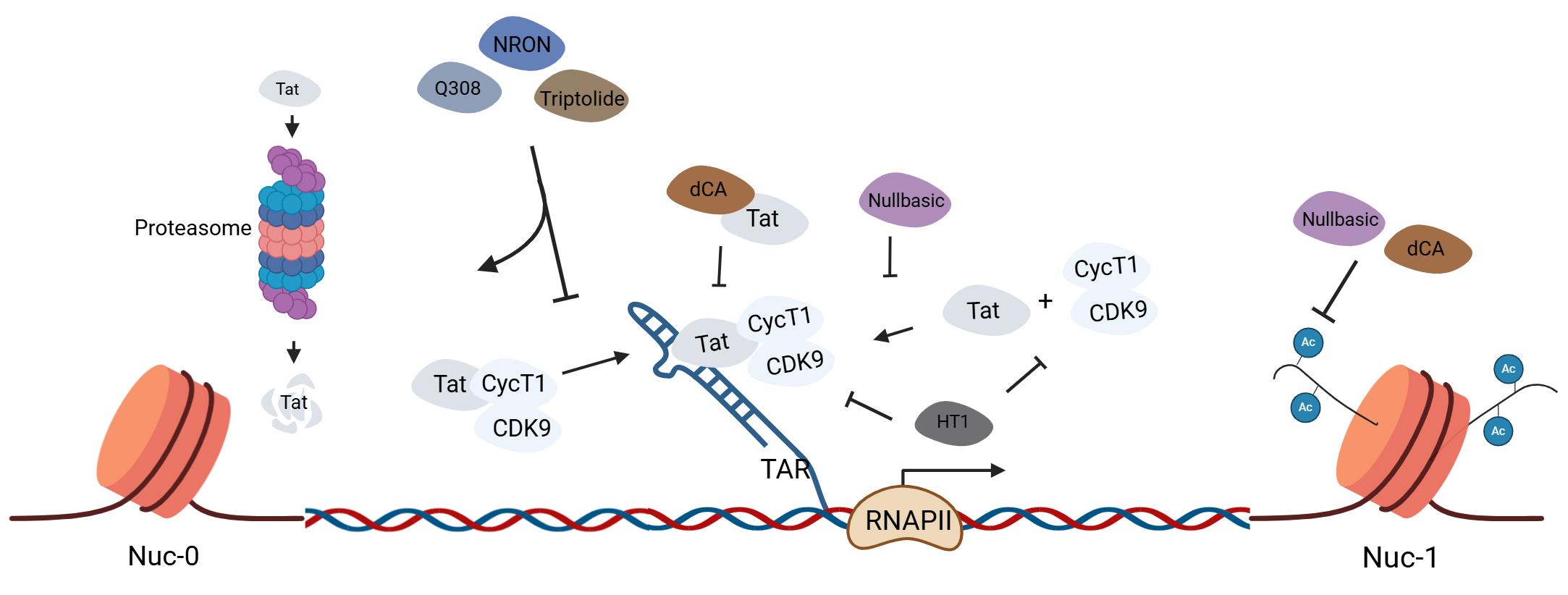
| [1] |
VAN HEUVEL Y, SCHATZ S, ROSENGARTEN J F, et al. Infectious RNA: human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) biology, therapeutic intervention, and the quest for a vaccine[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2022, 14(2): 138.
|
| [2] |
CHEN J, ZHOU T, ZHANG Y, et al. The reservoir of latent HIV[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 945956.
|
| [3] |
JIN H P, LI D S, LIN M H, et al. Tat-based therapies as an adjuvant for an HIV-1 functional cure[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(4): 415.
|
| [4] |
KAMORI D, UENO T. HIV-1 tat and viral latency: what we can learn from naturally occurring sequence variations[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8: 80.
|
| [5] |
PAU A K, GEORGE J M. Antiretroviral therapy: current drugs[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2014, 28(3): 371-402.
|
| [6] |
GARCÍA F, PLANA M, VIDAL C, et al. Dynamics of viral load rebound and immunological changes after stopping effective antiretroviral therapy[J]. AIDS, 1999, 13(11): F79-F86.
|
| [7] |
VANSANT G, BRUGGEMANS A, JANSSENS J, et al. Block-and-lock strategies to cure HIV infection[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(1): 84.
|
| [8] |
LI C, MOUSSEAU G, VALENTE S T. Tat inhibition by didehydro-Cortistatin A promotes heterochromatin formation at the HIV-1 long terminal repeat[J]. Epigenetics Chromatin, 2019, 12(1): 23.
