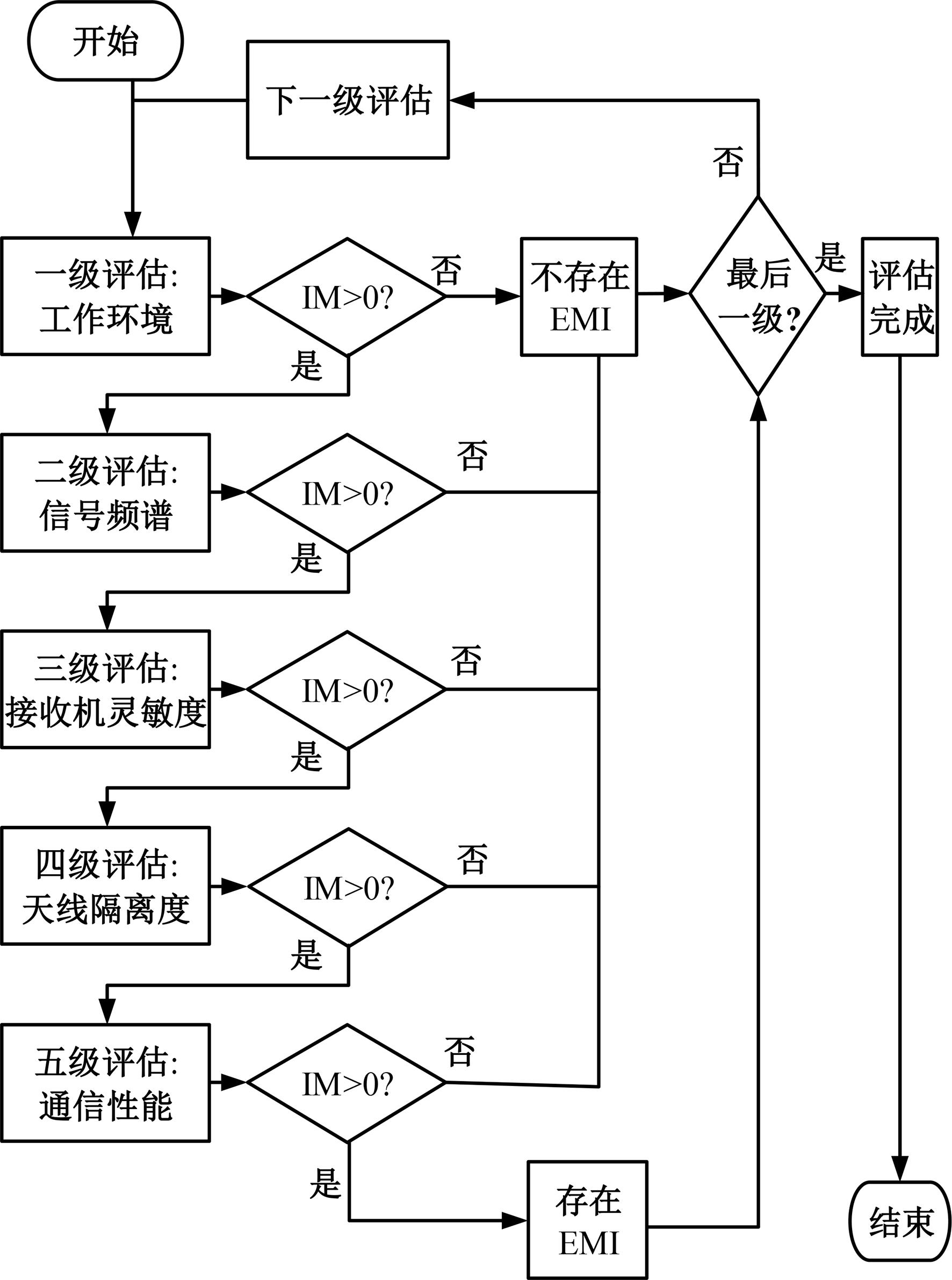
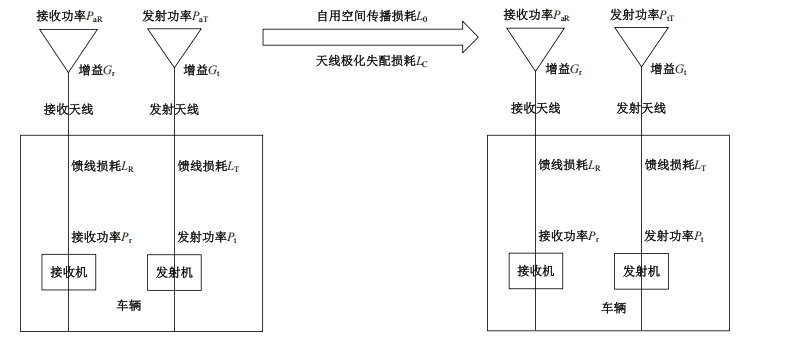
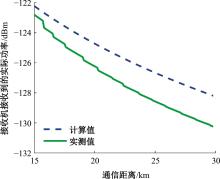
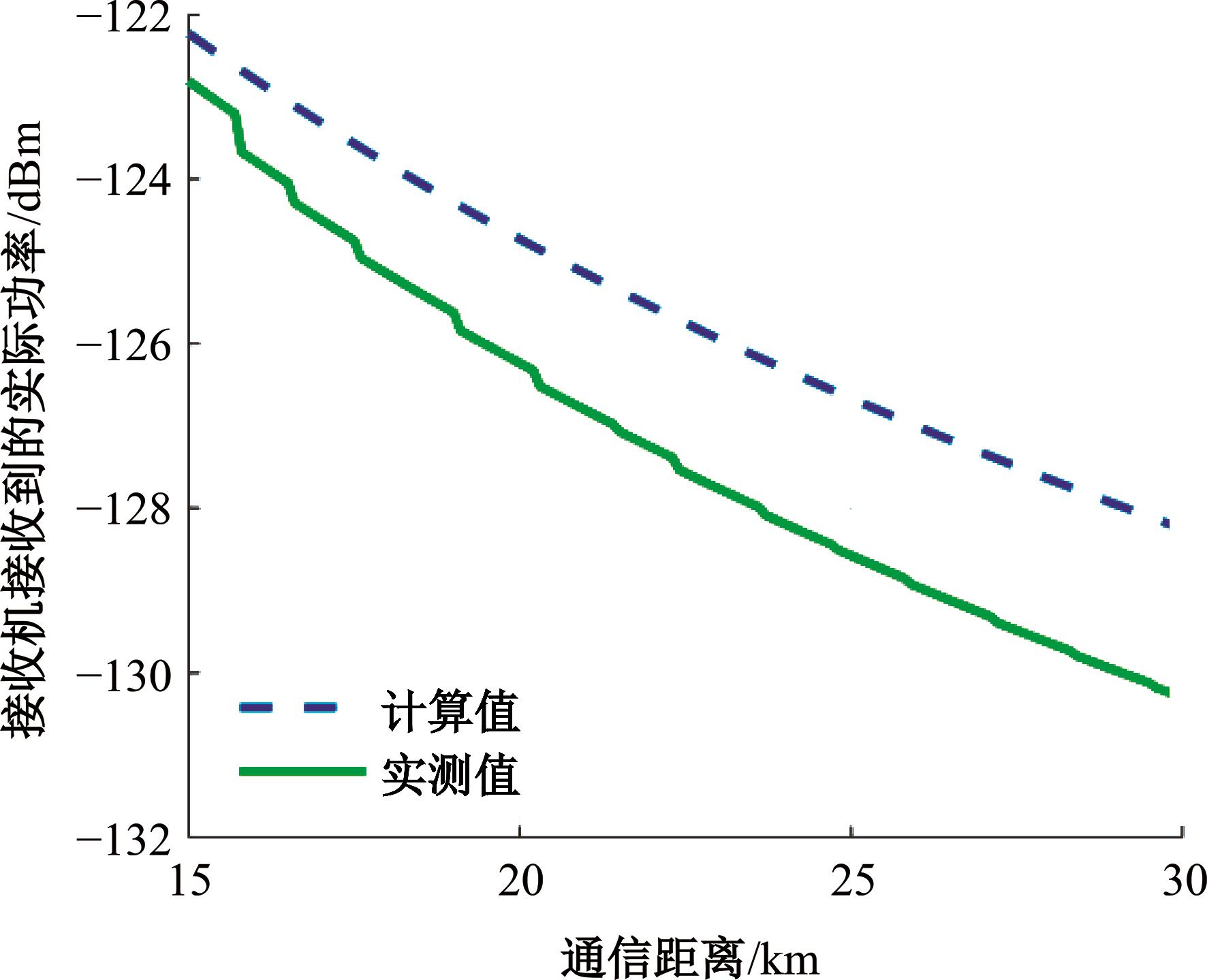
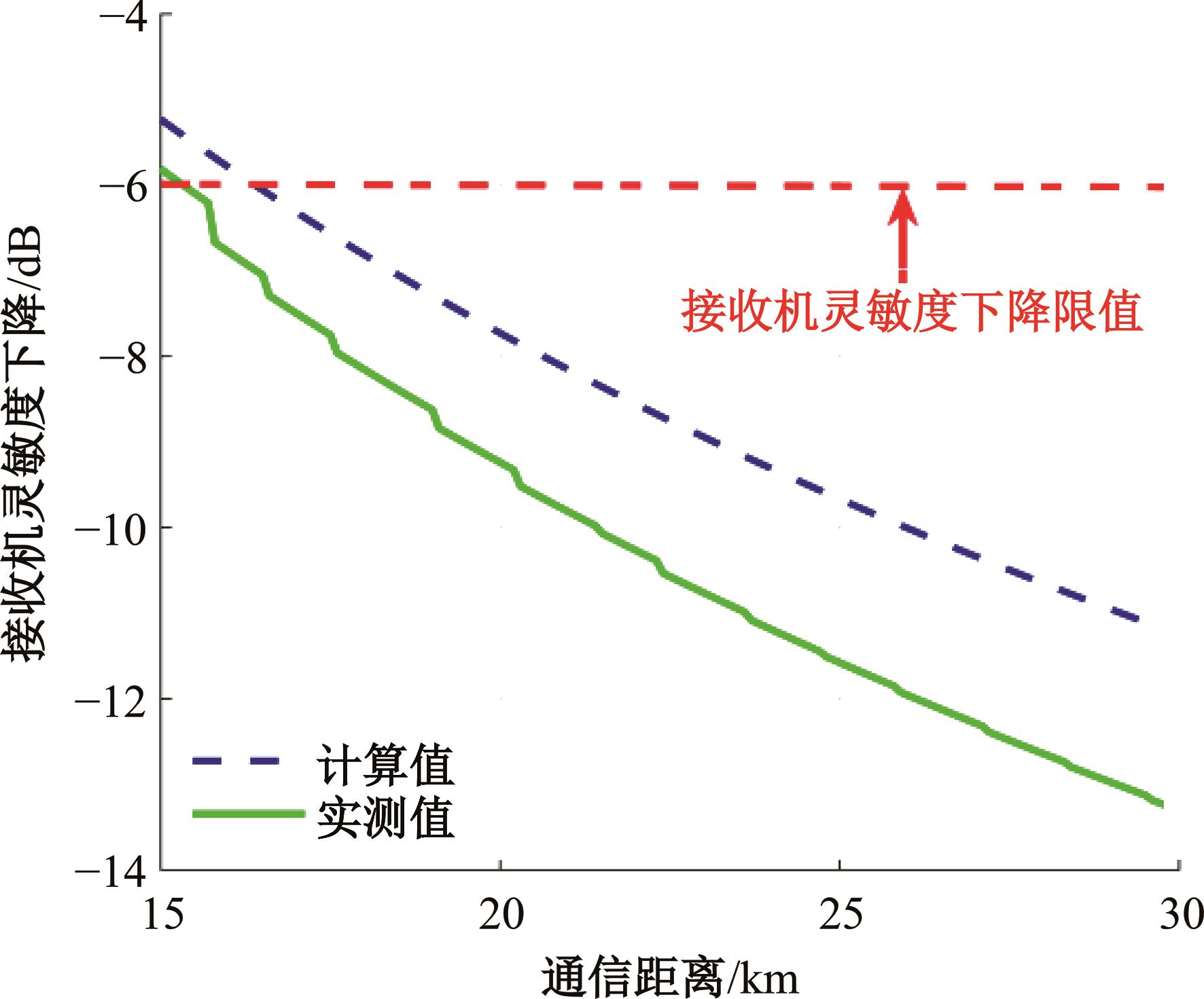
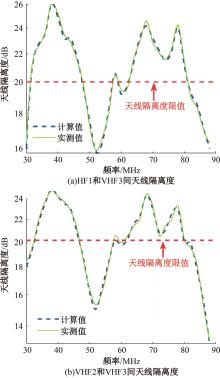
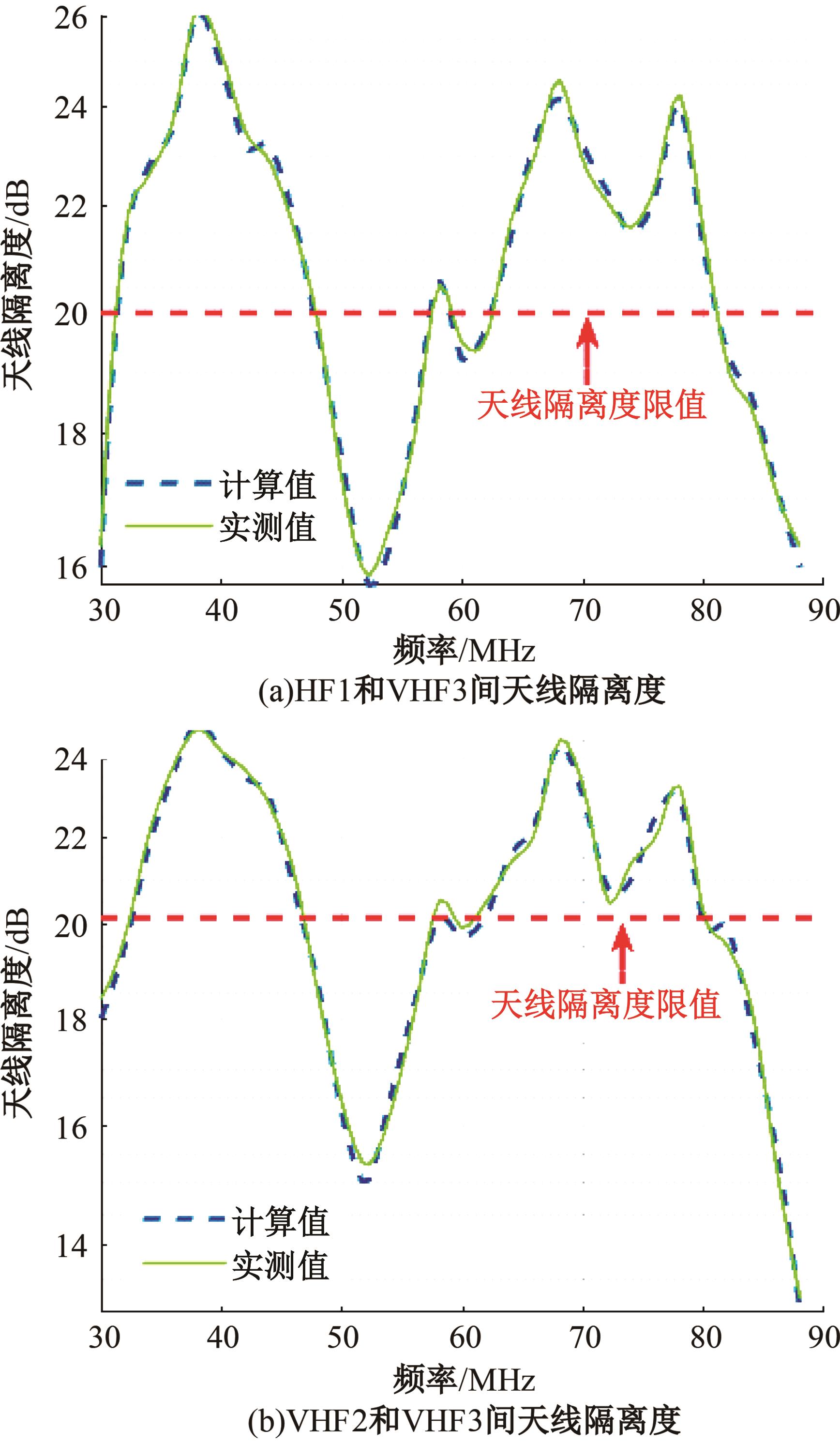
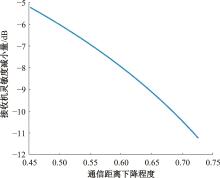
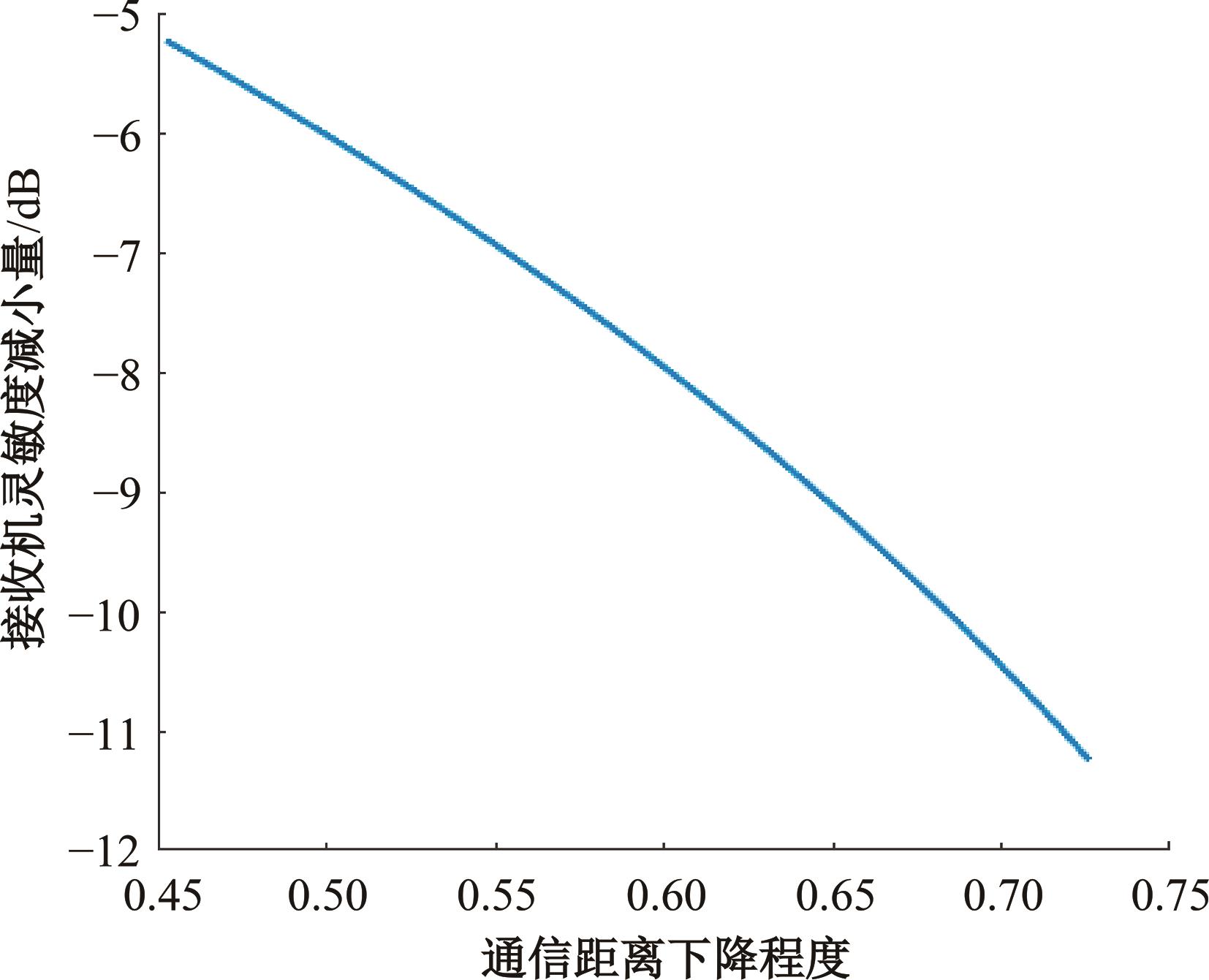
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1780-1787.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230811
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and analysis of the electromagnetic compatibility evaluation model for vehicular communication systems
Guang-shuo ZHANG1( ),Shi-wei ZHANG2,Yang-zhen Qin1,Fu-lin WU1,Bo JIANG1,Hong-min LU1(
),Shi-wei ZHANG2,Yang-zhen Qin1,Fu-lin WU1,Bo JIANG1,Hong-min LU1( )
)
- 1.School of Electronic Engineering,Xidian University,Xi'an 710071,China
2.China North Vehicle Research Institute,Beijing 100072,China
CLC Number:
- U463.67
| [1] | Wang K B, Lu H M, Chen C C, et al. Modeling of system-level conducted EMI of the high-voltage electric drive system in electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2022, 64(3): 741-749. |
