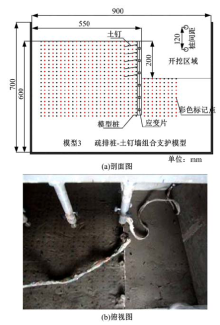
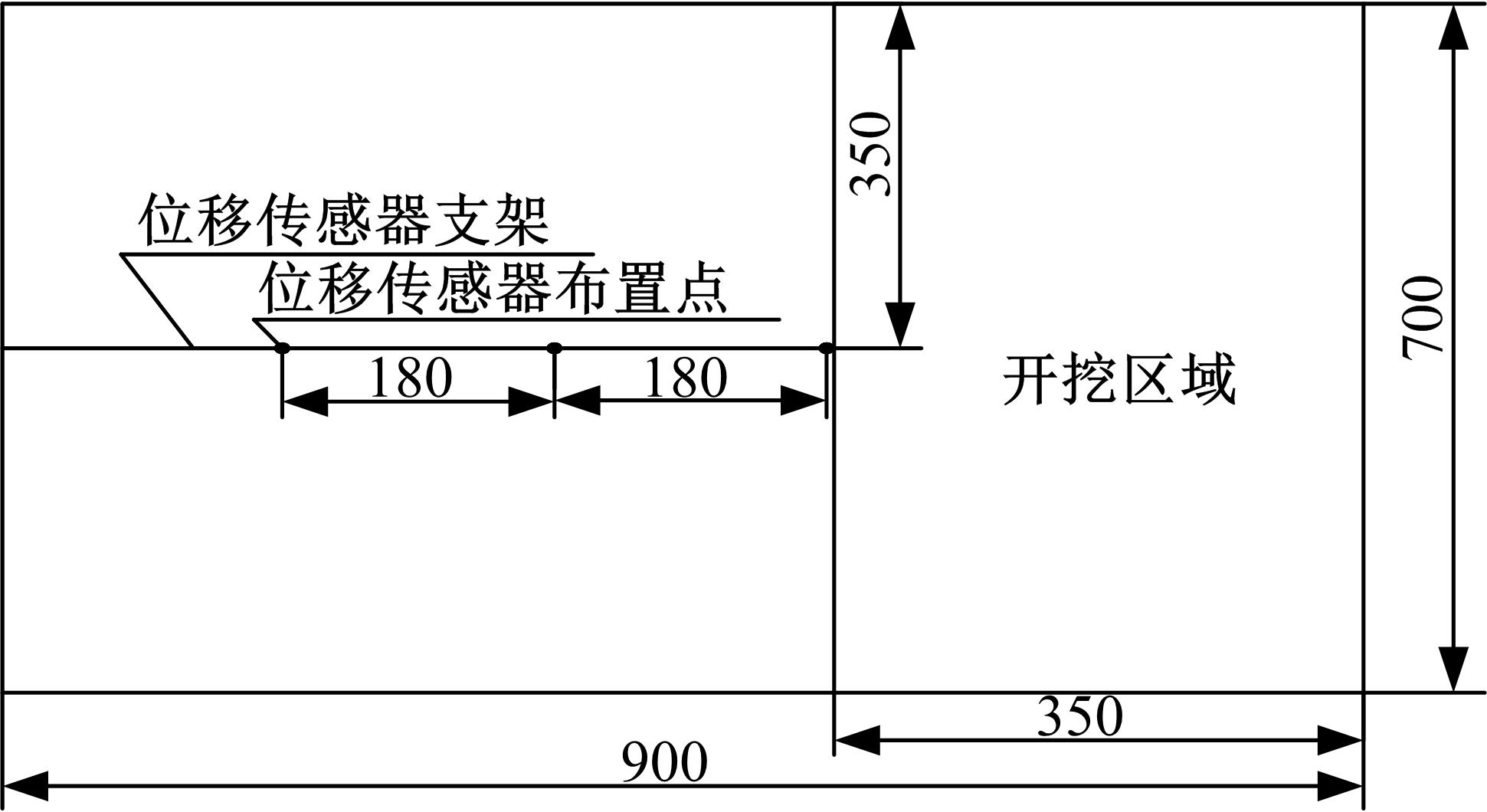
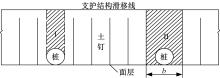
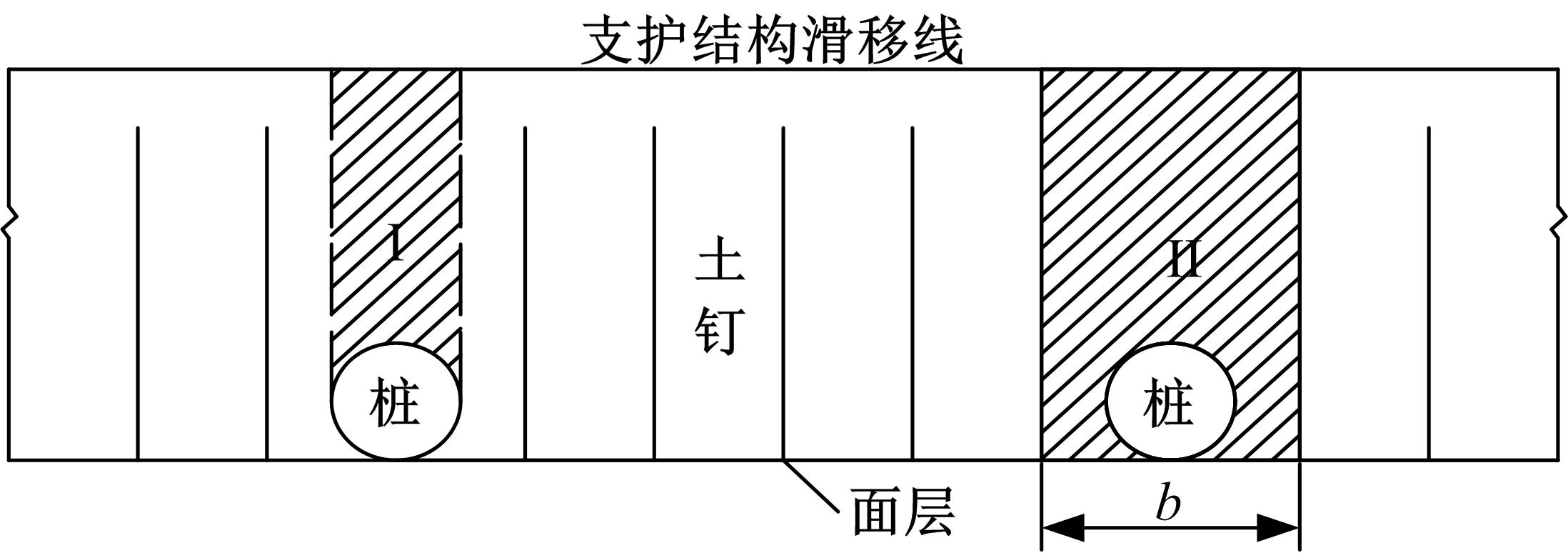
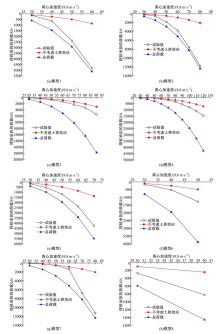
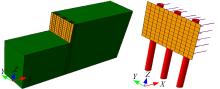
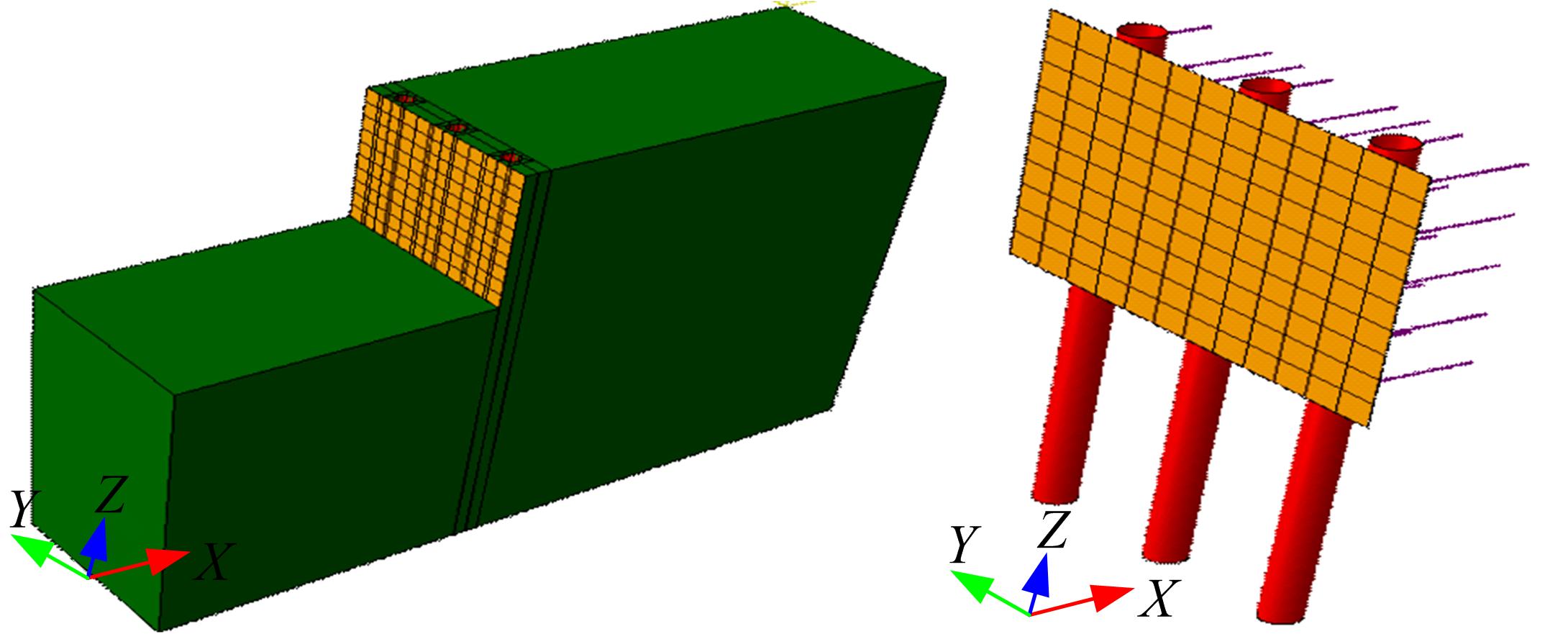
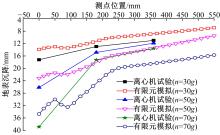
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1712-1724.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170805
Previous Articles Next Articles
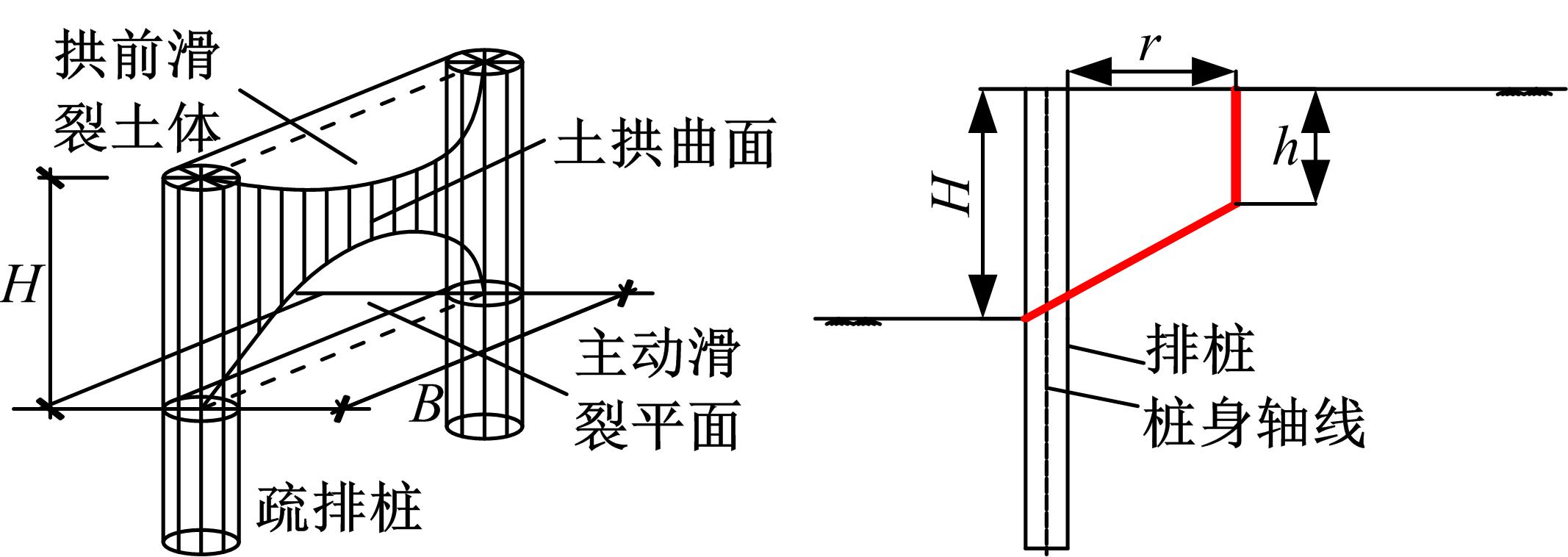
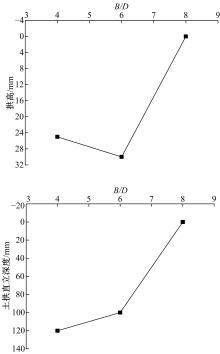
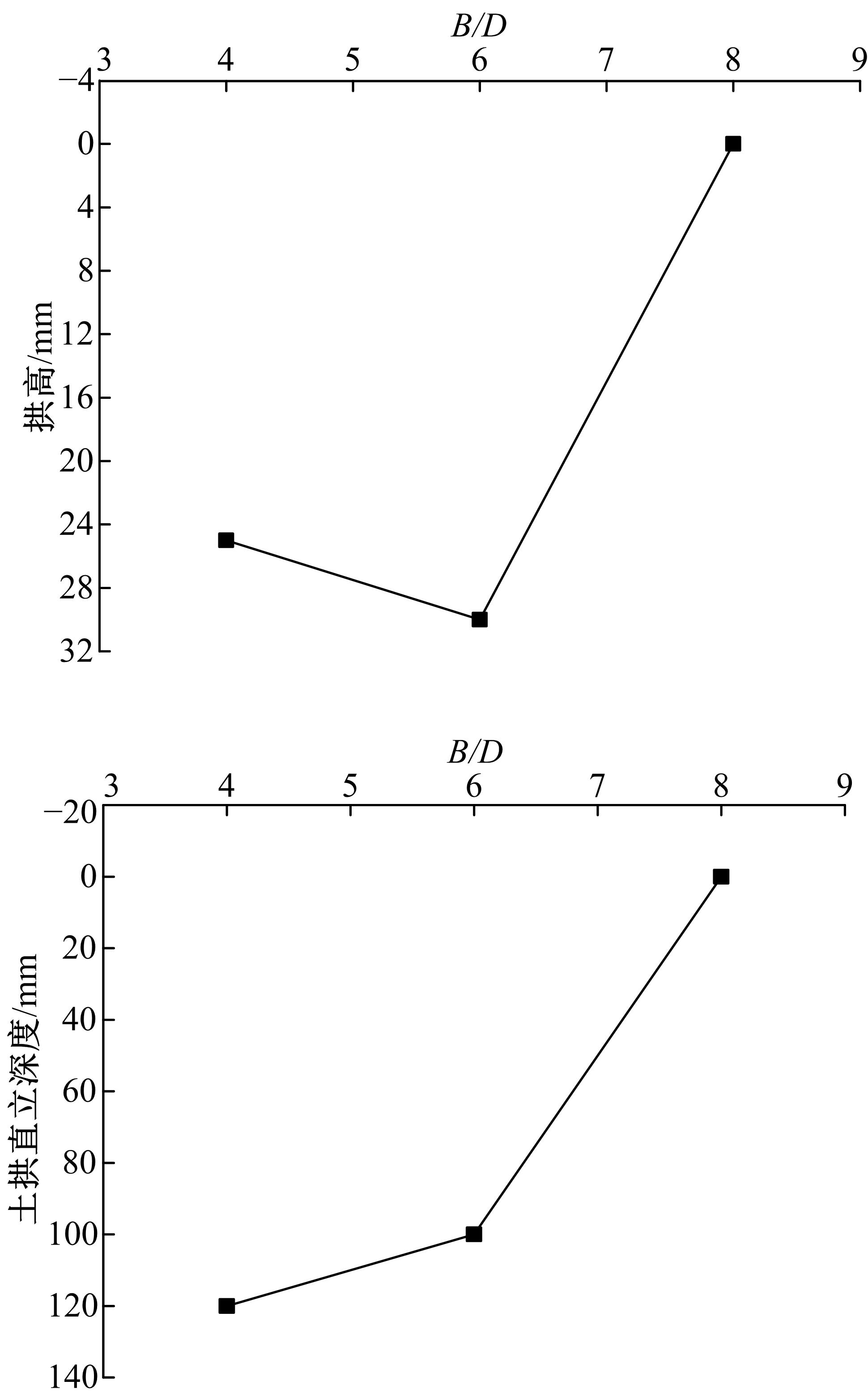
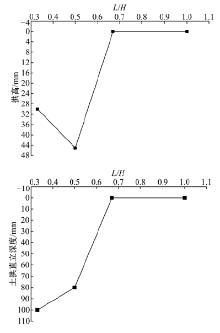
Experiment on soil arching effect of pit supporting structure with scattered row piles and soil nail wall
- 1. Zhejiang Provincial Institute of Communications Planning, Design & Research, Hangzhou 310006, China;
