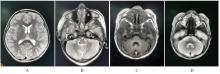
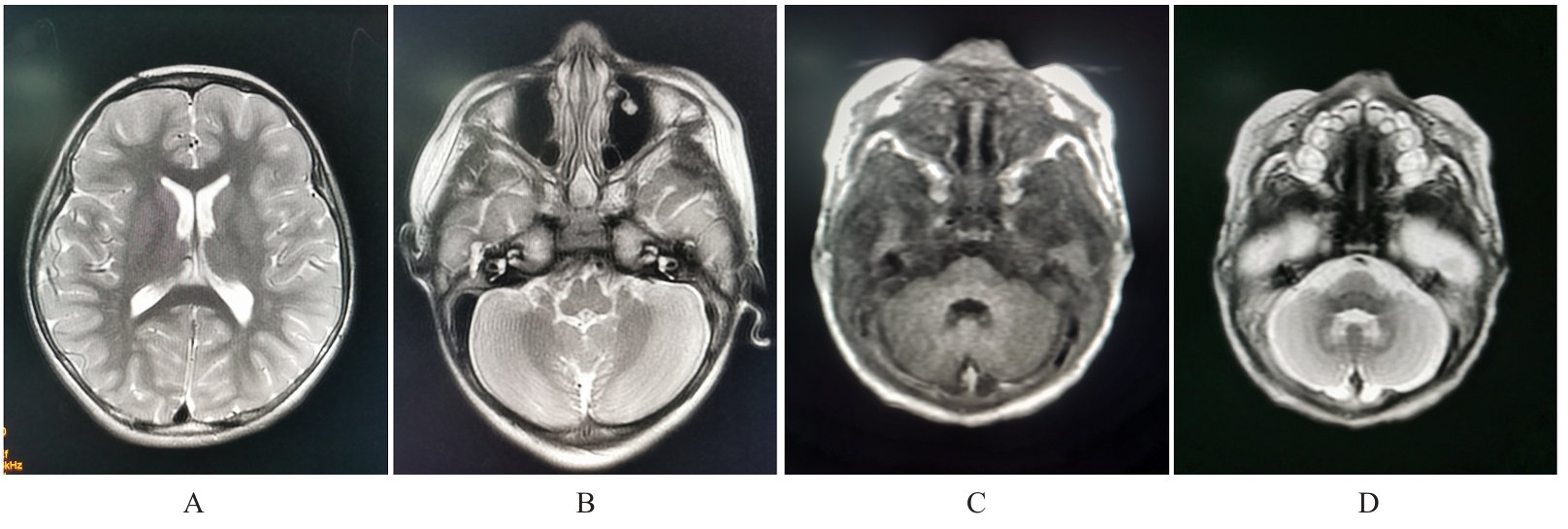
| 1 |
SZYCA R, LEKSOWSKI K. Cornelia de Lange syndrome-characteristics and laparoscopic treatment modalities of reflux based on own material[J]. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne, 2011, 6(3): 173-177.
|
| 2 |
OPITZ J M. The brachmann-de Lange syndrome[J]. Am J Med Genet, 1985, 22(1): 89-102.
|
| 3 |
BARISIC I, TOKIC V, LOANE M, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of Cornelia de Lange syndrome in Europe[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2008, 146A(1): 51-59.
|
| 4 |
MEI L B, LIANG D S, HUANG Y R, et al. Two novel NIPBL gene mutations in Chinese patients with Cornelia de Lange syndrome[J]. Gene, 2015, 555(2): 476-480.
|
| 5 |
SAROGNI P, PALLOTTA M M, MUSIO A. Cornelia de Lange syndrome: from molecular diagnosis to therapeutic approach[J]. J Med Genet, 2020, 57(5): 289-295.
|
| 6 |
KLINE A D, MOSS J F, SELICORNI A, et al. Diagnosis and management of Cornelia de Lange syndrome: first international consensus statement [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2018, 19(10): 649-666.
