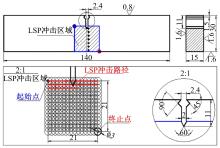
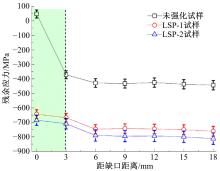
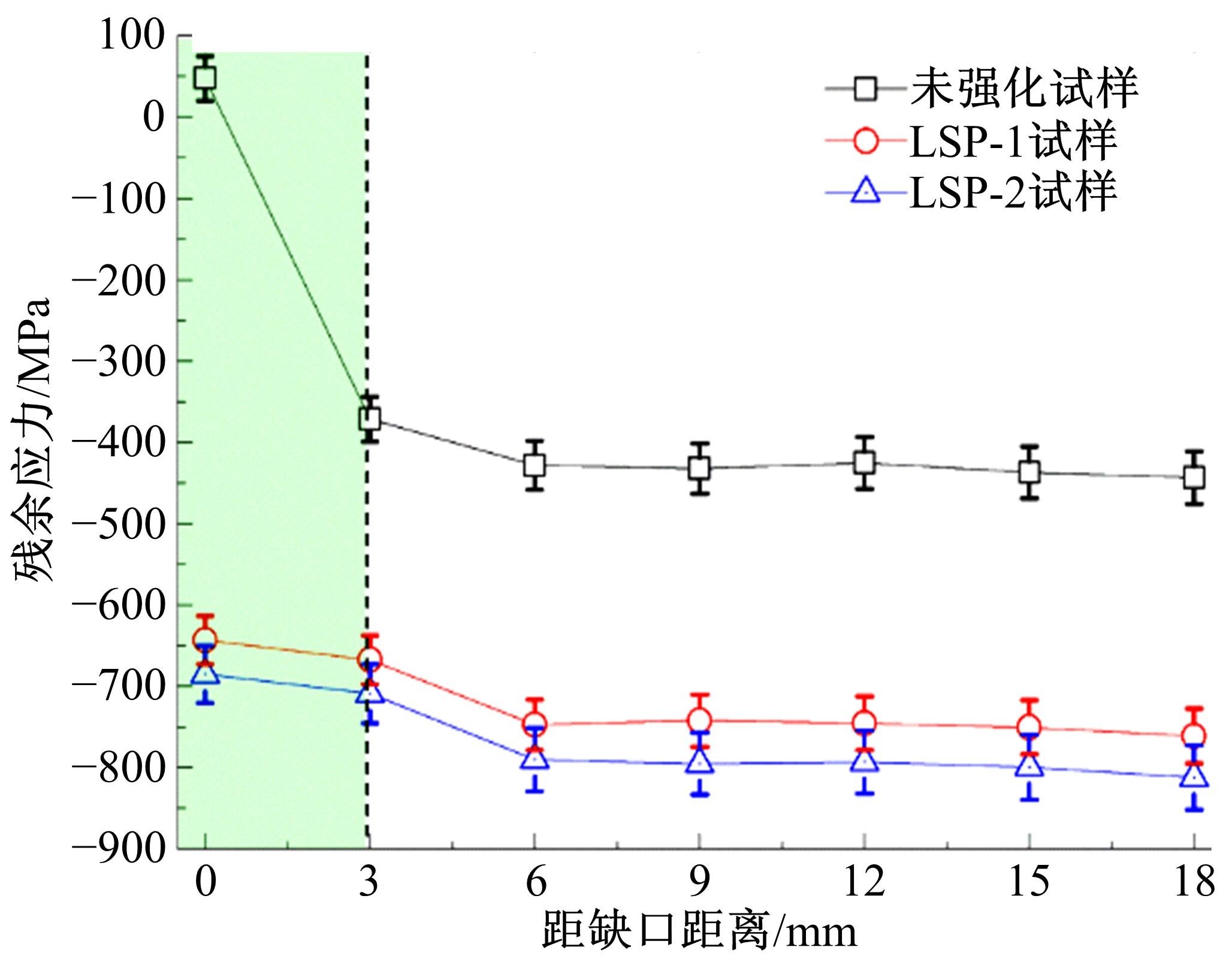
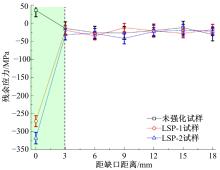
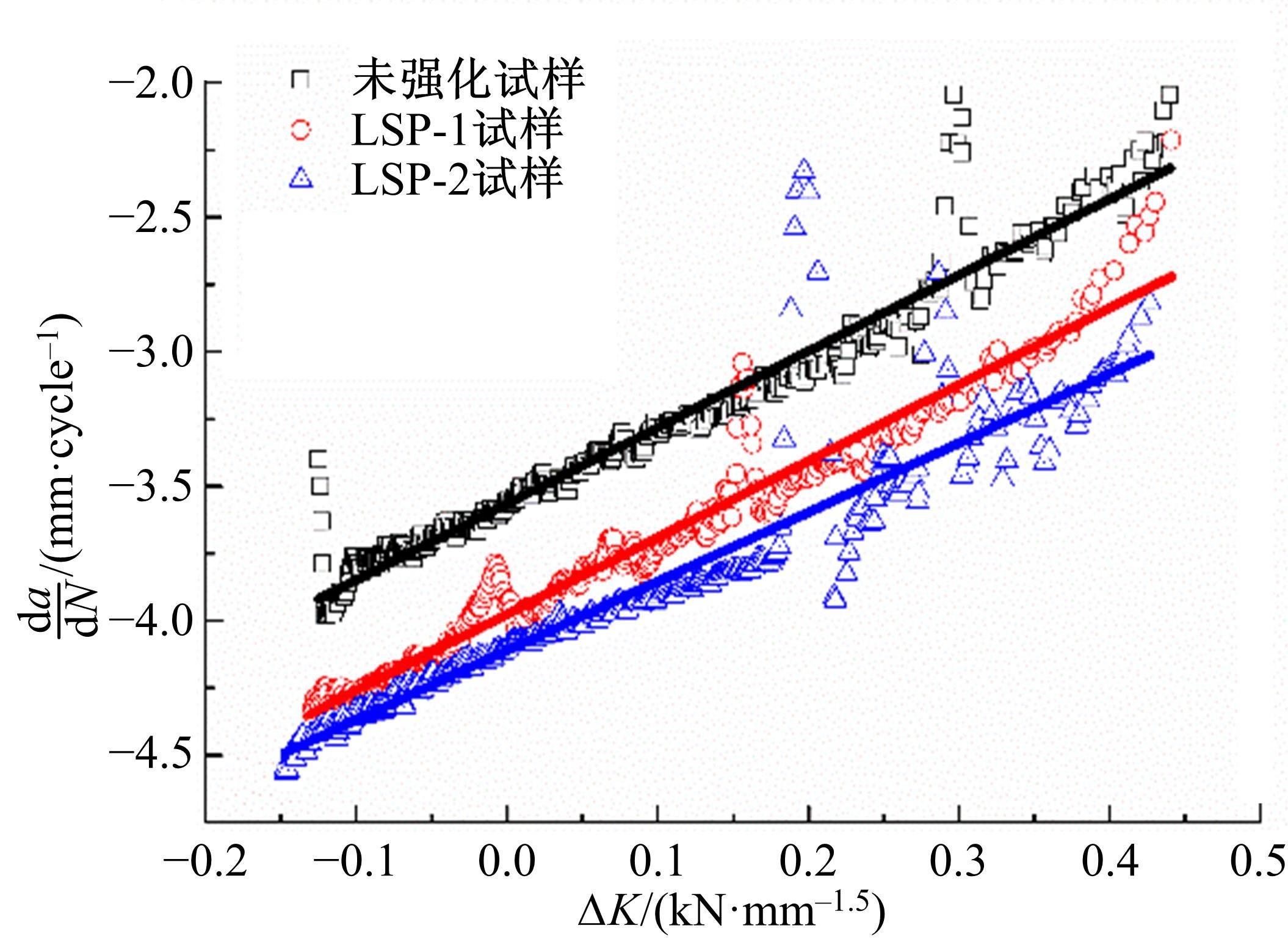
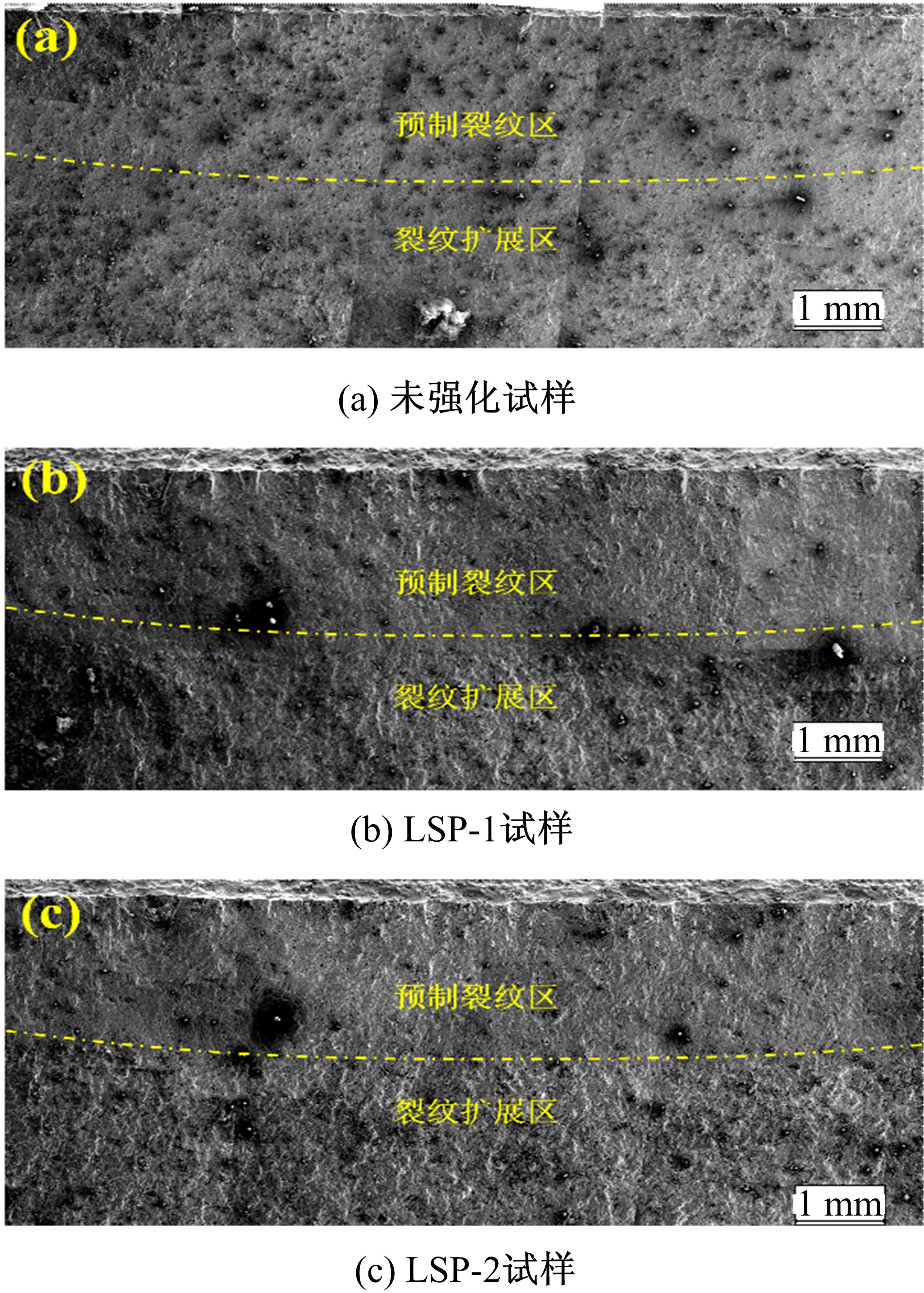
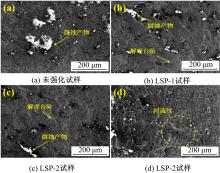
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 850-858.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180142
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of laser shock peening on corrosion fatigue behaviour of 2Cr13 stainless steel
Kai⁃yu LUO1( ),Yue⁃hua XING1,Qing⁃feng CHAI1,Shi⁃kai WU2,Ye⁃fang YIN1,Jin⁃zhong LU1
),Yue⁃hua XING1,Qing⁃feng CHAI1,Shi⁃kai WU2,Ye⁃fang YIN1,Jin⁃zhong LU1
- 1. School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
2. Beijing Engineering Researching Center of Laser Technology, Beijng University of Technology, Beijng 100124, China
CLC Number:
- TH16
| 1 | 冯爱新, 周鹏程, 聂贵锋, 等. 热处理和激光冲击对2Cr13马氏体不锈钢冲击韧性的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2012, 39(8):0803002. |
| FengAi⁃xin, ZhouPeng⁃cheng, NieGui⁃feng, et al. Influence of heat treatment and laser shock processing on impact toughness of 2Cr13 martensite stainless steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2012, 39(8):0803002. | |
| 2 | 徐庆东, 林鑫, 宋梦华,等. 激光成形修复2Cr13不锈钢热影响区的组织研究[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(5):605⁃613. |
| XuQing⁃dong, LinXin, SongMeng⁃hua, et al. Microstructure of heat⁃affected zone of laser forming repaired 2Cr13 stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(5):605⁃613. | |
