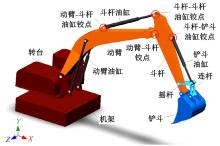
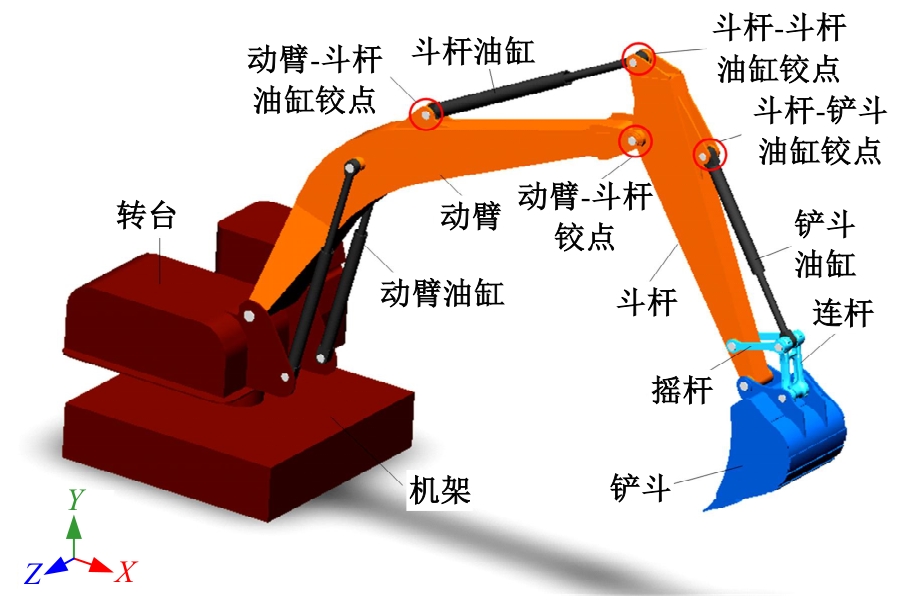
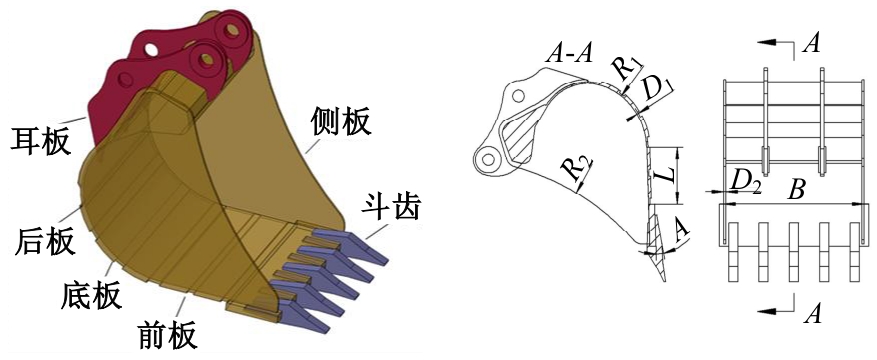
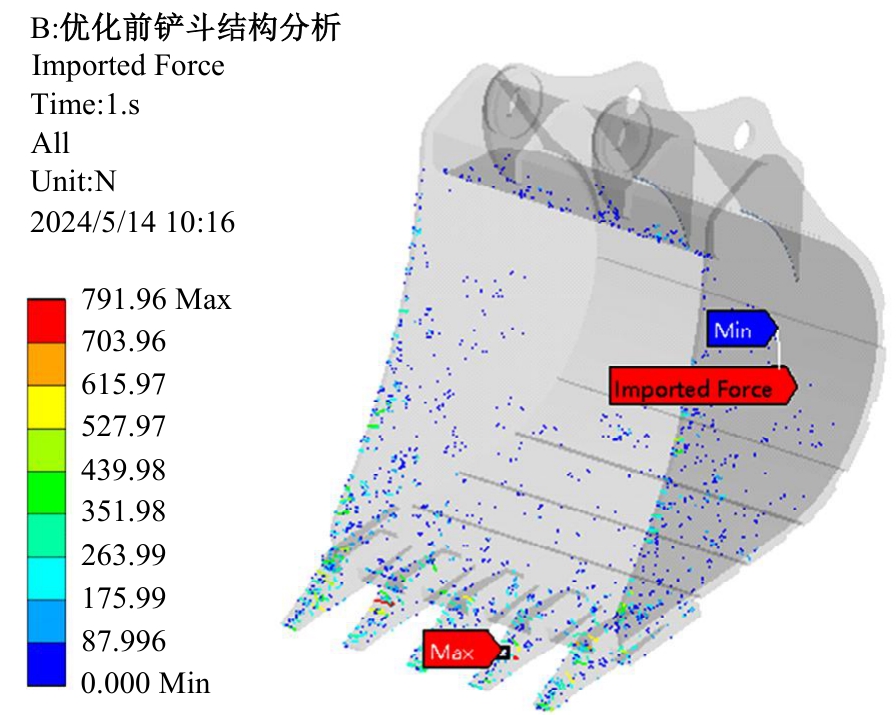
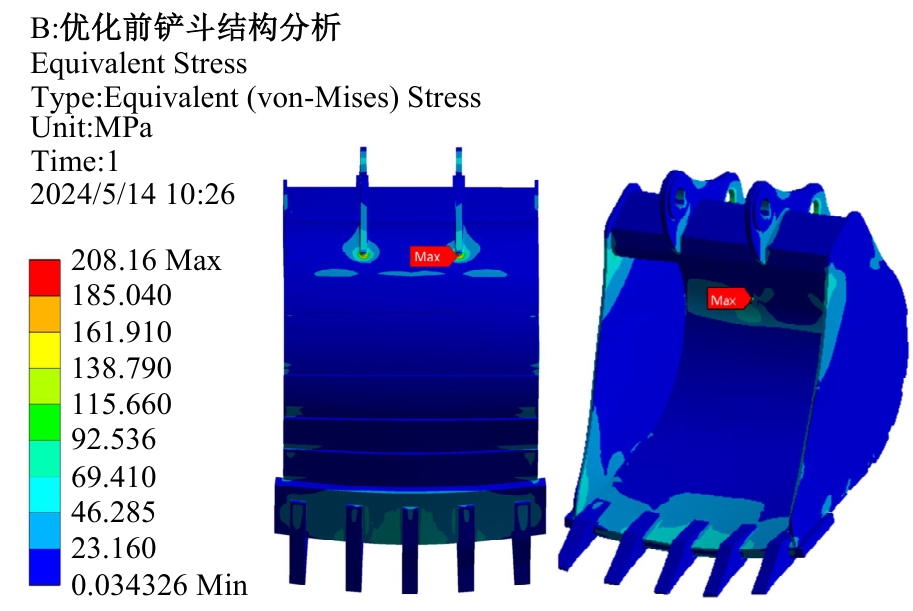
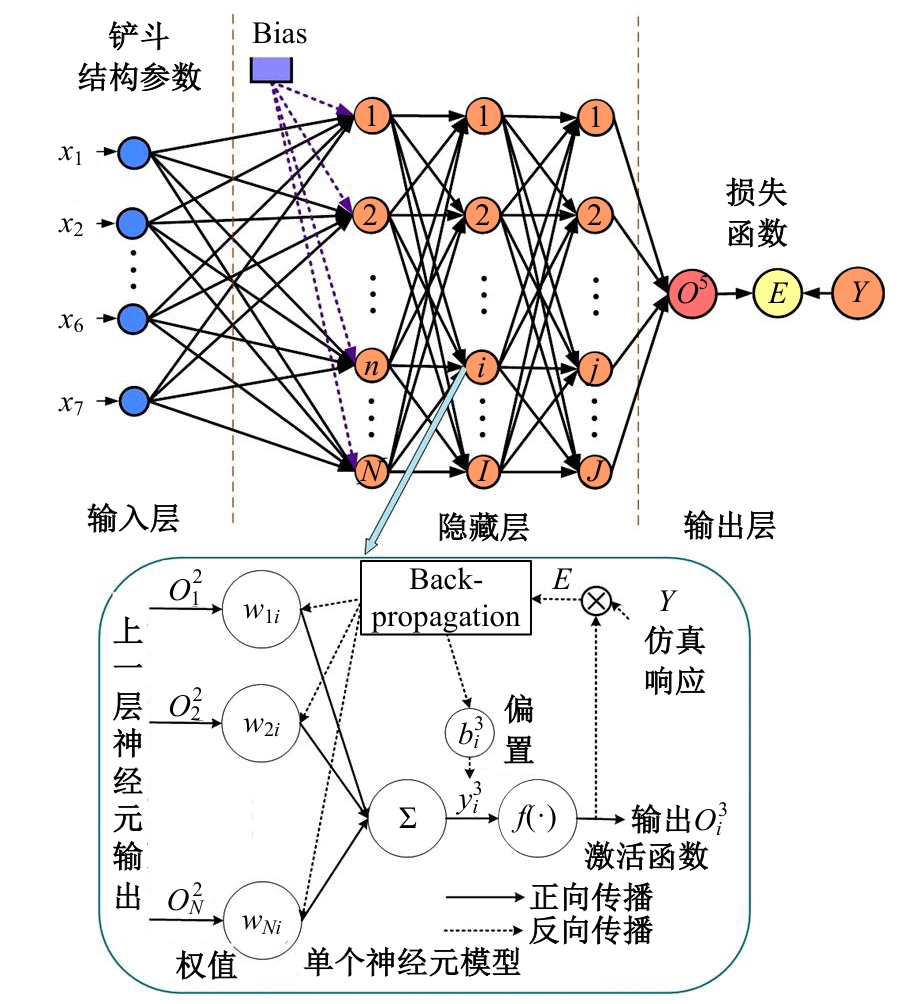
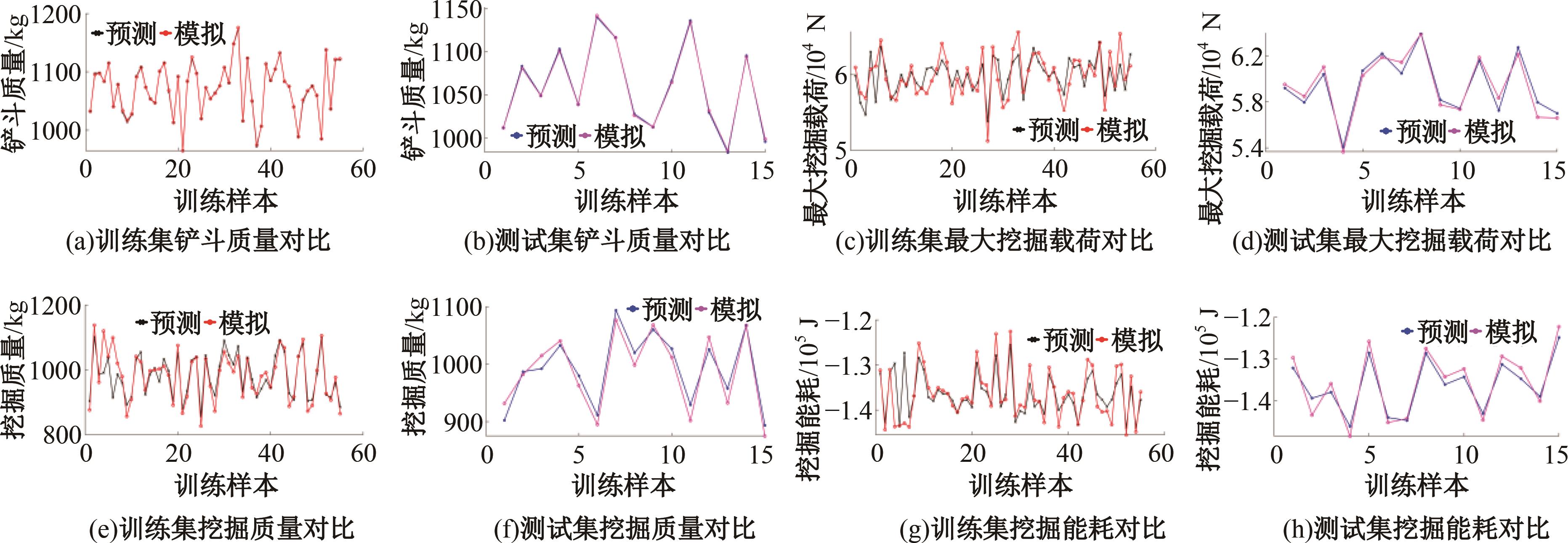
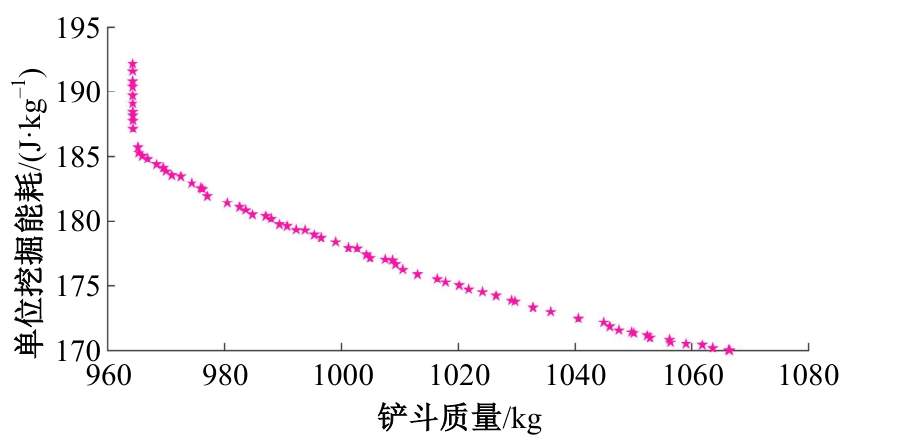
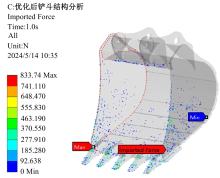
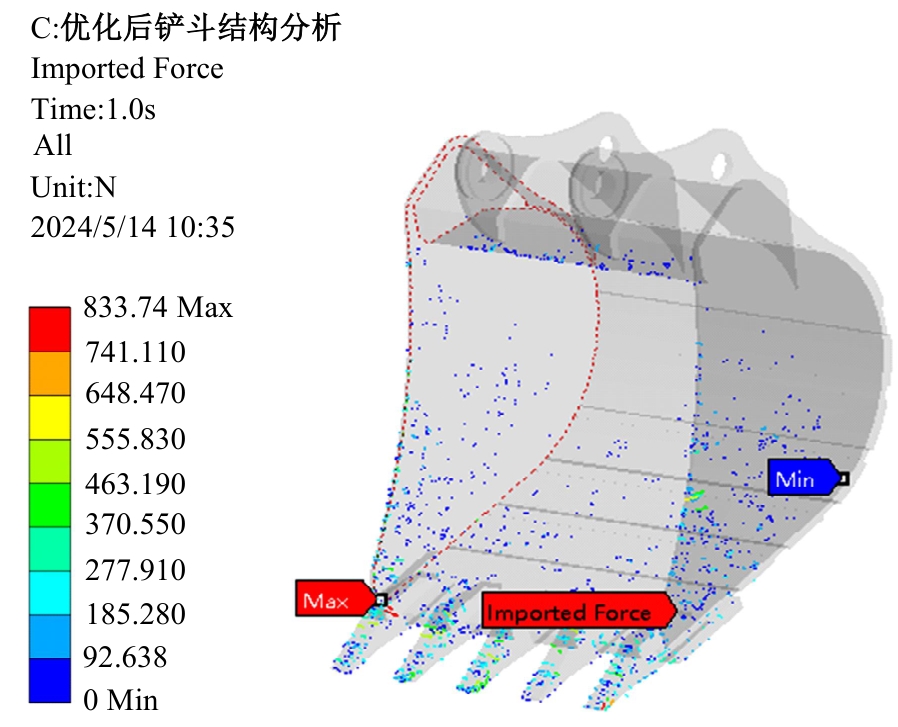
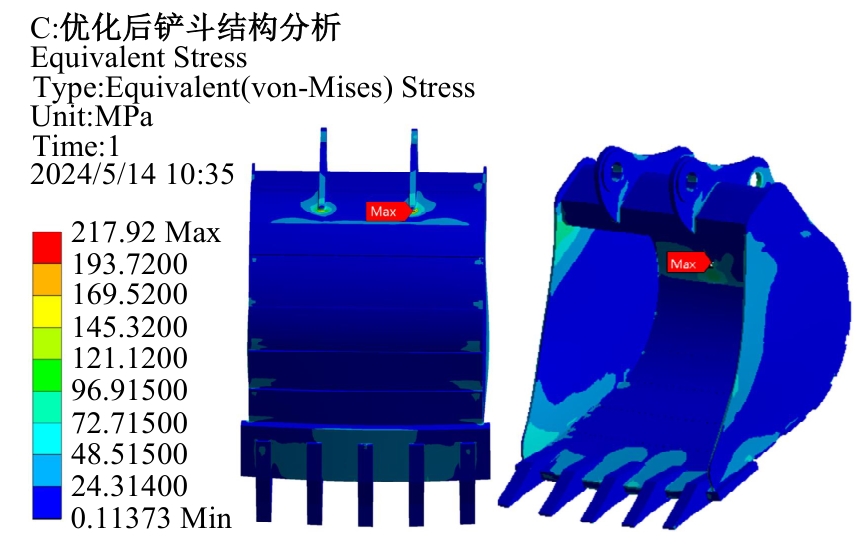
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3485-3497.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240322
Structural optimization design of excavator bucket based on improved depth surrogate model
Yi-xin CHEN( ),Zai-xu CHEN,Yong-sheng LIU,Shuai YANG,Hao-jie GUO,Jin-san JIA
),Zai-xu CHEN,Yong-sheng LIU,Shuai YANG,Hao-jie GUO,Jin-san JIA
- Key Laboratory of Road Construction Technology & Equipment,Ministry of Education,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- TU621
| [1] | 王同建, 杨书伟, 谭晓丹, 等. 基于DEM-MBD联合仿真的液压挖掘机作业性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(4): 811-818. |