|
| 7 |
ALONSO-GIL D, LOSADA A. NIPBL and cohesin: new take on a classic tale[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2023, 33(10): 860-871.
|
| 8 |
MUSIO A, SELICORNI A, FOCARELLI M L, et al. X-linked Cornelia de Lange syndrome owing to SMC1L1 mutations[J]. Nat Genet, 2006, 38(5): 528-530.
|
| 9 |
INFANTE E, ALKORTA-ARANBURU G, EL-GHARBAWY A. Rare form of autosomal dominant familial Cornelia de Lange syndrome due to a novel duplication in SMC3 [J]. Clin Case Rep, 2017, 5(8): 1277-1283.
|
| 10 |
KRAB L C, MARCOS-ALCALDE I, ASSAF M, et al. Delineation of phenotypes and genotypes related to cohesin structural protein RAD21[J]. Hum Genet, 2020, 139(5): 575-592.
|
| 11 |
LI Z L, LIU C, XIN H M, et al. Establishment of a transgene-free iPS cell line (SDQLCHi046-A) from a young patient bearing a HDAC8 mutation and suffering from Cornelia de Lange Syndrome[J]. Stem Cell Res, 2023, 66: 102984.
|
| 12 |
OLLEY G, ANSARI M, BENGANI H, et al. BRD4 interacts with NIPBL and BRD4 is mutated in a Cornelia de Lange-like syndrome[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(3): 329-332.
|
| 13 |
KUZNIACKA A, WIERZBA J, RATAJSKA M, et al. Spectrum of NIPBL gene mutations in Polish patients with Cornelia de Lange syndrome[J]. J Appl Genet, 2013, 54(1): 27-33.
|
| 14 |
MOSS J, PENHALLOW J, ANSARI M, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Cornelia de Lange syndrome: behavioral characteristics and changes with age[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2017, 173(6): 1566-1574.
|
| 15 |
周 平, 朱 琳, 范琼丽, 等. Cornelia de Lange综合征首个国际共识的解读[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2020, 22(8): 815-820.
|
| 16 |
GUTIERREZ-ESCRIBANO P, NEWTON M D, LLAURÓ A, et al. A conserved ATP- and Scc2/4-dependent activity for cohesin in tethering DNA molecules[J]. Sci Adv, 2019, 5(11): eaay6804.
|
| 17 |
TONKIN E T, WANG T J, LISGO S, et al. NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome[J]. Nat Genet, 2004, 36(6): 636-641.
|
| 18 |
GAO D Y, ZHU B J, CAO X, et al. Roles of NIPBL in maintenance of genome stability[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2019, 90: 181-186.
|
| 19 |
WEISS F D, CALDERON L, WANG Y F, et al. Neuronal genes deregulated in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome respond to removal and re-expression of cohesin[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2919.
|
| 20 |
BERMUDEZ V P, FARINA A, HIGASHI T L, et al. In vitro loading of human cohesin on DNA by the human Scc2-Scc4 loader complex[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109(24): 9366-9371.
|
| 21 |
REMESEIRO S, CUADRADO A, KAWAUCHI S, et al. Reduction of Nipbl impairs cohesin loading locally and affects transcription but not cohesion-dependent functions in a mouse model of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1832(12): 2097-2102.
|
| 22 |
FOGLIA M, GUARRERA L, KUROSAKI M, et al. The NIPBL-gene mutation of a Cornelia de Lange Syndrome patient causes deficits in the hepatocyte differentiation of induced Pluripotent Stem Cells via altered chromatin-accessibility[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2024, 81(1): 439.
|
| 23 |
MANNINI L, CUCCO F, QUARANTOTTI V, et al. Mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlation in Cornelia de Lange syndrome[J]. Hum Mutat, 2013, 34(12): 1589-1596.
|
| 24 |
KAUR M, BLAIR J, DEVKOTA B, et al. Genomic analyses in Cornelia de Lange syndrome and related diagnoses: novel candidate genes, genotype-phenotype correlations and common mechanisms[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2023, 191(8): 2113-2131.
|
 )
)