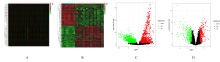
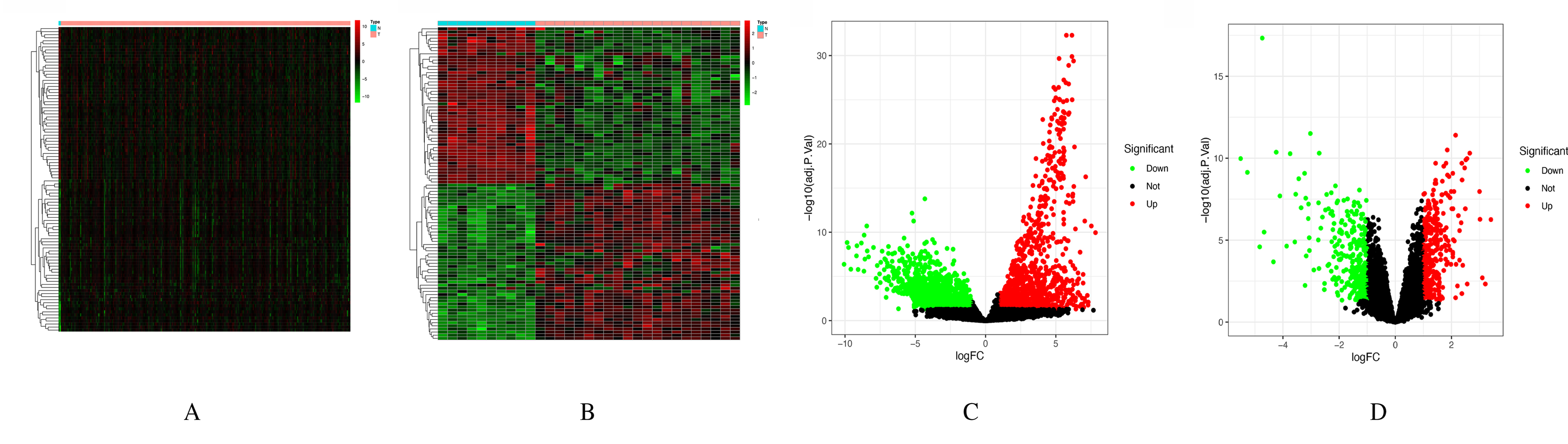
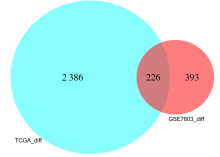
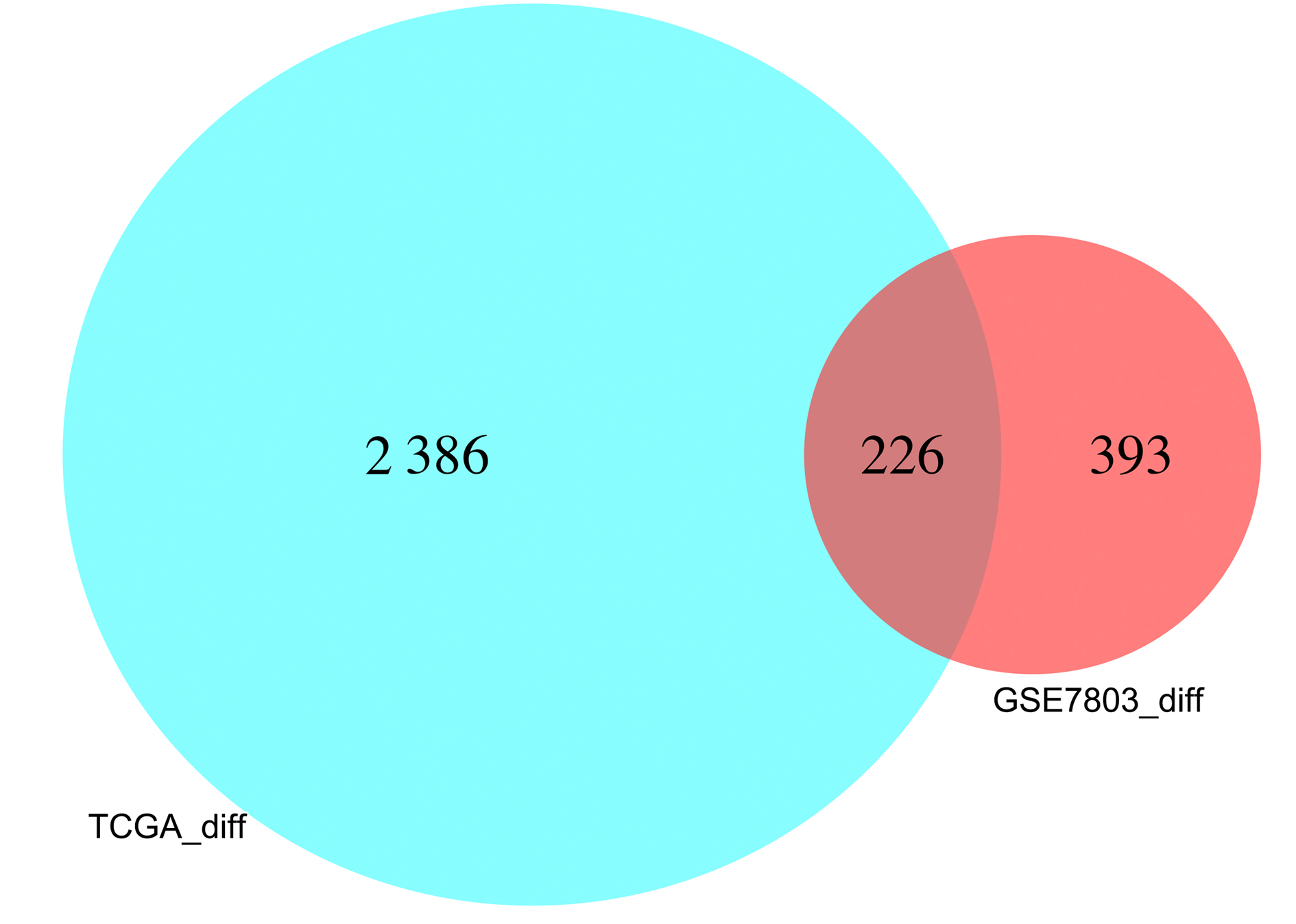
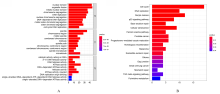
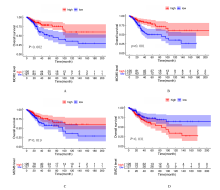
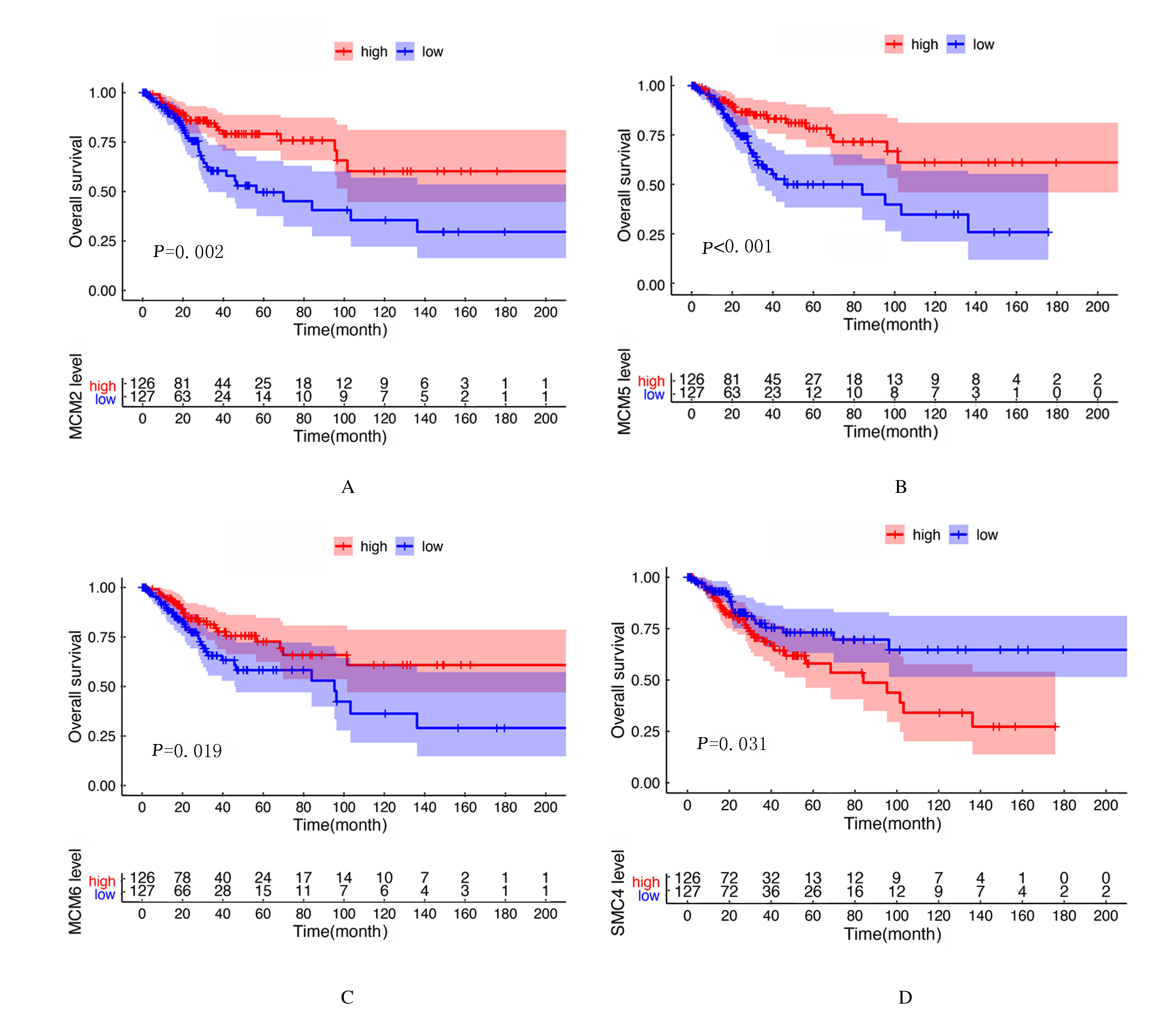
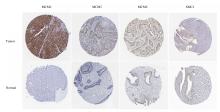
| 1 |
TORRE L A, BRAY F, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65 (2):87-108.
|
| 2 |
JEMAL A, BRAY F, CENTER M M, et al.Global cancer statistics [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61(2):69-90.
|
| 3 |
方丹妹.鳞癌抗原检测在宫颈癌及癌前病变诊断的价值 [J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2020, 11 (11):35-37.