| Wang Tong-jian, Yang Shu-wei, Tan Xiao-dan, et al. Performance analysis of hydraulic excavator based on DEM-MBD co-simulation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 811-818. | |
| [2] | 蔡敢为, 黄一洋, 田军伟, 等. 一种新型正铲液压挖掘机工作机构的研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(13): 132-143. |
| Cai Gan-wei, Huang Yi-yang, Tian Jun-wei, et al. Research on a new working mechanism of face-shovel hydraulic excavator[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(13): 132-143. | |
| [3] | Palomba I, Richiedei D, Trevisani A, et al. Estimation of the digging and payload forces in excavators by means of state observers[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 134: No.106356. |
| [4] | Saldaña R A, Bustos G A, Peña L D J, et al. Structural design of an agricultural backhoe using TA, FEA, RSM and ANN[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 172: No.105278. |
| [5] | Yuan Y L, Lv L Y, Wang S, et al. Multidisciplinary co-design optimization of structural and control parameters for bucket wheel reclaimer[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 15(3): 1-11. |
| [6] | Sun W, Peng X, Dou J, et al. Surrogate-based weight reduction optimization of forearm of bucket-wheel stacker reclaimer[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2020, 61(3): 1287-1301. |
| [7] | Shi Y P, Xia Y M, Zhang Y M, et al. Intelligent identification for working-cycle stages of excavator based on main pump pressure[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 109: No.102991. |
| [8] | Si J K, Zhao S Z, Feng H C, et al. Multi-objective optimization of surface-mounted and interior permanent magnet synchronous motor based on Taguchi method and response surface method[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 67-73. |
| [9] | Forrester I A, Keane J A. Recent advances in surrogate-based optimization[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2008, 45(1): 50-79. |
| [10] | Libano F, Rech P, Tambarar L, et al. On the reliability of linear regression and pattern recognition feedforward artificial neural networks in FPGAs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2018, 65(1): 288-295. |
