吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1584-1594.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250614
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
甲型流感病毒PR8感染小鼠早期记忆T淋巴细胞的改变及其意义
- 1.锦州医科大学附属第一医院心脏康复中心,辽宁 锦州 121000
2.锦州医科大学基础医学院免疫 教研室,辽宁 锦州 121000
Changes of early memory T lymphocytes in mice infected with influenza A virus PR8 and its significance
- 1.Cardiac Rehabilitation Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2.Department of Immunology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
摘要:
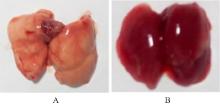
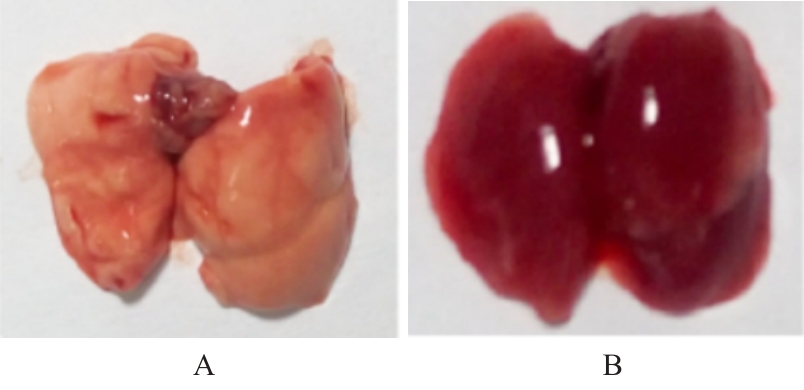
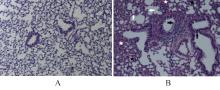
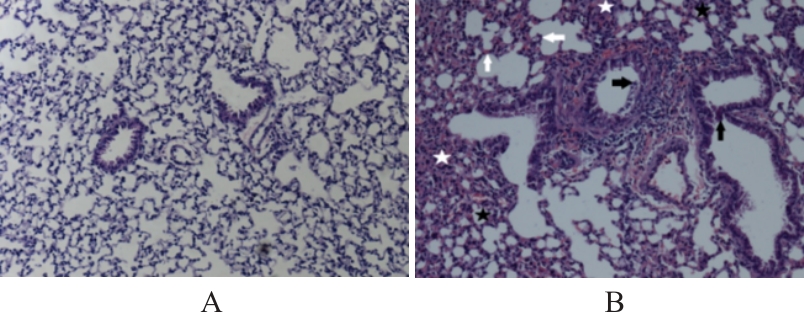
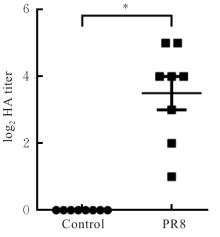
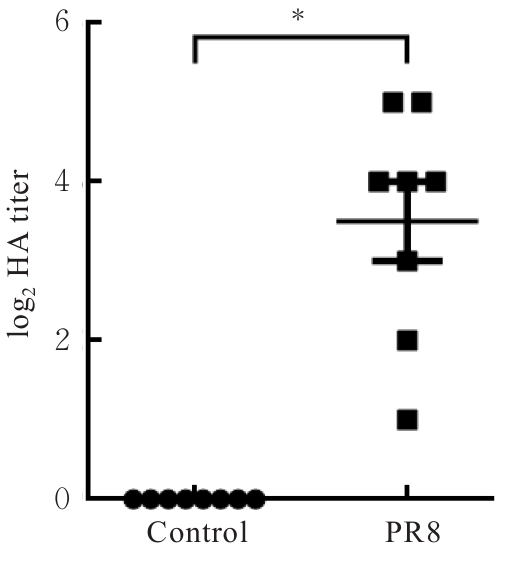
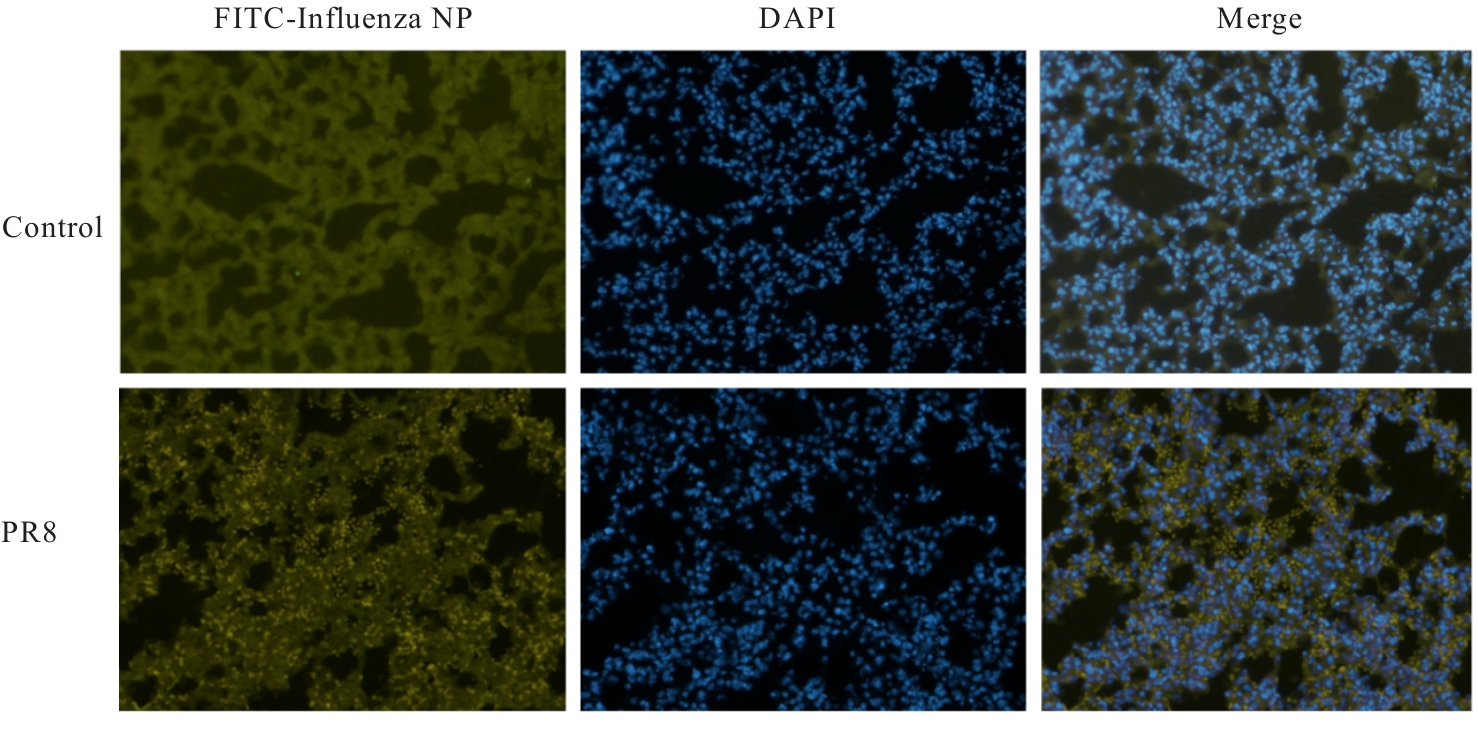
