吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2892-2897.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211278
基于模糊聚类最大树算法的高层建筑基坑工程风险识别方法
- 湖南大学 工商管理学院,长沙 410082
Risk identification method of foundation pit engineering of high⁃rise buildings based on fuzzy clustering maximum tree algorithm
Han-chao LIAO( ),Mi-yuan SHAN(
),Mi-yuan SHAN( )
)
- School of Business,Hunan University,Changsha 410082,China
摘要:
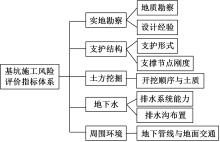
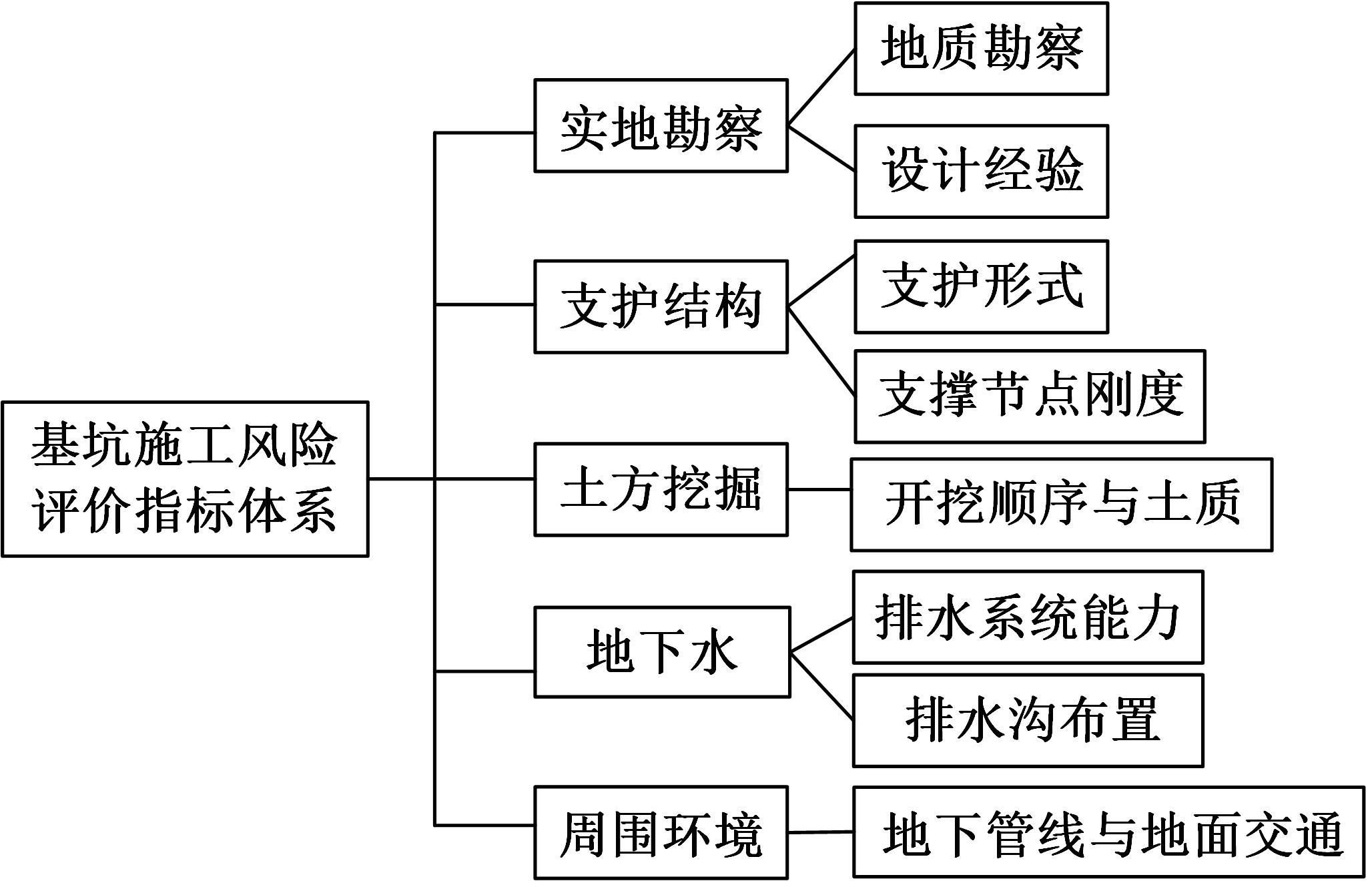
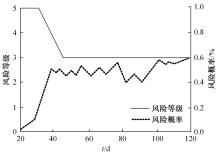
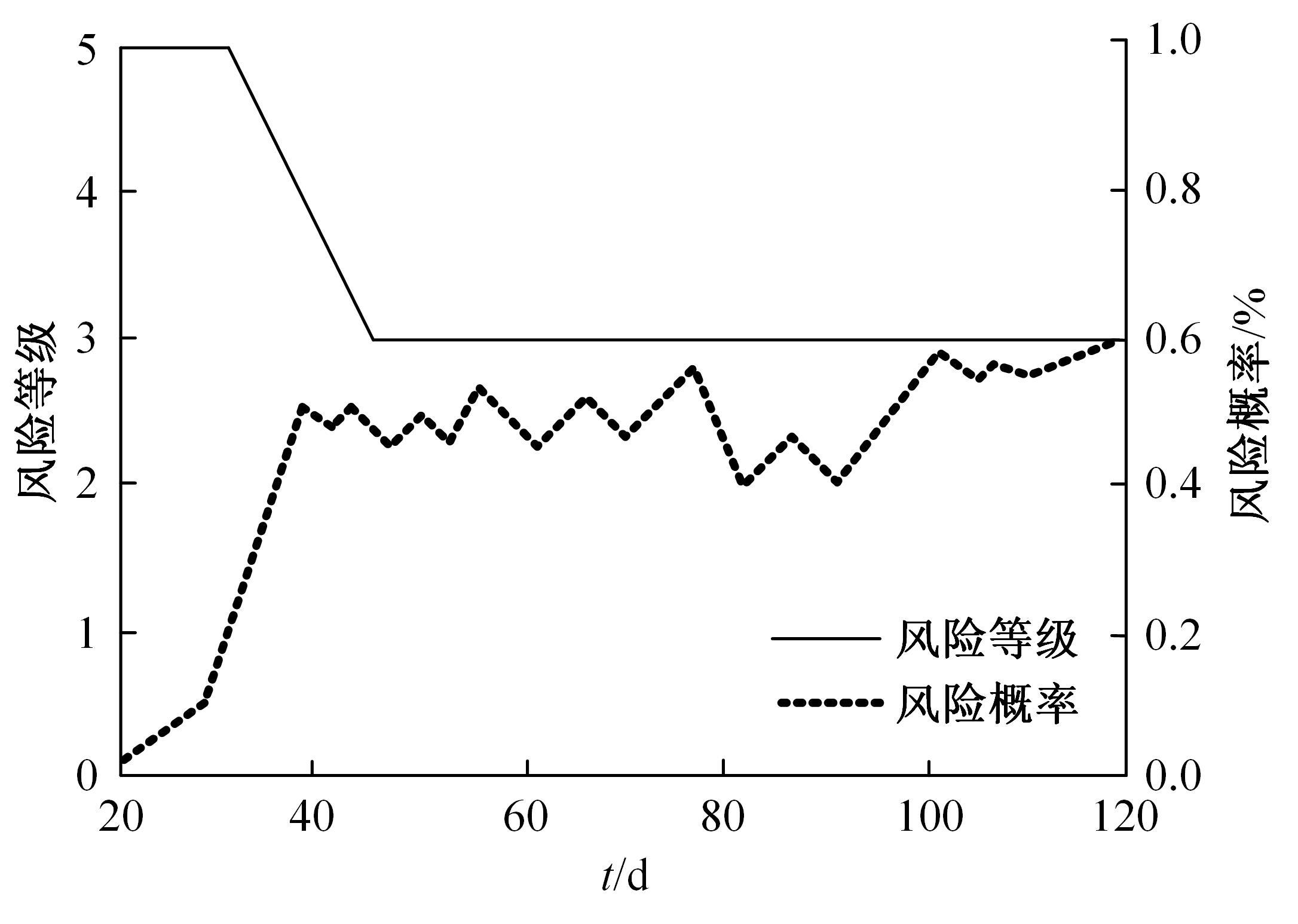
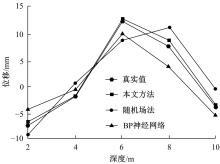
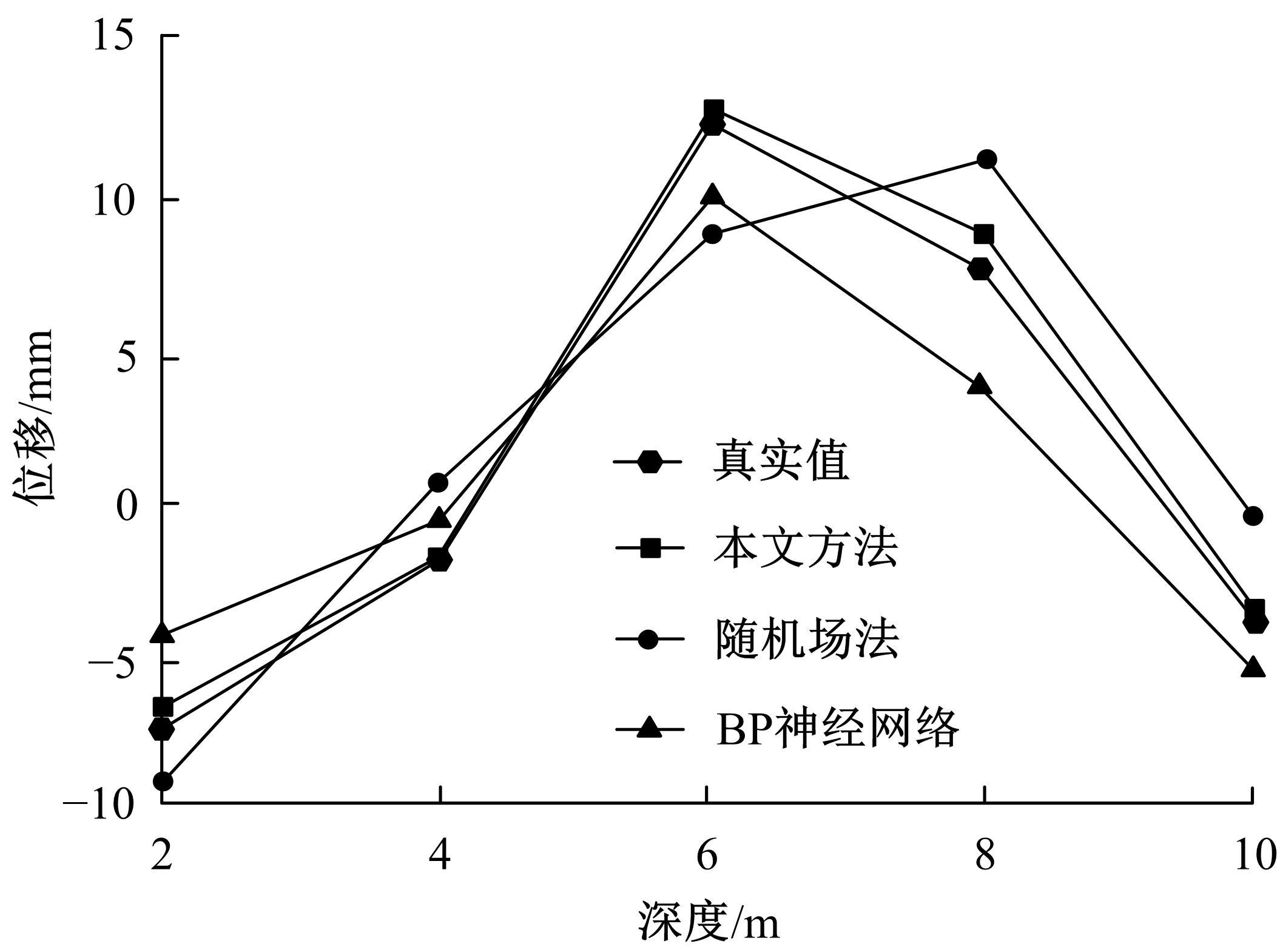
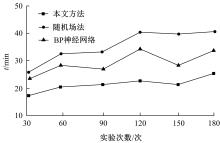
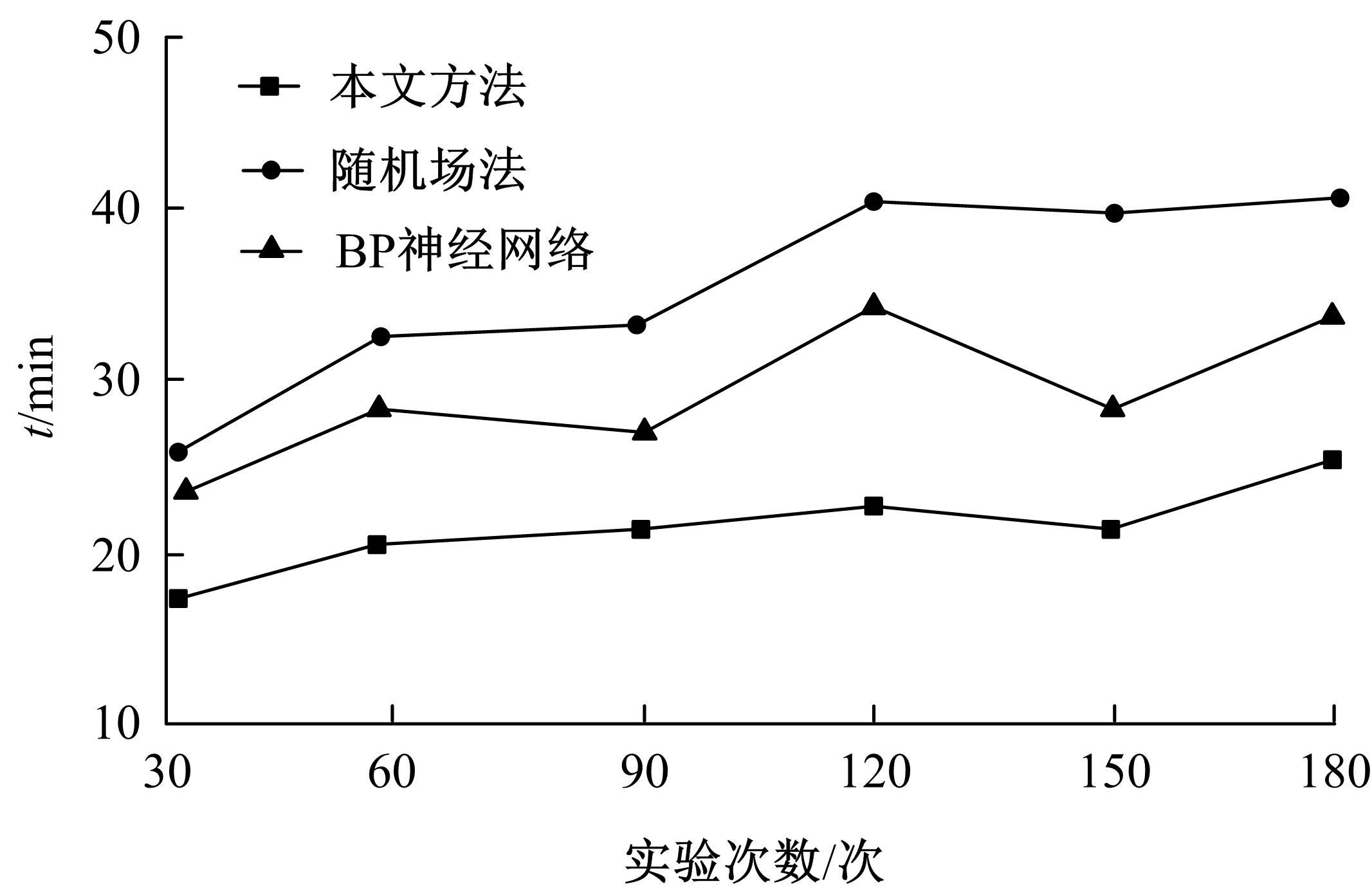
针对基坑工程勘察局限性和工程临时性等实质问题,提出了基于模糊聚类最大树算法的高层建筑基坑工程风险识别方法。通过绝对值减数法建立了模糊相似矩阵,标准化处理风险指标数据,使用风险评价指数划分基坑施工风险等级。利用模糊聚类定量计算影响元素之间的耦合关系,运用无向连通赋权图形式描述最大树结构,通过连接树结构内互相连通的顶点实现风险识别。仿真结果证明:本文方法能够在判定基坑工程风险等级的同时,准确描述风险的具体位置,识别正确率和效率均可达到预期要求,鲁棒性强。
中图分类号:
- TU94
| 1 | 钟春玲,梁东,张云龙,等. 体外预应力钢-混凝土组合简支梁自振频率计算[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2020,50(6):2159-2166. |
| Zhong Chun-ling, Liang Dong, Zhang Yun-long, et al. Calculation of natural frequency of externally prestressed steel-concrete composite simply supported beams[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(6):2159-2166. | |
