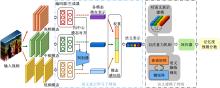
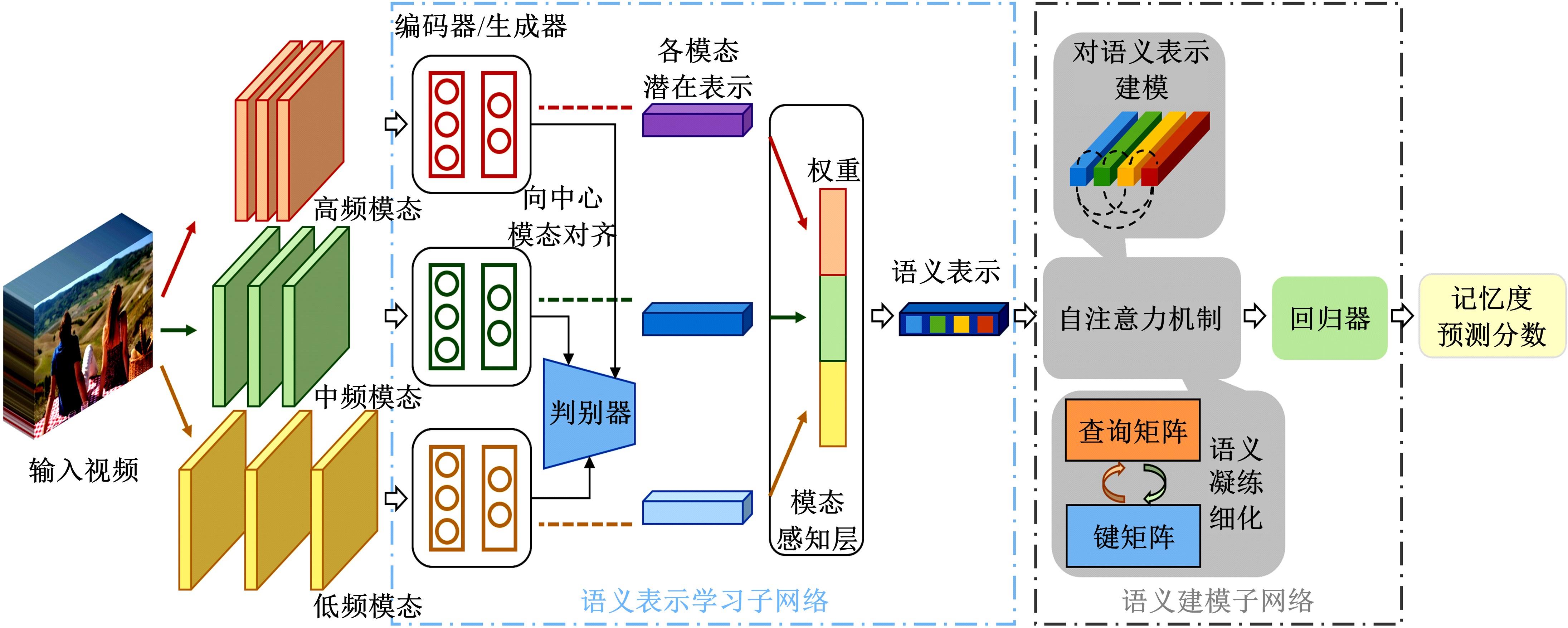
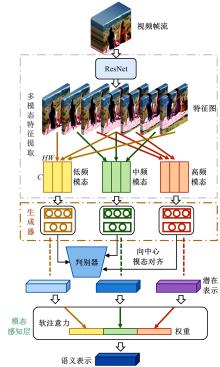
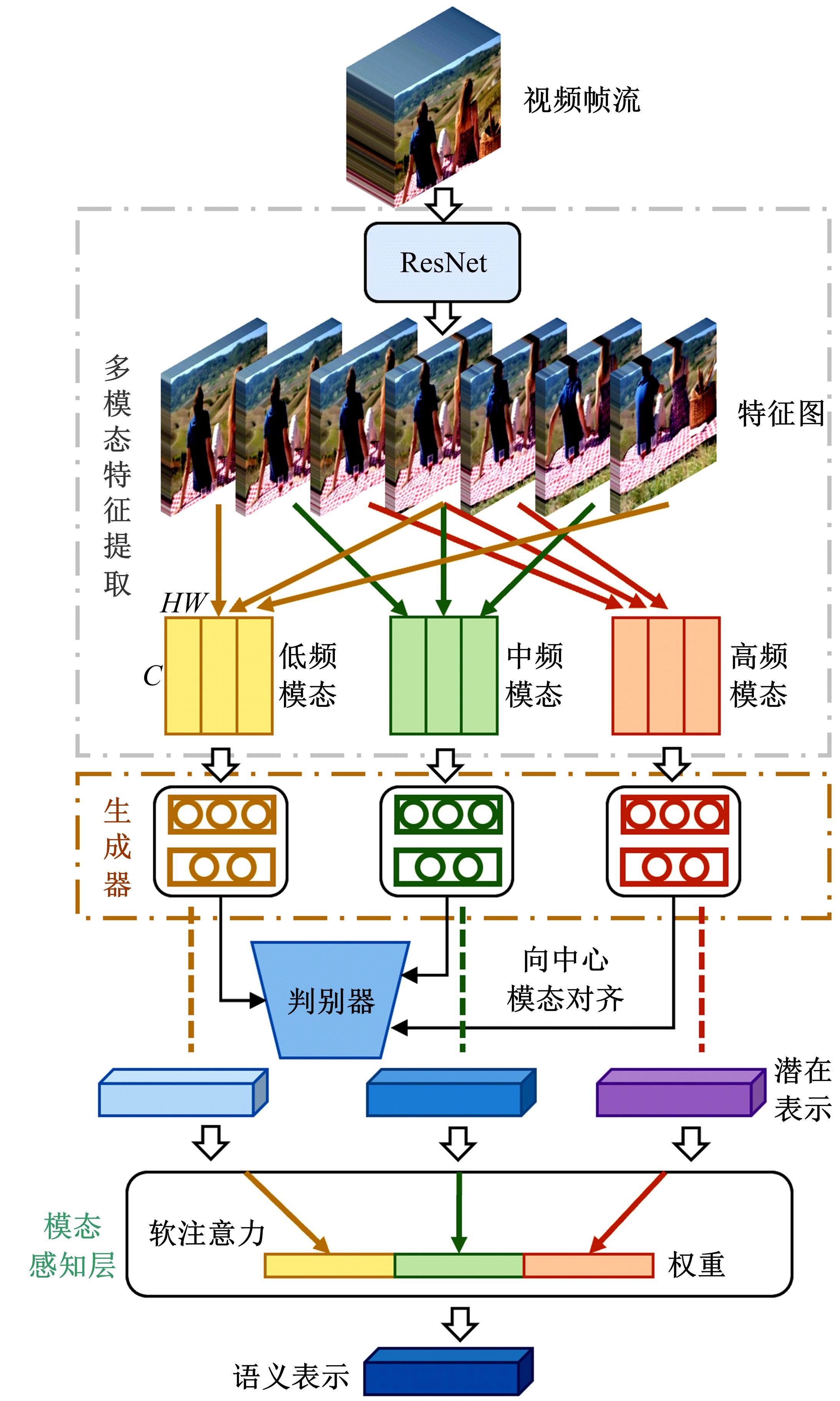
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1211-1219.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210842
Multi⁃modal self⁃attention network for video memorability prediction
Wei LYU( ),Jia-ze HAN,Jing-hui CHU,Pei-guang JING(
),Jia-ze HAN,Jing-hui CHU,Pei-guang JING( )
)
- School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Dhar S, Ordonez V, Berg T L. High level describable attributes for predicting aesthetics and interestingness[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado, USA, 2011: 1657-1664. |
| 2 | Lu X, Lin Z, Jin H, et al. Rating image aesthetics using deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(11): 2021-2034. |
| 3 | Deng Y, Loy C C, Tang X. Image aesthetic assessment: an experimental survey[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(4): 80-106. |
| 4 | Gygli M, Soleymani M. Analyzing and predicting GIF interestingness[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, USA, 2016: 122-126. |
| 5 | Demarty C H, Sjöberg M, Ionescu B, et al. Mediaeval 2017 predicting media interestingness task[C]∥MediaEval Workshop, Dublin, Ireland, 2017: 1-3. |
| 6 | Khosla A, Das Sarma A, Hamid R. What makes an image popular?[C]∥Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web, New York, USA, 2014: 867-876. |
| 7 | Deza A, Parikh D. Understanding image virality[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1818-1826. |
| 8 | Isola P, Xiao J, Parikh D, et al. What makes a photograph memorable?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 36(7): 1469-1482. |
| 9 | Cohendet R, Demarty C H, Duong N Q K, et al. VideoMem: constructing, analyzing, predicting short-term and long-term video memorability[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea(South), 2019: 2531-2540. |