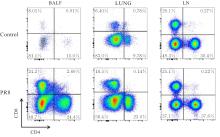
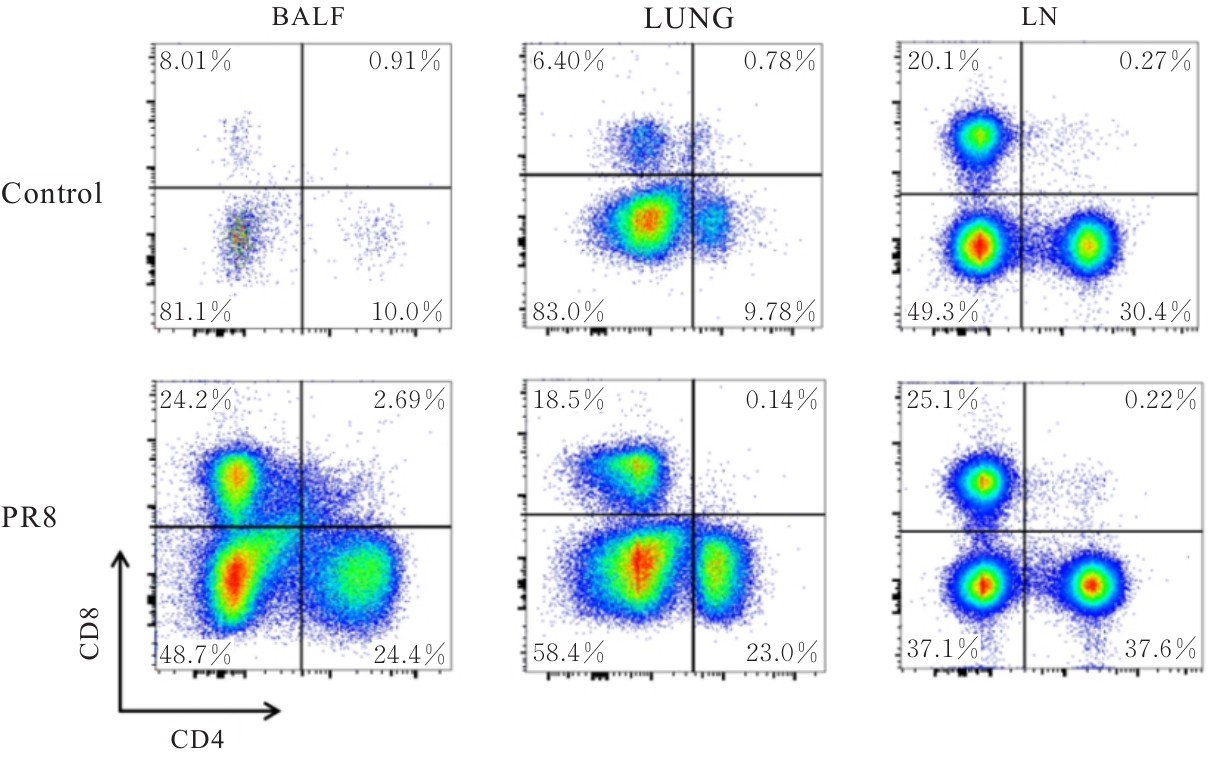
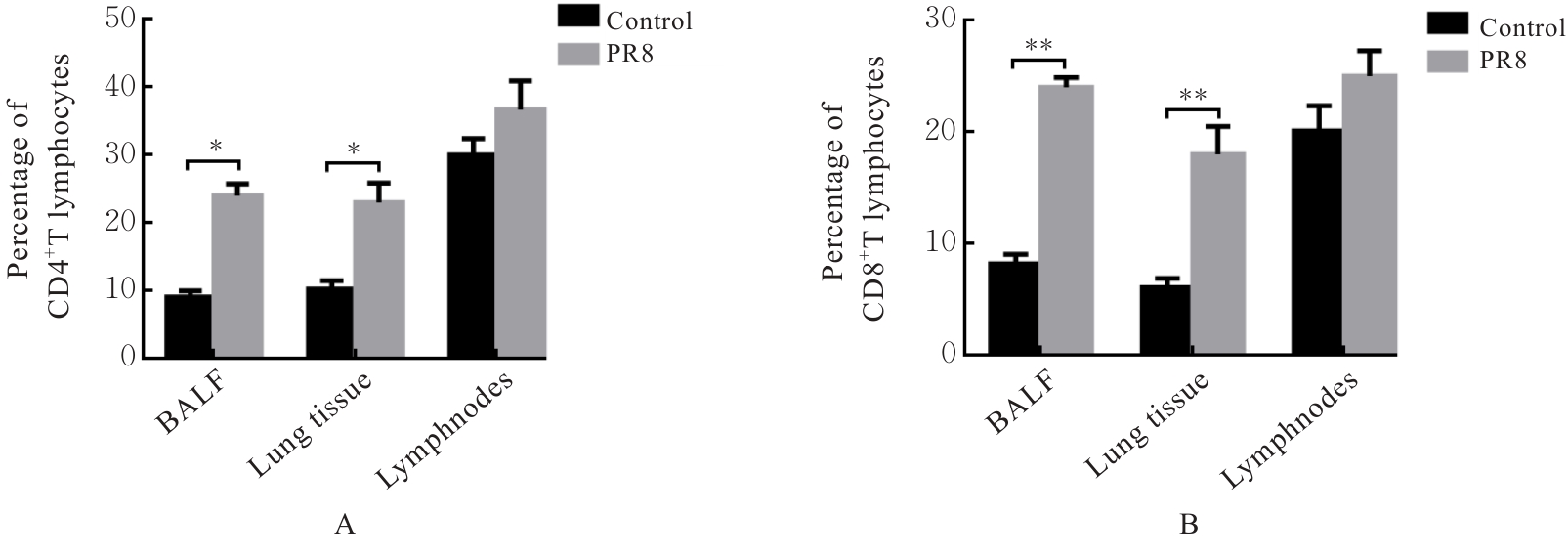
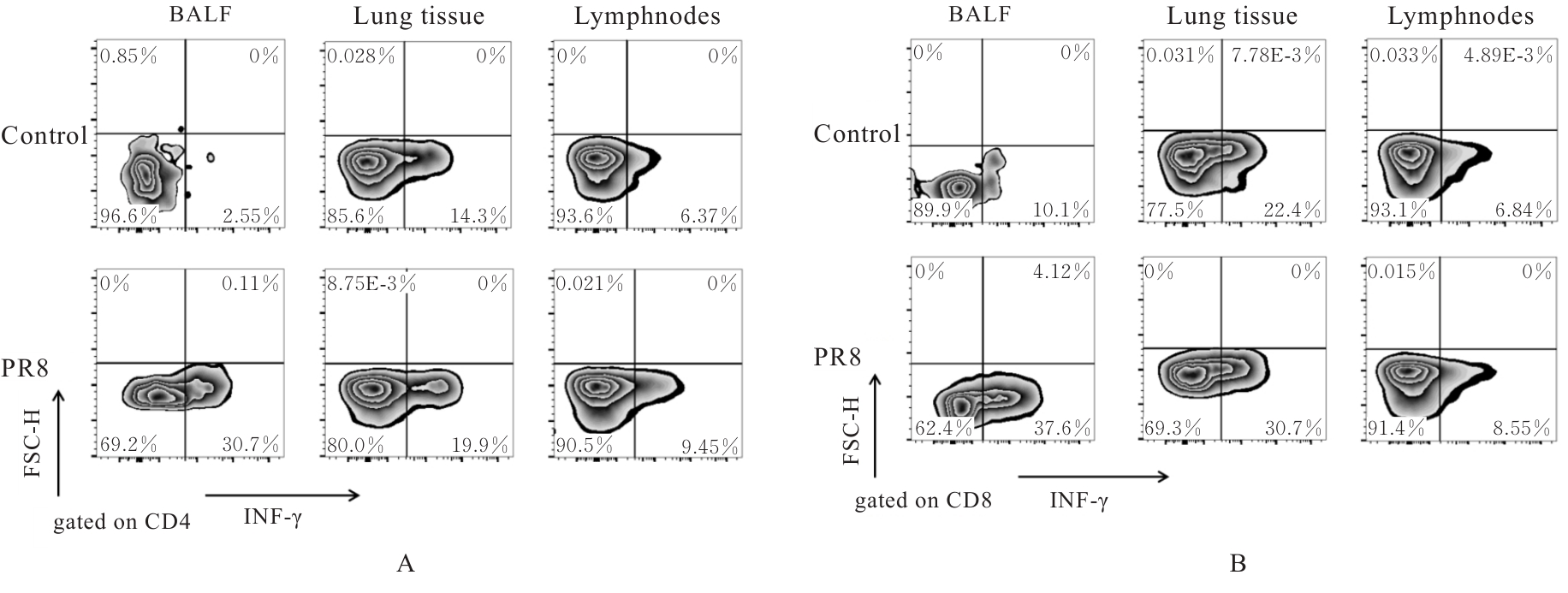
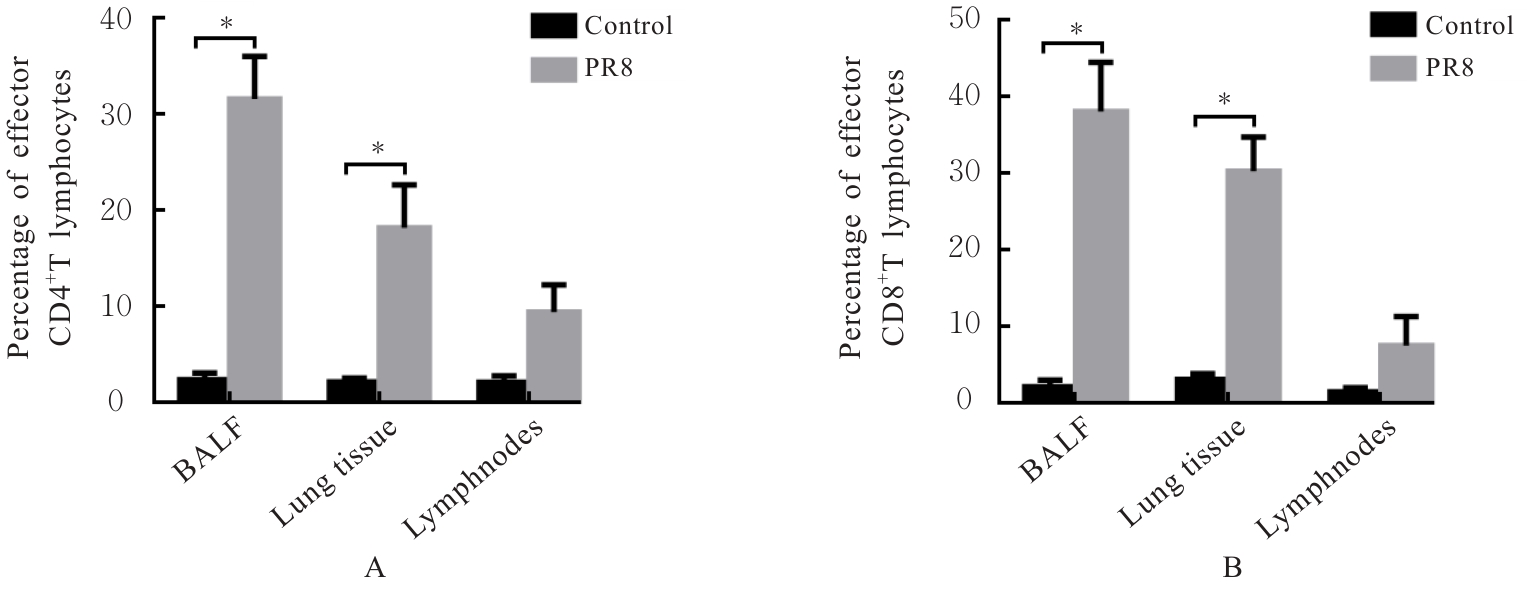
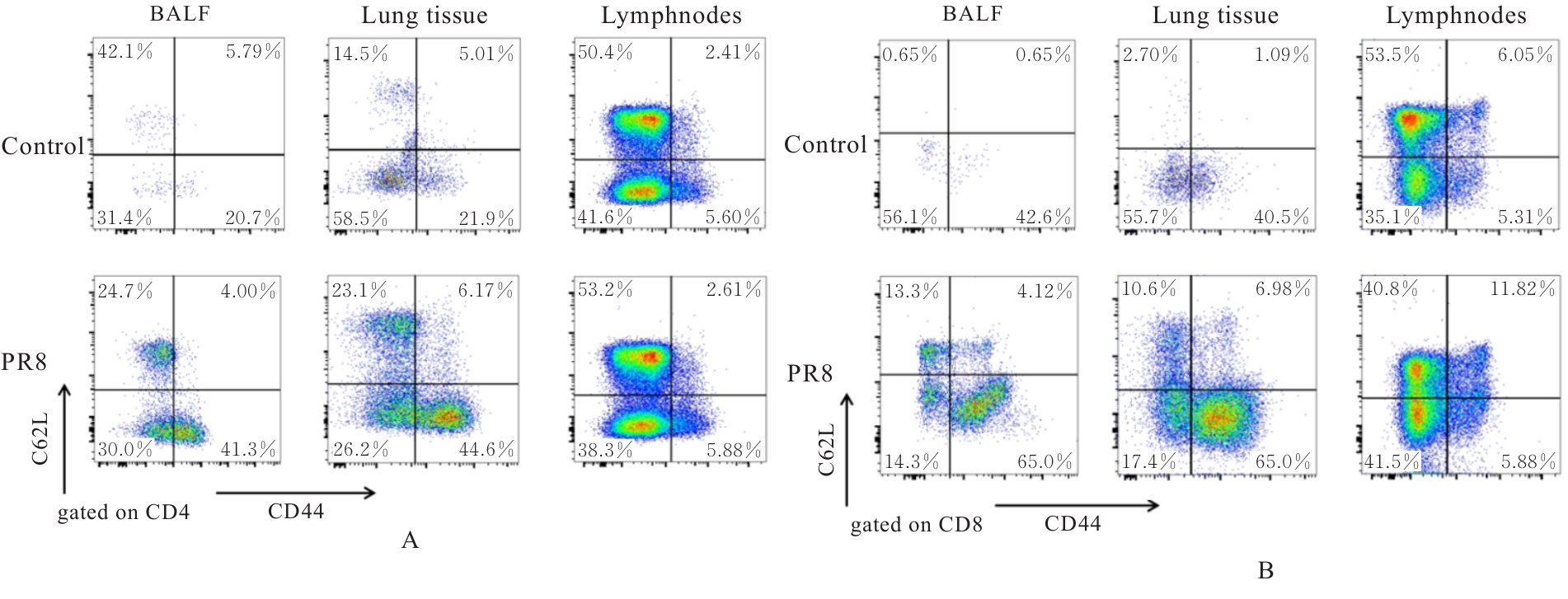
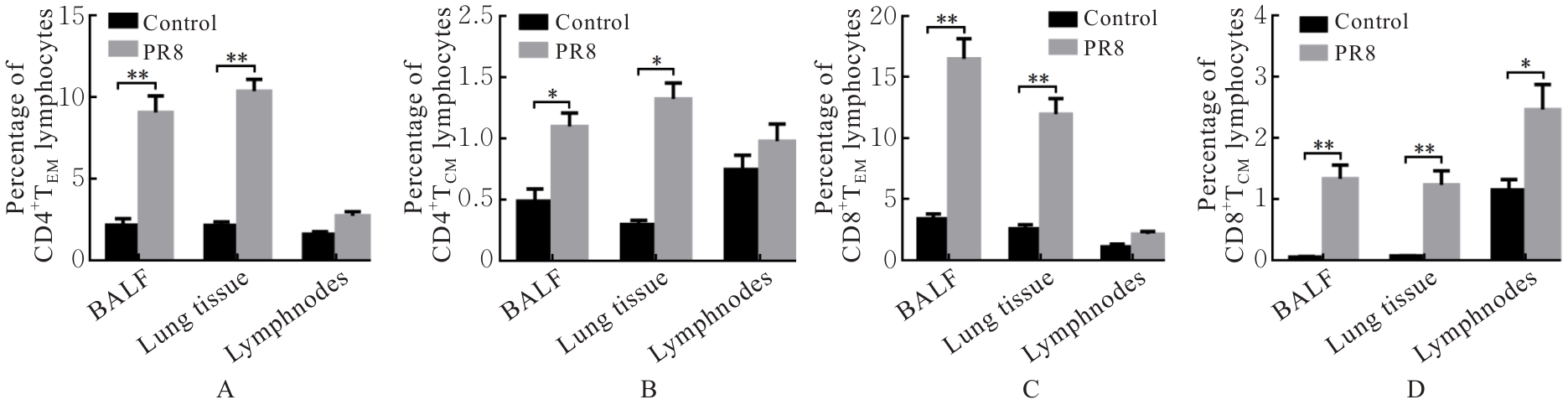
