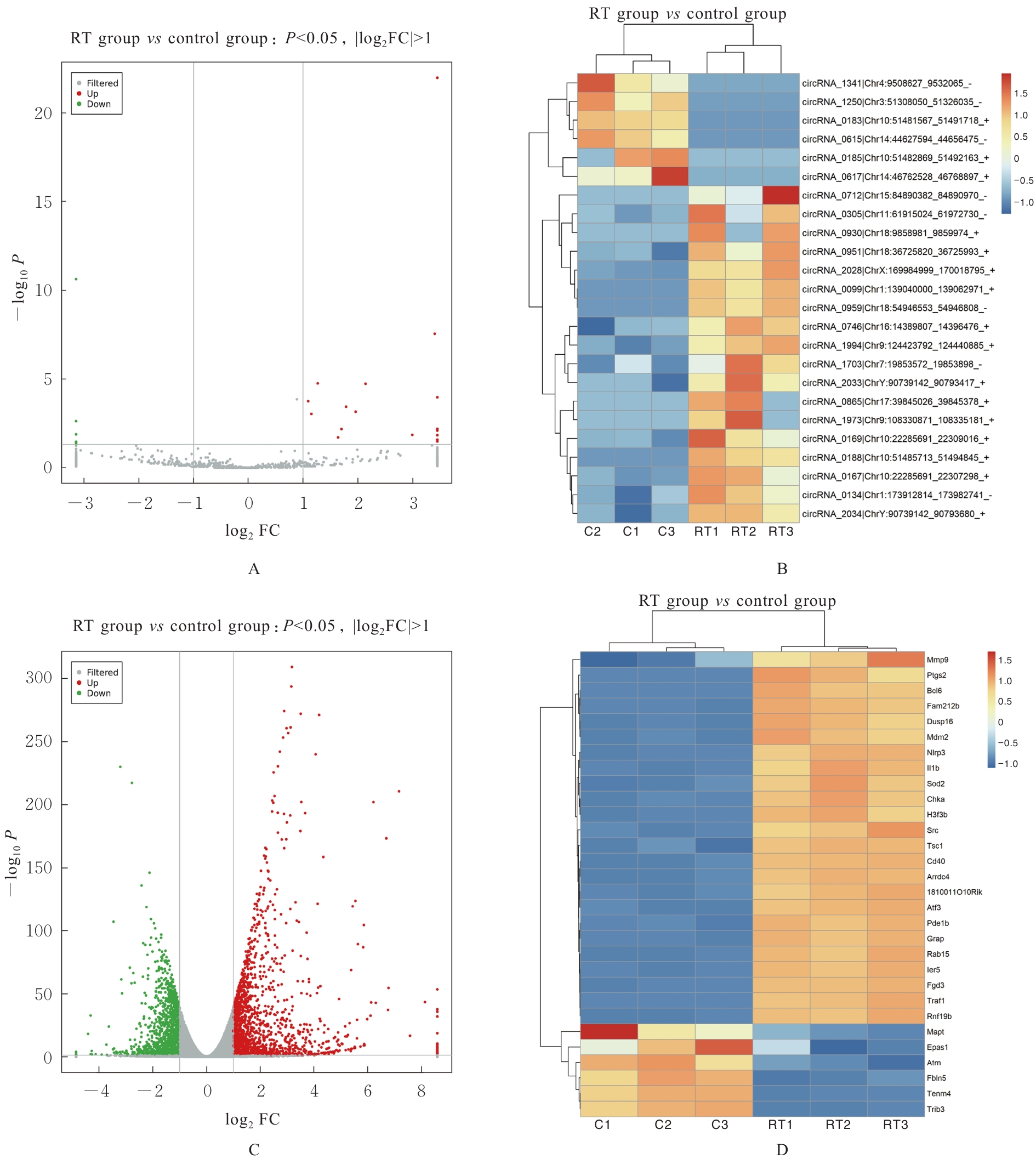
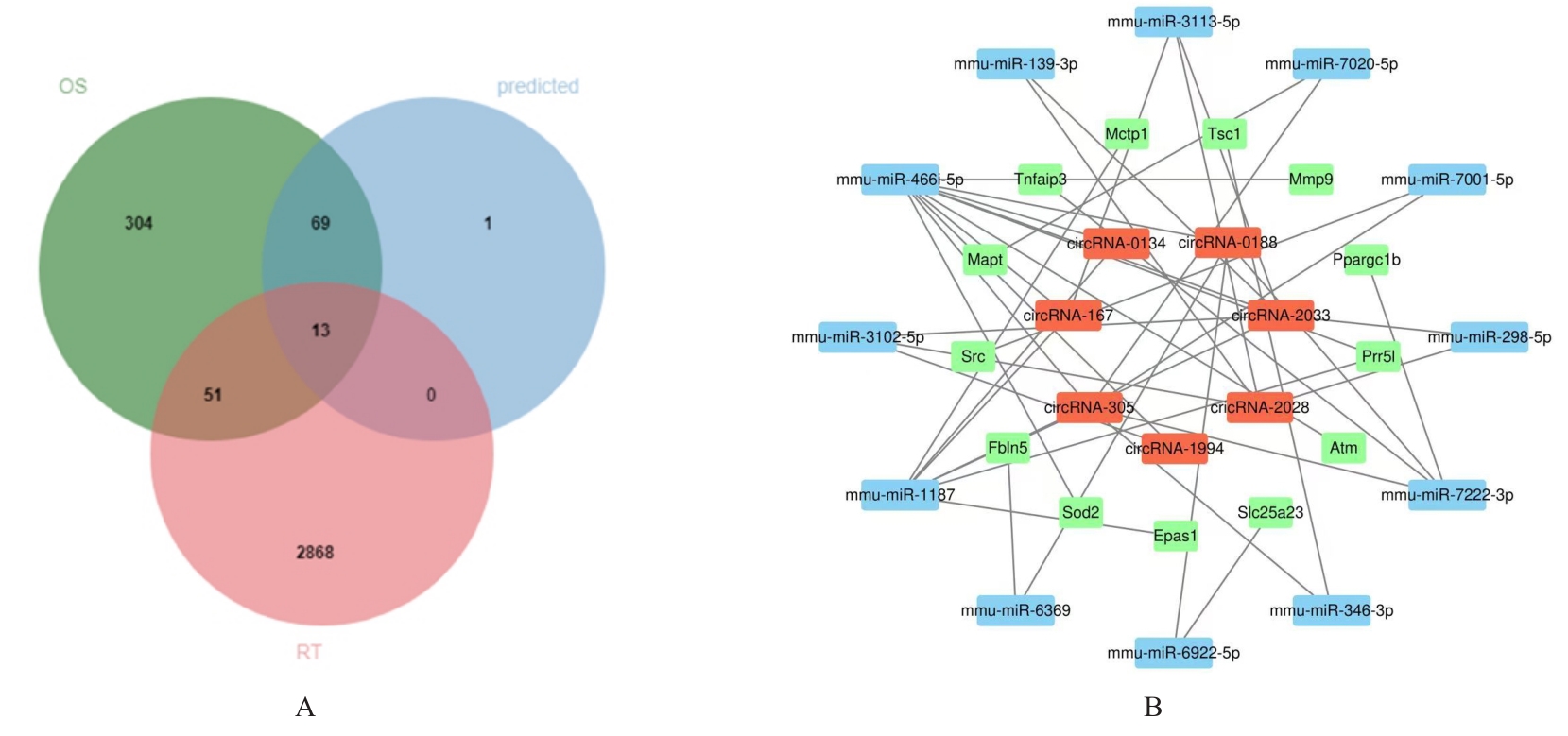
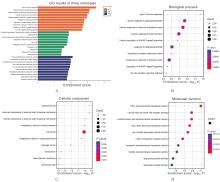
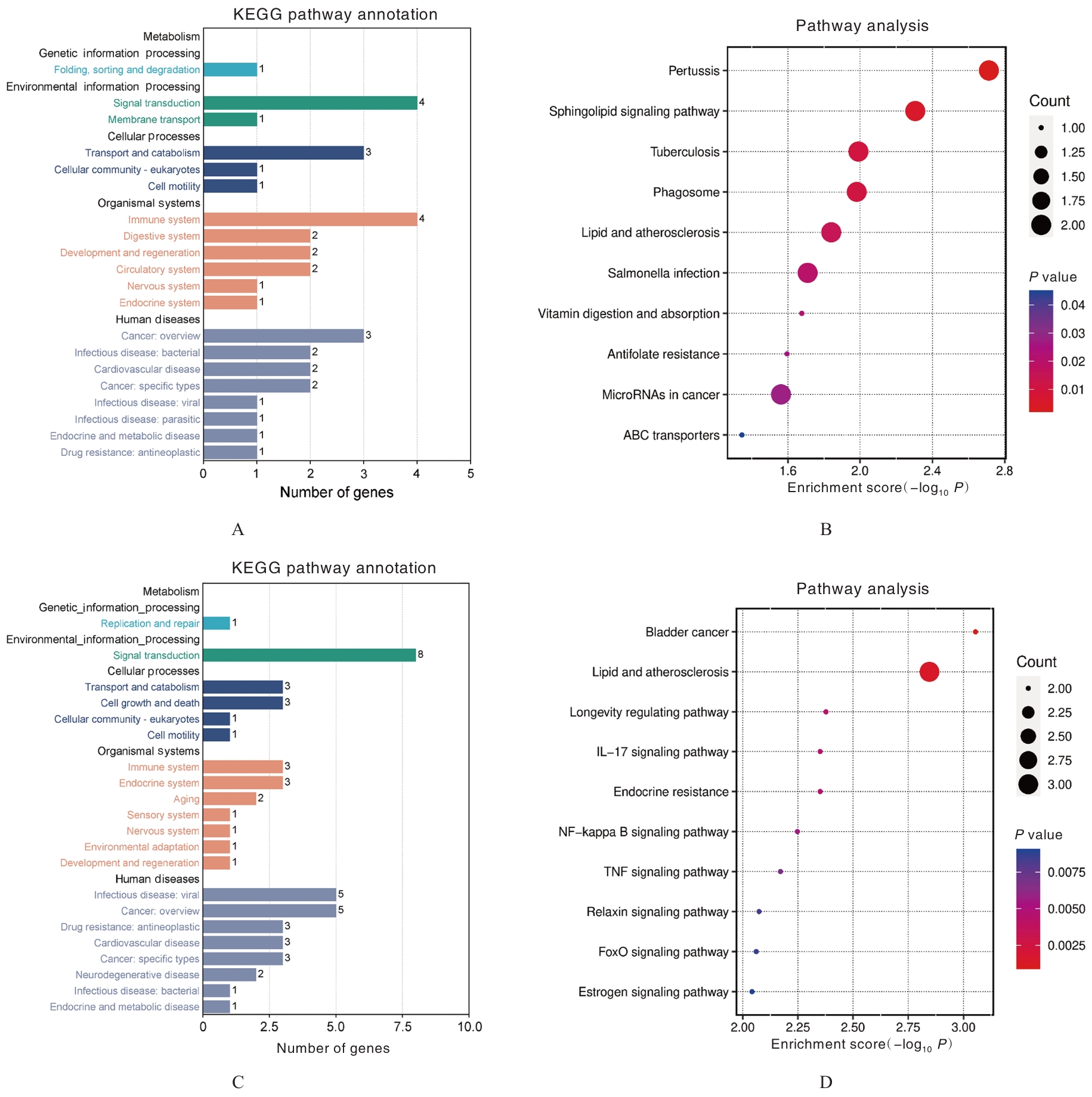
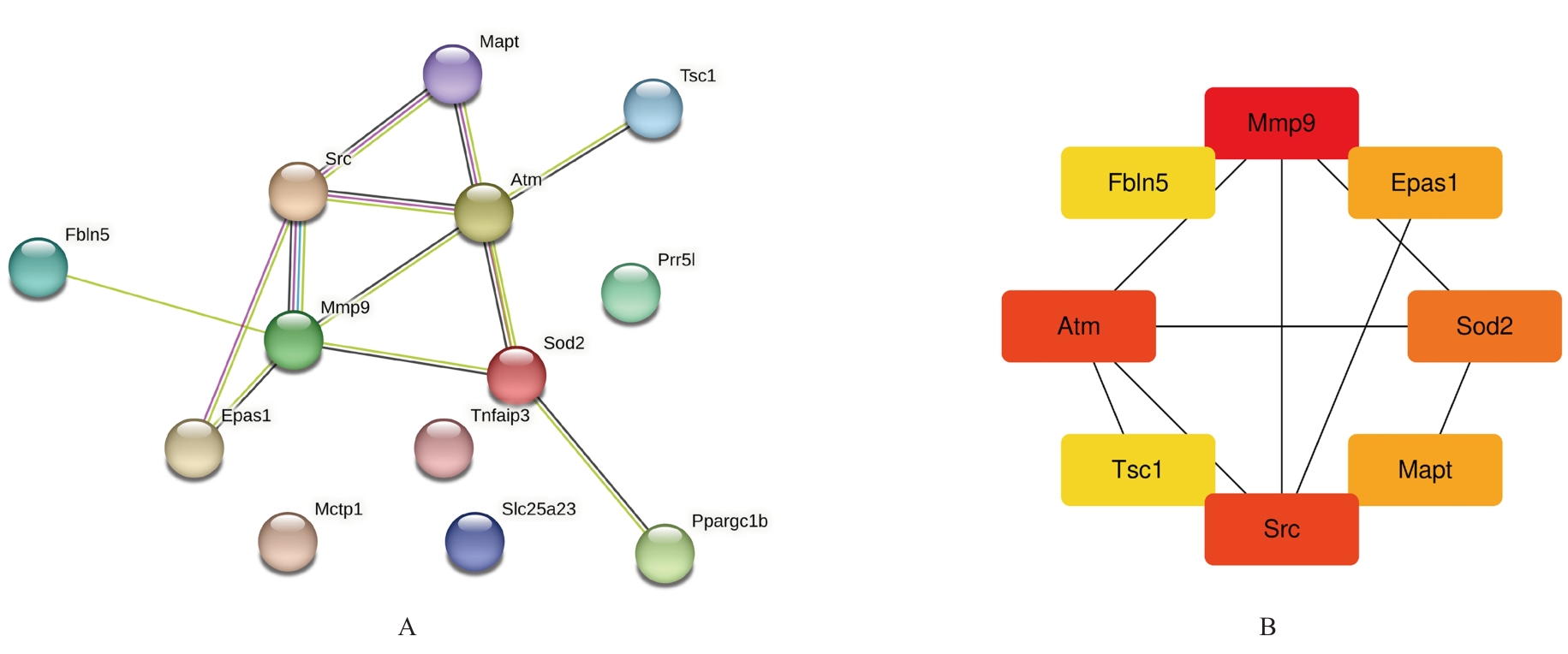
| [1] |
徐义峰, 柯诗文, 李可可, 等. 氧化应激和免疫浸润在特发性肺纤维化中的作用及中药防治研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2024, 40(10): 2108-2115.
|
| [2] |
于馨雅, 申元英, 郭 乐. Nrf2/HO-1通路在氧化应激和炎性反应中的作用[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2023, 52(7): 19-22.