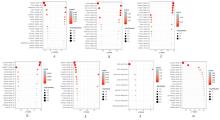
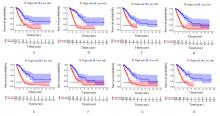
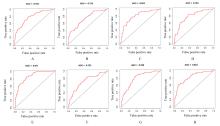
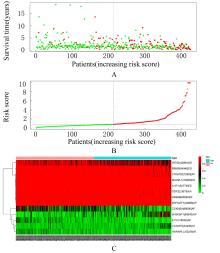
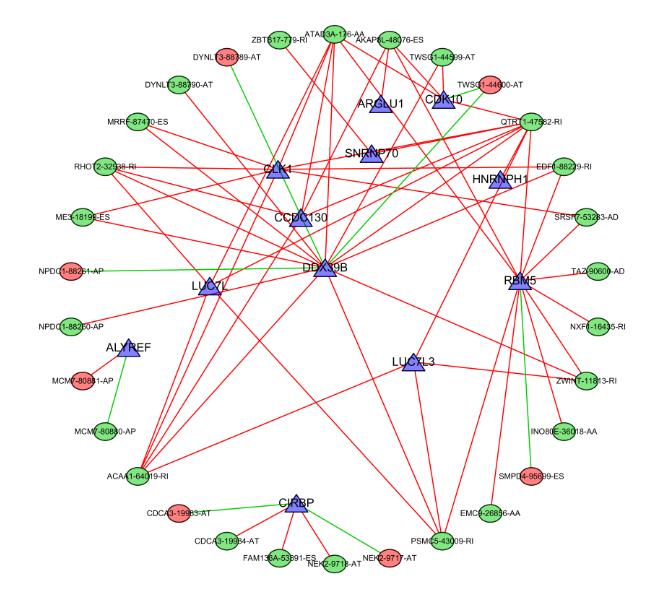
| 1 |
ZHANG G H, DONG R, KONG D M, et al. The effect of GLUT1 on the survival rate and immune cell infiltration of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: a meta and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(2): 223-238.
|
| 2 |
JIA K R, WU Y C, HUANG J, et al. Survival-associated alternative splicing events in pan-renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1317.
|
| 3 |
WAN Q, SANG X, JIN L, et al. Alternative splicing events as indicators for the prognosis of uveal melanoma[J]. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(2): E227.
|
| 4 |
CHEN H Q, CARROT-ZHANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Genomic and immune profiling of pre-invasive lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 5472.
|
| 5 |
RAVEH E, MATOUK I J, GILON M, et al. The H19 long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—a proposed unifying theory[J]. Mol Cancer, 2015, 14: 184.
|
| 6 |
ZHANG Y J, YAO X Y, ZHOU H, et al. OncoSplicing: an updated database for clinically relevant alternative splicing in 33 human cancers[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D1340-D1347.
|
| 7 |
SONG Q L, YI F T, ZHANG Y H, et al. CRKL regulates alternative splicing of cancer-related genes in cervical cancer samples and HeLa cell[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 499.
|
| 8 |
LIN C W, YU B W, ZHANG M, et al. Systematic analyses of the differentially expressed alternative splicing events in gastric cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 522831.
|
| 9 |
COOMER A O, BLACK F, GREYSTOKE A, et al. Alternative splicing in lung cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2019, 1862(11/12): 194388.
|
| 10 |
DE FRAIPONT F, GAZZERI S, CHO W C, et al. Circular RNAs and RNA splice variants as biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic response in the liquid biopsies of lung cancer patients[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 390.
|
| 11 |
WAN L D, YU W Y, SHEN E H, et al. SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing that promotes tumour progression offers a therapy target for colorectal cancer[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(1): 118-129.
|
| 12 |
URBANSKI L M, LECLAIR N, ANCZUKÓW O. Alternative-splicing defects in cancer: Splicing regulators and their downstream targets, guiding the way to novel cancer therapeutics[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2018, 9(4): e1476.
|
| 13 |
CERASUOLO A, BUONAGURO L, BUONAGURO F M, et al. The role of RNA splicing factors in cancer: regulation of viral and human gene expression in human papillomavirus-related cervical cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 474.
|
| 14 |
SOUBISE B, JIANG Y, DOUET-GUILBERT N,et al. RBM22, a key player of pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression regulation, is altered in cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(3): 643.
|
| 15 |
HUANG X Y, SHI H Y, SHI X H, et al. LncRNA FBXL19-AS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer through upregulating COL1A1 as a sponge of miR-193a-5p[J]. J Biol Res (Thessalon), 2021, 28(1): 20.
|
| 16 |
MELNYK J E, STERI V, NGUYEN H G, et al. The splicing modulator sulfonamide indisulam reduces AR-V7 in prostate cancer cells[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2020, 28(20): 115712.
|
| 17 |
WOJTUSZKIEWICZ A, ASSARAF Y G, MAAS M J,et al. Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer: the relevance in oncogenesis, treatment and drug resistance[J]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2015, 11(5): 673-689.
|
| 18 |
LIM B, KIM C, KIM J H, et al. Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in gastric cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis revealed by whole-exome sequencing of malignant ascites[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(7):8055-8066.
|
| 19 |
SONG H, WANG Y P, SHI C J, et al. SH3KBP1 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by activating EGFR signaling[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 583984.
|
| 20 |
SHI Y X, ZHU T, ZOU T, et al. Prognostic and predictive values of CDK1 and MAD2L1 in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 85235-85243.
|
| 21 |
LI J F, HE X, WU X T, et al. miR-139-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting MAD2L1[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2020, 2020: 2953598.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG J F, ZHANG J, XU S P, et al. Hypoxia-induced TPM2 methylation is associated with chemoresistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(2): 692-705.
|
| 23 |
LIU S W, ZENG F P, FAN G W, et al. Identification of hub genes and construction of a transcriptional regulatory network associated with tumor recurrence in colorectal cancer by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 649752.
|
| 24 |
VARISLI L. Identification of new genes downregulated in prostate cancer and investigation of their effects on prognosis[J].Genet Test Mol Biomarkers,2013,17(7): 562-566.
|
| 25 |
LIU Q, FANG L M, WU C J. Alternative splicing and isoforms: from mechanisms to diseases[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(3): 401.
|
| 26 |
PÉREZ-CALERO C, BAYONA-FELIU A, XUE X Y, et al. UAP56/DDX39B is a major cotranscriptional RNA-DNA helicase that unwinds harmful R loops genome-wide[J].Genes Dev,2020,34(13/14): 898-912.
|
| 27 |
AWASTHI S, CHAKRAPANI B, MAHESH A,et al. DDX39B promotes translation through regulation of pre-ribosomal RNA levels[J]. RNA Biol, 2018, 15(9): 1157-1166.
|
| 28 |
ZHANG H N, HE C C, GUO X X, et al. DDX39B contributes to the proliferation of colorectal cancer through direct binding to CDK6/CCND1[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 30.
|
| 29 |
XU Z Z, LI X M, LI H X, et al. Suppression of DDX39B sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agents via destabilizing BRCA1 mRNA[J].Oncogene,2020,39(47):7051-7062.
|
| 30 |
WEI J H, LU J, CAO Y, et al. DDX39B predicts poor survival and associated with clinical benefit of anti-PD-L1 therapy in ccRCC[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2021, 21(10): 849-859.
|
| 31 |
ISHIMI Y. Regulation of MCM2-7 function[J]. Genes Genet Syst, 2018, 93(4): 125-133.
|
| 32 |
WANG J Z, ZHU W, HAN J, et al. The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(7): 560-575.
|
 )
)