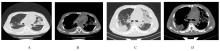
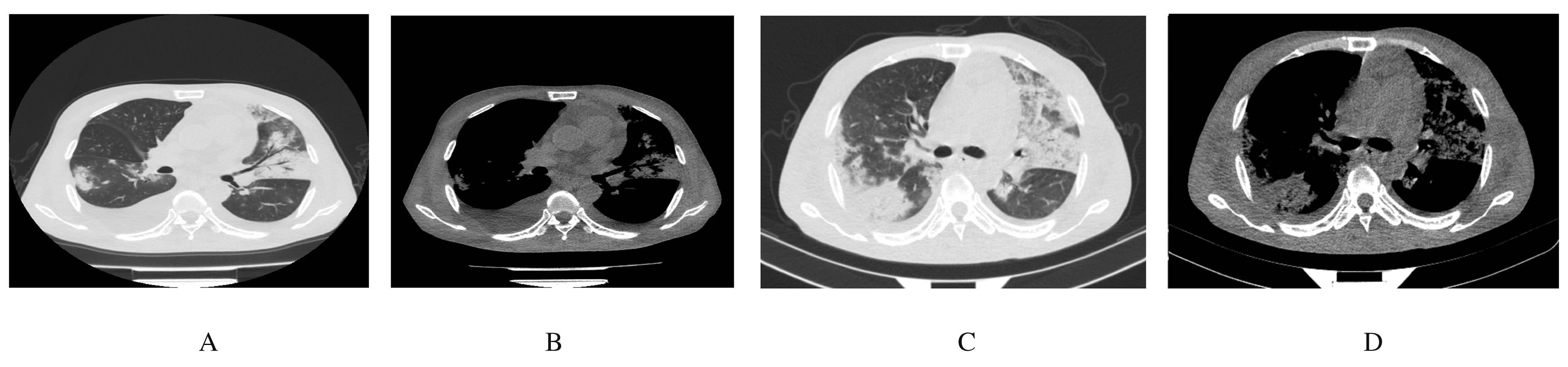
| [1] |
Shan GAO,Yutong WANG,Minqiu LU,Lei SHI,Bin CHU,Yuehua DING,Mengzhen WANG,Li BAO.
Analysis on causes for early death and its risk factors of patients with multiple myeloma in era of novel drugs
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 783-789.
|
| [2] |
Zhaohui WAN,Liang ZENG,Hui ZHOU,Jing LI,Changcheng LEI.
Protective effect of polyphyllin Ⅶ on acute lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 668-675.
|
| [3] |
CHI Ming, GAO Ling, WU Weiwei, ZHANG Boru, WANG Lei.
Improvement effect of berberine on acute lung injury and inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1194-1199.
|
| [4] |
SHI Xu, YU Xin, QU Xinglong, CAO Yang, ZHANG Guangjuan, LI Changyuan.
Effects of hypoxia and its downstream factor mirRNA-145 on differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 935-942.
|
| [5] |
WANG Chong, HAO Zheng, LIU Weiming, ZHAO Conghai, ZHANG Jinnan.
Epidural hematoma ossification after craniocerebral injury: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 628-630.
|
| [6] |
HUANG Qi, SHA Hui, CHEN Long, LYU Longlong, XU Shengming, ZHANG Zetian, ZHAO Song, JIN Fengyan, NIU Feng.
Expression levels of plasma lncRNA MALAT1, LincRNA-p21 and GAS5 in patients with multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia and their diagnostic significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 339-345.
|
| [7] |
WANG Xiaofei, QIN Zaisheng.
Effects of erlotinib on inflammatory response of marcrophages and ALIinduced by lipopolysaccharides in mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 457-461.
|
| [8] |
HE Jing, QI Di, WANG Daoxin.
Mechanism of insulin in up-regulating epithelial sodium channel α-subunit via mTORC2/SGK1 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 716-720.
|
| [9] |
PENG Jing, YUAN Ruili, WANG Xiaoqin, WU Feng, GUO Xuan.
Detection of expression levels of microRNA-181a and microRNA-20a in serum of patients with multiple myeloma and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(03): 625-630.
|
| [10] |
ZHEN Yong-zhan,JI Chun-mei,ZHAO Yu-fang,YAN Feng,LIU Xue-jun,WANG Mei-mei,XU Ai-jun.
Apoptosis-induction of lidamycin in human multiple
myeloma SKO-007 cells enhanced by bortezomid through
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1206-1210.
|
| [11] |
YUAN Ming-zhen,GAO Guang-yuan,LI Bo,DONG Chun-ling,WANG Si-yi, LIANG Hao-jun,LIU Xiang-liang,SUN Xiao-fei.
Role of instilled air in establishment of lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse model of acute lung injury
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1089-1093.
|
| [12] |
LUO Ling,WANG Dao-xin.
Influence of estradiol and progestogen in type Ⅱ alveolar ENaC in rats with acute lung injury
[J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 836-840.
|
| [13] |
WANG Xue-mei|CUI Jiu-wei|XIAO Zhong-ping|CHEN Lin|GAO Peng|FU Kun|.
Comparison of clinical efficacy between MPT and MP in elderly patients with multiple myeloma
[J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 999-1002.
|
| [14] |
MIAO Yu-dan,DONG Chun-ling,LIU ling,XIA Chang-li,SU Lue,LI Bo.
Establishment of mouse |model of acute lung injury with exposed and non-exposed intratracheal instillations and effectiveness comparison
[J]. J4, 2012, 38(3): 414-418.
|
| [15] |
YU Zhen-xiang, ZHAO Heng, PENG Li-ping.
Protective effects of PDS on oxidative damage in lung of hemorrhage-LPS two hits rats
[J]. J4, 2008, 34(4): 594-597.
|
 )
)