| [11] | Li F, Zurada J M, Liu Y, et al. Input layer regularization of multilayer feedforward neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 10979-10985. |
| [12] | 单德山, 张潇, 顾晓宇, 等. 基于多层感知深度学习的大跨度斜拉桥索力调整[J]. 桥梁建设, 2021, 51(1): 14-20. |
| Shan De-shan, Zhang Xiao, Gu Xiao-yu, et al. Cable force adjustment for long-span cable-stayed bridge based on multilayer perceptron deep learning[J]. Bridge Construction, 2021, 51(1): 14-20. | |
| [13] | 林景亮, 黄运保, 李海艳, 等. 基于深度代理模型的叉车臂架液压系统设计优化[J]. 中国机械工程, 2022, 33(3): 290-298. |
| Lin Jing-liang, Huang Yun-bao, Li Hai-yan, et al. Design optimization for hydraulic systems of forklift boom based on deep surrogate model[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(3): 290-298. | |
| [14] | 晏福, 徐建中, 李奉书. 混沌灰狼优化算法训练多层感知器[J].电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 872-879. |
| Yan Fu, Xu Jian-zhong, Li Feng-shu. Training multi-layer perceptrons using chaos grey wolf optimizer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 872-879. | |
| [15] | Moayedi H, Abdullahi M M, Nguyen H, et al. Comparison of dragonfly algorithm and harris hawks optimization evolutionary data mining techniques for the assessment of bearing capacity of footings over two-layer foundation soils[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2019, 37(1): 1-11. |
| [16] | Pandey C A, Tikkiwal A V. Stance detection using improved whale optimization algorithm[J]. Complex Intelligent Systems, 2021, 7(3): 1-24. |
| [17] | Xue Y, Tong Y L, Ferrante N. An ensemble of differential evolution and Adam for training feed-forward neural networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 608: 453-471. |
| [18] | Wang L, Liu Z C. Data-driven product design evaluation method based on multi-stage artificial neural network[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2021, 103: No.107117. |
| [19] | 南敬昌, 杜有益, 王明寰, 等. 深度学习架构神经网络对超宽带天线建模优化[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(13): 362-368. |
| Jing-chang Nan, Du You-yi, Wang Ming-huan, et al. Deep learning architecture and neural network optimization of ultra-wideband antenna modeling[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(13): 362-368. | |