| [2] | Wang K B, Lu H M, Li X J, et al. High-frequency modeling of the high-voltage electric drive system for conducted EMI simulation in electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 9(2): 2808-2819. |
| [3] | Qian W W, Yang Y L, Peng J H, et al. EMI modeling for vehicle body using characteristic mode analysis[C]∥2022 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (APEMC), Beijing, China, 2022: 732-734. |
| [4] | 赵晓凡. 新能源车高压电驱动系统电磁兼容关键技术[J]. 安全与电磁兼容, 2018(5): 9-10. |
| Zhao Xiao-fan. Key EMC technologies for high-voltage electrical drive system of new energy vehicle[J]. Safety & EMC, 2018(5): 9-10. | |
| [5] | Konstantinos P. Research on EMI from modern electric vehicles and their recharging systems[C]∥2020 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Rome, Italy, 2020: 1-6. |
| [6] | 系统电磁环境效应试验方法 [S]. |
| [7] | Alain A. EMC performances of a land army vehicle to respect integrated radios reception sensitivity: typical performances needed for "fitted for radio (ffr)" land vehicle[C]∥International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Los Angeles, USA, 2018: 303-308. |
| [8] | Zhao T, Liu X M, Sun P, et al. EMC vehicle-level layout design for railway vehicles in complex electromagnetic environment[C]∥11th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education, Wuyishan, China, 2021: 231-236. |
| [9] | 赵晓凡. 基于功能安全的电磁兼容及防护技术[J]. 微波学报, 2018, 34(): 406-409. |
| Zhao Xiao-fan. Electromagnetic compatibility and protection technology based on functional safety[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2018, 34(Sup.2): 406-409. | |
| [10] | Zhang P C, Sun Y T, Leung H, et al. A novel approach for qos prediction based on bayesian combinational model[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(11): 269-280. |
| [11] | Marc P, Marco A, Ferran S. Measurement and evaluation techniques to estimate the degradation produced by the radiated transients interference to the GSM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2015, 57(6): 1382-1390. |
| [12] | 张世巍,赵晓凡. 军用车辆外部射频干扰试验测试技术研究[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2016, 36(1): 7-13. |
