吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1606-1613.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240614
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
内侧前额叶皮质区核氧化还原蛋白对卒中后抑郁小鼠抑郁样行为的影响及其机制
- 南阳医学高等专科学校第一附属医院神经外科,河南 南阳 473058
Effect of nucleoredoxin in medial prefrontal cortex on depression-like behavior in mice with post-stroke depression and its mechanism
Dan ZHAO( ),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
- Department of Neurosurgery,First Affiliated Hospital,Nanyang Medical College,Nanyang 473058,China
摘要:
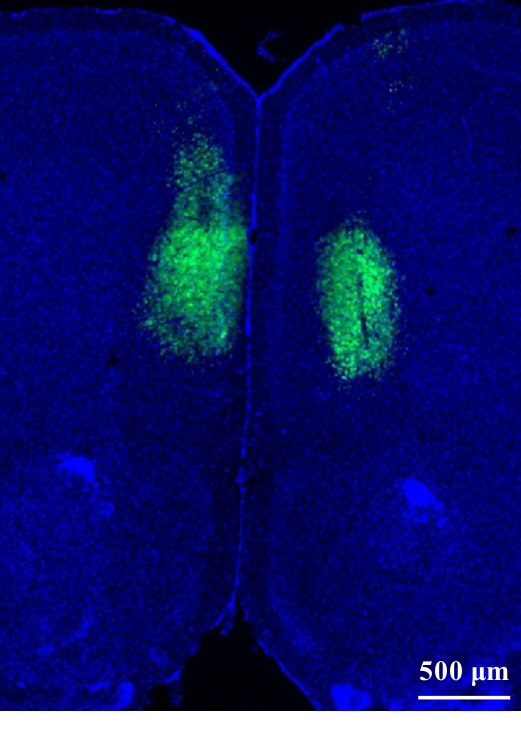
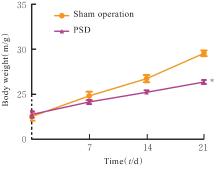
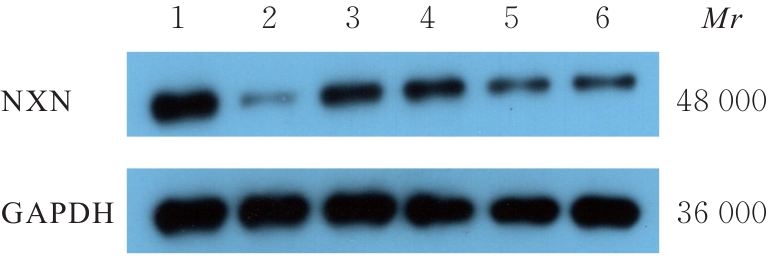
目的 探讨内侧前额叶皮质(mPFC)区核氧化还原蛋白(NXN)对小鼠卒中后抑郁(PSD)的影响,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 80只C57BL/6小鼠,随机选取42只分为NXN过表达腺相关病毒感染组(AAV-NXN-OE组,n=21)和阴性对照腺相关病毒感染组(AAV-NC组,n=21),剩余小鼠分为假手术组(n=20)和PSD组(n=18),注射NXN过表达腺相关病毒后,将AAV-NXN-OE组和AAV-NC组剩余小鼠分为PSD+AAV-NC组(n=18)和PSD+AAV-NXN-OE组(n=18)。术前3周,采用脑立体定位法向小鼠脑组织mPFC区注射NXN过表达腺相关病毒,显微镜下观察病毒在小鼠脑组织mPFC区表达情况,Western blotting法检测小鼠脑组织中NXN蛋白表达水平。采用线栓法建立大脑中动脉闭塞(MCAO)卒中模型,术后1周使用慢性不可预见的中等应激(CUMS)结合孤养法持续干预3周,构建PSD模型小鼠。造模期间监测小鼠体质量变化,造模结束后采用糖水偏好实验、悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验观察各组小鼠抑郁样行为学表现,生化法检测各组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中丙二醛(MDA)和还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,2',7'-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)荧光探针标记法检测各组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中活性氧(ROS)水平,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠脑组织mPFC区、杏仁核区和海马组织中NXN蛋白表达水平。 结果 PSD小鼠脑组织mPFC区有大量绿色荧光,表明携带ZsGreen绿色荧光蛋白标签的AAVs病毒在PSD小鼠脑组织mPFC区成功感染并表达。与AAV-NC组比较,AAV-NXN-OE组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中NXN蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,PSD组小鼠体质量增长缓慢(P<0.05),糖水偏好率明显降低(P<0.05),小鼠在悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验中不动时间均明显增加(P<0.05);与假手术组比较,PSD+AAV-NC组小鼠糖水偏好率明显降低(P<0.05),小鼠在悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验中不动时间均明显增加(P<0.05);与PSD+AAV-NC组比较,PSD+AAV-NXN-OE组小鼠糖水偏好率明显升高(P<0.05),小鼠在悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验中不动时间均明显减少(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,PSD+AAV-NC组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中MDA和ROS水平均明显升高(P<0.05),GSH水平和SOD活性均明显降低(P<0.05);与PSD+AAV-NC组比较,PSD+AAV-NXN-OE组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中MDA和ROS水平均明显降低(P<0.05),GSH水平和SOD活性均明显升高(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,PSD组小鼠脑组织mPFC区中NXN蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),杏仁核区和海马组织中NXN蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 小鼠脑组织mPFC区中NXN过表达可改善PSD小鼠抑郁样行为,其作用机制可能与调节氧化还原平衡有关。
中图分类号:
- R749.13