| 1 |
LI C, CAI Y, CHEN S H, et al. Classification and characterization of class Ⅲ malocclusion in Chinese individuals[J]. Head Face Med, 2016, 12(1): 31.
|
| 2 |
BUELLER H. Ideal facial relationships and goals[J]. Facial Plast Surg, 2018, 34(5): 458-465.
|
| 3 |
KIM M, LEE D Y, LIM Y K, et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of soft tissue changes after mandibular setback surgery in class Ⅲ malocclusion patients according to extent of mandibular setback, vertical skeletal pattern, and genioplasty[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2010, 109(5): e20-e32.
|
| 4 |
梁立卿, 孙 健, 李亚莉, 等. 正颌外科二维头影测量与三维面颅重建测量的比较[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2016, 30(6): 342-345, 351.
|
| 5 |
史雨林, 商洪涛, 田 磊, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(5): 612-616. 畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(5): 612-616.
|
| 6 |
刘文静, 史雨林, 许方方, 等. 偏突颌畸形患者手术前后面部软组织的三维测量研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018, 18(14): 2669-2673.
|
| 7 |
KAKLAMANOS E G, KOLOKITHA O E. Relation between soft tissue and skeletal changes after mandibular setback surgery:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Craniomaxillofac Surg,2016, 44(4): 427-435.
|
| 8 |
CHEUNG M Y, ALMUKHTAR A, KEELING A, et al. The accuracy of conformation of a generic surface mesh for the analysis of facial soft tissue changes[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0152381.
|
| 9 |
徐 陆, 吴 嵩, 许 衍, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错( )患者双颌术后面部各区域软组织三维改变的研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2021, 41(4): 337-341. )患者双颌术后面部各区域软组织三维改变的研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2021, 41(4): 337-341.
|
| 10 |
SHINDOI J M, MATSUMOTO Y, SATO Y, et al. Soft tissue cephalometric norms for orthognathic and cosmetic surgery[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 71(1): e24-e30.
|
| 11 |
RASTEAU S, SIGAUX N, LOUVRIER A, et al. Three-dimensional acquisition technologies for facial soft tissues-Applications and prospects in orthognathic surgery[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2020, 121(6): 721-728.
|
| 12 |
ONAGA Y, KAMIO T, TAKAKI T, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of soft and hard tissue changes following orthognathic surgery[J]. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll, 2021, 62(3): 151-161.
|
| 13 |
唐正龙, 王 兴, 伊 彪, 等. 正颌外科手术中出血量和术后肿胀程度的多因素相关性研究[J]. 贵阳医学院学报, 2008, 33(6): 610-613.
|
| 14 |
KAU C H, CRONIN A, DURNING P, et al. A new method for the 3D measurement of postoperative swelling following orthognathic surgery[J]. Orthod Craniofac Res, 2006, 9(1): 31-37.
|
| 15 |
NIKE E, RADZINS O, PIRTTINIEMI P, et al. Evaluation of facial soft tissue asymmetric changes in Class Ⅲ patients after orthognathic surgery using three-dimensional stereophotogrammetry[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2023, 52(3): 361-370.
|
| 16 |
HUANG L, LI Z C, YAN J, et al. Evaluation of facial soft tissue thickness in asymmetric mandibular deformities after orthognathic surgery[J]. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg, 2021, 43(1): 37.
|
| 17 |
CHOI S H, LEE H, HWANG J J, et al. Differences in soft-tissue thickness changes after bimaxillary surgery between patients with vertically high angle and normal angle[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2021, 159(1): 30-40.
|
| 18 |
JOSS C U, JOSS-VASSALLI I M, BERGÉ S J, et al. Soft tissue profile changes after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy for mandibular setback: a systematic review[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 68(11): 2792-2801.
|
| 19 |
SEO S W, JUNG Y S, BAIK H S. Three-dimensional analysis of midfacial soft tissue changes after maxillary posterior impaction and intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy for mandibular setback in class Ⅲ patients[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28(7): 1789-1796.
|
| 20 |
RUPPERTI S, WINTERHALDER P, RUDZKI I,et al.Changes in the facial soft-tissue profile after mandibular orthognathic surgery[J].Clin Oral Investig,2019,23(4): 1771-1776.
|
| 21 |
CHEN C M, CHEN M Y, CHENG J H, et al. Facial profile and frontal changes after bimaxillary surgery in patients with mandibular prognathism[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2018, 117(7): 632-639.
