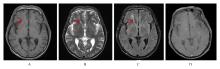
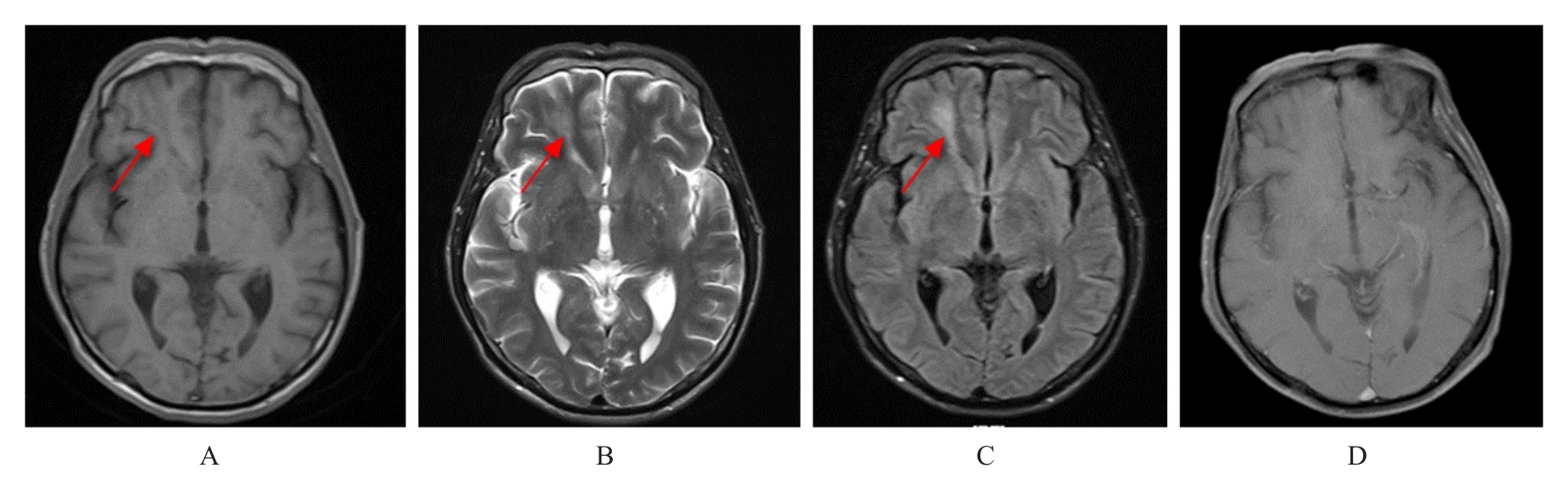
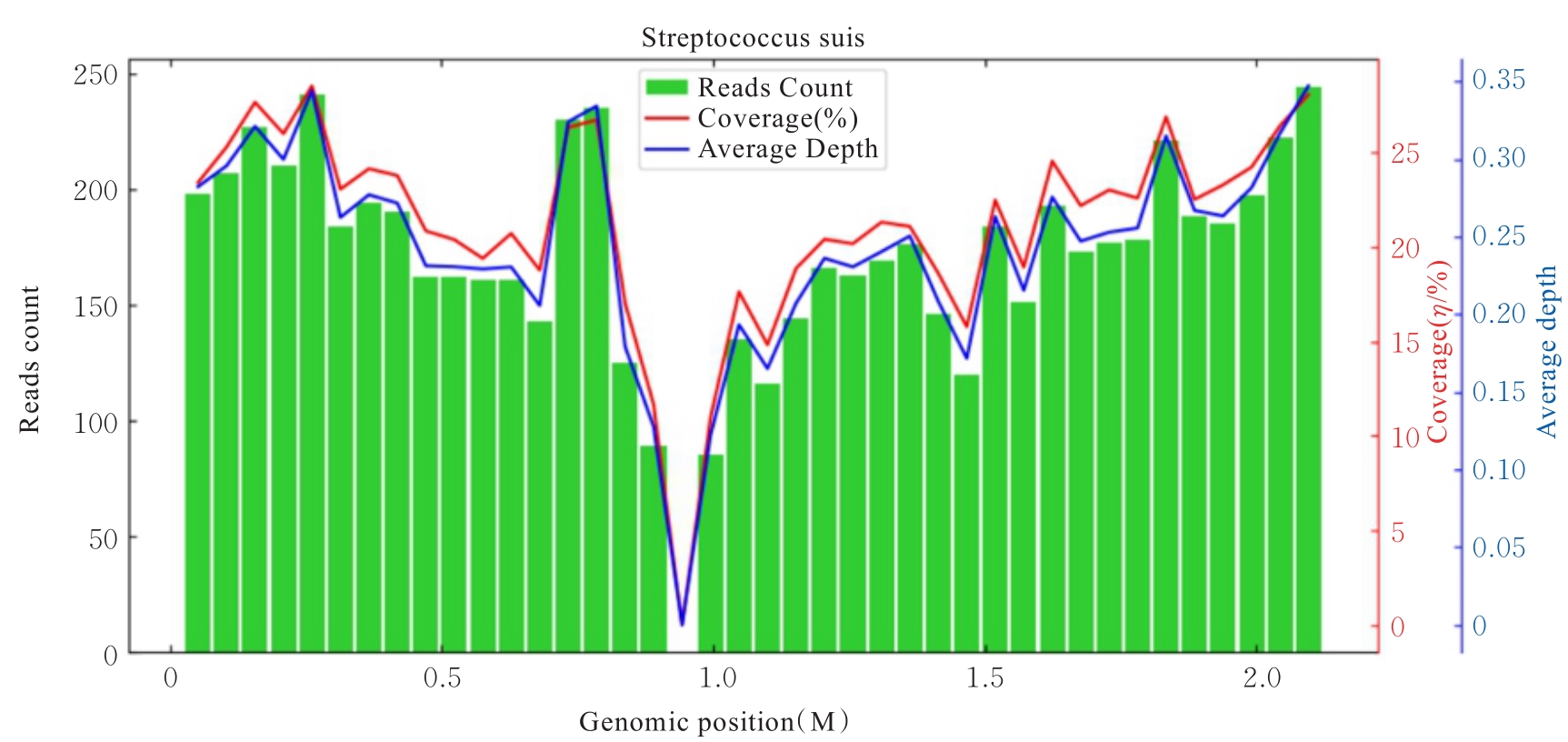
| 1 |
SANTOYA ESPINOSA L C, MORÁN DÍAZ D F, DÍAZ AGUIAR P, et al. Streptococcus suis meningitis[J]. Medicina(B Aires), 2024, 84(2): 329-332.