| 3 | 韩栋, 刘道新, 刘树涛. 汽轮机低压转子2Cr13不锈钢叶片断裂分析[J]. 机械工程材料, 2007, 31(7):45⁃48. |
| HanDong, LiuDao⁃xin, LiuShu⁃tao. Failure analysis of 2Cr13 stainless steel blade in a low pressure steam turbine[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 31(7):45⁃48. | |
| 4 | 李明珠, 赵云龙. 提高2Cr13马氏体不锈钢疲劳强度的工艺研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2010, 39(12):171⁃172. |
| LiMing⁃zhu, ZhaoYun⁃long. Study on improving fatigue strength technology of 2Cr13 martensitic stainless steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2010, 39(12):171⁃172. | |
| 5 | XiY T, LiuD X, DongH. Improvement of erosion and erosion⁃corrosion resistance of AISI420 stainless steel by low temperature plasma nitriding[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(18):5953⁃5958. |
| 6 | 赖志林, 汪诚, 李应红, 等. 激光冲击强化与超声喷丸对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢疲劳性能的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2013, 50(5):051403. |
| LaiZhi⁃lin, WangCheng, LiYing⁃hong, et al. Effects of laser shock peening and ultrasonic shot peening on fatigue property of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2013, 50(5):051403. | |
| 7 | ZhaoW, ZhangT, XinR, et al. Effects of thermally sprayed aluminum coating on the corrosion fatigue behavior of X80 steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2015, 24(6):974⁃983. |
| 8 | 王曼曼. 电弧喷涂铝涂层对X80钢海洋腐蚀疲劳裂纹萌生的影响[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东)材料科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| WangMan⁃man. Effects of aluminum spray coating on marine corrosion fatigue crack initiation of X80 steel[D]. Qingdao: College of Materials Scinence and Engineering,China University of Petroleum (East China), 2013. | |