|
| [9] |
SILICIANO R F, GREENE W C. HIV latency[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2011, 1(1): a007096.
|
| [10] |
GARCÍA M, BUZÓN M J, BENITO J M, et al. Peering into the HIV reservoir[J]. Rev Med Virol, 2018, 28(4): e1981.
|
| [11] |
KO A, KANG G B, HATTLER J B, et al. Macrophages but not astrocytes harbor HIV DNA in the brains of HIV-1-infected aviremic individuals on suppressive antiretroviral therapy[J]. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2019, 14(1): 110-119.
|
| [12] |
CASTRO-GONZALEZ S, COLOMER-LLUCH M, SERRA-MORENO R. Barriers for HIV cure: the latent reservoir[J]. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses, 2018, 34(9): 739-759.
|
| [13] |
POMERANTZ R J, SESHAMMA T, TRONO D. Efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires a threshold level of rev: potential implications for latency[J]. J Virol, 1992, 66(3): 1809-1813.
|
| [14] |
EMILIANI S, FISCHLE W, OTT M, et al. Mutations in the tat gene are responsible for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 postintegration latency in the U1 cell line[J]. J Virol, 1998, 72(2): 1666-1670.
|
| [15] |
DEEKS S G. HIV: shock and kill[J]. Nature, 2012, 487(7408): 439-440.
|
| [16] |
BOUCHAT S, GATOT J S, KABEYA K, et al. Histone methyltransferase inhibitors induce HIV-1 recovery in resting CD4+ T cells from HIV-1-infected HAART-treated patients[J]. AIDS, 2012, 26(12): 1473-1482.
|
| [17] |
QI X H, KOYA Y, SAITOH T, et al. Efficient induction of HIV-1 replication in latently infected cells through contact with CD4+ T cells: involvement of NF-kappaB activation[J]. Virology, 2007, 361(2): 325-334.
|
| [18] |
KHOURY G, MOTA T M, LI S, et al. HIV latency reversing agents act through Tat post translational modifications[J]. Retrovirology, 2018, 15(1): 36.
|
| [19] |
GALLO R C. Shock and kill with caution[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6309): 177-178.
|
| [20] |
SCARBOROUGH R J, GATIGNOL A. RNA interference therapies for an HIV-1 functional cure[J]. Viruses, 2017, 10(1): 8.
|
| [21] |
XIAO Q Q, GUO D Y, CHEN S L. Application of CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing in HIV-1/AIDS therapy[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2019, 9: 69.
|
| [22] |
MEDIOUNI S, CHINTHALAPUDI K, EKKA M K, et al. Didehydro-cortistatin A inhibits HIV-1 by specifically binding to the unstructured basic region of tat[J]. mBio, 2019, 10(1): e02662-18.
|
| [23] |
ZHOU C L, HUANG Y F, LI Y B, et al. A new small-molecule compound, Q308, silences latent HIV-1 provirus by suppressing tat- and FACT-mediated transcription[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2021, 65(12): e0047021.
|
| [24] |
CAFARO A, SCHIETROMA I, SERNICOLA L, et al. Role of HIV-1 tat protein interactions with host receptors in HIV infection and pathogenesis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(3): 1704.
|
| [25] |
AJASIN D, EUGENIN E A. HIV-1 tat: role in bystander toxicity[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2020, 10: 61.
|
| [26] |
ASAMITSU K, FUJINAGA K, OKAMOTO T. HIV tat/P-TEFb interaction: a potential target for novel anti-HIV therapies[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(4): 933.
|
| [27] |
RAZOOKY B S, PAI A, AULL K, et al. A hardwired HIV latency program[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(5): 990-1001.
|
| [28] |
DONAHUE D A, KUHL B D, SLOAN R D, et al. The viral protein Tat can inhibit the establishment of HIV-1 latency[J]. J Virol, 2012, 86(6): 3253-3263.
|
| [29] |
DEMARCHI F, D’ADDA DI FAGAGNA F, FALASCHI A, et al. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB by the Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1[J]. J Virol, 1996, 70(7): 4427-4437.
|
| [30] |
TA T M, MALIK S, ANDERSON E M, et al. Insights into persistent HIV-1 infection and functional cure: novel capabilities and strategies[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 862270.
|
| [31] |
LIN X, IRWIN D, KANAZAWA S, et al. Transcriptional profiles of latent human immunodeficiency virus in infected individuals: effects of Tat on the host and reservoir[J]. J Virol, 2003, 77(15): 8227-8236.