| [20] | 孔翔. 大型矿用挖掘机铲斗结构优化设计[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学机械工程学院,2018. |
| Kong Xiang. Structure optimization design of large mining excavator bucket[D]. Dalian: School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2018. | |
| [21] | 雷睿. 液压挖掘机铲斗挖掘效率优化设计研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学机械工程学院,2018. |
| Lei Rui. Optimal design of excavation efficiency of hydrualic excavator bucket[D]. Hangzhou: College of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2018. | |
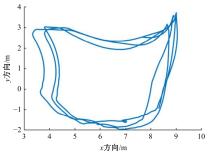
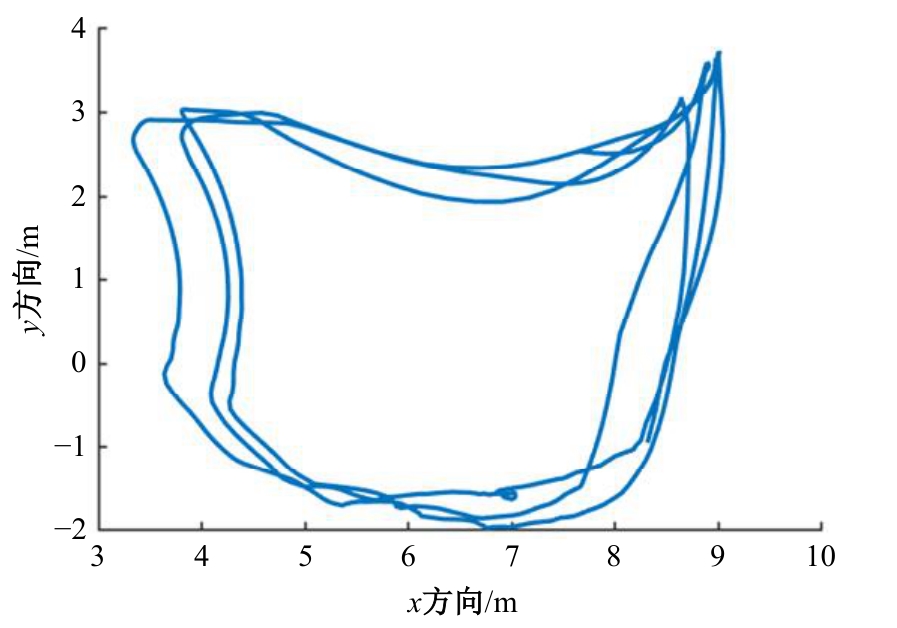
| [22] | 陈一馨, 刘永生, 吕彭民. 挖掘机载荷谱试验的作业介质及作业类型[J]. 筑路机械与施工机械化, 2018, 5(12): 117-122. |
| Chen Yi-xin, Liu Yong-sheng, Lv Peng-min, et al. Operation medium and type of load spectrum test of excavator[J]. Road Machinery & Construction Mechanization, 2018, 5(12): 117-122. | |
| [23] | 刘坤宇, 苏宏杰, 李飞宇, 等. 基于响应曲面法的土壤离散元模型的参数标定研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2021, 42(9): 143-149. |