| 2 | 钱雪忠,姚琳燕. 面向稀疏高维大数据的扩展增量模糊聚类算法[J]. 计算机工程,2019,45(6):75-81, 88. |
| Qian Xue-zhong, Yao Lin-yan. Extended incremental fuzzy clustering algorithm for sparse high-dimensional big data[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019,45(6):75-81, 88. | |
| 3 | Ren X, Fan W, Li J, et al. Building information model-based finite element analysis of high-rise building community subjected to extreme earthquakes[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2019, 22(4):971-981. |
| 4 | 王飞球,黄健陵,符竞,等. 基于BP神经网络的跨既有线高速铁路桥梁施工安全风险评估[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(5):1129-1136. |
| Wang Fei-qiu, Huang Jian-ling, Fu Jing, et al. Risk assessment of construction safety of high-speed railway bridge across existing lines based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019,16(5):1129-1136. | |
| 5 | 华莹,何军,赵金城. 高层建筑施工现场危险区域识别及评估方法研究[J].施工技术,2019,48(6):100-104. |
| Hua Ying, He Jun, Zhao Jin-cheng. Research on identification and evaluation method of hazardous area of high-rise building construction site[J]. Construction Technology, 2019, 48(6):100-104. | |
| 6 | Nakaguro M, Sato Y, Tada Y, et al. Prognostic implication of histopathologic indicators in salivary duct carcinoma: proposal of a novel histologic risk stratification model[J]. American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 2019, 44(4):526-535. |
| 7 | 荀志远,张丽敏,徐瑛莲,等. 基于组合赋权云模型的装配式建筑安全风险评价[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2020,50(7):302-310. |
| Xun Zhi-yuan, Zhang Li-min, Xu Ying-lian, et al. Evaluation of prefabricated buildings safety risk based on combination weighting and cloud model[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2020,50(7):302-310. | |
| 8 | Wang W Y, Wang Y. Diagnosis index system setup for implementation status management in large-scale construction projects[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021(1): 1-9. |
| 9 | 郭文娟. 大数据背景下的房屋建筑施工风险评估模型[J]. 科技通报,2019,35(4):198-201. |
| Guo Wen-juan. Risk assessment model for building construction under the background of big data[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2019,35(4):198-201. | |
| 10 | Chen W, Zhang G, Jiao Y, et al. Unascertained measure-set pair analysis model of collapse risk evaluation in mountain tunnels and its engineering application[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 25(6):1-17. |
