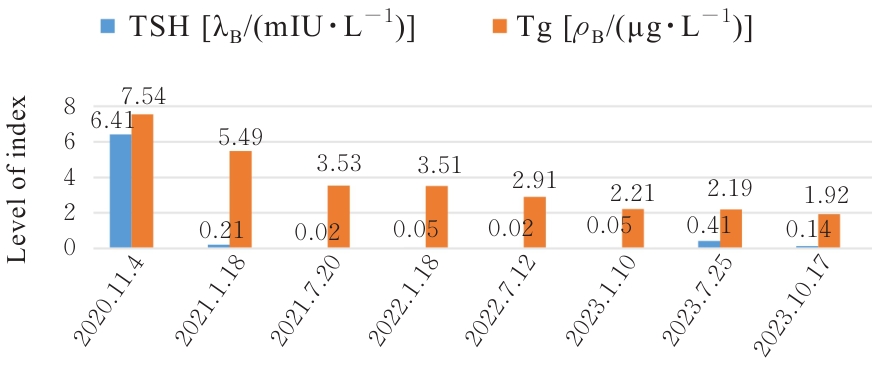
| [1] |
Xiangjin HU,Xiumei SUN,Kai CHEN,Guomin WU.
Changes of upper airway in patient with skeletal class Ⅱ malocclusion accompanied by OSAHS after maxillomandibular advancement surgery: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 493-500.
|
| [2] |
Qi ZHANG,Xiaoyuan XU,Yumiao WU,Han ZHANG,Zhiqiang HU,Jiamin YUAN,Yuchen CUI,Xianchun ZHU.
Treatment of skeletal class Ⅱ high angle malocclusion patient by clear aligner therapy combined with orthognathic surgery: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 508-515.
|
| [3] |
Luyao WANG,Chenxi ZHAO,Wanze ZHANG,Linlin LIU.
Second primary tracheal adenoid cystic carcinoma:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 215-221.
|
| [4] |
Jinping ZHANG,Lingling TONG,Lu GAO,Hongjing CHENG,Minjia SHENG.
Parasitic leiomyoma of abdominal wall complicated with disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis : A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1432-1437.
|
| [5] |
Wenqing RUAN,Zerun FU,Yi HUANG,Longyun LI,Yao SUN,Kai LI.
Application of hypotension prediction index in intraoperative hemodynamic management of robot-assisted laparoscopic cystectomy:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1130-1136.
|
| [6] |
Shaoning KAN,Han WU,Shuangji LI,Jingcheng XIANG,Yuyang LI,Liou JIN,Weiwei LIU.
Simple bone cyst in ipsilateral maxilla and mandible:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 551-555.
|
| [7] |
Rui ZHANG,Peng YU,Hao ZHANG,Yaru DONG,Ying PEI.
Personalized surgical treatment of severe cicatricial ectropion: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1615-1619.
|
| [8] |
Feifei JIA,Hao ZHOU,Xin YANG,Ruotong XING,Xinrui WANG,Yanjun CAI,Wanyu LI.
Hepatolenticular degeneration with mental disorder as first symptom:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1620-1624.
|
| [9] |
Qinghua PING,Wenjing ZHU,Jianxin XIA.
Pustular psoriasis treated with secukinumab during pregency: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1599-1603.
|
| [10] |
Qingshuai WANG,Bo CHEN,Hairui ZHANG,Xiongfeng TANG,Xue GAO,Yingzhi LI.
Arthroscopic treatment of subsynovial hemangioma of knee joint: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1034-1039.
|
| [11] |
Yunke LUO,Jian ZHANG,Wenwen ZHANG,Zongsheng DUAN,Hushan WANG,Yiheng WANG.
Intracranial aneurysm rupture complicated with acute myocardial infarction: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 777-781.
|
| [12] |
Shengnan YANG,Xue WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Tianyu ZHAO,Ying PAN,Dayong DING.
Retroperitoneal giant lymphangioma: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 508-513.
|
| [13] |
Wanyi GU,Cheng ZHI,Chunxia LIU.
Intrathyroid thymic carcinoma: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1580-1585.
|
| [14] |
Qian LI,Jingyi YUAN,Jiaqi ZHOU,Min ZHAO,Ke WANG.
Pulmonary imaging changes as first manifestation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 796-800.
|
| [15] |
Junjie HOU,Xuguang MI,Xiaonan LI,Xiaonan LI,Ying YANG,Xianzhuo JIANG,Ying ZHOU,Zhiqiang NI,Ningyi JIN,Yanqiu FANG.
Treatment of advanced rectal cancer with rectovaginal fistula through bevacizumab combined with FOLFIRI regimen: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 790-795.
|
 )
)