| 9 | 罗开玉, 周阳, 鲁金忠, 等. 激光冲击强化对316L不锈钢熔覆层微观结构和性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(4):0402005. |
| LuoKai⁃yu, ZhouYang, LuJin⁃zhong, et al. Influence of laser shock peening on microstructure and property of cladding layer of 316L stainless steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(4):0402005. | |
| 10 | 李兴成. 激光冲击强化AZ31镁合金的腐蚀性能研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学材料科学与工程学院, 2014. |
| LiXing⁃cheng. Investigation of laser shock processing on corrosion resistance of AZ31 magnesium alloy[D]. Zhenjiang: College of Materials and Science, Jiangsu University, 2014. | |
| 11 | 孙昀杰, 周建忠, 黄舒,等. 激光喷丸医用Ti6Al4V合金的耐生物腐蚀性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(7):0702003. |
| SunYun⁃jie, ZhouJian⁃zhong, HuangShu, et al. Research on biological corrosion resistance of medical Ti6Al4V alloy subjected to laser peening[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(7):0702003. | |
| 12 | 任旭东, 张田, 张永康, 等. 激光冲击处理提高00Cr12合金的疲劳性能[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(8):2111⁃2115. |
| RenXu⁃dong, ZhangTian, ZhangYong⁃kang, et al. Improving fatigue properties of 00Cr12 alloy by laser shock processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2010, 37(8):2111⁃2115. | |
| 13 | ZhouJ Z, HuangS, ZuoL D, et al. Effects of laser peening on residual stresses and fatigue crack growth properties of Ti⁃6Al⁃4V titanium alloy[J]. Optics & Lasers in Engineering, 2014, 52(1):189⁃194. |
