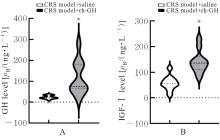
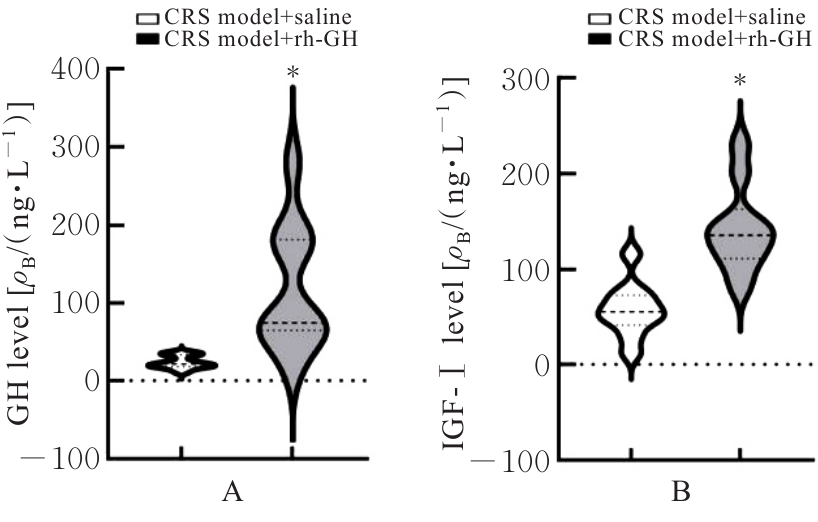
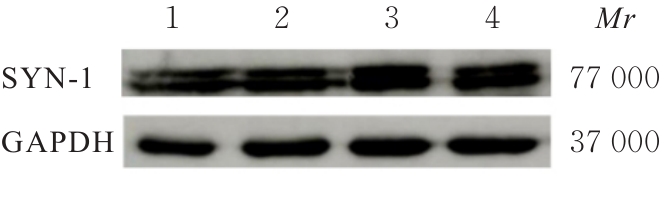
| [1] |
GREENBERG P, CHITNIS A, LOUIE D, et al. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2019)[J]. Adv Ther, 2023, 40(10): 4460-4479.
|
| [2] |
LÉPINE J P, BRILEY M. The increasing burden of depression[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2011, 7(): 3-7.
|
| [3] |
BONFIGLIO J J, INDA C, REFOJO D, et al. The corticotropin-releasing hormone network and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: molecular and cellular mechanisms involved[J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2011, 94(1): 12-20.
|
| [4] |
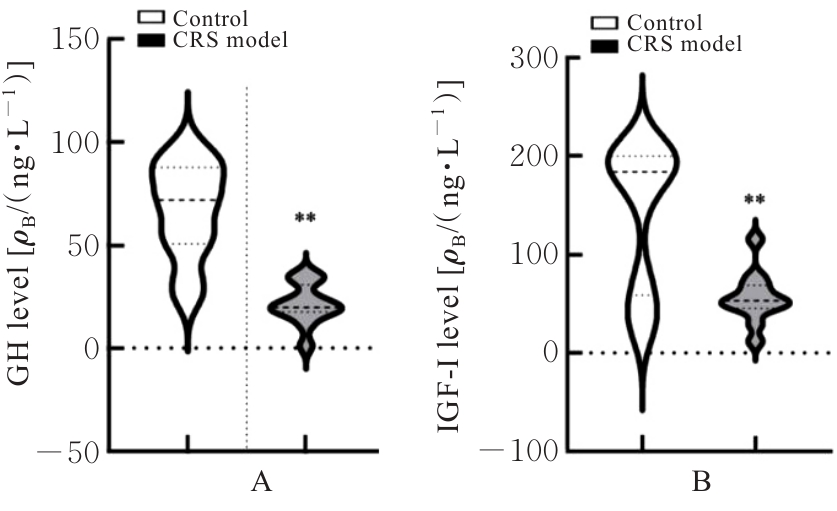
ALGAHTANY M, SHARMA S, FAHOUM K, et al. The role of growth hormone in depression: a human model[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 661819.
|
| [5] |
KARACHALIOU F H, KARAVANAKI K, SIMATOU A, et al. Association of growth hormone deficiency (GHD) with anxiety and depression: experimental data and evidence from GHD children and adolescents[J]. Hormones (Athens), 2021, 20(4): 679-689.