|
| [32] |
ALI A, MISHRA R, KAUR H, et al. HIV-1 Tat: an update on transcriptional and non-transcriptional functions[J]. Biochimie, 2021, 190: 24-35.
|
| [33] |
LIANG T Z, ZHANG Q, WU Z Y, et al. UHRF1 suppresses HIV-1 transcription and promotes HIV-1 latency by competing with p-TEFb for ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation of tat[J]. mBio, 2021, 12(4): e0162521.
|
| [34] |
KONG W L, BISWAS A, ZHOU D W, et al. Nucleolar protein NOP2/NSUN1 suppresses HIV-1 transcription and promotes viral latency by competing with Tat for TAR binding and methylation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2020, 16(3): e1008430.
|
| [35] |
LU H S, LI Z C, XUE Y H, et al. Viral-host interactions that control HIV-1 transcriptional elongation[J]. Chem Rev, 2013, 113(11): 8567-8582.
|
| [36] |
AOKI S, WATANABE Y, SANAGAWA M, et al. Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, anti-angiogenic steroidal alkaloids, from the marine sponge Corticium simplex[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(10): 3148-3149.
|
| [37] |
RICE A P. Unexpected mutations in HIV-1 that confer resistance to the tat inhibitor didehydro-cortistatin A[J]. mBio, 2019, 10(4): e01547-19.
|
| [38] |
KESSING C F, NIXON C C, LI C, et al. In vivo suppression of HIV rebound by didehydro-cortistatin A, a “block-and-lock” strategy for HIV-1 treatment[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 21(3): 600-611.
|
| [39] |
MOUSSEAU G, KESSING C F, FROMENTIN R, et al. The tat inhibitor didehydro-cortistatin A prevents HIV-1 reactivation from latency[J]. mBio, 2015, 6(4): e00465.
|
| [40] |
LI C, MORI L, VALENTE S T. The block-and-lock strategy for human immunodeficiency virus cure: lessons learned from didehydro-cortistatin A[J]. J Infect Dis, 2021, 223(12 ): 46-53.
|
| [41] |
MEDIOUNI S, JABLONSKI J, PARIS J J, et al. Didehydro-cortistatin A inhibits HIV-1 Tat mediated neuroinflammation and prevents potentiation of cocaine reward in Tat transgenic mice[J]. Curr HIV Res, 2015, 13(1): 64-79.
|
| [42] |
MEREDITH L W, SIVAKUMARAN H, MAJOR L, et al. Potent inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a tat mutant[J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(11): e7769.
|
| [43] |
JIN H P, LI D S, SIVAKUMARAN H, et al. Shutdown of HIV-1 transcription in T cells by nullbasic, a mutant tat protein[J]. mBio, 2016, 7(4): e00518-16.
|
| [44] |
RUSTANTI L, JIN H P, LOR M, et al. A mutant Tat protein inhibits infection of human cells by strains from diverse HIV-1 subtypes[J]. Virol J, 2017, 14(1): 52.
|
| [45] |
LIN M H, SIVAKUMARAN H, JONES A, et al. A HIV-1 Tat mutant protein disrupts HIV-1 Rev function by targeting the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX1[J]. Retrovirology, 2014, 11: 121.
|
| [46] |
FRALDI A, VARRONE F, NAPOLITANO G, et al. Inhibition of tat activity by the HEXIM1 protein[J]. Retrovirology, 2005, 2: 42.
|
| [47] |
LEOZ M, KUKANJA P, LUO Z P, et al. HEXIM1-Tat chimera inhibits HIV-1 replication[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2018, 14(11): e1007402.
|
| [48] |
LUO H, VONG C T, CHEN H B, et al. Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Chin Med, 2019, 14: 48.
|
| [49] |
LIANG X, XIE R X, SU J F, et al. Inhibition of RNA polymerase Ⅲ transcription by Triptolide attenuates colorectal tumorigenesis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 217.
|
| [50] |
WAN Z T, CHEN X L. Triptolide inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by promoting proteasomal degradation of Tat protein[J]. Retrovirology, 2014, 11: 88.
|
| [51] |
HERMAN A B, TSITSIPATIS D, GOROSPE M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(12): 2252-2266.
|
| [52] |
LI J, CHEN C C, MA X C, et al. Long noncoding RNA NRON contributes to HIV-1 latency by specifically inducing tat protein degradation[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11730.
|
| [53] |
JEONG E, MARTINA J A, CONTRERAS P S, et al. The FACT complex facilitates expression of lysosomal and antioxidant genes through binding to TFEB and TFE3[J]. Autophagy, 2022, 18(10): 2333-2349.
|