| Zhang Shi-wei, Zhao Xiao-fan. Research of external rf immunity test technique for military vehicles[J]. Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement, 2016, 36(1): 7-13. | |
| [13] | 赵家升, 杨显清, 杨德强. 电磁兼容原理与技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012. |
| [14] | Zhou P, Lv Y H, Chen Z H, et al. System-level EMC assessment for military vehicular communication systems based on a modified four-level assessment model[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(8): 39-53. |
| [15] | 李修和. 战场电磁环境建模与仿真[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014. |
| [16] | 路宏敏, 余志勇, 李万玉. 工程电磁兼容[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2019. |
| [17] | 武南开, 苏东林, 何洪涛, 等. 机载超短波电台邻道干扰减敏特性建模与评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(3): 481-487. |
| Wu Nan-kai, Su Dong-lin, He Hong-tao, et al. Modeling and evaluation of adjacent channel interference desensitization characteristics of airborne ultra-short wave radio [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2017, 43(3): 481-487. | |
| [18] | ITU-R P. The concept of transmission loss for radio links: 341-7[Z]. Geneva: International Telecommunication Union-Radiocommunication Sector, 2019. |
| [19] | Malmstrom J, Frid H, Jonsson B L G, et al. Approximate methods to determine the isolation between antennas on vehicles[C]∥2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Okinawa, Japan, 2016: 131-132. |
| [20] | 张光硕. 装甲车车载天线系统电磁兼容分析[D]. 西安:西安电子科技大学电子工程学院, 2015. |
| Zhang Guang-shuo. Electromagnetic compatibility analysis of vehicle antenna system of armored vehicle [D]. Xi'an: School of Electronic Engineering, Xidian University, 2015. | |
| [21] | 军用无线电台车通用规范 [S]. |
| [22] | 通信设备话音质量与等级标准与评测方法 [S]. |
| [1] | Kai-yu YANG,Wei LIU,Tian-hao WANG,Xian-li YU,Yin-han GAO,Xi-lai MA. A calculation method for uncertainty of crosstalk in multi⁃conductor transmission line [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 747-753. |
| [2] | YANG Cheng, SONG Ping, PENG Wen-jia, JIN Hao-long, PAN Zhi-qiang. Design of armored vehicle integrated test system based on hybrid bus [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 186-198. |