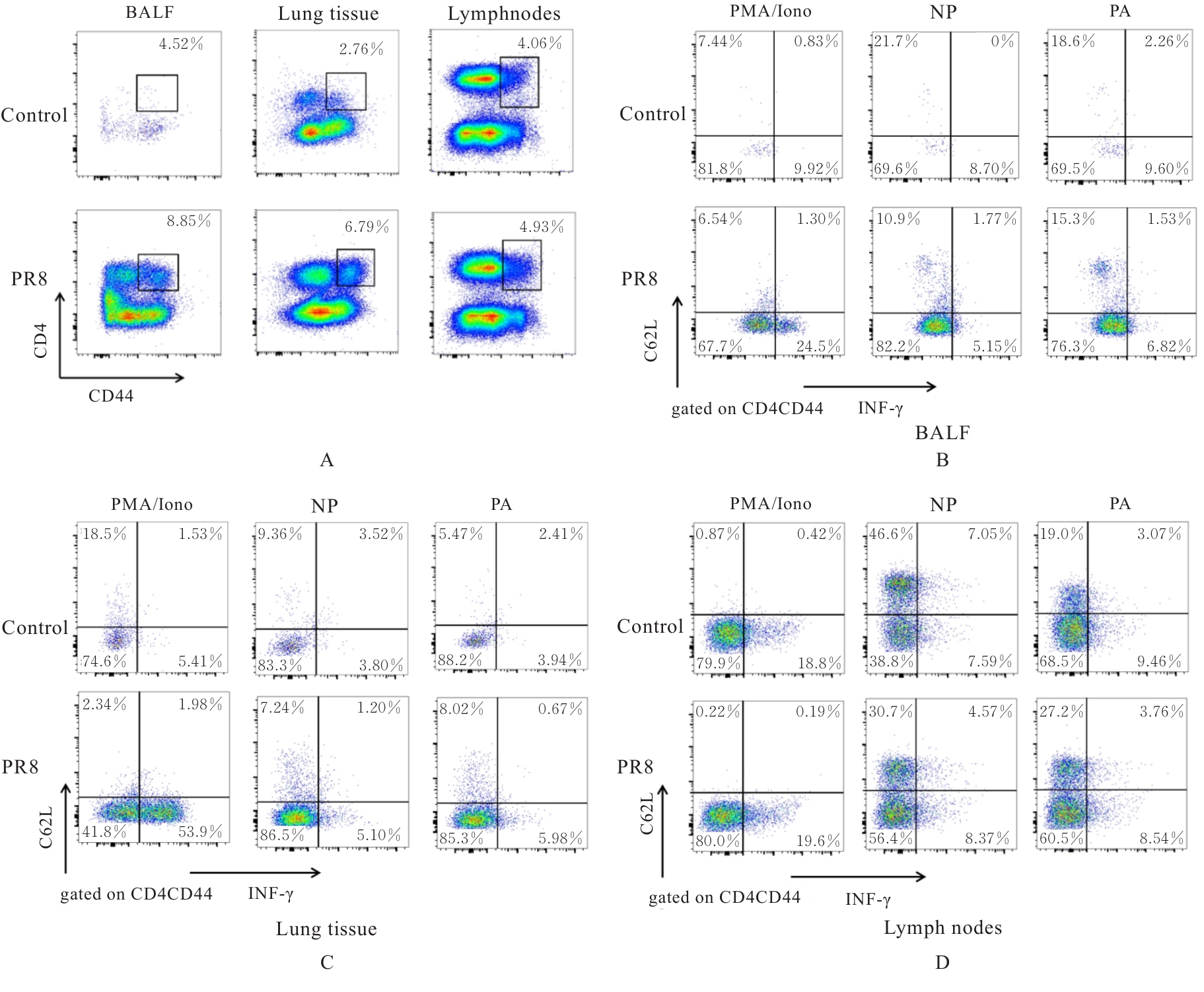
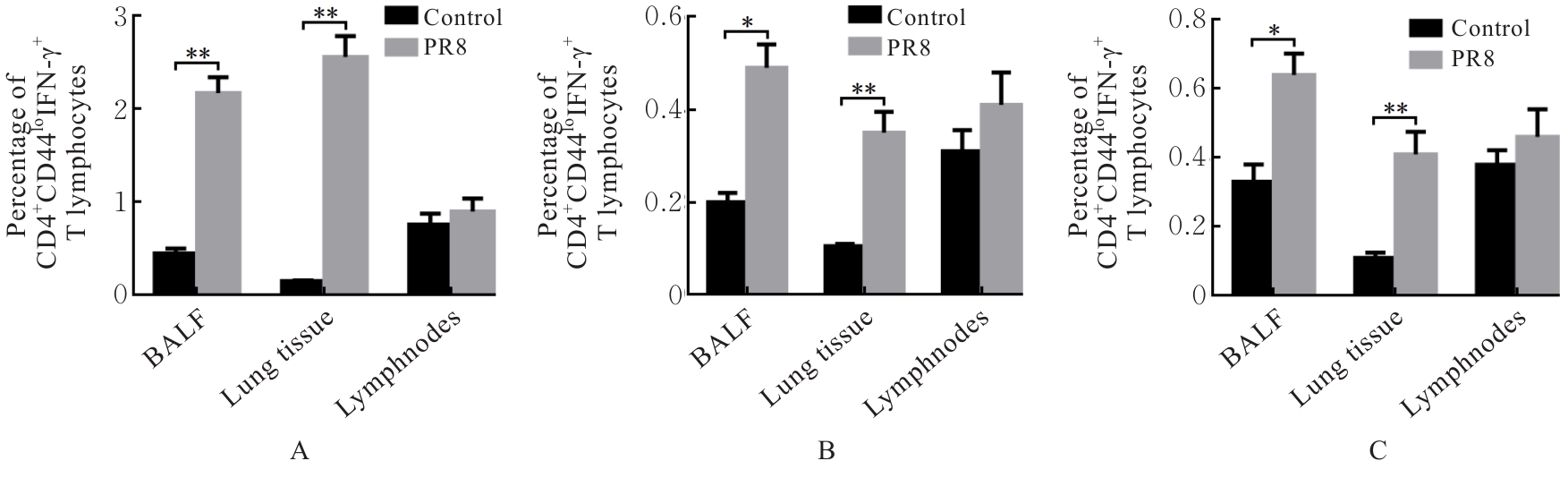
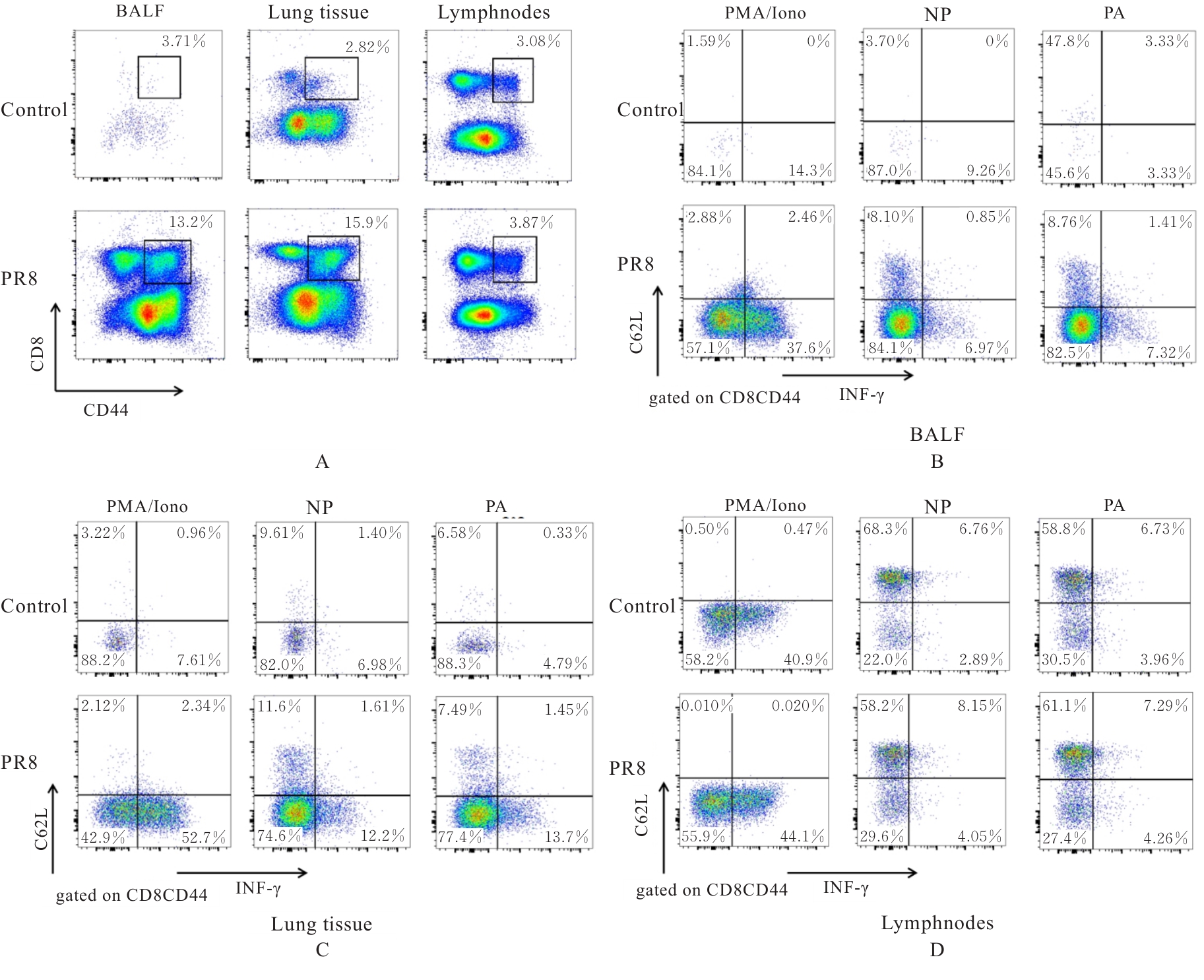
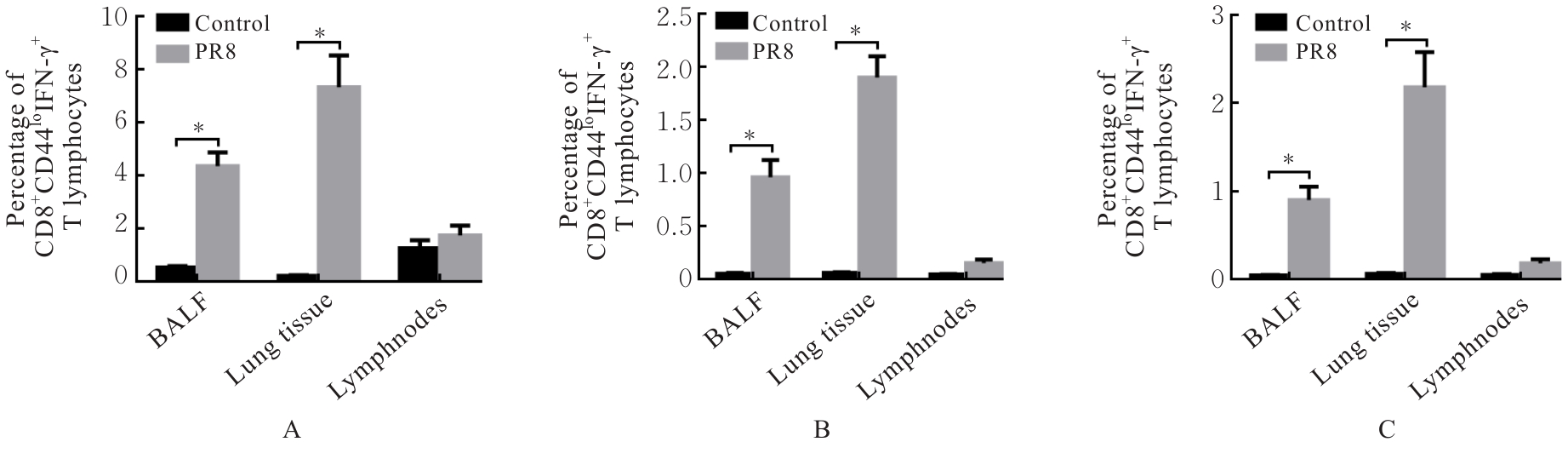
目的 探讨早期记忆T淋巴细胞(TM)在甲型流感病毒(H1N1)PR8感染小鼠后的变化情况,并阐明其意义。 方法 将32只C57BL/6小鼠随机分为对照组和流感病毒(PR8)组,每组16只。