|
| [6] |
BUTLER T, HARVEY P, CARDOZO L, et al. Epilepsy, depression, and growth hormone[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2019, 94: 297-300.
|
| [7] |
MCGAULEY G A. Quality of life assessment before and after growth hormone treatment in adults with growth hormone deficiency[J]. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl, 1989, 356: 70-72;discussion 73-74.
|
| [8] |
ARWERT L I, DEIJEN J B, MÜLLER M, et al. Long-term growth hormone treatment preserves GH-induced memory and mood improvements: a 10-year follow-up study in GH-deficient adult men[J]. Horm Behav, 2005, 47(3): 343-349.
|
| [9] |
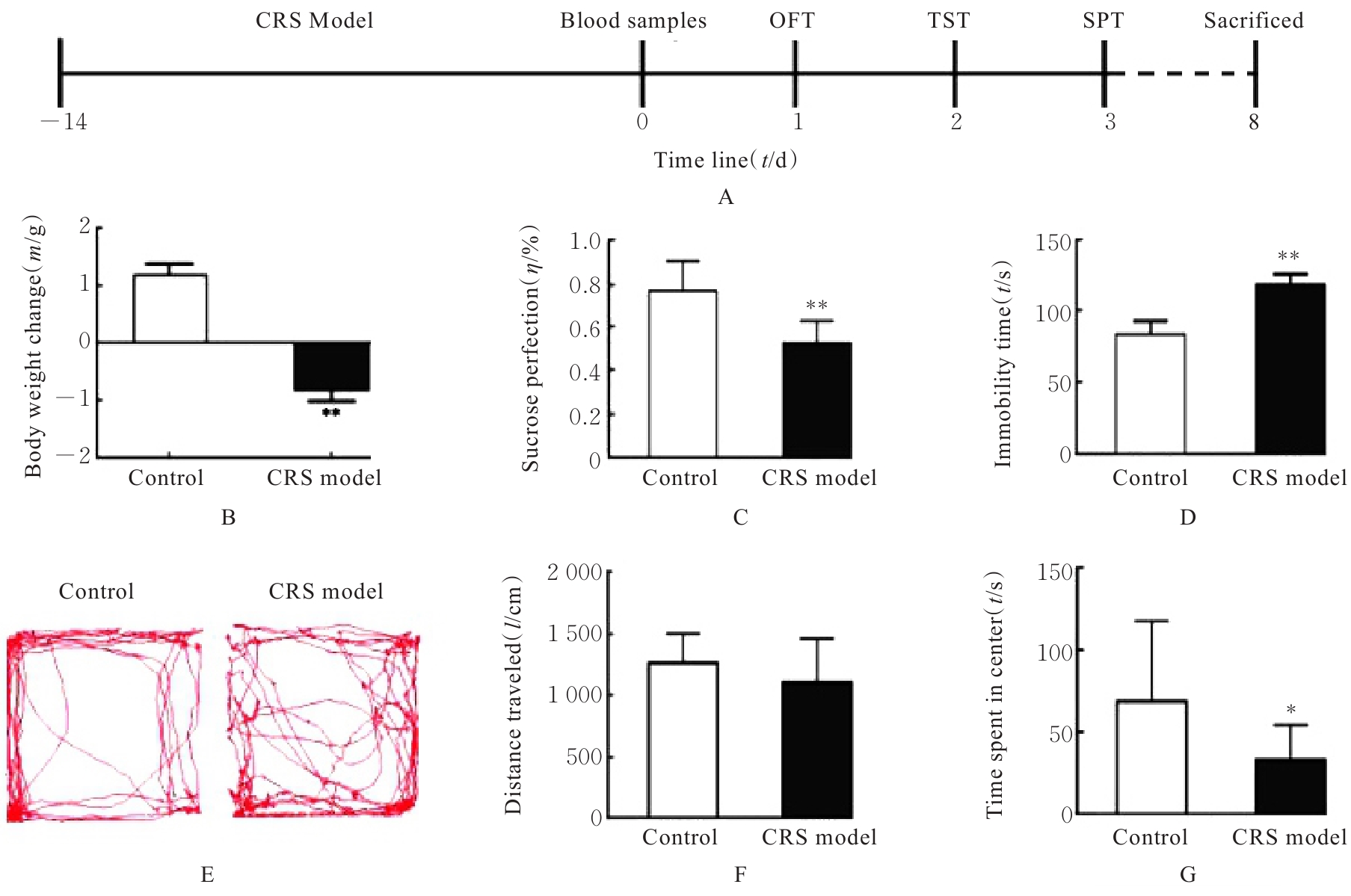
SON H, YANG J H, KIM H J, et al. A chronic immobilization stress protocol for inducing depression-like behavior in mice[J]. J Vis Exp, 2019(147): DOI: 10.3791/59546.