| 14 | GeM Z, XiangJ Y. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and fatigue crack growth rate of AZ31B magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016, 680:544⁃552. |
| 15 | BegumZ, PoonguzhaliA, BasuR, et al. Studies of the tensile and corrosion fatigue behaviour of austenitic stainless steels[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(4):1424⁃1432. |
| 16 | 周建忠, 徐增闯, 黄舒, 等. 基于不同应力比下激光喷丸强化6061⁃T6铝合金的疲劳裂纹扩展性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2011, 38(9):0903006. |
| ZhouJian⁃zhong, XuZeng⁃chuang, HuangShu, et al. Effects of different stress ratios on fatigue crack growth in laser shot peened 6061⁃T6 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2011, 38(9):0903006. | |
| 17 | 汪诚, 赖志林, 何卫锋, 等. 激光冲击次数对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢高周疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(1):0103001. |
| WangCheng, LaiZhi⁃lin, HeWei⁃feng, et al. Effect of multi⁃impact on high cycle fatigue properties of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel subject to laser shock processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(1):0103001. | |
| 18 | ParisP C, ErdoganF. A critical analysis of crack propagation laws[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1963, 85(4):528⁃533. |
| 19 | 张洁, 顾祥, 祝乐, 等. 激光冲击强化后7050铝合金疲劳寿命的数值模拟[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(12):3192⁃3195. |
| ZhangJie, GuXiang, ZhuLe, et al. Numerical simulation of fatigue life of 7050 aluminum alloy processed by laser shock processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2010, 37(12):3192⁃3195. | |