|
| 4 |
宋适寅.宫颈鳞状上皮肿瘤的病理诊断价值分析 [J]. 当代医学, 2020, 26 (17):173-174.
|
| 5 |
TOMCZAK K, CZERWINSKA P,WIZNEROWICZ M.The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA):an immeasurable source of knowledge [J]. Contemp Oncol Poznan Pol, 2015, 19 (1A):A68-A77.
|
| 6 |
BARRETT T, WILHITE S E, LEDOUX P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41 (Database issue):D991-995.
|
| 7 |
CRISTESCU R, LEE J, NEBOZHY M, et al. Molecular analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes [J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21 (5):449-456.
|
| 8 |
KIM E, JUNG S, PARK W S, et al.Upregulation of SLC2A3 gene and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma: analysis of TCGA data [J].BMC Cancer,2019,19(1):1-10.
|
| 9 |
KIM I, CHOI S, KIM S. BRCA-Pathway: a structural integration and visualization system of TCGA breast cancer data on KEGG pathways [J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2018, 19 ():42.
|
| 10 |
LIU X, WANG J, CHEN M, et al.Combining data from TCGA and GEO databases and reverse transcription quantitative PCR validation to identify gene prognostic markers in lung cancer [J]. Oncol Targets Ther, 2019, 12:709-720.