2. Department of Road and Bridge, Zhejiang Highway Technicians College, Hangzhou 310023, China
CLC Number:
- TU47
| [1] | 宋广, 黄建华, 宋二祥 . 超前微桩复合土钉支护三维非线性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2010,32(增刊1):151-155. |
| Song Guang, Huang Jian-hua, Song Er-xiang . Three dimensional nonlinear analysis of composite soil nailing with micro piles for deep excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010,32(Sup.1):151-155. | |
| [2] |
吴忠诚, 杨志银, 罗小满 , 等. 疏排桩锚-土钉墙组合合支护结构稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006,25(增刊2):3607-3613.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.z2.042 |
|
Wu Zhong-cheng, Yang Zhi-yin, Luo Xiao-man , et al. Stability analysis of scattered row pile-soil-nailed wall protection structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006,25(Sup.2):3607-3613.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.z2.042 |
|
| [3] |
公宝兴, 孙振 . 钢管桩与土钉墙联合支护设计研究[J]. 国防交通工程与技术, 2005(1):65-68.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3953.2005.01.020 |
|
Gong Bao-xing, Sun Zhen . The design of the retaining support with steel tube piles and soil-nail wall[J]. Traffic Engineering and Technology National Defence, 2005(1):65-68.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3953.2005.01.020 |
|
| [4] |
杨志银 . 复合土钉墙技术在深圳的应用与发展[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2006,28(增刊):1673-1676.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.z1.082 |
|
Yang Zhi-yin . Development and application of composite soil nailing walls in Shenzhen[D]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006,28(Sup.):1673-1676.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.z1.082 |
