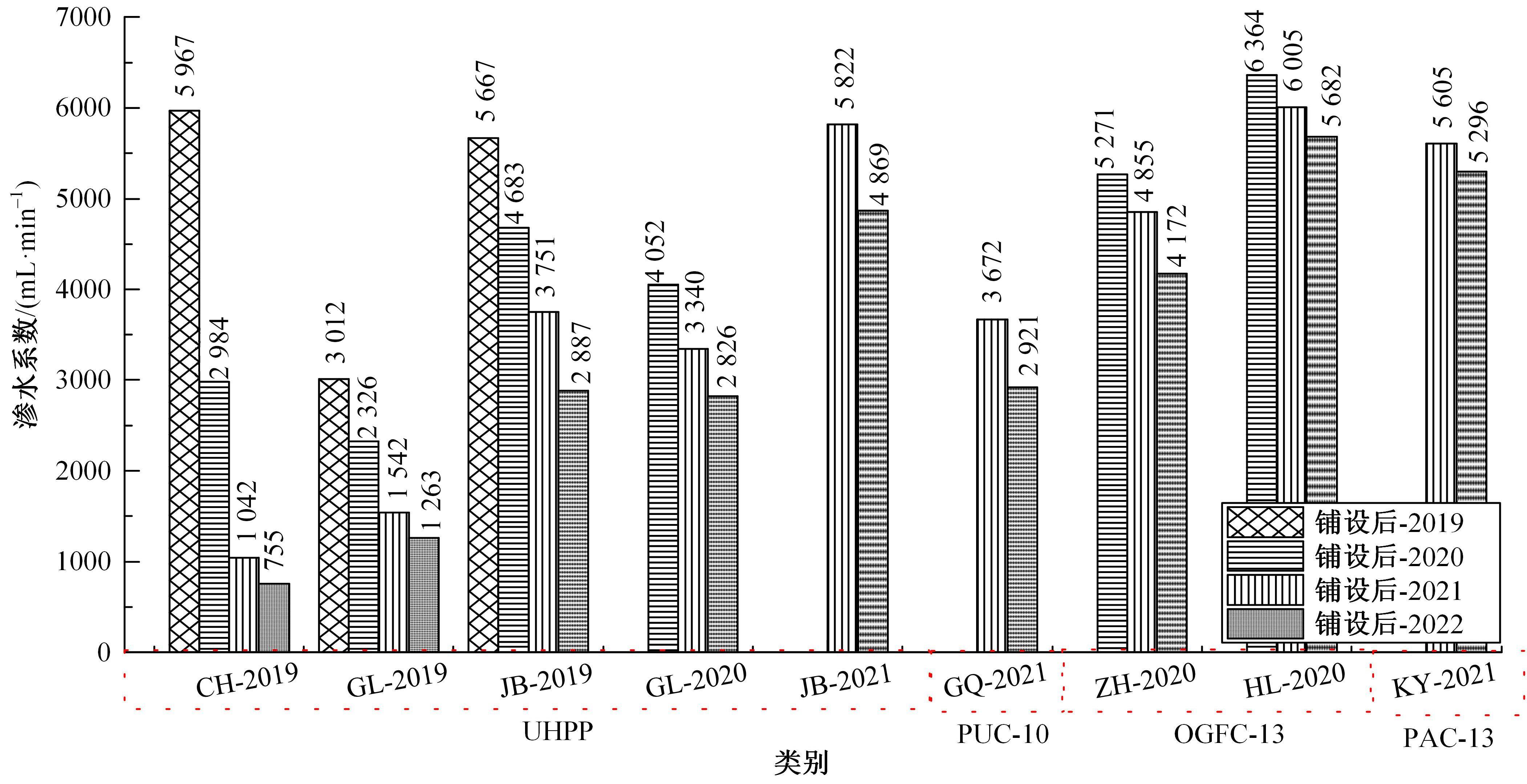
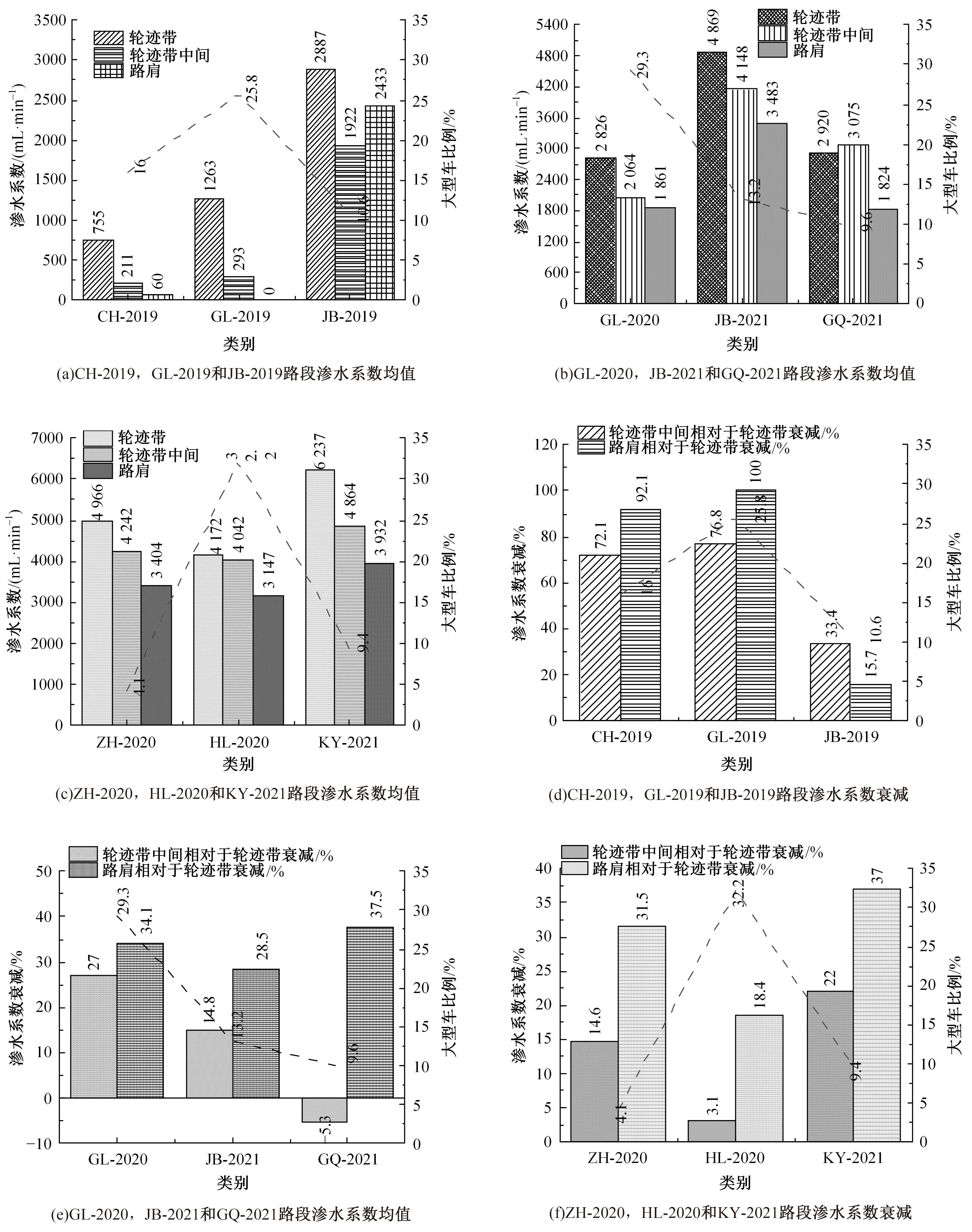
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2941-2951.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230110
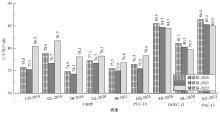
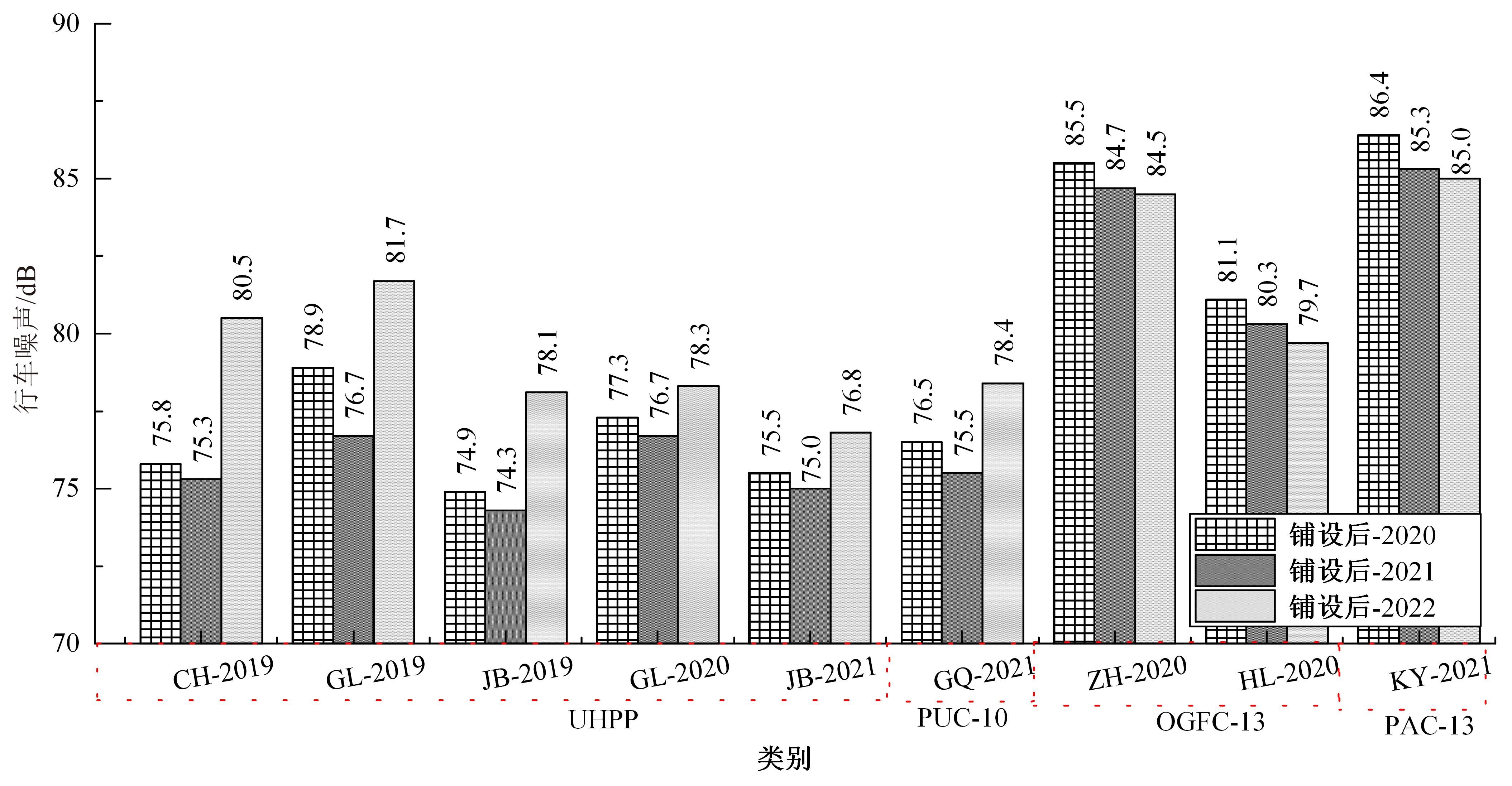
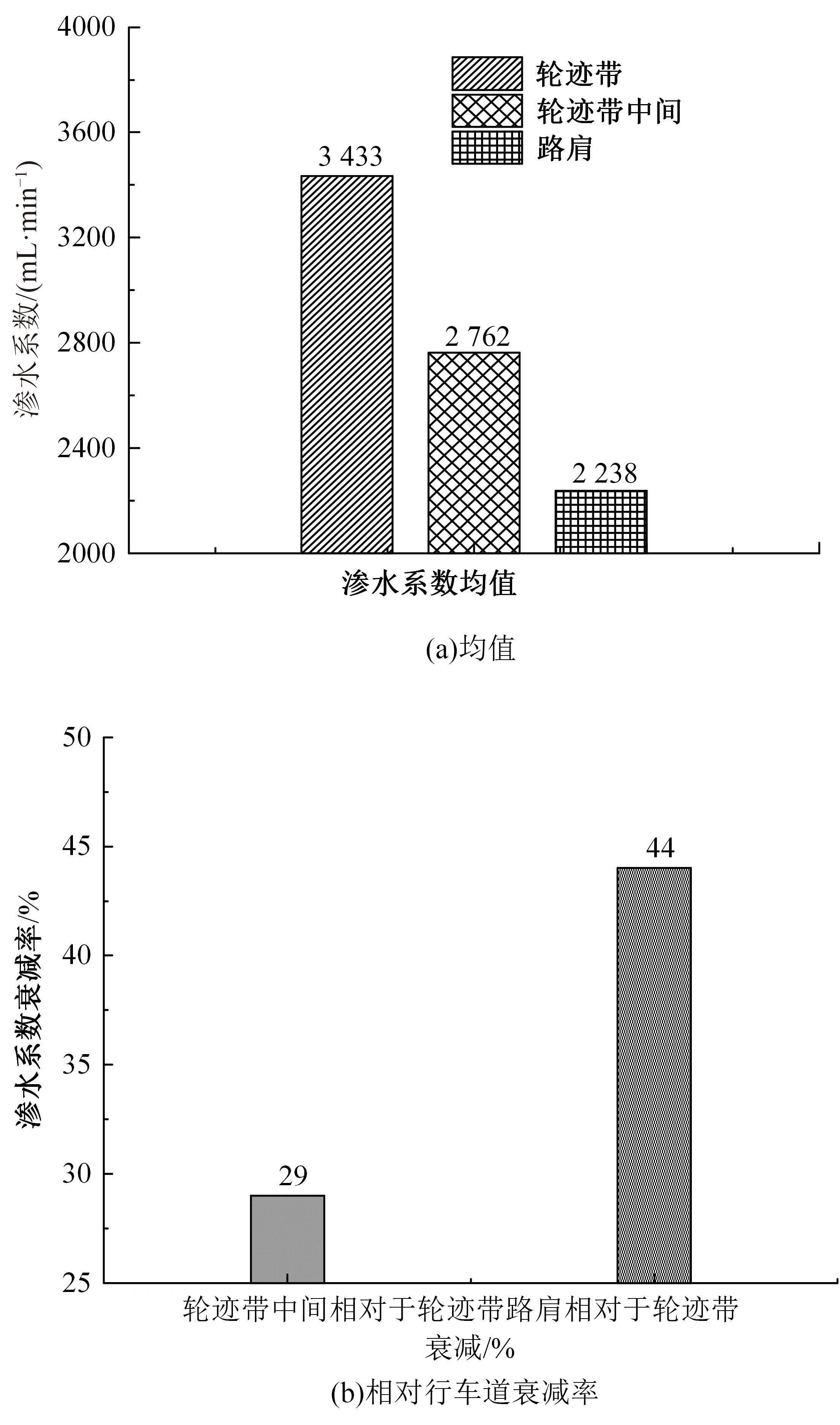
Pavement performance tracking and testing of porous asphalt pavement
Zheng-sen CAI1,2( ),Yu WU2,Xin-quan XU2,Jian-wei FAN1,Tao MA1,Hong-rou ZENG2
),Yu WU2,Xin-quan XU2,Jian-wei FAN1,Tao MA1,Hong-rou ZENG2
- 1.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
2.Guangdong Hualu Communications Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510420,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| 1 | Zeng Q, Hao W, Lee J. Investigating the impacts of real-time weather conditions on freeway crash severity: a Bayesian spatial analysis[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(8):No.2768. |