|
| 11 |
张 军.7 900例35~64岁农村妇女宫颈癌检查结果分析 [J]. 卫生职业教育, 2019, 37 (23):136-138.
|
| 12 |
乔友林, 赵宇倩.宫颈癌的流行病学现状和预防[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志(电子版), 2015, 11 (2):1-6.
|
| 13 |
曹 欢, 刘 冰, 王晓丹. 宫颈病变流行病学分析及宫颈冷冻治疗新进展 [J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 12 (8):1129-1132.
|
| 14 |
DONG J, WANG Q, LI L,et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 contributes to cell growth and invasion in cervical cancer by acting as a sponge for MiR-424-5p [J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45 (5):2086-2094.
|
| 15 |
LIU X F, LI X Y, ZHENG P S,et al.DAX1 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and tumorigenicity through activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway via GSK3beta [J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9 (3):339.
|
| 16 |
NAHAND J S, TAGHIZADEH-BOROUJENI S, KARIMZADEH M, et al.microRNAs: New prognostic, diagnostic, and therapeutic biomarkers in cervical cancer [J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234 (10):17064-17099.
|
| 17 |
DAS M, SINGH S, PRADHAN S, et al.MCM paradox: abundance of eukaryotic replicative helicases and genomic integrity [J]. Mol Biol Int, 2014, 2014:574850.
|
| 18 |
FOWLER C G,CHIASSON K B, LESLIE T H,et al.Auditory function in rhesus monkeys: effects of aging and caloric restriction in the Wisconsin monkeys five years later [J]. Hear Res, 2010, 261 (1/2):75-81.
|
| 19 |
CHEUNG C H Y, HSU C L, CHEN K P, et al. MCM2-regulated functional networks in lung cancer by multi-dimensional proteomic approach [J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7 (1):13302.
|
| 20 |
ISSAC M S M, YOUSEF E, TAHIR M R, et al. MCM2, MCM4, and MCM6 in breast cancer: Clinical utility in diagnosis and prognosis [J].Neoplasia, 2019, 21 (10):1015-1035.
|
| 21 |
REN B, YU G, TSENG G C, et al. MCM7 amplification and overexpression are associated with prostate cancer progression [J].Oncogene,2006,25 (7):1090-1098.
|
| 22 |
YANG J, XIE Q, ZHOU H, et al.Proteomic analysis and NIR-II imaging of MCM2 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Proteome Res, 2018, 17 (7):2428-2439.
|
| 23 |
DEWAR J M, WALTER J C. Mechanisms of DNA replication termination [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18 (8):507-516.
|
| 24 |
GIAGINIS C, GIAGINI A,TSOUROUFLIS G,et al.MCM-2 and MCM-5 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma: clinical significance and comparison with Ki-67 proliferative marker [J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2011, 56 (3):777-785.
|
| 25 |
CHEN Q Y, LIU L C, WANG J B,et al.CDK5RAP3 inhibits the translocation of MCM6 to influence the prognosis in gastric cancer[J].J Cancer,2019,10 (19):4488-4498.
|
| 26 |
ABE S, KURATA M, SUZUKI S, et al. Minichromosome maintenance 2 bound with retroviral Gp70 is localized to cytoplasm and enhances DNA-damage-induced apoptosis [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7 (6):e40129.
|
| 27 |
高 峻, 杨宏新.微小染色体维持蛋白在肿瘤研究中的进展 [J]. 包头医学院学报, 2014, 30 (1):137-139.
|
| 28 |
DENG M, SUN J, XIE S,et al.Inhibition of MCM2 enhances the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cell to carboplatin [J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(3):2258-2266.
|
| 29 |
ZHANG C, KUANG M, LI M, et al. SMC4, which is essentially involved in lung development, is associated with lung adenocarcinoma progression [J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:34508.
|
| 30 |
ZHOU B, YUAN T, LIU MG, et al.Overexpression of the structural maintenance of chromosome 4 protein is associated with tumor de-differentiation, advanced stage and vascular invasion of primary liver cancer [J]. Oncol Rep, 2012, 28 (4):1263-1268.
|
 )
)