| 10 | Brady T F, Konkle T, Alvarez G A, et al. Visual long-term memory has a massive storage capacity for object details[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(38): 14325-14329. |
| 11 | Khosla A, Raju A S, Torralba A, et al. Understanding and predicting image memorability at a large scale[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2390-2398. |
| 12 | Shekhar S, Singal D, Singh H, et al. Show and recall: Learning what makes videos memorable[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2730-2739. |
| 13 | Cohendet R, Yadati K, Duong N Q K, et al. Annotating, understanding, and predicting long-term video memorability[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, New York, USA, 2018: 178-186. |
| 14 | Borth D, Chen T, Ji R, et al. Sentibank: large-scale ontology and classifiers for detecting sentiment and emotions in visual content[C]∥Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Barcelona, Spain, 2013: 459-460. |
| 15 | Hara K, Kataoka H, Satoh Y. Can spatiotemporal 3d cnns retrace the history of 2d cnns and imagenet?[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6546-6555. |
| 16 | 王小玉, 胡鑫豪, 韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 285-292. |
| Wang Xiao-yu, Hu Xin-hao, Han Chang-lin. Face pencil drawing algorithms based on generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 285-292. | |
| 17 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2017: 5998-6008. |
| 18 | Yang C, Xu Y, Shi J, et al. Temporal pyramid network for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 591-600. |
| 19 | Zhou R, Shen Y D. End-to-end adversarial-attention network for multi-modal clustering[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 14619-14628. |
| 20 | Fajtl J, Argyriou V, Monekosso D, et al. Amnet: Memorability estimation with attention[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6363-6372. |