|
| 22 |
NIKE E, RADZINS O, PIRTTINIEMI P, et al. Evaluation of facial soft tissue asymmetric changes in Class Ⅲ patients after orthognathic surgery using three-dimensional stereophotogrammetry[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2023, 52(3): 361-370.
|
| 23 |
杜琎佳, 沈 晨, 阚全龙, 等. 成人骨性Ⅲ类错(牙合)患者不同垂直骨面型基骨及牙弓宽度的特征[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(4): 555-559.
|
| 24 |
JUNG Y J, KIM M J, BAEK S H. Hard and soft tissue changes after correction of mandibular prognathism and facial asymmetry by mandibular setback surgery: three-dimensional analysis using computerized tomography[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2009, 107(6): 763-771.e8.
|
| 25 |
KOH C H, CHEW M T. Predictability of soft tissue profile changes following bimaxillary surgery in skeletal class Ⅲ Chinese patients[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2004, 62(12): 1505-1509.
|
| 26 |
吴雨桐, 孙 健, 李亚莉, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错 正颌手术前、后面部软、硬组织变化比率的三维研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(2): 158-164. 正颌手术前、后面部软、硬组织变化比率的三维研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(2): 158-164.
|
| 27 |
吴雨桐. 骨性Ⅲ类错 正颌手术前后面部软硬组织变化比率的三维研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019. 正颌手术前后面部软硬组织变化比率的三维研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019.
|
 畸形患者正颌术后颏部软组织和骨组织形态变化及其影响因素分析
畸形患者正颌术后颏部软组织和骨组织形态变化及其影响因素分析
 )
)
 )
)
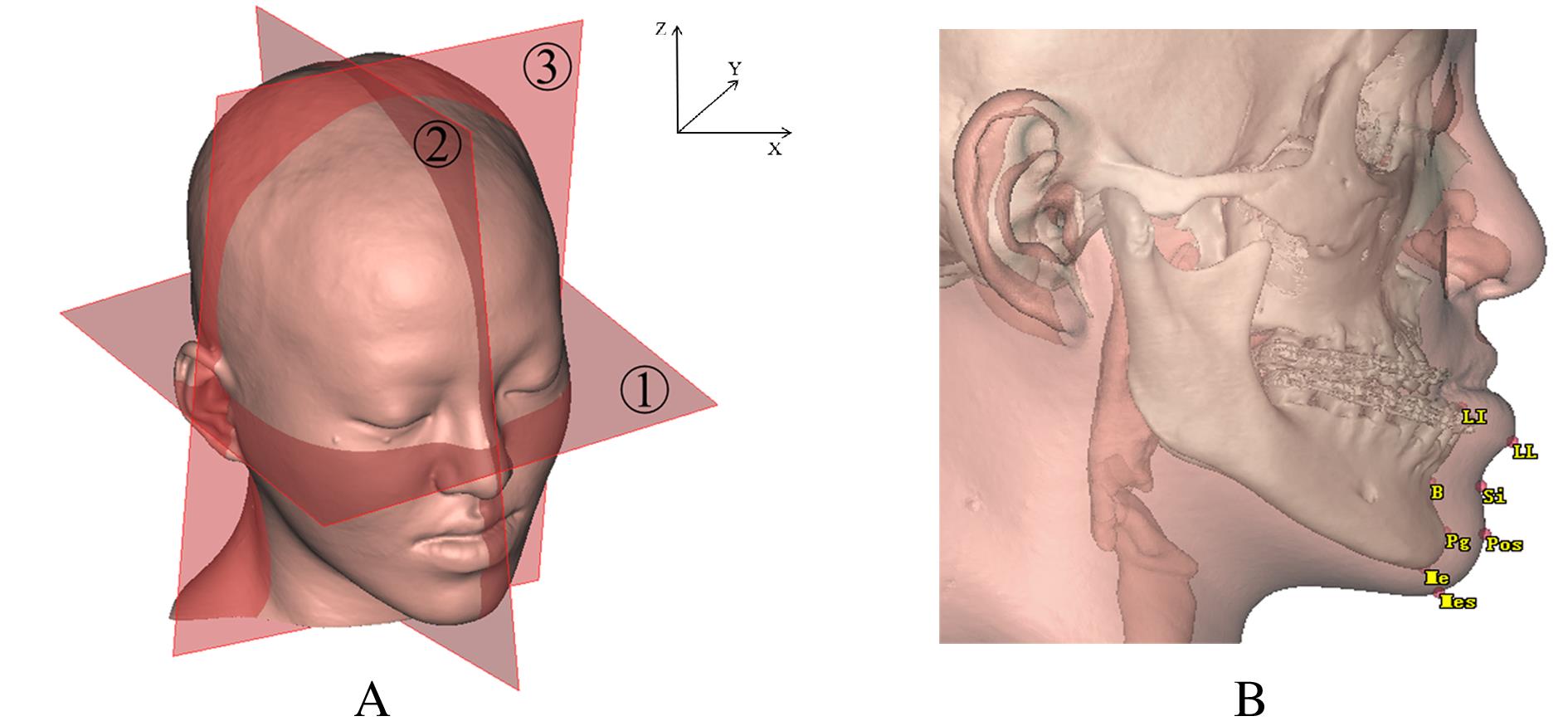
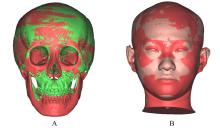
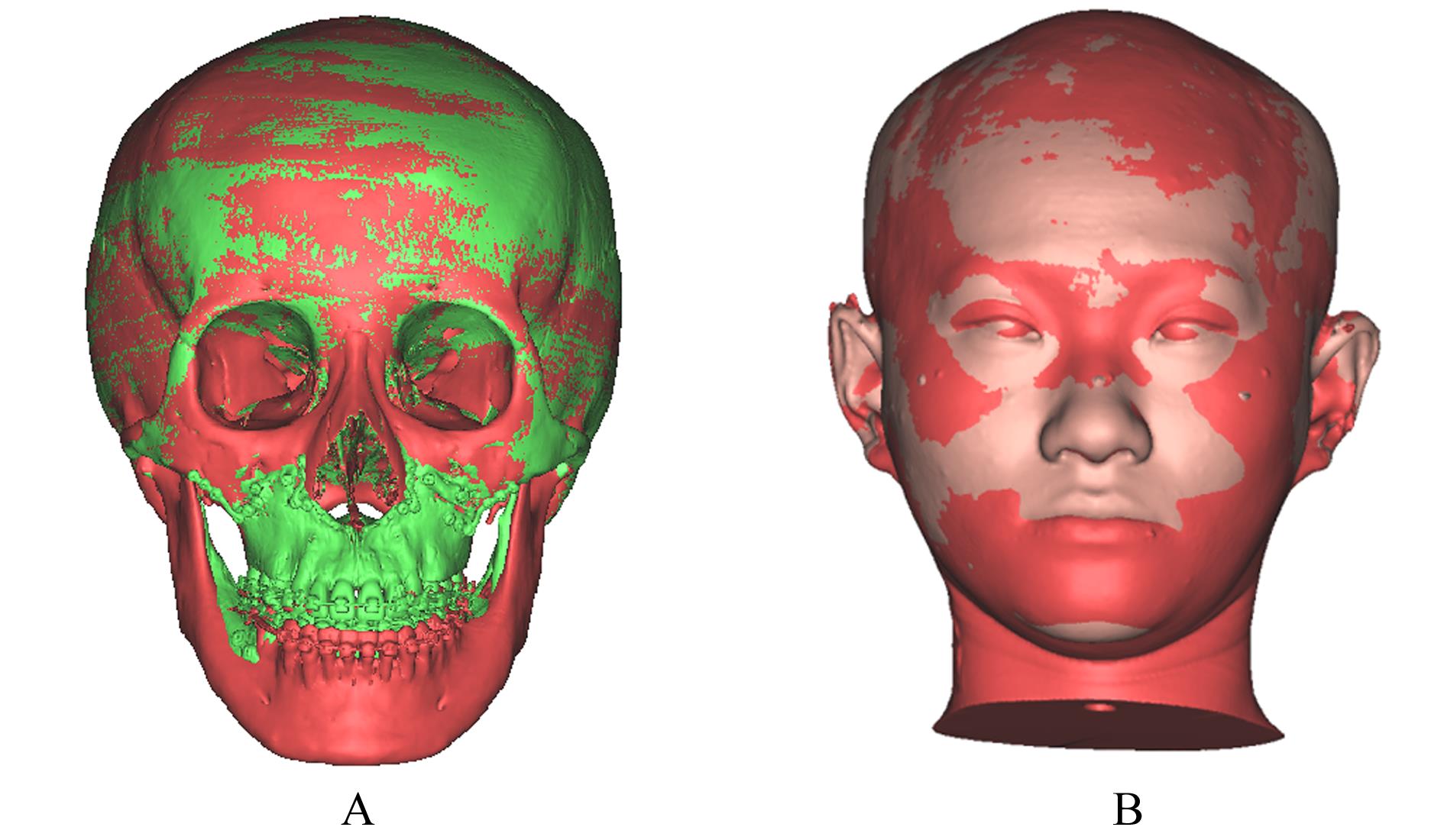
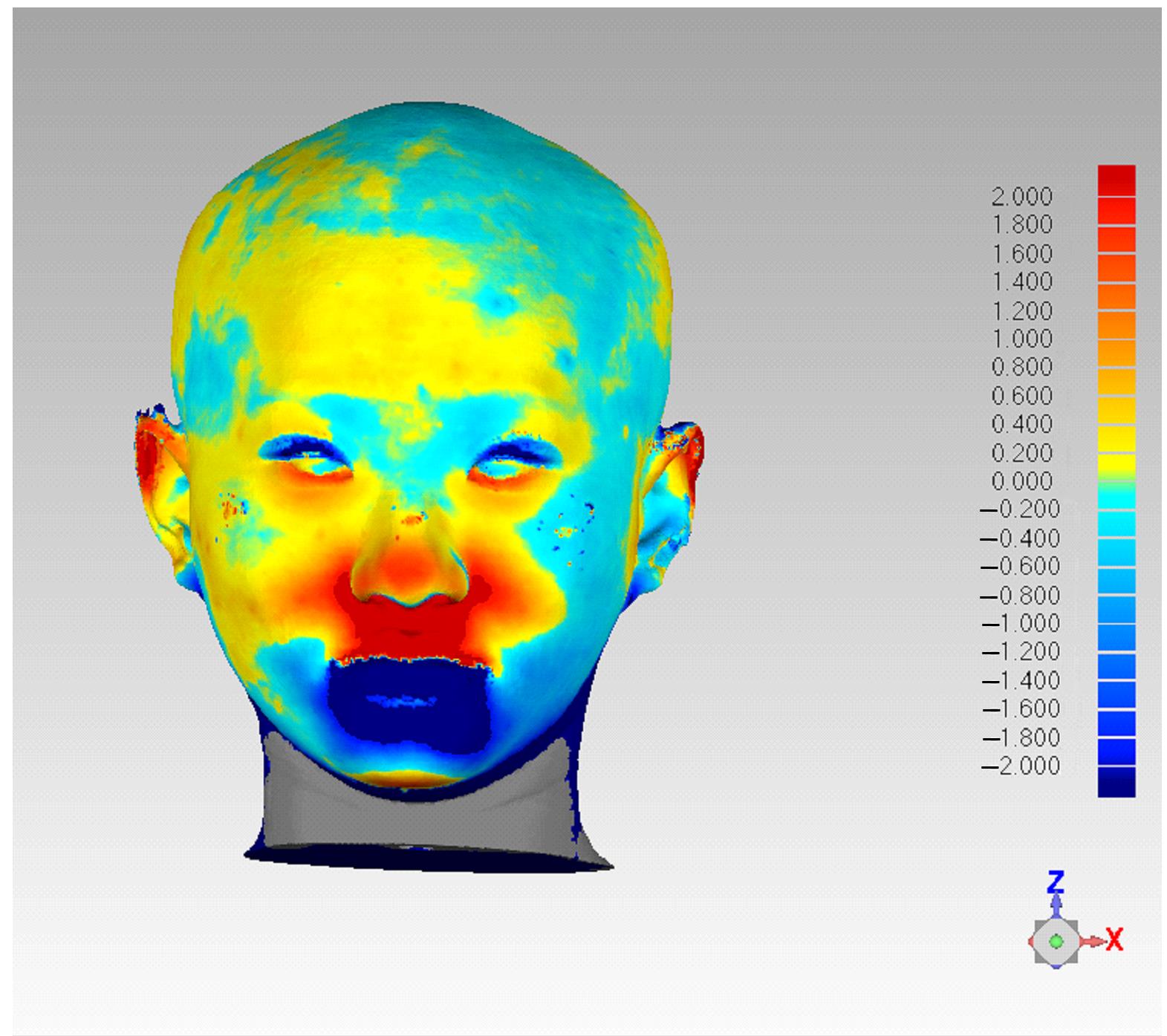
 畸形患者正颌术后颏部软组织和骨组织形态变化,并分析其影响因素。 方法 收集于本院行双颌正颌手术的成人患者19例,其中男性患者9例,女性患者10例。所有患者于术前1周(T0)和术后12个月(T1)进行全头颅计算机断层扫描(CT)获取面部数据,采用ProPlan CMF 3.0软件进行术前及术后面部软组织和骨组织的三维重建和配准。测量并计算颏部软组织厚度和解剖标记点于水平、矢状和垂直向上移动量的相关性及比值。 结果 正颌术后下颌后退量以下唇红唇及颏唇沟区最大,沿此区域向周边扩散软组织后退量逐渐递减。颏下区后退量较小,在颏下点处颏部有前出趋势。与T0时比较,T1时下唇度突点(LL)软组织厚度增加(P<0.05)。线性回归分析,水平向(X)上,随着骨组织向左移动,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.795,R2=0.832)、颏唇沟点(Si)(B=0.876,R2=0.987)、软组织颏前点(Pos)(B=0.890,R2=0.971)和软组织颏下点(Mes)(B=0.942,R2=0.978)均呈负向改变,向左移动,软组织和骨组织移动方向一致;矢状向(Y)上,随着骨组织向后移动,