| [3] | YANG Cheng, SONG Ping, PENG Wen-jia, DENG Gao-shou, LIU Xiong-jun. Design of host computer platform for armored vehicle integrated test system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1796-1803. |
| [4] | SHEN Xuan-jing, FAN Zi-long, LYU Ying-da, CHEN Hai-peng. Image tampering assessment model based on statistical features [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1232-1238. |
| [5] | GAO Yin-han, AN Zhan-yang, WANG Ju-xian, WANG Tian-hao, LIU Chang-ying, ZHANG Jun-dong. Application of equivalent cable bundle method in time domain radiation sensitivity of automotive cable harness [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 946-952. |
| [6] | ZHOU Feng-dao,DONG Wei,BAO Zhi-qiang,XUE Kai-chang,HU Yue,SUN Cai-tang. Three-phase EMI filter based on switching power supply [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 216-221. |
| [7] | TIAN Li-yuan,WANG Qing-nian,WANG Peng-yu. FlexRay network development of dual-motor hybrid power-train system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 585-591. |
| [8] | WANG Jian-lin, YANG Yin-sheng, WANG Xue-ling. Evaluation of land use in Yellow river delta based on extension data mining [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 479-483. |
| [9] | AN Jing, WU Jun-feng, WU Yi-hui. Electromagnetic compatibility design of electronic control system for attitude control flywheel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(4): 998-1003. |
| [10] | ZHANG Cheng, LIAO Jian-Xin, WANG Chun, NI Ping. Study on realtime quantitative evaluation of service operating quality [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 586-0591. |
| [11] | Xie Ning, Zhao Xiao-hui, Mo Xiu-ling,Sun Yu-jing . Performance analysis of UWB receiver using Pre-Rake combining [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(05): 1192-1196. |
| [12] | Gao Yin-han, Ma Xi-lai, Chen Ru-na. Electromagnetic compatibility prediction of automobile based on fuzzy inference [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(03): 399-0403. |
| [13] | LU Xiao-fang, WANG Chuan, ZHAO Shu-kuan. Evaluation model of regional competition ability of talents [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2003, (3): 82-85. |
|