| 2 | 马翔,倪富健,李强.排水面层渗流模型及参数[J].东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014,44(2): 381-385. |
| Ma Xiang, Ni Fu-jian, Li Qiang. Seepage model and parameters of drainage surface layer[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2014,44(2): 381-385. | |
| 3 | 杨军,王昊鹏,吴琦. 潮湿沥青路面抗滑性能数值模拟[J].长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2016,36(3):25-32. |
| Yang Jun, Wang Hao-peng, Wu Qi. Numerical simulation of skid resistance of wet asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2016,36(3):25-32. | |
| 4 | 李明亮,袁春坤,李俊,等.车辙变形对多孔沥青路面排水性能的影响[J].长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 40(1):107-115. |
| Li Ming-liang, Yuan Chun-kun, Li Jun, et al. Effect of rutting deformation on drainage performance of porous asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2020,40(1):107-115. | |
| 5 | 郑彬双.无人驾驶车辆制动过程沥青路面抗滑特性及感应需求研究[D].南京:东南大学交通学院,2021. |
| Zheng Bin-shuang. Research on skid resistance characteristics and sensing demand of asphalt pavement during braking of unmanned vehicles[D]. Nanjing:School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2021. | |
| 6 | 何兆益,李金凤,周文,等.多孔沥青混合料的动态模量及其预估模型[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022,52(6):1375-1385。 |
| He Zhao-yi, Li Jin-feng, Zhou Wen, et al. Dynamic modulus and prediction model of porous asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition). 2022,52(6): 1375-1385. | |
| 7 | .公路路基路面现场测试规程 [S]. |
| 8 | Chen J, Yin X, Wang H, et al. Evaluation of durability and functional performance of porous polyurethane mixture in porous pavement[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 188: 12-19. |
| 9 | Zhang J, Cui X, Li L, et al. Sediment transport and pore clogging of a porous pavement under surface runoff[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2017, 18(Sup.3):240-248. |