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG T, WU D M, LUO P W, et al. CircNEIL3 mediates pyroptosis to influence lung adenocarcinoma radiotherapy by upregulating PIF1 through miR-1184 inhibition[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(2): 167.
|
| [4] |
LI M Z, HUA Q H, SHAO Y T, et al. Circular RNA circBbs9 promotes PM2.5-induced lung inflammation in mice via NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Environ Int, 2020, 143: 105976.
|
| [5] |
王俊虹, 吴 绘, 魏茂提. BALB/c小鼠免疫重组蓖麻毒素B链蛋白的免疫机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2016, 32(12): 1758-1760.
|
| [6] |
TESH V L. The induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins and ricin[J]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2012, 357: 137-178.
|
| [7] |
IORDANOV M S, PRIBNOW D, MAGUN J L, et al. Ribotoxic stress response: activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1997, 17(6): 3373-3381.
|
| [8] |
XU Y X, DONG M X, SUN C B, et al. Caspase-3/Gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis contributes to Ricin toxin-induced inflammation[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2024, 396: 19-27.
|
| [9] |
JOMOVA K, RAPTOVA R, ALOMAR S Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2023, 97(10): 2499-2574.
|
| [10] |
WEN S, LI S L, LI L L, et al. circACTR2: a novel mechanism regulating high glucose-induced fibrosis in renal tubular cells via pyroptosis[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2020, 43(3): 558-564.
