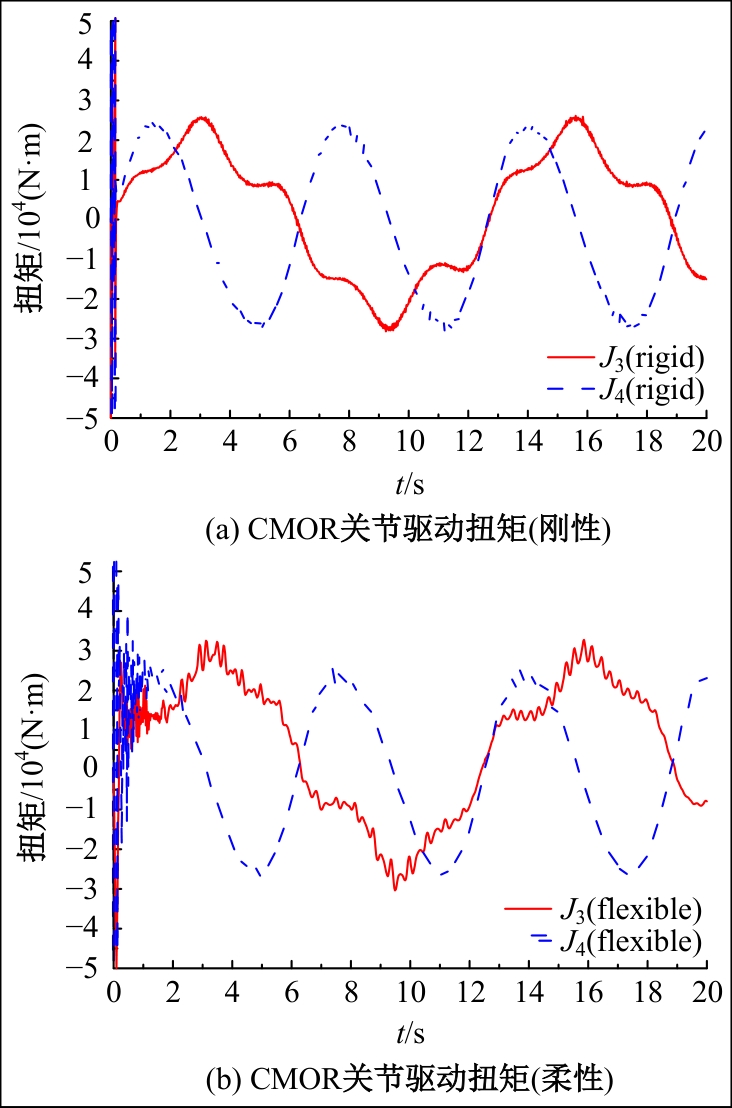
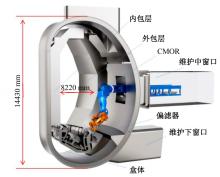
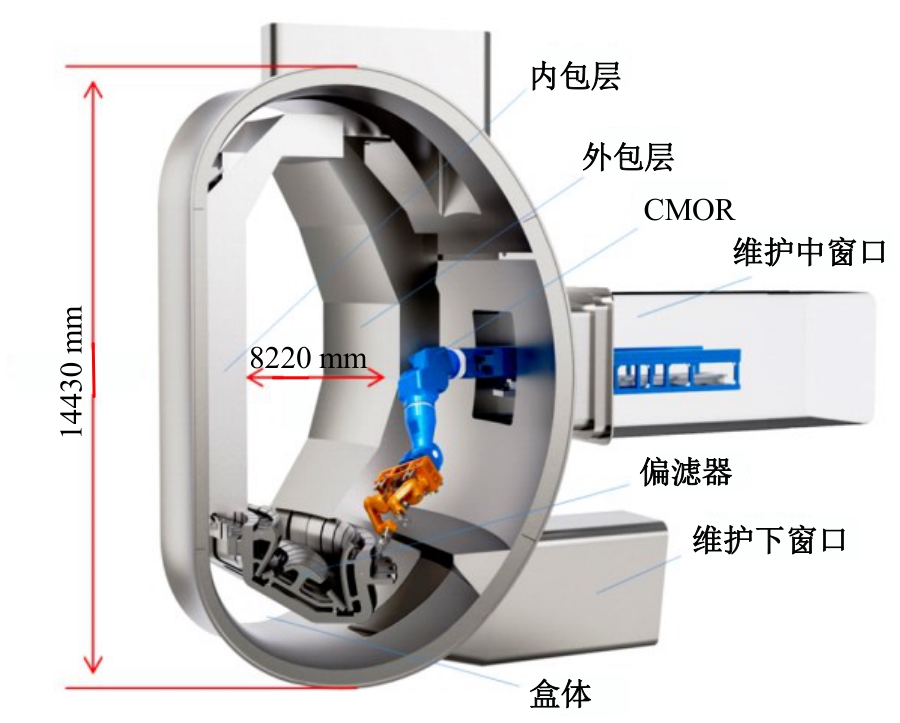
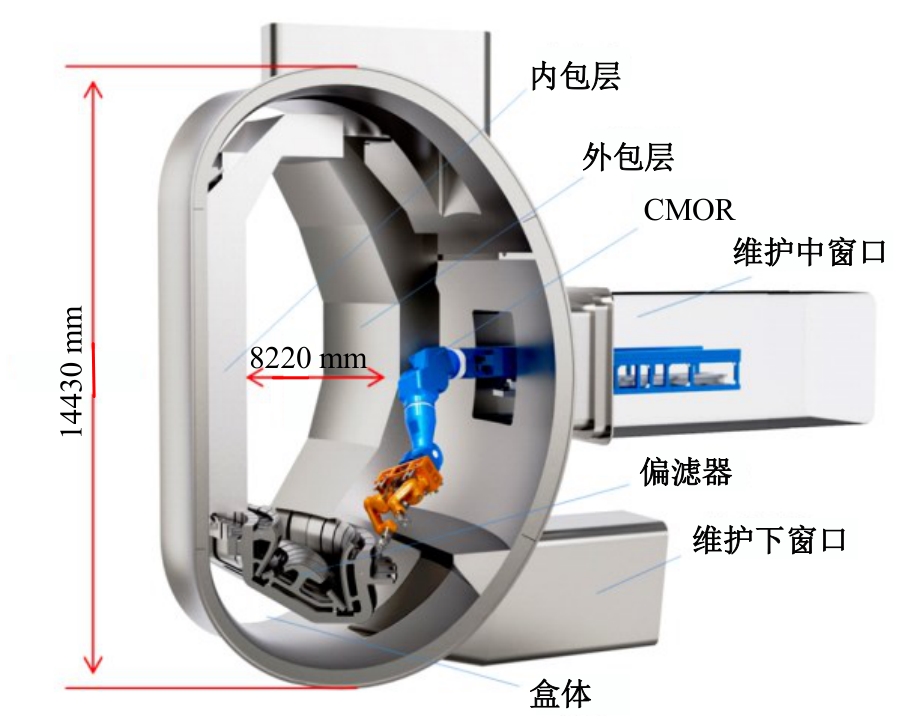
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 52-62.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231431
Previous Articles Next Articles
Robust adaptive accuracy control of large manipulator for fusion reactor
Cong-ju ZUO1,2,3( ),Guo-dong QIN1,Hong-tao PAN1,Yong CHENG1,Pu-cheng ZHOU3,Xiao-yan QIN3,Wei-hua WANG1(
),Guo-dong QIN1,Hong-tao PAN1,Yong CHENG1,Pu-cheng ZHOU3,Xiao-yan QIN3,Wei-hua WANG1( )
)
- 1.Institute of Plasma Physics,Chinese Academy of Science,Hefei 230031,China
2.University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
3.Department of Information Engineering,Army Academy of Artillery and Air Defense,Hefei 230031,China
CLC Number:
- TP241.3
| 1 | 李建刚. 聚变工程实验堆装置主机设计[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2016. |
| 2 | Song Y T, Li J G, Wan Y X, et al. Engineering design of the CFETR machine[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2022, 183: No.113247. |
| 3 | 周振国. ITER MPD 旋转关节结构设计[D]. 西安:中国科学技术大学工程科学学院, 2018. |
| Zhou Zhen-guo. Structural design of ITER MPD rotary joint[D]. Xi'an: School of Engineering Science,University of Science and Technology of China, 2018. | |
| 4 | Qin G D, Ji A H, Wang W, et al. Analyzing trajectory tracking accuracy of a flexible multi-purpose deployer[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2020, 151: No.111396. |
| 5 | Manuelraj M S, Dutta P, Gotewal K K, et al. Structural analysis of ITER multi-purpose deployer[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2016, 109: 1296-1301. |
| 6 | 龙海波, 杨家其, 尹靓,等. 基于鲁棒优化的不确定需求下应急物资配送多目标决策模型[J].吉林大学学报工学版, 2023, 53(4): 1078-1084. |
| Long Hai-bo, Yang Jia-qi, Yin Liang, et al. Robust optimization-based multi-objective decision model for emergency material distribution under uncertain demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1078-1084. | |