|
| 2 |
马惠东,金亮,万凤英, 等. 猪链球菌致化脓性脑膜炎1例[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2018, 18(2): 201-202.
|
| 3 |
于凤芝, 乔立东, 李长军, 等. 猪链球菌病的诊断与防治[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2018, 39(6): 85-86.
|
| 4 |
HUONG V T L, HA N, HUY N T, et al. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and outcomes of Streptococcus suis infection in humans[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2014, 20(7): 1105-1114.
|
| 5 |
朱钱迎, 张 青, 李克诚, 等. 人感染猪链球菌Ⅱ型菌株的毒力基因及分子分型特征分析[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2016, 17(3): 202-206.
|
| 6 |
饶文燕, 郑悦康, 吴衍恒. 中山市12株人源2型猪链球菌生物学特性研究及PFGE分型分析[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2022, 33(2): 16-20.
|
| 7 |
RAYANAKORN A, GOH B H, LEE L H, et al. Risk factors for Streptococcus suis infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 13358.
|
| 8 |
ÁGOSTON Z, TERHES G, HANNAUER P, et al. Fatal case of bacteremia caused by Streptococcus suis in a splenectomized man and a review of the European literature[J]. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung, 2020, 67(3): 148-155.
|
| 9 |
周伟忠, 谈忠鸣, 刘文东, 等. 2010—2019年江苏省人感染猪链球菌病流行病学、病原学及临床特征[J]. 江苏预防医学, 2021, 32(2): 178-179, 205.
|
| 10 |
徐 魁, 王 巍, 文心田, 等. 四川主要养猪地区猪2型链球菌血清流行病学调查[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2017, 39(5): 370-373.
|
| 11 |
RAYANAKORN A, ADEMI Z, LIEW D, et al. Burden of disease and productivity impact of Streptococcus suis infection in Thailand[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2021, 15(1): e0008985.
|
| 12 |
SEELE J, TAUBER S C, BUNKOWSKI S,et al. The inflammatory response and neuronal injury in Streptococcus suis meningitis[J]. BMC Infect Dis,2018,18(1):297.
|
| 13 |
LIU T T, LIU H F, JIA Y J. Streptococcus suis meningitis in China: a case report[J].Front Public Health,2024,12: 1369703.
|
| 14 |
VAN SAMKAR A, BROUWER M C, SCHULTSZ C, et al. Streptococcus suis meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].PLoS Negl Trop Dis,2015,9(10): e0004191.
|
| 15 |
FENG Y J, ZHANG H M, WU Z W,et al. Streptococcus suis infection: an emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases?[J].Virulence,2014, 5(4): 477-497.
|
| 16 |
HUONG V T L, TURNER H C, KINH N V,et al. Burden of disease and economic impact of human Streptococcus suis infection in Viet Nam[J]. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2019, 113(6): 341-350.
|
| 17 |
RICHARDSON M P, REID A, TARLOW M J,et al. Hearing loss during bacterial meningitis[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1997, 76(2): 134-138.
|
| 18 |
DOMÍNGUEZ-PUNARO M C, KOEDEL U, HOEGEN T,et al. Severe cochlear inflammation and vestibular syndrome in an experimental model of Streptococcus suis infection in mice[J].Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2012, 31(9): 2391-2400.
|
| 19 |
翁声通, 俞晓玲, 官升灿,等. 人感染猪链球菌脑膜炎并发听力障碍的临床治疗研究[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2018, 11(35): 5-7.
|
| 20 |
SHEN B, TONG L Y, QIU J,et al. Suppurative meningitis complicated with arthritis caused by Streptococcus suis infection: a case report[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2024, 17: 561-569.
|
| 21 |
ANTIC I, BROTHERS K M, STOLZER M,et al. Gene acquisition by a distinct phyletic group within Streptococcus pneumoniae promotes adhesion to the ocular epithelium[J]. mSphere, 2017, 2(5): e00213-17.
|
| 22 |
WANG S J, WANG G, TANG Y D, et al. Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection induces splenomegaly with splenocyte apoptosis[J].Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10(6): e0321022.
|
| 23 |
LI Z, XU M, HUA X. Endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Streptococcus suis infection: a case report[J].BMC Ophthalmol, 2022, 22(1): 165.
|
| 24 |
何 婷, 王 廉. 猪链球菌脑膜炎并发双眼内源性眼内炎一例[J]. 眼科,2023, 32(1): 74-75.
|
| 25 |
HOA N T, CHIEU T T, NGHIA H D,et al. The antimicrobial resistance patterns and associated determinants in Streptococcus suis isolated from humans in southern Vietnam, 1997-2008[J].BMC Infect Dis,2011, 11: 6.
|
| 26 |
刘海珠, 袁晓明. 人猪链球菌感染的临床实验室诊断研究进展[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报,2016, 32(5): 490-493.
|