| 11 | 李蒙,邹健,刘苹,等. 基于BIM的隧道施工安全风险辨识模型研究[J].工业安全与环保,2019,45(5):69-71. |
| Li Meng, Zou Jian, Liu Ping, et al. Research on tunnel construction safety risk identification model based on BIM[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019,45(5):69-71. | |
| 12 | Lu Y, Gong P, Tang Y, et al. BIM-integrated construction safety risk assessment at the design stage of building projects[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 124(2): No.103553. |
| 13 | 黄俊斌,张国维,闫肃,等. 基于物联网技术的建筑火灾风险动态评估[J]. 消防科学与技术,2020,39(10):1371-1375. |
| Huang Jun-bin, Zhang Guo-wei, Yan Su, et al. Dynamic assessment of building fire risk based on internet of things technology[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2020,39(10):1371-1375. | |
| 14 | Baat M, Wieringa N, Droge S, et al. Smarter sediment screening: effect-based quality assessment, chemical profiling, and risk identification[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 53(24):14479-14488. |
| 15 | 吴贤国,冯宗宝,秦文威,等. 基于物元理论和证据理论的盾构隧道施工邻近建筑物风险评价[J].铁道标准设计,2020,64(4):104-110. |
| Wu Xian-guo, Feng Zong-bao, Qin Wen-wei, et al. Risk assessment of adjacent buildings induced by shield tunneling construction based on matter-element theory and extension theory[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2020,64(4):104-110. | |