| 7 | 王宏志,王婷婷,兰淼淼,等.基于位置跟踪的机械臂多电机新型滑模控制策略[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2024,54(5): 1443-1458. |
| Wang Hong-zhi, Wang Ting-ting, Lan Miao-miao, et al. A novel sliding mode control strategy for multi-motor of robotic arm based on position tracking[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024,54(5): 1443-1458. | |
| 8 | 周挺, 徐宇工, 吴斌. 球形机器人的自适应分数阶PI~λD~μ滑模速度控制方法[J].吉林大学学报工学版, 2021, 51(2): 728-737. |
| Zhou Ting, Xu Yu-gong, Wu Bin. Adaptive fractional order PI~λD~μ sliding mode velocity control method for spherical robots[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 728-737. | |
| 9 | 杨超, 郭佳, 张铭钧. 基于RBF神经网络的作业型AUV自适应终端滑模控制方法及实验研究[J].机器人, 2018, 40(3): 336-345. |
| Yang Chao, Guo Jia, Zhang Ming-jun. Adaptive terminal sliding mode control method based on RBF neural networkfor operational AUV and its experimental research[J]. Robot, 2018, 40(3): 336-345. | |
| 10 | 赵兴强, 刘振, 高存臣. 机械臂系统自适应神经网络滑模控制器设计[J]. 控制工程,2023, 30(9): 1624-1629. |
| Zhao Xing-qiang, Liu Zhen, Gao Cun-chen. Adaptive neural network-based sliding mode controller design for manipulator systems[J]. Control Engineering, 2023, 30(9): 1624-1629. | |
| 11 | Alian A, Zareinejad M, Talebi H A. Curvature tracking of a two-segmented soft finger using an adaptive sliding-mode controller[J]. IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 28(1): 50-59. |
| 12 | Cao G Q, Zhao X Y, Ye C L, et al. Fuzzy adaptive PID control method for multi mecanum wheeled mobile robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 36(4): 2019-2029. |
| 13 | Ding L, Niu L Z, Su Y, et al. Dynamic finite element modeling and simulation of soft robots[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 35(1): 1-11. |
| 14 | 陈昊然, 张宇, 段昊宇翔, 等. 串联机器人模态仿真与实验[J].制造业自动化, 2023, 45(10): 115-119. |
| Chen Hao-ran, Zhang Yu, Duan Hao-yuxiang, et al. Modal simulation and experiment of series robot[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2023, 45(10): 115-119. | |