|
| [10] |
CHEN X W, LIU X F, LUAN S X, et al. Optogenetic activation of the lateral habenulaD1R-ventral tegmental area circuit induces depression-like behavior in mice[J]. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2024, 274(4): 867-878.
|
| [11] |
UENO H, TAKAHASHI Y, MURAKAMI S, et al. Effect of simultaneous testing of two mice in the tail suspension test and forced swim test[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 9224-9238.
|
| [12] |
FIGUEIREDO CERQUEIRA M M, CASTRO M M L, VIEIRA A A, et al. Comparative analysis between Open Field and Elevated Plus Maze tests as a method for evaluating anxiety-like behavior in mice[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(4): e14522.
|
| [13] |
TANG M L, CHEN M, LI Q. Paeoniflorin ameliorates chronic stress-induced depression-like behavior in mice model by affecting ERK1/2 pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 11329-11341.
|
| [14] |
MAHAJAN T, CROWN A, CHECKLEY S, et al. Atypical depression in growth hormone deficient adults, and the beneficial effects of growth hormone treatment on depression and quality of life[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2004, 151(3): 325-332.
|
| [15] |
JARRETT D B, MIEWALD J M, KUPFER D J. Recurrent depression is associated with a persistent reduction in sleep-related growth hormone secretion[J]. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1990, 47(2): 113-118.
|
| [16] |
KUTCHER S, MALKIN D, SILVERBERG J, et al. Nocturnal Cortisol, thyroid stimulating hormone, and growth hormone secretory profiles in depressed adolescents[J]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 1991, 30(3): 407-414.
|
| [17] |
崔林雨, 王婧雅, 段婧瑶, 等. TSPO配体YL-IPA08对脂多糖诱导的小鼠抑郁和焦虑样行为的缓解作用及其抗炎机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2024, 49(12): 1417-1425.
|
| [18] |
NIETO-ESTÉVEZ V, DEFTERALI Ç, VICARIO-ABEJÓN C. IGF-Ⅰ: a key growth factor that regulates neurogenesis and synaptogenesis from embryonic to adult stages of the brain[J]. Front Neurosci, 2016, 10: 52.
|
| [19] |
ABE H, MOLITCH M E, VAN WYK J J, et al. Human growth hormone and somatomedin C suppress the spontaneous release of growth hormone in unanesthetized rats[J]. Endocrinology, 1983, 113(4): 1319-1324.
|
| [20] |
YUEN K C J, MASEL B E, REIFSCHNEIDER K L, et al. Alterations of the GH/IGF-Ⅰ axis and gut microbiome after traumatic brain injury: a new clinical syndrome?[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 105(9): dgaa398.
|
| [21] |
DAS S K, BARHWAL K, HOTA S K, et al. Disrupting monotony during social isolation stress prevents early development of anxiety and depression like traits in male rats[J]. BMC Neurosci, 2015, 16: 2-14.
|
| [22] |
DUMAN C H, SCHLESINGER L, TERWILLIGER R, et al. Peripheral insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ produces antidepressant-like behavior and contributes to the effect of exercise[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2009, 198(2): 366-371.
|
| [23] |
FRAGO L M, PAÑEDA C, DICKSON S L, et al. Growth hormone (GH) and GH-releasing peptide-6 increase brain insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ expression and activate intracellular signaling pathways involved in neuroprotection[J]. Endocrinology, 2002, 143(10): 4113-4122.
|
| [24] |
NARAI H, NAGANO I, ILIEVA H, et al. Prevention of spinal motor neuron death by insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ associating with the signal transduction systems in SODG93A transgenic mice[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2005, 82(4): 452-457.
|
| [25] |
KONDO M. Molecular mechanisms of exercise-induced hippocampal neurogenesis and antidepressant effects[J]. JMA J, 2023, 6(2): 114-119.
|
 )
)