Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 222-227.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220128
• Clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
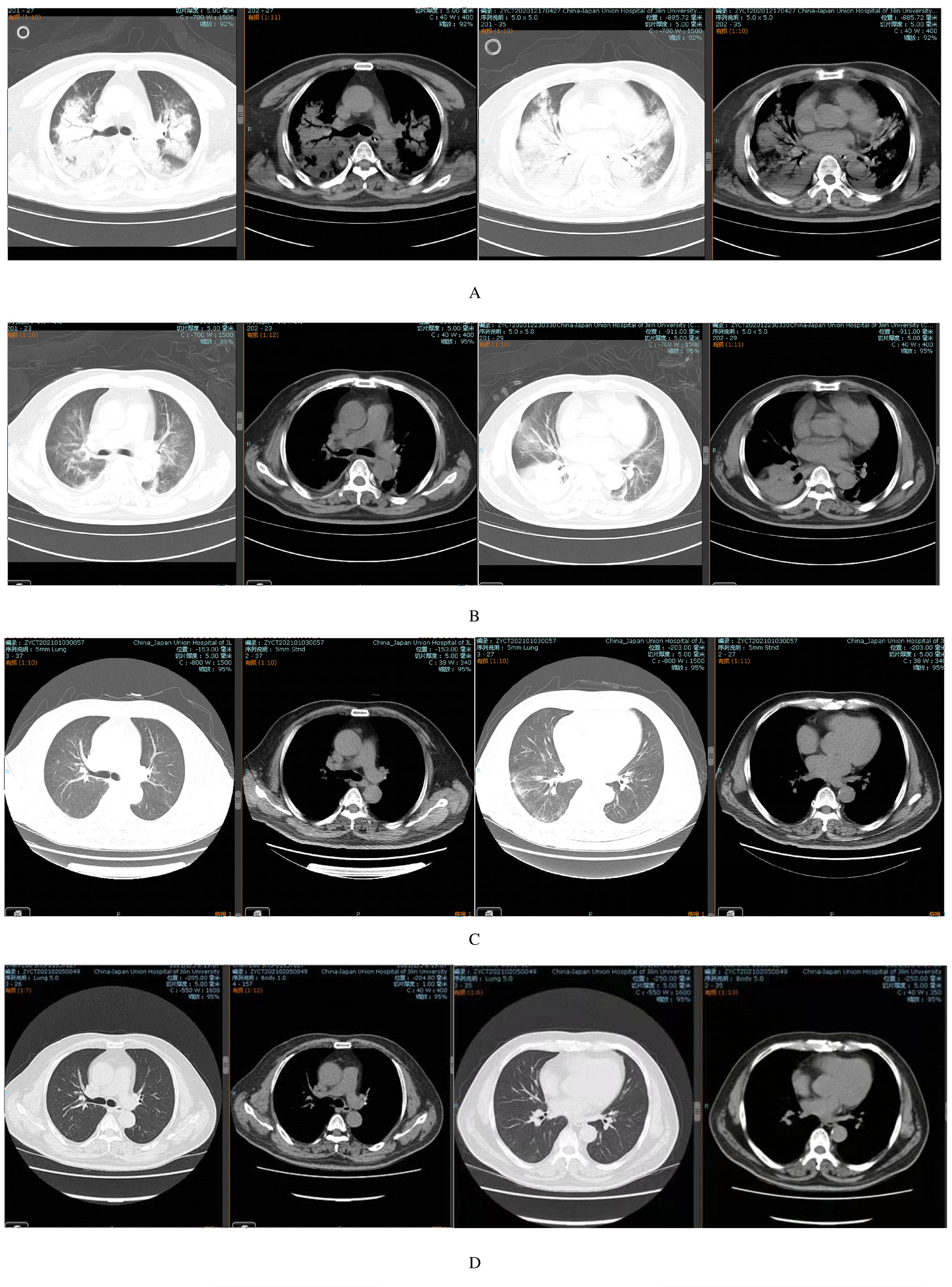
Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia:A report of 2 cases and literature review
Luowei HE,Ye WANG,Dujuan YU,Zhiying CHEN( )
)
- Department of Respiratory Medicine,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
CLC Number:
- R563.1