| 15 | 高强.基于假设模态法的柔性机械臂瞬时变形响应分析[J].自动化与仪器仪表, 2019(12): 65-67. |
| Gao Qiang. Analysis of transient deformation response for flexible robotic manipulator using assumed mode method[J]. Automation and Instrumentation, 2019(12): 65-67. | |
| 16 | Abele E, Weigold M, Rothenbücher S. Modeling and identification of an industrial robot for machining applications[J]. Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 56(1): 387-390. |
| 17 | 张成新, 余跃庆. 具有关节柔性和臂柔性的机器人操作受限物体的动力学建模[J]. 机械工程学报, 2003, 39(6): 9-12. |
| Zhang Cheng-xin, Yu Yue-qing. Dynamic modeling of robot arm with joint and link flexibility manipulating a constrained object[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 39(6): 9-12. | |
| 18 | 刘娜. 煤矿焊接机器人刚柔耦合动力学与动态特性研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学机电与信息工程学院, 2018. |
| Liu Na. Research on rigid-flexible coupling dynamics and dynamic characteristics of welding robot for coal mines[D]. Beijing:School of Mechanical,Electrical and Information Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology, 2018. | |
| 19 | Niu B, Zhao J. Stabilization and L2-gain analysis for a class of cascade switched nonlinear systems: An average dwell-time method[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 2011, 5(4): 671-680. |
| 20 | 欧攀,尉青锋,陈末然. 基于振动特征的火炮身管打击精度控制仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021,38(6): 18-21, 77. |
| Pan Ou, Wei Qing-Feng, Chen Mo-Ran. simulation of gun barrel strike precision control based on vibration characteristics[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(6): 18-21, 77. | |
| 21 | Luo G Y, Zou L, Wang Z L, et al. A novel kinematic parameters calibration method for industrial robot based on levenberg-marquardt and differential evolution hybrid algorithm[J]. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 71: No.102165. |
| [1] | YANG Da-peng, JIANG Li, ZHAO Jing-dong, LIU Hong . Control of prosthetic hand based on electrocephalogram [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(05): 1225-1230. |
|
||