| 20 | 李媛, 何卫锋, 聂祥樊, 等. 激光冲击TC17钛合金疲劳裂纹扩展试验[J]. 中国表面工程, 2017, 30(3):40⁃47. |
| LiYuan, HeWei⁃feng, NieXiang⁃fan, et al. Fatigue crack growth behavior of TC17 titanium alloy with laser shock peening[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2017, 30(3):40⁃47. | |
| 21 | BergantZ, TrdanU, GrumJ. Effects of laser shock processing on high cycle fatigue crack growth rate and fracture toughness of aluminium alloy 6082⁃T651[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2016, 87:444⁃455. |
| 22 | NieX F, HeW, ZangS, et al. Effect study and application to improve high cycle fatigue resistance of TC11 titanium alloy by laser shock peening with multiple impacts[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2014, 253(9):68⁃75. |
| 23 | PrabhakaranS, KulkarniA, VasanthG, et al. Laser shock peening without coating induced residual stress distribution, wettability characteristics and enhanced pitting corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 428:17⁃30. |
| 24 | 葛茂忠, 项建云, 张永康. 激光冲击处理对AZ31B镁合金力学性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2013(9):54⁃59. |
| GeMao⁃zhong, XiangJian⁃yun, ZhangYong⁃kang. Effect of laser shock processing on mechanical properties of AZ31B magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2013(9):54⁃59. |
| [1] | Jin⁃zhong LU,Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO. Effect of coverage layer on corrosion resistance of 6061⁃T6 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 842-849. |
|