|
| [11] |
POLISENO L, SALMENA L, ZHANG J W, et al. A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7301): 1033-1038.
|
| [12] |
LATZ E, XIAO T S, STUTZ A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013, 13(6): 397-411.
|
| [13] |
KLOTZ L O. Redox regulation of FoxO activity: impact on micronutrient homeostasis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2015, 86: S13.
|
| [14] |
LIANG D, WANG Q L, ZHANG W B, et al. JAK/STAT in leukemia: a clinical update[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 25.
|
| [15] |
WANG J J, FU D D, SENOUTHAI S, et al. Critical roles of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB survival axis in angiotensin II-induced podocyte injury[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(6): 5134-5144.
|
| [16] |
LOU W Y, DING B S, WANG J N, et al. The involvement of the hsa_circ_0088494-miR-876-3p-CTNNB1/CCND1 axis in carcinogenesis and progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 605940.
|
| [17] |
ZHU L N, YANG T, LI L J, et al. TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4696.
|
| [18] |
CHEN F J, XING Y F, CHEN Z J, et al. Competitive adsorption of microRNA-532-3p by circular RNA SOD2 activates Thioredoxin Interacting Protein/NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 pathway and promotes pyroptosis of non-alcoholic fatty hepatocytes[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2024, 29(1): 250.
|
| [19] |
SLACK S, BATTAGLIA A, CIBERT-GOTON V, et al. EphrinB2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2B via Src-family kinases during inflammatory hyperalgesia[J]. Neuroscience, 2008, 156(1): 175-183.
|
| [20] |
TANG J, XIAO Y Z, LIN G X, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of NLRP3 by the Src family kinase Lyn suppresses the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Sci Signal, 2021, 14(706): eabe3410.
|
| [21] |
张晓文, 张 婵, 张 迪, 等. 川楝素通过MMP9抑制肾癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(4): 793-798, 803.
|
| [22] |
胡 佳, 张海霞, 苏婉露, 等. 间充质干细胞对2型糖尿病小鼠糖尿病肾病进展的影响及其机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023, 48(4): 383-393.
|
| [23] |
LI M X, LIN Y F, PALCHIK G A, et al. The catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase is required for cellular resistance to oxidative stress independent of DNA double-strand break repair[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2014, 76: 278-285.
|
| [24] |
ERTTMANN S F, HÄRTLOVA A, SLONIECKA M, et al. Loss of the DNA damage repair kinase ATM impairs inflammasome-dependent anti-bacterial innate immunity[J]. Immunity, 2016, 45(1): 106-118.
|
| [25] |
WILLIAMSON M R, SHUTTLEWORTH A, CANFIELD A E, et al. The role of endothelial cell attachment to elastic fibre molecules in the enhancement of monolayer formation and retention, and the inhibition of smooth muscle cell recruitment[J]. Biomaterials, 2007, 28(35): 5307-5318.
|
| [26] |
NGUYEN A D, ITOH S, JENEY V, et al. Fibulin-5 is a novel binding protein for extracellular superoxide dismutase[J]. Circ Res, 2004, 95(11): 1067-1074.
|
| [27] |
SCHLUTERMAN M K, CHAPMAN S L, KORPANTY G, et al. Loss of fibulin-5 binding to beta1 integrins inhibits tumor growth by increasing the level of ROS[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2010, 3(5/6): 333-342.
|
| [28] |
MAJMUNDAR A J, WONG W J, SIMON M C. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 40(2): 294-309.
|
| [29] |
SEMENZA G L. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine[J]. Cell, 2012, 148(3): 399-408.
|
| [30] |
XUE X, RAMAKRISHNAN S, ANDERSON E, et al. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 activates the inflammatory response in the intestinal epithelium to promote colitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145(4): 831-841.
|
| [31] |
STRANG K H, GOLDE T E, GIASSON B I. MAPT mutations, tauopathy, and mechanisms of neurodegeneration[J]. Lab Investig, 2019, 99(7): 912-928.
|
| [32] |
BRADFORD X, FERNANDES H J R, SNOWDEN S G. Changes in oxidised phospholipids in response to oxidative stress in Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) mutant dopamine neurons[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2024, 13(5): 508.
|
 ),葛淑敏1(
),葛淑敏1( )
)
 ),Shumin GE1(
),Shumin GE1( )
)