| Liu Kun-yu, Su Hong-jie, Li Fei-yu, et al. Research on parameter calibration of soil discrete element model based on response surface method[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2021, 42(9): 143-149. | |
| [24] | 顿国强, 陈海涛, 纪文义. 基于EDEM仿真与SolidWorks Simulation的凿式深松铲有限元分析[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2017, 51(5): 678-682. |
| Guo-qiang Dun, Chen Hai-tao, Ji Wen-yi. Finite element analysis of chisel-type deep shovel based on EDEM and Solid Works Simulation[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2017, 51(5): 678-682. | |
| [25] | Coetzee C. Review: calibration of the discrete element method[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 310: 104-142. |
| [26] | 张锐, 韩佃雷, 吉巧丽, 等. 离散元模拟中沙土参数标定方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(3): 49-56. |
| Zhang Rui, Han Dian-lei, Ji Qiao-li, et al. Calibration methods of sandy soil parameters in simulation of discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(3): 49-56. | |
| [27] | Maasa A L, Hannun A Y, Ng A Y. Rectifier n onlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]∥Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: PMLR, 2013: 456-462. |
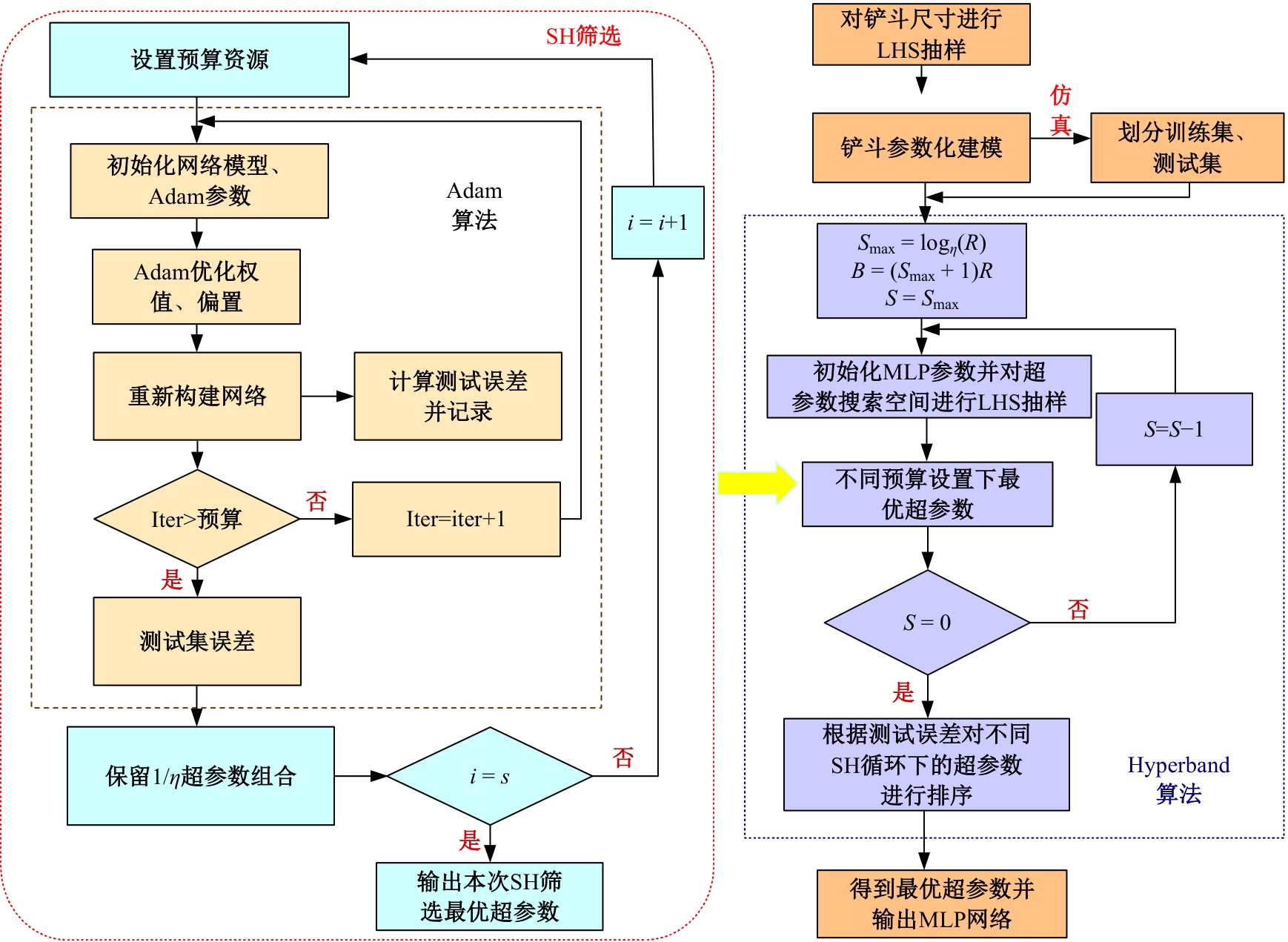
| [28] | Li L S, Kevin J, Giulia D, et al. Hyperband: a novel bandit-based approach to hyperparameter optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2018, 18(1): 6765-6816. |
| [1] | Guo-fa LI,Ze-quan CHEN,Jia-long HE. New adaptive sampling strategy for structural reliability analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 1975-1981. |
| [2] | MAO Yu-ze, WANG Li-qin. Influence of squirrel-cage flexible support on the dynamic performance of ball bearing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
| [3] | LIU Ying, ZHANG Kai, YU Xiang-jun. Multi-objective optimization of hydrostatic bearing of hollow shaft based on surrogate model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1130-1137. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yan, HUANG He, REN Lu-quan. Drag reduction experiment of bionic excvavtor bucket teeth [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 126-130. |
|
||