对照组小鼠鼻滴30 μL无菌磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS),PR8组小鼠给予鼻滴2 LD50 PR8病毒液。于第10天处死小鼠,收集支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)、肺组织和淋巴结用于后续实验。HE染色观察2组小鼠肺组织病理形态表现,血凝试验、实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和免疫荧光法检测小鼠肺组织病毒感染情况,流式细胞术检测2组小鼠BALF、肺组织和淋巴结中T淋巴细胞、效应性T淋巴细胞、中央型TM淋巴细胞(TCM)和效应性TM淋巴细胞(TEM)及核蛋白(NP)/聚合酶酸性蛋白(PA)特异性TEM淋巴细胞百分率。 结果 与对照组比较,PR8组小鼠肺组织出现明显的病理损伤,且肺组织病毒效价和NP蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,PR8组小鼠BALF和肺组织中CD4+T淋巴细胞、CD8+T淋巴细胞、效应性CD4+T淋巴细胞、效应性CD8+T淋巴细胞、CD4+TEM淋巴细胞和CD8+TEM淋巴细胞百分率均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,PR8组小鼠BALF和肺组织中CD4+TCM、CD8+TCM、CD4+TEM、CD8+TEM及NP/PA特异性CD4+TEM和CD8+TEM淋巴细胞百分率均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),淋巴结中CD8+TCM淋巴细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 流感病毒感染可诱导机体T淋巴细胞增殖分化为效应性T淋巴细胞,在呼吸道黏膜局部早期建立保守表位NP/PA的特异性TM淋巴细胞。
中图分类号:
- R392