| 10 | Cui L, Bhattacharya S. Choice of aggregates for permeable pavements based on laboratory tests and DEM simulations[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2015, 18(1/2):160-168. |
| 11 | .排水沥青路面设计与施工技术规范 [S]. |
| 12 | 张璠,陈荣生.排水性沥青路面混合料的渗透性能试验测试技术[J].东南大学学报:自然科学版,2010,40(6):1288-1292. |
| Zhang Fan, Chen Rong-sheng. Test and testing technology for permeability of drainage asphalt pavement mixtures[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2010,40(6): 1288-1292. | |
| 13 | 陈锋,季天剑.排水性沥青路面的排水性能研究[J].南京航空航天大学学报,2017,49(4):568-573. |
| Chen Feng, Ji Tian-jian. Study on the drainage performance of drainage asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 49(4): 568-573. |
| [1] | Zu-zhong LI,Meng-yuan LI,Wei-dong LIU,Xiao-xiao PANG,Hao Tang,Xue-lei ZHANG,Chen-yang MA. Surface modification of bagasse fibers and road performances of asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1738-1745. |
| [2] | Chen JIN,Meng-yuan ZENG,Di-fei WU. Damage identification of concrete pavement joint using vibration transmissibility [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1736-1745. |
| [3] | Jun-qing ZHU,Xue-ru ZHAO,Tao MA,Xiao-ming HUANG,Hong-zhou ZHU. Monitoring road geological disaster based on satellite remote sensing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1861-1872. |
| [4] | Shu-wei ZHANG,Zhong-yin GUO,Zhen YANG,Ben-min LIU. Application of multi⁃fractal features of driving performance in driver fatigue detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 557-564. |
| [5] | Jian-ming LING,Hui CHEN,Jin-song QIAN,Ding ZHOU. Dynamic resilient modulus for unsaturated clay soils considering effect of limited moisture content fluctuation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 613-620. |
|
||