| 16 | Man S S, Chan A, Alabdulkarim S. Quantification of risk perception: development and validation of the construction worker risk perception(CoWoRP) scale[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 71:25-39. |
| 17 | Yang J, Wang J, Wei G, et al. An adaptive probabilistic mapping matrix search algorithm for vulnerability analysis of PPS[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 131:433-442. |
| 18 | 李依霖. 复杂网络隐私信息传输入侵风险评估仿真[J].计算机仿真,2020,37(6):156-159, 164. |
| Li Yi-lin. Intrusion risk assessment simulation of big data privacy information transmission in complex network[J]. Computer Simulation, 2020,37(6):156-159, 164. | |
| 19 | Kayhan B M, Cebi S, Kahraman C. Determining and prioritizing main factors of supplier reliability in construction industry[J]. Journal of Multiple-valued Logic and Soft Computing, 2019, 32(1/2):111-134. |
| 20 | Stewart M G, Li J. Risk-based assessment of blast-resistant design of ultra-high performance concrete columns[J]. Structural Safety, 2021, 88(3):No.102030. |
| [1] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [2] | 董伟智,张爽,朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [3] | 王喆, 杨柏婷, 刘昕, 刘群, 宋现敏. 基于模糊聚类的驾驶决策判别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. |
| [4] | 司建波, 姚燕, 郭蔚莹, 杨芳. 基于模糊聚类的Web用户聚类方法与实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 485-488. |
| [5] | 吉淑娇, 朱明, 胡汉平, 邢笑雪. 基于特征匹配的视频稳像算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 322-325. |
| [6] | 王彦会, 郭孔辉, 卢炳武, 应国增, 秦民. 基于多元统计分析的车辆操纵稳定性客观评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 6-11. |
| [7] | 申铉京1,2,王开业1,2,千庆姬3,刘英杰4,李想4. 基于自适应气球力Snake模型的图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1394-1400. |
| [8] | 周显国,陈大可,苑森淼. 基于改进模糊聚类分析的医学脑部MRI图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 381-0385. |
| [9] | 姜桂艳,郭海锋,吴超腾 . 基于感应线圈数据的城市道路 交通状态判别方法 [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(增刊): 37-0042. |
| [10] | 张建国,雷雨龙,王健,陆晓惠 . 基于BP神经网络的换档品质评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(05): 1019-1022. |
| [11] | 邱长波,张佳,施梦. 企业信息化成熟度阶段分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(04): 976-980. |
| [12] | 徐新卫,周良,徐晓明,丁秋林 . Web主动服务中基于混合挖掘的用户意图辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(02): 419-0423. |
| [13] | 鹿应荣,杨印生,吕锋 . 基于模糊聚类分析的车辆优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊2): 147-151. |
| [14] | 马飞, 王利政. 基于内在结构的企业核心竞争力评价体系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (1): 163-167. |
|