|
| [5] |
杨志银, 张俊, 王凯旭 . 复合土钉墙技术的研究及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2005,27(2):153-156.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.02.004 |
|
Yang Zhi-yin, Zhang Jun, Wang Kai-xu . Development of composite soil nailing walls[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005,27(2):153-156.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.02.004 |
|
| [6] | Hewlett W J, Randolph M F . Analysis of piled embankments[J]. Ground Engineering, 1988,21(3):12-18. |
| [7] |
Low B K, Tang S K, Choa V . Arching in piled embankments[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994,120(11):1917-1938.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:11(1917) |
| [8] |
曹卫平, 陈仁朋, 陈云敏 . 桩承式加筋路堤土拱效应试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007,29(3):436-441.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.03.021 |
|
Cao Wei-ping, Chen Ren-peng, Chen Yun-min . Experimental investigation on soil arching in piled reinforced embankment[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007,29(3):436-441.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.03.021 |
|
| [9] | 曹卫平, 凌道盛, 陈云敏 . 刚性桩加固高速公路软基土拱效应现场试验研究及其与解析解的比较[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007,29(10):1576-1581. |
| Cao Wei-ping, Ling Dao-sheng, Chen Yun-min . Field test on soil arching of highway embankments reinforced with rigid piles and their comparison with current analytical methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007,29(10):1576-1581. | |
| [10] |
Ito T, Matsui T . Methods to estimate lateral force acting on stabilizing piles[J]. Soils and Foundation, 1975,15(4):43-59.
doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.15.4_43 |
| [11] | Ito T . Extended design method for multi row stabilizing piles against landslide[J]. Soils and Foundation, 1982,22(1):1-13. |
| [12] |
Bosscher J, Gray H . Soil arching in sandy slopes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1986,112(6):626-645.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1986)112:6(626) |
| [13] | 朱碧堂, 温国炫, 刘一亮 . 基坑开挖和支护中土层拱效应的理论分析[J]. 建筑技术, 2002,33(2):97-98. |
| Zhu Bi-tang, Wen Guo-xuan, Liu Yi-liang . Theoretical analysis of soil in excavation and retaining works[J]. Architecture Technology, 2002,33(2):97-98. | |
| [14] |
周德培, 肖世国, 夏雄 . 边坡工程中抗滑桩合理桩间距的探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004,26(1):132-135.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.01.025 |
|
Zhou De-pei, Xiao Shi-guo, Xia Xiong . Discussion on rational spacing between adjacent anti-slide piles in some cutting slope projects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004,26(1):132-135.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.01.025 |
|
| [15] |
贾海莉, 王成华, 李江洪 . 基于土拱效应的抗滑桩与护壁桩的桩间距分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2004,12(1):98-103.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.01.018 |
|
Jia Hai-li, Wang Cheng-hua, Li Jiang-hong . Analysis of pile spacing between anti-sliding piles and pertaining piles in accordance with soil arching effect[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004,12(1):98-103.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.01.018 |
|
| [16] |
蒋良潍, 黄润秋, 蒋忠信 . 黏性土桩间土拱效应计算与桩间距分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2006,27(3):445-450.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.021 |
|
Jiang Liang-wei, Huang Run-qiu, Jiang Zhong-xin . Analysis of soil arching effect between adjacent piles and their spacing in cohesive soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006,27(3):445-450.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.021 |
|
| [17] | 古海东, 杨敏 . 考虑土拱效应的疏排桩支护基坑内力和变形分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2014,35(12):3531-3540. |
| Gu Hai-dong, Yang Min . Analysis of internal forces and displacement of pit supporting structure with scattered row piles considering soil arching effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014,35(12):3531-3540. | |
| [18] | 古海东, 杨敏 . 土钉墙在疏排桩支护基坑中的加固效果试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015,48(1):129-138. |
| Gu Hai-dong, Yang Min . Experimental study on reinforcement effect of soil-nailed wall in pit excavation supported with scattered row piles[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015,48(1):129-138. | |
| [19] | JGJ120—2012. 建筑基坑支护计算规程[S]. |
| [20] | 古海东, 杨敏 . 疏排桩-土钉墙组合支护结构排桩荷载分担比试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2013,35(2):102-110. |
| Gu Hai-dong, Yang Min . Experimental study on pile load sharing ratio of composite structure with scattered piles and soil nailing[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2013,35(2):102-110. |
| [1] | SU Ying-she,YANG Yuan-yuan. Analysis of load transfer ratio of soil arching in sparse row piles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 400-405. |
|