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.882,R2=0.934)、Si(B=0.946,R2=0.847)、Pos(B=0.839,R2=0.909)和Mes(B=0.666,R2=0.455)均向后移动,软组织和骨组织组织移动方向一致;垂直向(Z)上,随着骨组织的上移,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.932,R2=0.686)、Si(B=0.834,R2=0.469)和Mes(B=0.925,R2=0.709)均向下移动;Pos(B=0.487,R2=0.444)向上移动。在水平、矢状和垂直向上各颏部解剖标记点软组织移动量(ΔSM)和骨组织移动量(ΔBM)相关性较强(0.6<r<1.0,P<0.01)。 结论 骨性Ⅲ类错
畸形患者正颌术后颏部软组织和骨组织形态变化,并分析其影响因素。 方法 收集于本院行双颌正颌手术的成人患者19例,其中男性患者9例,女性患者10例。所有患者于术前1周(T0)和术后12个月(T1)进行全头颅计算机断层扫描(CT)获取面部数据,采用ProPlan CMF 3.0软件进行术前及术后面部软组织和骨组织的三维重建和配准。测量并计算颏部软组织厚度和解剖标记点于水平、矢状和垂直向上移动量的相关性及比值。 结果 正颌术后下颌后退量以下唇红唇及颏唇沟区最大,沿此区域向周边扩散软组织后退量逐渐递减。颏下区后退量较小,在颏下点处颏部有前出趋势。与T0时比较,T1时下唇度突点(LL)软组织厚度增加(P<0.05)。线性回归分析,水平向(X)上,随着骨组织向左移动,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.795,R2=0.832)、颏唇沟点(Si)(B=0.876,R2=0.987)、软组织颏前点(Pos)(B=0.890,R2=0.971)和软组织颏下点(Mes)(B=0.942,R2=0.978)均呈负向改变,向左移动,软组织和骨组织移动方向一致;矢状向(Y)上,随着骨组织向后移动,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.882,R2=0.934)、Si(B=0.946,R2=0.847)、Pos(B=0.839,R2=0.909)和Mes(B=0.666,R2=0.455)均向后移动,软组织和骨组织组织移动方向一致;垂直向(Z)上,随着骨组织的上移,颏部软组织解剖标记点LL(B=0.932,R2=0.686)、Si(B=0.834,R2=0.469)和Mes(B=0.925,R2=0.709)均向下移动;Pos(B=0.487,R2=0.444)向上移动。在水平、矢状和垂直向上各颏部解剖标记点软组织移动量(ΔSM)和骨组织移动量(ΔBM)相关性较强(0.6<r<1.0,P<0.01)。 结论 骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形患者正颌术后水平、矢状和垂直向上颏部软组织变化均受骨组织移动的影响,且呈正相关关系,水平向和矢状向相关性较强,垂直向相关性较弱。
畸形患者正颌术后水平、矢状和垂直向上颏部软组织变化均受骨组织移动的影响,且呈正相关关系,水平向和矢状向相关性较强,垂直向相关性较弱。 

 畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(5): 612-616.
畸形患者双颌手术前后面部软组织变化的三维研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(5): 612-616. )患者双颌术后面部各区域软组织三维改变的研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2021, 41(4): 337-341.
)患者双颌术后面部各区域软组织三维改变的研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2021, 41(4): 337-341. 正颌手术前、后面部软、硬组织变化比率的三维研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(2): 158-164.
正颌手术前、后面部软、硬组织变化比率的三维研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(2): 158-164. 正颌手术前后面部软硬组织变化比率的三维研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019.
正颌手术前后面部软硬组织变化比率的三维研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019.