| 21 | Giryes R, Sapiro G, Bronstein A M. Deep neural networks with random Gaussian weights: a universal classification strategy?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3444-3457. |
| 22 | 郭晓然, 罗平, 王维兰. 基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| Guo Xiao-ran, Luo Ping, Wang Wei-lan. Chinese named entity recognition based on Transformer encoder[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. | |
| 23 | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[J/OL]. [2020-10-22]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 24 | Chen H, Wang Y, Guo T, et al. Pre-trained image processing transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 12299-12310. |
| 25 | Touvron H, Cord M, Douze M, et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 2021: 10347-10357. |
| 26 | Chen Y, Li J, Xiao H, et al. Dual path networks[J/OL].[2021-11-12]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 27 | Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929-1958. |
| 28 | Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, USA, 2014: 2672-2680. |
| 29 | Greff K, Srivastava R K, Koutník J, et al. LSTM: A search space odyssey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 28(10): 2222-2232. |
| 30 | Smola A J, Schölkopf B. A tutorial on support vector regression[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3): 199-222. |
| 31 | Fonarow G C, Adams K F, Abraham W T, et al. Risk stratification for in-hospital mortality in acutely decompensated heart failure: classification and regression tree analysis[J]. JAMA, 2005, 293(5): 572-580. |
| 32 | Prasad A M, Iverson L R, Liaw A. Newer classification and regression tree techniques: bagging and random forests for ecological prediction[J]. Ecosystems, 2006, 9(2): 181-199. |
| 33 | Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 785-794. |
| [1] | Le-ping LIN,Zeng-tong LU,Ning OUYANG. Face reconstruction and recognition in non⁃cooperative scenes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2941-2946. |
|
||